Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Exercise 2 - Embryology Lab
Загружено:
Ivy Cruz0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
109 просмотров2 страницыExercise 2 - Embryology Lab
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документExercise 2 - Embryology Lab
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
109 просмотров2 страницыExercise 2 - Embryology Lab
Загружено:
Ivy CruzExercise 2 - Embryology Lab
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Exercise 2 2.
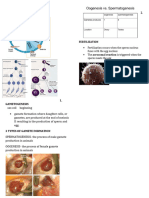
1 Fertilization of a Microlecithal Egg
Fertilization & Maturation Stage Unfertilized egg
- Extensive membranes observed in fertilized eggs are
In animals in general, fertilization is the direct interaction and absent here
fusion of two germinal cells (one egg and one spermatozoan), o Vacuolated cytoplasm
resulting in the initiation of cleavage, gastrulation and the species- o Inconspicuous nuclei
specific developmental program that characterizes each organism. o Thin cell membranes
Ascaris o Elongated and larger than fertile egg
o Thin shelled
- Parasitic nematode in the intestine of some animals o Shell ranges from irregular mammillations to relatively
- Well-developed reproductive system smooth layer completely lacking
- Sexes are separate
- Ascaris eggs - Transparent
Sperm penetration stage
o Each branch of eh shaped reproductive tract in the female
begins with a coiled and threadlike ovary and enlarges at - Characterized by the presence of the sperm head inside
the posterior region as the uterus. the egg.
o The uteri of the two branches unite for form the vagina, - Sperm heads are seen as small, dense and triangular
which ends in the genital pore or vulva. bodies.
o During copulation and insemination, the sperm cells enter - Within the cytoplasm of an oocyte, which has been
the eggs in the genital tract even before they have penetrated by a sperm cell, its nucleus, will be seen as one
completed the final stage in oogenesis. having a different shape of consistency.
o Fertilization occurs at the end of the uterus nearest the - Usually, during this stage, the cell is in its primary oocyte
oviduct. stage.
o Stage of development: Primary Oocyte
The first maturation division of oogenesis takes places o Presence of bivalents
simultaneously with ovulation. The secondary oocyte thus formed o Heads of spermatozoa small, dense triangular bodies
remain in such condition and waits for fertilization to occur. o After fertilization: forms fertilization membrane and outer
In vertebrates, meiosis progresses as far as the metaphase of the shell (Chitinous shell)
second maturation division.
Primary oocytes
If no fertilization takes place, it will just degenerate. Have a vacuolated cytoplasm
Inconspicuous nuclei
If sperm entrance takes place, the second maturation division is Thin cell membrane
continued. After fertilization, they become surrounded
A series of events then happen that triggers development. These by a fertilization membrane and thick
events are triggered by the presence of sperm at the egg surface. outer shell.
Meiosis II can only continue after this has
If the sperm penetrates the egg prior to the completion or even the happened.
start of meiosis, the sperm head or nucleus stays in the cytoplasm Sperm heads may also be seen between
of the egg until the female nucleus is formed. oocytes.
Fertilization is regarded complete when the male and female Maturation stage
chromosomes are joined. The zygote is thus formed.
First polar body formation
Ascaris have diploid number of 4.
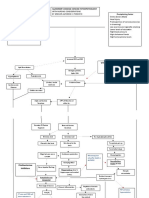
Stages of Maturation During the separation of the members of
1. Maturation Stage the homologous pair, two groups of four
2. Sperm Penetration Stage chromosomes can be observed in the cell.
3. Pronuclear Stage Chromosomes appear as bread-like
4. Fusion Stage structures.
5. Early Cleavage Tetrads that will be part of the polar body
will be found in the periphery of the
primary oocyte.
Such a cell may also show the extruded first
or primary polar body on its surface. This
appears lie a small spherical structure
attached on the membrane of the oocyte
and enveloped by the cytoplasm. It can
also be observed on the fertilization - In some cases, an array of microtubules can be observed
membrane (inner layer of the chitinous near the centrioles of the female and male nuclei. This
layer) as a black streak. terminates the process of fertilization.
o Fusion of male and female pronuclei
At this point, the sperm head should be transforming into a o Presence of 2 polar bodies (inner-2nd polar body; outer-1st
pronuclei. The HAPLOID sperm head and some cytoplasm from the polar body) or 1 polar body (2nd polar body near the outer
spermatozoan are drawn into the cytoplasm of the egg. Its nucleus covering; 1st polar body already extruded from the shell)
then swells, its centriole generates an array of microtubules, and it o Perivitelline space space between the egg and the
becomes the male pronucleus. The male pronucleus therefore is the fertilization membrane
nucleus of the sperm after it has penetrated the cytoplasm of the o Stage of development: Ovum
ovum and enlarges. The nucleus of the ovum, on the other hand,
which is a product of the second meiotic division is called a female Early cleavage
pronucleus.
- Cleavage and later developmental processes occur while
the egg is still inside the uterus
Second polar body formation o Stage of Development: Zygote
o Diploid
- A second polar is formed when a secondary oocyte o Entire cell dividing. Observe the phase of mitosis
extrudes one half of its longitudinal split chromosomes. (Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase)
- A second polar body looks exactly like a first polar body.
It is a 2nd polar body if:
1. Two black streaks are observed an it is the inner streak.
2. Only one streak appears, but the female pronucleus is
already formed.
It must be noted however that aside from the second polar body, an
ootid is also formed after the 2nd meiotic division. There is really no
clear distinction between an ootid and an ovum. However, the male
and the female pronuclei will fuse only if the egg cell (ovum) is
already functional.
Pronuclear stage
- Before the actual fusion of the male and female pronuclei,
the oocyte has yet to complete the maturation process.
- In this condition, the male pronucleus appears as a dense
body near the center of the egg.
- The perivitelline space (between the egg and the
fertilization membrane) is filled with fluid.
o Formation of Second polar bodies
o Separation of sister chromatids
o 2nd polar body extruded (2 polar bodies will be seen; the
outer one is the first and the inner one is the second polar
body)
o Stage of development: Ootid
Fusion stage
- Female and male pronuclei fuse following their migration
towards along each other.
- Either the female pronucleus migrates to the male or the
male pronucleus migrates to the female resulting to the
fusion of the membranes of these pronuclei, which
produces the diploid zygote nucleus.
- This is differentiated therefore from the pronuclear stage
because the membranes of the male and female
pronuclei are fusing.
Вам также может понравиться
- Oogenesis and Embryology EssentialsДокумент52 страницыOogenesis and Embryology EssentialsRaoulSusanto SusantoОценок пока нет
- Exp 2 4.1 1Документ11 страницExp 2 4.1 1Carlo MendozaОценок пока нет
- Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis ExplainedДокумент11 страницSpermatogenesis and Oogenesis ExplainedMarianne LopezОценок пока нет
- Animal Development: Egg SpermДокумент3 страницыAnimal Development: Egg Spermオリーバ スティーブンОценок пока нет
- Midterm GenHisto ReviewerДокумент12 страницMidterm GenHisto ReviewerNATALIE NICOLE GABASОценок пока нет
- Biology Lectures Finals-2Документ12 страницBiology Lectures Finals-2Jaina Alexandra MendozaОценок пока нет
- Stages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoДокумент3 страницыStages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoLynnelljhyen MALUBAYОценок пока нет
- Anbt - 608: Submitted ToДокумент50 страницAnbt - 608: Submitted ToMayuriGulhaneОценок пока нет
- Early Embryonic Development and Organ FormationДокумент43 страницыEarly Embryonic Development and Organ FormationKriztine Mae GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Spgbio 2 ReviewerДокумент37 страницSpgbio 2 ReviewerKaycee HeokkaidoОценок пока нет
- Zebra FishДокумент2 страницыZebra FishmantamadОценок пока нет
- Concepcion e ImplantacionДокумент10 страницConcepcion e ImplantacionDiana Estefany Varas MaguiñaОценок пока нет
- Cell Division: There Are Two Types of Cell Divisions Which Are andДокумент23 страницыCell Division: There Are Two Types of Cell Divisions Which Are andapi-3706483Оценок пока нет
- Animal Diversity and DevelopmentДокумент68 страницAnimal Diversity and DevelopmentGabrielle Salamanca CastuloОценок пока нет
- Development Status'Документ2 страницыDevelopment Status'Millence MyrОценок пока нет
- CH 47 - Animal DevelopmentДокумент70 страницCH 47 - Animal DevelopmentSofiaОценок пока нет
- 35 TramДокумент7 страниц35 TramUchiha ItachiОценок пока нет
- Spermatogenesis, OogenesisДокумент16 страницSpermatogenesis, Oogenesisannita100% (1)
- EMBRYOLOGY - First Week of Human DevelopmentДокумент7 страницEMBRYOLOGY - First Week of Human DevelopmentMeow CattoОценок пока нет
- GAMETOGENESIS: THE PRODUCTION OF EGGS AND SPERMДокумент16 страницGAMETOGENESIS: THE PRODUCTION OF EGGS AND SPERManaghaОценок пока нет
- Gametogenesis: by Anagha Jose Class - Xii Reg ScienceДокумент16 страницGametogenesis: by Anagha Jose Class - Xii Reg ScienceanaghaОценок пока нет
- LZT 304 M.sc. III RD Seema Rai 22.12.14Документ28 страницLZT 304 M.sc. III RD Seema Rai 22.12.14naveen kumarОценок пока нет
- Lecture 8 - 30.12.2022Документ17 страницLecture 8 - 30.12.2022Adnan Mohammad Adnan HailatОценок пока нет
- Embryology Kul FKДокумент65 страницEmbryology Kul FKFahreza ArraisyОценок пока нет
- The Significance of MeiosisДокумент5 страницThe Significance of MeiosisKaren CasternoboОценок пока нет
- Animal ReproductionДокумент17 страницAnimal ReproductionRey OrbeОценок пока нет
- Development of Frog Umanga Chapagain Read OnlyДокумент9 страницDevelopment of Frog Umanga Chapagain Read OnlySubarna PudasainiОценок пока нет
- Fertilization - CCRGДокумент27 страницFertilization - CCRGTushar AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Embryology IДокумент94 страницыEmbryology Imasemola koketsoОценок пока нет
- Module 3 CytogeneticsДокумент23 страницыModule 3 CytogeneticsFrances Riane SimoyОценок пока нет
- PDF - Curs 5a An 1 Sem 1 ENG - Fertilization and First WeekДокумент26 страницPDF - Curs 5a An 1 Sem 1 ENG - Fertilization and First Weekachraf rabadiОценок пока нет
- Frog EmbryologyДокумент8 страницFrog EmbryologyklumabanОценок пока нет
- Female Reproductive SystemДокумент23 страницыFemale Reproductive SystemSheena PasionОценок пока нет
- I. Embryology: Germinal Vesicle.-The Germinal Vesicle or Nucleus Is A Large Spherical Body Which at First Occupies AДокумент7 страницI. Embryology: Germinal Vesicle.-The Germinal Vesicle or Nucleus Is A Large Spherical Body Which at First Occupies AEzra GenerosoОценок пока нет
- I. Embryology: Germinal Vesicle.-The Germinal Vesicle or Nucleus Is A Large Spherical Body Which at First Occupies AДокумент7 страницI. Embryology: Germinal Vesicle.-The Germinal Vesicle or Nucleus Is A Large Spherical Body Which at First Occupies AEzra GenerosoОценок пока нет
- KM GametogenesisДокумент42 страницыKM GametogenesisKALAMYA BRIAN BWAYOОценок пока нет
- Beginning)Документ7 страницBeginning)Jaina Alexandra MendozaОценок пока нет
- Dr. Ravichandran Doraiswamy Professor of AnatomyДокумент70 страницDr. Ravichandran Doraiswamy Professor of AnatomySiva SrinivasanОценок пока нет
- Reproduction PPT 6 PHYSIOLOGY OF PREGNANCYДокумент98 страницReproduction PPT 6 PHYSIOLOGY OF PREGNANCYlisanames.23Оценок пока нет
- I. Embryology: Yolk.-The Yolk Comprises (1) The Cytoplasm of The Ordinary Animal Cell With Its Spongioplasm andДокумент7 страницI. Embryology: Yolk.-The Yolk Comprises (1) The Cytoplasm of The Ordinary Animal Cell With Its Spongioplasm andEzra GenerosoОценок пока нет
- I. Embryology: Yolk.-The Yolk Comprises (1) The Cytoplasm of The Ordinary Animal Cell With Its Spongioplasm andДокумент7 страницI. Embryology: Yolk.-The Yolk Comprises (1) The Cytoplasm of The Ordinary Animal Cell With Its Spongioplasm andEzra GenerosoОценок пока нет
- Lec 07Документ11 страницLec 07itsmenana1308Оценок пока нет
- 2b. Types of Egg and CleavageДокумент55 страниц2b. Types of Egg and CleavageManisha BishtОценок пока нет
- Phylogenetics Is The Study of Evolutionary Relationships Among Biological EntitiesДокумент14 страницPhylogenetics Is The Study of Evolutionary Relationships Among Biological EntitiesThuvishka PrabagarОценок пока нет
- 1NU03-13 Developement, Aging, and HeredityДокумент9 страниц1NU03-13 Developement, Aging, and HeredityKeila RosalesОценок пока нет
- Key Events in DevelopmentДокумент83 страницыKey Events in DevelopmentMelatiОценок пока нет
- Fertilization & Implantation ExplainedДокумент9 страницFertilization & Implantation Explainedhussain AltaherОценок пока нет
- Process of FertilisationДокумент5 страницProcess of FertilisationGeorgia SloanОценок пока нет
- Fertilization & ImplantationДокумент61 страницаFertilization & ImplantationchidimmaОценок пока нет
- The Scientific Self: Learning ObjectivesДокумент9 страницThe Scientific Self: Learning ObjectivesDaniel RafonОценок пока нет
- OogenesisДокумент23 страницыOogenesisFeri ArdiansyahОценок пока нет
- Fetal Development Occurs in 3 Stages:: BlastomeresДокумент7 страницFetal Development Occurs in 3 Stages:: BlastomeresSofiaLopezОценок пока нет
- Cleavage: The Main Process of Animal DevelopmentДокумент123 страницыCleavage: The Main Process of Animal DevelopmentNUR ASMA RIZKYОценок пока нет
- The Development of FrogДокумент13 страницThe Development of FrogRhonnel Manatad AlburoОценок пока нет
- Embryology SummaryДокумент23 страницыEmbryology SummaryChiderahОценок пока нет
- Arihant REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMSДокумент12 страницArihant REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMSSiddharth JagannathanОценок пока нет
- Fertilization and Maturation: Exercise 2Документ19 страницFertilization and Maturation: Exercise 2Abi Garcia100% (1)
- Embryology01-FertilizationToGastrulationbackupДокумент42 страницыEmbryology01-FertilizationToGastrulationbackupArini Sabila FaizaОценок пока нет
- The Cell as the Basic Unit of LifeДокумент18 страницThe Cell as the Basic Unit of LifeJiboy MixОценок пока нет
- Botany ReviewerДокумент23 страницыBotany ReviewerIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Evolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesДокумент1 страницаEvolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Love, Loss and Life's Deepest QuestionsДокумент3 страницыLove, Loss and Life's Deepest QuestionsIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Muscular System Comparative Anatomy LabДокумент2 страницыMuscular System Comparative Anatomy LabIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- 4mm Frog EmbryoДокумент3 страницы4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Exercise 3 - Embryology LabДокумент3 страницыExercise 3 - Embryology LabIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Exercise 1 - Embryology LabДокумент7 страницExercise 1 - Embryology LabIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- CH 10 MusclesДокумент5 страницCH 10 MusclesIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Evolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesДокумент1 страницаEvolution and Diversity of Woody and Seed Plants: Chapter 5 on LignophytesIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Chordates TaxaДокумент1 страницаChordates TaxaIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- 4mm Frog EmbryoДокумент3 страницы4mm Frog EmbryoIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Acd 4 Arm and Cubital FossaДокумент32 страницыAcd 4 Arm and Cubital FossaIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- 7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabДокумент3 страницы7mm Frog Embryo - EMBLabIvy Cruz100% (1)
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabДокумент4 страницы10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- 24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabДокумент3 страницы24 Hour Chick Embryo - Embryology LabIvy Cruz50% (2)
- CPPI Presentation Borres Et Al.Документ19 страницCPPI Presentation Borres Et Al.Ivy CruzОценок пока нет
- Circulatory Sytem of The CatДокумент3 страницыCirculatory Sytem of The CatIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Histo 1st ShiftДокумент25 страницHisto 1st ShiftIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- 2017 Year at A Glance PDFДокумент1 страница2017 Year at A Glance PDFtoanomisОценок пока нет
- Abdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationДокумент4 страницыAbdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Abdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationДокумент4 страницыAbdominis Contract To Actively Aid ExhalationIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Kingdom ProtozoaДокумент3 страницыKingdom ProtozoaIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Phylum Chordata TaxonomyДокумент1 страницаPhylum Chordata TaxonomyIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- The Catholic Social Teachings is reputed as the ChurchÕs Best Kept SecretДокумент3 страницыThe Catholic Social Teachings is reputed as the ChurchÕs Best Kept SecretIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Bryophytes Taxonomy ReviewerДокумент1 страницаBryophytes Taxonomy ReviewerIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Mitochondria and Golgi in Adipose CellsДокумент3 страницыMitochondria and Golgi in Adipose CellsIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Legend: Phylum - Violet Class - Blue Subclass - Green Order - Red Family - Orange Genus - Yellow Species - PinkДокумент1 страницаLegend: Phylum - Violet Class - Blue Subclass - Green Order - Red Family - Orange Genus - Yellow Species - PinkIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Gymnosperm TaxaДокумент1 страницаGymnosperm TaxaIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Ana Chem Lab NotesДокумент2 страницыAna Chem Lab NotesIvy CruzОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsДокумент10 страницPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Semester 1 FinalДокумент29 страницSemester 1 FinalBudi NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Ethics: Foundations of Moral ValuationДокумент7 страницEthics: Foundations of Moral ValuationCyril ColladoОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1Документ5 страницProblem Set 1sxmmmОценок пока нет
- 10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesДокумент9 страниц10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesPreeti KachhawaОценок пока нет
- Social Emotional Lesson Plan 1Документ6 страницSocial Emotional Lesson Plan 1api-282229828Оценок пока нет
- Part 3. Scaffolding Children's Understanding and Use of Language PDFДокумент7 страницPart 3. Scaffolding Children's Understanding and Use of Language PDFMaksym BuchekОценок пока нет
- Destined To ReignДокумент7 страницDestined To ReignMichael B. BolotaoloОценок пока нет
- Merged Fa Cwa NotesДокумент799 страницMerged Fa Cwa NotesAkash VaidОценок пока нет
- FZD School of ArtДокумент5 страницFZD School of ArtRaqib Hasan ApuОценок пока нет
- Documentary Photography: Exploring Cultural Change in TibetДокумент29 страницDocumentary Photography: Exploring Cultural Change in TibetSofia YosseОценок пока нет
- Jsi Eng Paper 1Документ4 страницыJsi Eng Paper 1Sharifah Jannatul AjilahОценок пока нет
- Aquinas' EthicsДокумент33 страницыAquinas' EthicsRBCD INDUSTRIAL SUPPLY100% (1)
- 05 The Milesian NaturalistsДокумент18 страниц05 The Milesian NaturalistsDr René Mario Micallef, SJ, STDОценок пока нет
- Understanding First Language AcquisitionДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding First Language AcquisitionShiela Mae Saladaga TanОценок пока нет
- NafsДокумент3 страницыNafsMabub_sddqОценок пока нет
- NSCC Great Expectations 09Документ6 страницNSCC Great Expectations 09HDTT_09101199Оценок пока нет
- V.I.P. Very Important Points: Dr. Adel Al HarbiДокумент143 страницыV.I.P. Very Important Points: Dr. Adel Al HarbiSukainah AL-AbkaryОценок пока нет
- Ovl QC Manual-2012Документ78 страницOvl QC Manual-2012Sonu SihmarОценок пока нет
- Crisostomo Et Al. v. Atty. Nazareno, A.C. No. 6677, June 10, 2014Документ6 страницCrisostomo Et Al. v. Atty. Nazareno, A.C. No. 6677, June 10, 2014Pamela TambaloОценок пока нет
- Seminar Assignments Ticket Vending MachineДокумент13 страницSeminar Assignments Ticket Vending MachineCandy SomarОценок пока нет
- Quiz Template: © WWW - Teachitscience.co - Uk 2017 28644 1Документ49 страницQuiz Template: © WWW - Teachitscience.co - Uk 2017 28644 1Paul MurrayОценок пока нет
- CBRC Let Ultimate Learning Guide Social ScienceДокумент112 страницCBRC Let Ultimate Learning Guide Social ScienceAigene Pineda100% (2)
- Cws FinalДокумент13 страницCws Finalapi-282878271Оценок пока нет
- Ajzen - Constructing A Theory of Planned Behavior QuestionnaireДокумент7 страницAjzen - Constructing A Theory of Planned Behavior QuestionnaireEstudanteSax100% (1)
- 300 Signs and Symptoms of Celiac DiseaseДокумент7 страниц300 Signs and Symptoms of Celiac DiseaseIon Logofătu AlbertОценок пока нет
- Taxation of RFCs and NFCs in PHДокумент4 страницыTaxation of RFCs and NFCs in PHIris Grace Culata0% (1)
- Validation Guide: For Pharmaceutical ExcipientsДокумент16 страницValidation Guide: For Pharmaceutical ExcipientsSanjayaОценок пока нет
- Virtual Intimacies - Media, Affect, and Queer Sociality (PDFDrive) PDFДокумент180 страницVirtual Intimacies - Media, Affect, and Queer Sociality (PDFDrive) PDFNick JensenОценок пока нет
- Islamic Capital Markets: The Role of Sukuk: Executive SummaryДокумент4 страницыIslamic Capital Markets: The Role of Sukuk: Executive SummaryiisjafferОценок пока нет