Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Abbott v. Sandoz Establishes Bright-Line Rule for Product-by-Process Patent Claims
Загружено:
shivanshuОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Abbott v. Sandoz Establishes Bright-Line Rule for Product-by-Process Patent Claims
Загружено:
shivanshuАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Abbott v.
Sandoz
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Abbott v. Sandoz was a US patent law case argued before the United States Court of Appeals for
the Federal Circuit that established a bright-line ruling regarding claims of patent infringement
relating to disagreements over so-called "product-by-process" claims. The case was decided on May
18, 2009.[1][2][3]
Contents
[hide]
1 Background
2 Case
3 Decision
4 Importance
5 References
Background[edit]
Abbott Labs had a patent on a specific drug called Omnicef used to combat ear infections. Lupin
Limited had a court rule that a generic form of Omnicef it produced did not infringe on Abbott's patent
since their process to make the drug was different. After the court had ruled in Lupin's favor, Abbott
appealed and the case was combined with several other legal suits against smaller pharmaceutical
companies, and thus was renamed Abbott v. Sandoz. The federal court affirmed the lower court's
decision.[1][2][3]
Case[edit]
For several years, the courts have disagreed on the product-by-process definition. Product-by-
process refers to the question of determining if a product is legally different from another if it is
created by a different process. Federal courts have offered contradictory resolutions on the subject.
The court determined that a patent may limit itself if it specifically defines the process of creation.[1][2][3]
Decision[edit]
Despite the legal discrepancies, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) held that
using a different process in this case did not infringe on Abbott's patent and ruled in Sandoz's favor,
along with ruling in favor of the other small pharmaceuticals companies. Since Abbott had not
patented all processes to create its drug, it could not protect from the processes being used by
others.[1][2][3]
Importance[edit]
This case further enforces the product-by-process definition, and holds that a patent does not protect
from infringement through a different process unless necessarily described. Patent-holders seeking
to cover their products entirely must find ways to protect every process to create the same item if
they want complete protection from infringement.[1][2][3]
Вам также может понравиться
- Survey of IP OutlineДокумент73 страницыSurvey of IP OutlinePatrick PaulОценок пока нет
- Petition for Certiorari: Denied Without Opinion Patent Case 93-1413От EverandPetition for Certiorari: Denied Without Opinion Patent Case 93-1413Оценок пока нет
- Patent InfringementДокумент39 страницPatent InfringementBindu SharmaОценок пока нет
- Case Study - Novartis V UOI PDFДокумент15 страницCase Study - Novartis V UOI PDFRaGa JoThiОценок пока нет
- Gevo, Inc. v. Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC, Et Al., C.A. Nos. 12-301-SLR, 12-448-SLR (D. Del. Dec. 16, 2013)Документ6 страницGevo, Inc. v. Butamax Advanced Biofuels LLC, Et Al., C.A. Nos. 12-301-SLR, 12-448-SLR (D. Del. Dec. 16, 2013)gbrodzik7533Оценок пока нет
- Tax 1Документ1 страницаTax 1Alok RamanОценок пока нет
- Section 3 (D) of Patents Act 1970: Novartis v. U.O.IДокумент1 страницаSection 3 (D) of Patents Act 1970: Novartis v. U.O.IAlok RamanОценок пока нет
- Novartis V Union of India - A Case StudyДокумент2 страницыNovartis V Union of India - A Case StudyHersh Desai100% (1)
- Important Case Studies Related To Pharmaceutical Patents: 1. AzithromycinДокумент2 страницыImportant Case Studies Related To Pharmaceutical Patents: 1. AzithromycinPallab DattaОценок пока нет
- In The United States District Court ForДокумент10 страницIn The United States District Court ForAerst2Оценок пока нет
- Patent CasesДокумент7 страницPatent CasesRishabh JainОценок пока нет
- Case Analysis of Novartis Ag V. Uoi.-People'S Right V. Commercial InterestДокумент4 страницыCase Analysis of Novartis Ag V. Uoi.-People'S Right V. Commercial InterestyashОценок пока нет
- In The United States District Court For The District of DelawareДокумент13 страницIn The United States District Court For The District of DelawareAerst2Оценок пока нет
- Famous Judgements in PatentsДокумент3 страницыFamous Judgements in PatentsDevvrat garhwalОценок пока нет
- Order On Defendants' Motion To Bifurcate: Overhauser Law Offices LLCДокумент4 страницыOrder On Defendants' Motion To Bifurcate: Overhauser Law Offices LLCRenee CookОценок пока нет
- AngioDynamics, Inc. v. Biolitec AG, 1st Cir. (2015)Документ15 страницAngioDynamics, Inc. v. Biolitec AG, 1st Cir. (2015)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Business Law AA 03.03.2021Документ4 страницыBusiness Law AA 03.03.2021Anamika ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Case SummaryДокумент2 страницыCase SummaryVinayОценок пока нет
- Medtronic, Inc. v. Mirowski Family Ventures, LLC 12-1128 - h315Документ14 страницMedtronic, Inc. v. Mirowski Family Ventures, LLC 12-1128 - h315Doc_Rx9Оценок пока нет
- Filed: Patrick FisherДокумент25 страницFiled: Patrick FisherScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Sucampo Pharmaceutic v. Astellas Pharma, 4th Cir. (2006)Документ11 страницSucampo Pharmaceutic v. Astellas Pharma, 4th Cir. (2006)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- For P170 Photocopy and Bookbind, Dean Only Discussed Chapter 1 of The Book)Документ6 страницFor P170 Photocopy and Bookbind, Dean Only Discussed Chapter 1 of The Book)gaelanОценок пока нет
- Top Ten Patent Cases: Case Name Issue StatusДокумент18 страницTop Ten Patent Cases: Case Name Issue StatusJames LindonОценок пока нет
- Taming The Doctrine of Equivalents in Light of Patent FailureДокумент29 страницTaming The Doctrine of Equivalents in Light of Patent FailureSantosh PatiОценок пока нет
- In The United States District Court For The District of DelawareДокумент12 страницIn The United States District Court For The District of DelawareYCSTBlogОценок пока нет
- 00064-05 2d130oДокумент6 страниц00064-05 2d130olegalmattersОценок пока нет
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitДокумент8 страницUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Novartis AG vs Union of India: A Landmark Case on PatentabilityДокумент13 страницNovartis AG vs Union of India: A Landmark Case on PatentabilityRyan SinhaОценок пока нет
- Bowman - Monsanto: Self-Replicating Seeds David - Goliath DON Quixote - Windmills?Документ66 страницBowman - Monsanto: Self-Replicating Seeds David - Goliath DON Quixote - Windmills?akwadОценок пока нет
- United States Court of Appeals, Tenth CircuitДокумент13 страницUnited States Court of Appeals, Tenth CircuitScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Novartis Verdict Upholds India's Balancing of Patent Rights and Access to MedicineДокумент7 страницNovartis Verdict Upholds India's Balancing of Patent Rights and Access to Medicineमधुकर आनंदОценок пока нет
- Novartis Vs IndiaДокумент3 страницыNovartis Vs IndiaAbhishek Suresh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Medtronic, Inc. v. Mirowski Family Ventures, LLC, 134 S. Ct. 843 (2014)Документ14 страницMedtronic, Inc. v. Mirowski Family Ventures, LLC, 134 S. Ct. 843 (2014)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Top Ten Patent Cases (Supreme Court)Документ35 страницTop Ten Patent Cases (Supreme Court)James LindonОценок пока нет
- LemleyДокумент64 страницыLemleyMeshandren NaidooОценок пока нет
- 9a WIPO Arbitration Case ExamplesДокумент9 страниц9a WIPO Arbitration Case ExamplesАндрей СергеевичОценок пока нет
- Not PrecedentialДокумент6 страницNot PrecedentialScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Novartis. SummaryДокумент3 страницыNovartis. SummaryDechen KhonglahОценок пока нет
- 2009-07-08 Church and Dwight v. Abbott (Brown)Документ36 страниц2009-07-08 Church and Dwight v. Abbott (Brown)svlawgeek100% (2)
- AstraZeneca v. Dr. ReddysДокумент14 страницAstraZeneca v. Dr. ReddysMarkman AdvisorsОценок пока нет
- RQ28B2B30Документ7 страницRQ28B2B30slachrummy4Оценок пока нет
- United States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitДокумент36 страницUnited States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- AngioDynamics, Inc. v. Biolitec AG, 1st Cir. (2015)Документ16 страницAngioDynamics, Inc. v. Biolitec AG, 1st Cir. (2015)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- PATENTДокумент12 страницPATENTthilakОценок пока нет
- Organisation of Pharmaceutical Producers of India: Issue 12, June 2009Документ31 страницаOrganisation of Pharmaceutical Producers of India: Issue 12, June 2009rahulОценок пока нет
- DXCM ABT Appeal 3 Jan 24Документ12 страницDXCM ABT Appeal 3 Jan 24XDL1Оценок пока нет
- Meijer, Inc. v. Biovail Corp., No. 05-7066, 05-7069, 05-7084, 06-7118Документ21 страницаMeijer, Inc. v. Biovail Corp., No. 05-7066, 05-7069, 05-7084, 06-7118IPCreature100% (1)
- PRAKASH OCHWANI C-17 BBA LLB 5th Year IPRДокумент9 страницPRAKASH OCHWANI C-17 BBA LLB 5th Year IPRPRAKASH OCHWANIОценок пока нет
- Interim Relief and Intellectual Property IssueДокумент9 страницInterim Relief and Intellectual Property IssueChinmoy MishraОценок пока нет
- DM Research, Etc. v. College of American, 170 F.3d 53, 1st Cir. (1999)Документ8 страницDM Research, Etc. v. College of American, 170 F.3d 53, 1st Cir. (1999)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Supreme Court of The United States: Medtronic, Inc. V. Mirowski Family Ventures, LLCДокумент14 страницSupreme Court of The United States: Medtronic, Inc. V. Mirowski Family Ventures, LLCpauloverhauserОценок пока нет
- NovartisДокумент3 страницыNovartisRavi VedyaОценок пока нет
- 13-08-01 Verizon AdvAgencies Ford Motion To Participate in HearingДокумент17 страниц13-08-01 Verizon AdvAgencies Ford Motion To Participate in HearingFlorian MuellerОценок пока нет
- Medicis Pharmaceutical Corp., Et Al. v. Actavis Mid Atlantic LLCДокумент7 страницMedicis Pharmaceutical Corp., Et Al. v. Actavis Mid Atlantic LLCYCSTBlogОценок пока нет
- Societe Des Produits NestleДокумент1 страницаSociete Des Produits NestleJulie Ann Joy GarciaОценок пока нет
- United States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitДокумент13 страницUnited States Court of Appeals: For The First CircuitScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Aktiebolaget Electrolux v. Armatron International, Inc., Aktiebolaget Electrolux v. Armatron International, Inc., 999 F.2d 1, 1st Cir. (1993)Документ9 страницAktiebolaget Electrolux v. Armatron International, Inc., Aktiebolaget Electrolux v. Armatron International, Inc., 999 F.2d 1, 1st Cir. (1993)Scribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
- Evergreening of Patent: Dr. Vijay OakДокумент6 страницEvergreening of Patent: Dr. Vijay OaksathiyaОценок пока нет
- Novratis Case Law AnalysisДокумент12 страницNovratis Case Law AnalysisdhruvsheoranОценок пока нет
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitДокумент20 страницUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsОценок пока нет
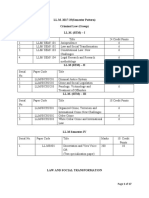
- LL.M. Criminal Law Course OverviewДокумент17 страницLL.M. Criminal Law Course OverviewshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Mats Law School Ll.M. One Year Programme: Syllabus 1st Semester (July-December)Документ26 страницMats Law School Ll.M. One Year Programme: Syllabus 1st Semester (July-December)Saurabh BaraОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFДокумент1 страницаCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFДокумент1 страницаCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент3 страницыCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент2 страницыCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент2 страницыCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент1 страницаCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент8 страницCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFДокумент1 страницаCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFДокумент1 страницаCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote Online PDFshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент1 страницаCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент9 страницCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Civil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineДокумент3 страницыCivil Services - Microsoft OneNote OnlineshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Synopsis Law of Contracts - I Communication of Acceptance by Instantaneous ModesДокумент2 страницыSynopsis Law of Contracts - I Communication of Acceptance by Instantaneous ModesshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Law of AnimalДокумент10 страницLaw of AnimalshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Quick reference usernames and passwordsДокумент3 страницыQuick reference usernames and passwordsshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Sunil Gupta and Ors Vs State of Madhya Pradesh and Ors On 2 May, 1990Документ11 страницSunil Gupta and Ors Vs State of Madhya Pradesh and Ors On 2 May, 1990shivanshuОценок пока нет
- Review PetitionДокумент22 страницыReview PetitionshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Does the Declaration Express the Will of the StateДокумент3 страницыDoes the Declaration Express the Will of the StateshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Viewpoint of Overseas Nations On Freedom of Expression: ST THДокумент15 страницViewpoint of Overseas Nations On Freedom of Expression: ST THshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Water Pollution Laws in India: A Critical AnalysisДокумент49 страницWater Pollution Laws in India: A Critical AnalysisshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Laws and Principles of Guardianship in IndiaДокумент18 страницLaws and Principles of Guardianship in IndiashivanshuОценок пока нет
- Instructions Ll.m.Документ3 страницыInstructions Ll.m.shivanshuОценок пока нет
- Code of Conduct - Insider TradingДокумент17 страницCode of Conduct - Insider TradingshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Service Tax Reforms in IndiaДокумент57 страницService Tax Reforms in IndiashivanshuОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentДокумент1 страницаNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentshivanshuОценок пока нет
- CPC RohitДокумент2 страницыCPC RohitshivanshuОценок пока нет
- Abstract CompanyДокумент1 страницаAbstract CompanyshivanshuОценок пока нет