Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
EngIT - Jan 2013 - LVDT PDF
Загружено:
mehdiОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
EngIT - Jan 2013 - LVDT PDF
Загружено:
mehdiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Automation and Control
Technical
The LVDT: construction and
principles of operation
Information from Accutronics
A linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) is an absolute displacement transducer that converts a linear displacement or position
from a mechanical reference (or zero) into a proportional electrical signal containing phase (for direction) and amplitude information
(for distance).
The LVDT operation does not require electrical other, with insulation between them, in Fig. 1 is at the mechanical zero (or null position)
contact between the moving part (probe or (a) and (b) the windings are wound both at is called the null voltage; as the phase
core rod assembly) and the transformer, but the same time using custom designed, dual angle at null position is 90, the null voltage
rather relies on electromagnetic coupling; carriage computerised winding machines. is a quadrature voltage. This residual
this and the fact that they operate without This method saves manufacturing time voltage is due to the complex nature of
any built-in electronic circuitry are the primary and also creates secondary windings with the LVDT electrical model, which includes
reasons why LVDTs have been widely used in symmetrical capacitance distribution and the parasitic capacitances of the windings.
applications where long life and high reliability therefore allows meeting specifications more This complex nature also explains why
under severe environments are a required, easily. the phase angle of (Va- Vb) is not exactly
such as military/aerospace applications. 0 or 180 when the core is away from the
Principles of operation
null position.
Construction
When the primary coil is excited with a sine
The LVDT consists of a primary coil wound over wave voltage (Vin excitation), it generates a Temperature effects, origins
the whole length of a non-ferromagnetic bore variable magnetic field which, concentrated While the temperature coefficient of
liner coil form or bobbin, usually made from by the core, induces the secondary sine sensitivity (sensitivity is the output per unit
plastic or a ceramic material. Two secondary wave voltages. While the secondary windings of displacement) is determined by the
coils are wound on top of the primary coil are designed so that the differential output number of winding turns, the resistance of
for long stroke LVDTs (i.e. for actuator main voltage (Va- Vb) is proportional to the core the windings, the geometry of the armature,
RAM) or each side of the primary coil for short position from null, the (Va- Vb) phase shift with and the resistivity and permeability of the
stroke LVDTs (i.e. for electro-hydraulic servo- reference to the excitation (close to 0 or metals used in the LVDT construction, the
valve or EHSV). The two secondary windings close to 180 depending on the direction) null position shift with temperature is solely
are typically connected in opposite series determines the direction away from the affected by the expansion coefficients
(differential). mechanical zero position. The zero position, and lengths of the materials used in the
called null position, is defined as the core
construction of the transducer; it is therefore
A ferromagnetic core, attached to the position where the phase angle of the (Va- Vb)
object to be measured, slides along the axis a highly predictable and repeatable
differential output is 90.
of the tube and magnetically couples the reference position.
primary to the secondary winding turns that The LVDT: construction and principle of Ratiometric operation for low temperature
are located along the length of the core. operation coefficient of sensitivity
Even though the secondary windings of the The differential output between the two The LVDT can be designed so that the sum
long stroke LVDT are shown on top of each secondary outputs (Va- Vb) when the core of the secondary voltages (Va+ Vb) remains
Fig. 1 a: LVDT cross-section, short stroke. Fig. 1 b: LVDT cross-section, long stroke.
EngineerIT - January 2013 41
Fig. 2: LVDT schematic. Fig. 3: LVDT waveforms.
constant over the displacement measuring the reference temperature; Ca and Cb are sensor. Even if the power is switched off,
range. By designing the signal conditioning the temperature co-efficients of sensitivity when switched on the LVDT shows the same
electronic circuitry to measure the difference for Va and Vb respectively. If Ca and Cb measurement. This means that no positional
over sum ratio R = (Va- Vb)/(Va+ Vb), one can are assumed equal (for a first order information is used. LVDTs are commonly used
approximation), then the ratio is in for positive feedback in servo mechanisms
see that the temperature coefficient of
dependent of temperature: and for automated measurements in
sensitivity can be dramatically reduced, as
demonstrated below. [Va(t)- Vb(t)] / [Va(t)+ Vb(t)] = [Va(70F)- Vb(70F)] / machinetools,amongstmanyother
[Va(70F)+Vb(70F)] scientific and industrial applications.
Secondary output voltages function of
temperature: or Contact Tobie Muller,
Accutronics,
Va(t)=Va(70F)*Ca Vb(t)=Vb(70F)*Cb R(t) = R(70F)
Tel 011 781-2645,
The variable t is the temperature; 70F is A LVDT can be used as an absolute position tmuller@accutronics.co.za
42 January 2013 - EngineerIT
Вам также может понравиться
- Principles of The LVDTДокумент3 страницыPrinciples of The LVDTWalid FattahОценок пока нет
- TEJAS M & M ReportДокумент6 страницTEJAS M & M ReportSachin AОценок пока нет
- DECE Lab IeДокумент7 страницDECE Lab IemurthyОценок пока нет
- LVDTДокумент6 страницLVDTSobia JamilОценок пока нет
- What Is An LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) ?Документ3 страницыWhat Is An LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) ?muhammad aliОценок пока нет
- Ls CДокумент4 страницыLs CkylegazeОценок пока нет
- Principle of LVDT OperationДокумент4 страницыPrinciple of LVDT OperationivanОценок пока нет
- Linear Variable Differential TransformerДокумент3 страницыLinear Variable Differential TransformerArbaz KhanОценок пока нет
- 6415 FundamentalsImprovements KZ-DC 20101025 WebДокумент13 страниц6415 FundamentalsImprovements KZ-DC 20101025 Websaravanan chennanОценок пока нет
- LVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer: Presented By: Shantanu Inderesh Harsh Presentation Made By: ShantanuДокумент10 страницLVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer: Presented By: Shantanu Inderesh Harsh Presentation Made By: Shantanuindresh singhОценок пока нет
- Instrumentation & Process Control VivaДокумент17 страницInstrumentation & Process Control VivaHarshaОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- Seminar Project LVDT: - To Study The Basics, ConstructionДокумент9 страницSeminar Project LVDT: - To Study The Basics, ConstructionNaeem SaifОценок пока нет
- LVDT - Working Principle Construction Types, Advantages and ApplicationsДокумент11 страницLVDT - Working Principle Construction Types, Advantages and ApplicationsKunal AhiwaleОценок пока нет
- Aim of The Experiment: Linear Variable Differential TransformerДокумент20 страницAim of The Experiment: Linear Variable Differential TransformerAryan BatraОценок пока нет
- Design of A Buck Converter PDFДокумент4 страницыDesign of A Buck Converter PDFDaniel PancheОценок пока нет
- Mm322 Lab 5 - LVDTДокумент3 страницыMm322 Lab 5 - LVDTKelemedi DreuОценок пока нет
- Linear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTДокумент7 страницLinear Variable Differential Transformer LVDTRajeev ValunjkarОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 UpdatedДокумент22 страницыExperiment 1 Updatedyoho hohoОценок пока нет
- Reactive Power FlowДокумент7 страницReactive Power FlowDeena DevarajОценок пока нет
- Control of A Grid-Connected Double-Fed Induction Generator Wind TurbineДокумент7 страницControl of A Grid-Connected Double-Fed Induction Generator Wind TurbineRevuОценок пока нет
- MeggerДокумент23 страницыMeggerbertovalen100% (1)
- LVDT Working PrincipleДокумент2 страницыLVDT Working Principlekulwinder030373Оценок пока нет
- Understanding Power MOSFET Avalanche OperationДокумент12 страницUnderstanding Power MOSFET Avalanche OperationJorge Alberto Romero CoronaОценок пока нет
- 2 - Analogue Electonics ST PaulsДокумент39 страниц2 - Analogue Electonics ST PaulsthuanОценок пока нет
- Variable Displacement Transformer, TransducerДокумент3 страницыVariable Displacement Transformer, TransducerArunОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1: LVDT: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыExperiment 1: LVDT: ObjectiveManish PuraswaniОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ29 страницLecture 2Azriq BahariОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Рейтинг: 2.5 из 5 звезд2.5/5 (3)
- Study On Transient Overvoltages in The Converter Station of HVDC-MMC LinksДокумент7 страницStudy On Transient Overvoltages in The Converter Station of HVDC-MMC LinksGoriparthi SambasievaraavОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual Power ElectronicsДокумент39 страницLab Manual Power ElectronicsZainab AnwarОценок пока нет
- Monitoring and Protection of Distribution Transformer Using GSM ModuleДокумент5 страницMonitoring and Protection of Distribution Transformer Using GSM Moduleatheb12345Оценок пока нет
- aspublishedonIEEEXplore TIE2349876Документ10 страницaspublishedonIEEEXplore TIE2349876josmelОценок пока нет
- Scott and L Brance TransformersДокумент9 страницScott and L Brance TransformersRicardo A VergaraОценок пока нет
- Design Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Solar InverterДокумент5 страницDesign Fabrication and Performance Analysis of Solar InverterSyed ZadaaОценок пока нет
- Adaptive Hysteretic Comparator With Op-Amp Threshold Level Setting-2008Документ4 страницыAdaptive Hysteretic Comparator With Op-Amp Threshold Level Setting-2008Suhas ShirolОценок пока нет
- Experiment 2 Circuit Simplification A. Series and Parallel Circuit. B. Star and Delta TransformationДокумент12 страницExperiment 2 Circuit Simplification A. Series and Parallel Circuit. B. Star and Delta TransformationronakОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics LabДокумент6 страницPower Electronics LabRafeyОценок пока нет
- Linear Variable Differential TransducerДокумент2 страницыLinear Variable Differential TransducerAnonymous s6xbqCpvSWОценок пока нет
- No Item Units Required Tendered: 2.12 Power TransformersДокумент27 страницNo Item Units Required Tendered: 2.12 Power TransformersdienlangchuОценок пока нет
- Relayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01Документ43 страницыRelayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01kenlavie2Оценок пока нет
- LVDT Intro - PDF 4Документ6 страницLVDT Intro - PDF 4mehdiОценок пока нет
- M 136Документ6 страницM 136vinoth kumarОценок пока нет
- Control & Measurement Practical Iv Semester, B.Tech Ee Course Code: Eec273Документ5 страницControl & Measurement Practical Iv Semester, B.Tech Ee Course Code: Eec273JomeОценок пока нет
- Paper9 Zellagui PDFДокумент17 страницPaper9 Zellagui PDFGunjan GaganОценок пока нет
- Multilin: Synchronism Check EquipmentДокумент26 страницMultilin: Synchronism Check EquipmentĐức Nguyễn XuânОценок пока нет
- A ZVS-PWM Single-Phase Inverter Using A ZVS Transformer-Isolated Step-Up Down DC LinkДокумент5 страницA ZVS-PWM Single-Phase Inverter Using A ZVS Transformer-Isolated Step-Up Down DC Linkjuan8aОценок пока нет
- Electronic Circuits 1Документ119 страницElectronic Circuits 1mohan100% (1)
- Chaper 5 Power Conditioning: Presentation #4Документ20 страницChaper 5 Power Conditioning: Presentation #4Sabri BouloumaОценок пока нет
- Design and Simulation of Triggering Circ PDFДокумент4 страницыDesign and Simulation of Triggering Circ PDFYimy GarciaОценок пока нет
- Exp LVDTДокумент4 страницыExp LVDTSuneesh EОценок пока нет
- Controlled Switching of Circuit Breaker and Its Site MeasurementДокумент4 страницыControlled Switching of Circuit Breaker and Its Site MeasurementprabhuОценок пока нет
- EC6304 Uw PDFДокумент119 страницEC6304 Uw PDFsivadhanuОценок пока нет
- EXP 1-10 Manual HV LabbbbbbbbbbbbbbvbbbbbbbbДокумент37 страницEXP 1-10 Manual HV LabbbbbbbbbbbbbbvbbbbbbbbDEEPAK KUMAR SINGHОценок пока нет
- HVDC PowerДокумент70 страницHVDC PowerHibba HareemОценок пока нет
- WEG Thermal Overload Relays RW enДокумент24 страницыWEG Thermal Overload Relays RW enshift EngineerОценок пока нет
- A5 EXPERIMENT LVDT and RVDTДокумент14 страницA5 EXPERIMENT LVDT and RVDTDuminduJayakodyОценок пока нет
- Traffic Flow Theory: Epartment of Ivil NgineeringДокумент2 страницыTraffic Flow Theory: Epartment of Ivil NgineeringmehdiОценок пока нет
- Urban Gridlock: Macroscopic Modeling and Mitigation Approaches Carlos F. DaganzoДокумент8 страницUrban Gridlock: Macroscopic Modeling and Mitigation Approaches Carlos F. DaganzomehdiОценок пока нет
- A1.05-Pipe Joints and GasketsДокумент2 страницыA1.05-Pipe Joints and GasketsmehdiОценок пока нет
- Traffic Flow Theory: Epartment of Ivil NgineeringДокумент2 страницыTraffic Flow Theory: Epartment of Ivil NgineeringmehdiОценок пока нет
- Gaging Probes Get Results - 2013-06-10 - Quality MagazineДокумент5 страницGaging Probes Get Results - 2013-06-10 - Quality MagazinemehdiОценок пока нет
- Consortium: Critical State Soil MechanicsДокумент12 страницConsortium: Critical State Soil MechanicsmehdiОценок пока нет
- Slyt 680Документ6 страницSlyt 680mehdiОценок пока нет
- RCC Dams in Spain. Present and Future (Inglés)Документ15 страницRCC Dams in Spain. Present and Future (Inglés)mehdiОценок пока нет
- Reminder - Upcoming Form 2290 Deadline For Vehicles 1st Used in January - ExpressTruckTax BlogДокумент5 страницReminder - Upcoming Form 2290 Deadline For Vehicles 1st Used in January - ExpressTruckTax BlogmehdiОценок пока нет
- C1609C1609M 30264Документ9 страницC1609C1609M 30264mehdiОценок пока нет
- LVDT Intro - PDF 4Документ6 страницLVDT Intro - PDF 4mehdiОценок пока нет
- Technology Services: Software Downloads..Документ2 страницыTechnology Services: Software Downloads..mehdiОценок пока нет
- Understanding Errors in Hand-Held Measuring Instruments - Modern Machine ShopДокумент5 страницUnderstanding Errors in Hand-Held Measuring Instruments - Modern Machine ShopmehdiОценок пока нет
- Simpleware For Pavement Research: Case StudyДокумент2 страницыSimpleware For Pavement Research: Case StudymehdiОценок пока нет
- Asphalt Plants555Документ4 страницыAsphalt Plants555mehdiОценок пока нет
- Review On Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Method: Raman Kumar Dr. Pardeep Kumar GuptaДокумент6 страницReview On Mechanistic-Empirical Pavement Design Method: Raman Kumar Dr. Pardeep Kumar GuptamehdiОценок пока нет
- DW 2224 999 1421 1004 05 Model 2Документ1 страницаDW 2224 999 1421 1004 05 Model 2mehdiОценок пока нет
- HF G ArticleДокумент5 страницHF G ArticlemehdiОценок пока нет
- LVDT Intro - PDF 4Документ6 страницLVDT Intro - PDF 4mehdiОценок пока нет
- Modified Asphalt Research Center (MARC) IPas and IPas-2 Software PackagesДокумент2 страницыModified Asphalt Research Center (MARC) IPas and IPas-2 Software PackagesmehdiОценок пока нет
- Agreement Between SubjectДокумент6 страницAgreement Between SubjectYanaОценок пока нет
- Hybrid CodeДокумент19 страницHybrid CodeThuận Nguyễn vănОценок пока нет
- (IJCST-V6I6P22) :prof. Sudhir Morey, Prof. Sangpal SarkateДокумент7 страниц(IJCST-V6I6P22) :prof. Sudhir Morey, Prof. Sangpal SarkateEighthSenseGroupОценок пока нет
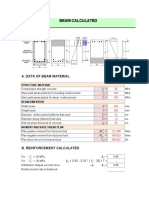
- Balok 30x50 PDFДокумент4 страницыBalok 30x50 PDFdethaОценок пока нет
- Hand Book of Electronics: January 2010Документ16 страницHand Book of Electronics: January 2010DanyBobОценок пока нет
- Troubleshooting CAT 3516B and 3516 B High Displacement EnginesДокумент164 страницыTroubleshooting CAT 3516B and 3516 B High Displacement EnginesFamilia Marín Cadena84% (19)
- Lab 3Документ8 страницLab 3Mian BlalОценок пока нет
- Anderol 6320: H1 High Performance Food Grade Gear LubricantДокумент1 страницаAnderol 6320: H1 High Performance Food Grade Gear Lubricanteka prayataОценок пока нет
- Quiz 1 Will Be Reviewed in Discussion Sessions On Wednesday/Thursday Units 2 & 3 Homework Sets Due Sunday at 11:59 PM Use The Help Lab (JFB Rotunda) For Homework Help!Документ39 страницQuiz 1 Will Be Reviewed in Discussion Sessions On Wednesday/Thursday Units 2 & 3 Homework Sets Due Sunday at 11:59 PM Use The Help Lab (JFB Rotunda) For Homework Help!Vishal SinghОценок пока нет
- GPS318 Tracker Communication Protocol V1 5Документ25 страницGPS318 Tracker Communication Protocol V1 5Yellows OchentaОценок пока нет
- Determination of Benzoic Acid and Salicylic Acid PDFДокумент5 страницDetermination of Benzoic Acid and Salicylic Acid PDFFadilah QonitahОценок пока нет
- Eddy AxialДокумент20 страницEddy Axialandrea19711971Оценок пока нет
- Exam Ccts 3Документ10 страницExam Ccts 3atik rahmanОценок пока нет
- Carbonates: Mineral GroupsДокумент33 страницыCarbonates: Mineral GroupsJay Suganob100% (1)
- S4 HW Ans Sheet (CH - 18 Salts and Neutralization) - SДокумент3 страницыS4 HW Ans Sheet (CH - 18 Salts and Neutralization) - STSZ HIN CHANОценок пока нет
- BPMN With PrologДокумент6 страницBPMN With PrologCarlos Gomes de BarrosОценок пока нет
- CP200Документ2 страницыCP200tzimistigrisОценок пока нет
- WSZ ControllerДокумент6 страницWSZ ControllerAtiqur Rahman AtiqОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics Engine Management SystemДокумент10 страницBasic Electronics Engine Management SystemRailyn Tagwalan Timol100% (1)
- POPAdrian-Petru L2 PDFДокумент8 страницPOPAdrian-Petru L2 PDFTomescu MadalinОценок пока нет
- Deep Learning Based Trajectory Optimization For UAVДокумент23 страницыDeep Learning Based Trajectory Optimization For UAVSalil SharmaОценок пока нет
- Arduino Based Photovore Robot: Ece 6231 Communication System DesignДокумент37 страницArduino Based Photovore Robot: Ece 6231 Communication System Designeun mun kangОценок пока нет
- March 25, 2021 Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 8 Content StandardsДокумент8 страницMarch 25, 2021 Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade 8 Content StandardsJohn Carl AparicioОценок пока нет
- Segway RMP-based Robotic Transport SystemДокумент14 страницSegway RMP-based Robotic Transport SystemSungkwan ParkОценок пока нет
- Four Corners-East and WestДокумент9 страницFour Corners-East and WesttrelteopetОценок пока нет
- Material HPLCДокумент19 страницMaterial HPLCIsmil ImamaОценок пока нет
- Truckcrn PDFДокумент6 страницTruckcrn PDFDusan VeljkovicОценок пока нет
- Lab Suite User ManualДокумент108 страницLab Suite User ManualluisgeologoОценок пока нет
- Amte 235 - Cooling-SystemsДокумент86 страницAmte 235 - Cooling-Systemssololol colonelОценок пока нет