Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Knbts-Blood Donation Guidelines
Загружено:
Migori ArtОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Knbts-Blood Donation Guidelines
Загружено:
Migori ArtАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Page |1
KENYA BLOOD TRANSFUSION SERVICES
BRIEF
GUIDELINES-DONOR SERVICES
1 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |2
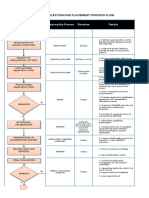
HANDOUT OF SESSION PREPARATION:
APPROPRIATE/ACCURATE
DONOR EDUCATION MATERIALS: Obtain/review Donor Session
All medical eligibility questions Worksheet/Timetable:
should be referred to NBTS staff
(team leader). Contains session/prior
DONOR EVALUATION Mini
session information and
physical examination is
projections; distance;
performed as per SOP. Donor
directions and road
is deferred appropriately as
conditions; site
per sop, and deferral
contacts/description; and any
documentation/ information
completed
Prepare/pack mobile vehicle
according to mobile session
checklist DONOR CONSENT:
Review, master card
followed by signature/date
of donor and date of
Leave for the session not later than time donation then evaluate as
out (See donor recruiters flowchart) per SOP
Upon arrival at mobile site, Donor moves to collection
persons in charge are bed where phlebotomist
contacted by the team leader verifies donor/blood bag
IDs, reviews questionnaire
and any documentation
present as per SOP(s)
Set up collection area according to Team
Leaders assessment/instructions
(JOB AIDE) Phlebotomist selects
vein and prepares the
site appropriately and
performs
The team leader creates rapport with the
donors and address any issue arising VENIPUNCTURE: as
from donor mobilisation by the recruiter. per SOP
DONOR QUESTIONNAIRE: Completed
only by NBTS-trained staff as per SOPs;
Process explained to donor and donor
questions answered and terminologies
explained simply
2 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |3
CHECKLIST
1. Laboratory Coats/Dust Coats 23. Blood weighing scale
2. Rubber gloves 24. Pilot tube sealers/strippers
3. Pair of scissors 25. Donor beds/donor chairs
4. Beakers (100mls/50mls) 26. Phlebotomy trays (contents as
5. Master cards/Donor per job aide)
Questionnaires 27. Mackintosh
6. Record books/Registers 28. Pillows
7. Donor weighing scales 29. First Aid box
8. Blood pressure machine(s) 30. Bed sheets
9. Copper sulphate for 31. Mattresses
haemoglobin estimation 32. Blankets
(working solution) 33. Fluids for donor refreshment
10. Blood Lancets 34. Bottle opener
11. Capillary tubes 35. Towel for wiping sodas
12. Stickers (Labels) 36. Snacks for donors
13. Blood bags 37. Donor awards (if available)
14. Vacuitainers 4-7ml 38. Cool boxes
15. Tube racks 39. Ice packs
16. Gauze 40. Max min thermometers
17. Portable plastic chairs and 41. Hypochlorite solution
tables 42. Waste baskets and bin liners
18. Dry cotton swabs 43. Sharps containers (Safety box)
19. Skin disinfectants 44. Rubber bands
20. Strapping 45. Bar soap.
21. Tourniquets 46. Water
22. Squeeze balls 47. Clips/artery forceps
3 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |4
PREPARATION OF BLOOD DONATION SITE
1.0 PROCEDURE
1.1 Identify the ideal donation site which should be:
Clean
Spacious
Well lit
Well ventilated
1.2 Identify the donor selection site
1.3 Identify and prepare donor evaluation site.
1.4 Identify and prepare site for hemoglobin estimation
1.5 Identify and prepare site for registration
1.6 Strategically position the waste disposal receptacles (bleeding area, cutting area, refreshment area and Hb
estimation area)
1.7 Assemble and arrange the donor chairs/donor beds
1.8 Set the phlebotomy trays (refer to job aide).
1.9 Set-up a cutting table (refer to job aide).
1.10 Strategically position the sharp disposal tins / safety boxes at hemoglobin estimation site and cutting area.
PRE-DONATION COUNSELING AND DONOR DEFFERAL
SEE ATTACHED QUESTIONAIRE FORM
4 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |5
HB ESTIMATION BY COPPER SULPHATE METHOD
1.0 PURPOSE-To provide a procedure on how to determine hemoglobin levels of blood donors using Copper Sulphate
method.
2.0 SCOPE-To ensures the determination of blood donors hemoglobin levels using Copper Sulphate method are performed
correctly.
3.0 REFERENCE
3.1 KNBTS SOPs 1st Edition 2003
4.0 DEFINITION-HB: Haemoglobin.
5.0 RESPONSIBLE PERSON-Laboratory Technologist/Technician
6.0 EQUIPEMENT-
7.0 PROCEDURE
7.1 Prepare tray as per job aide. Fill beaker full with Copper Sulphate working solution.
7.2 Explain procedure to donor
7.3 Clean finger.
7.4 Select site for pricking pulp space on top or side of the finger.
7.5 Hold swab and place spirit on it.
7.6 Grip donors middle finger between your thumb and your second third fingers of your left hand or right hand if left
handed.
7.7 Clean the area selected.
7.8 Prick the skin with lancet, squeeze and wipe off the first drop. Do not squeeze repeatedly as this may dilute the
blood and lower Hb.
7.9 Fill the capillary tube full with blood, avoid letting air into the capillary tube.
7.10 Hold the capillary tube straight 1 cm above beaker of copper sulphate and allow a drop of blood onto Copper
sulphate. It is important not to shake the capillary tube to assist the drop. Give the drop no more than 10 seconds
to sink.
7.11 If the drop of blood floats, Hb is inadequate, if the drop sinks, Hb is adequate. Donor with inadequate Hb must be
appropriately deferred.
7.12 Copper sulphate solution should be changed after every 50 tests and every day. (Change copper sulphate solution
after every 50th test if using 100 ml beaker and after every 25th test when using 50 ml beaker).
8.0 DOCUMENTATION-Master Card
DONOR REGISTRATION
1.0 PURPOSE-To provide a procedure for proper registration of donors
2.0 SCOPE-To ensure that donors are registered properly
3.0 REFERENCE
3.1 AABB Technical Manual, 14th Edition
3.2 KNBTS SOPs 1st Edition 2003
DEFINITION-Regular donor: One who donates at least every six months.
4.0 RESPONSIBLE PERSON-Clerk
5.0 EQUIPEMENT-Not applicable
6.0 PROCEDURE
6.1 Clerk fills the venue register accordingly.
6.2 Clerk receives donor after evaluation.
6.3 Clerk records donor demographics in the clinic register.
6.4 Clerk confirms that there is no damage and also confirms the expiry date of the blood bag.
6.5 Clerk sticks the donor labels on the:
6.5.1 Clinic Register
6.5.2 Lab Register
6.5.3 Master Card
5 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |6
PERFORMING VENEPUNCTURE
1.0 PURPOSE: to provide procedure on how to perform venepuncture
2.0 SCOPE: to ensure venepuncture is performed correctly.
3.0 REFERENCE
3.1 AABB Technical Manual, 14th Edition
3.2KNBTS 1st Edition 2003
5.0 RESPONSIBLE PERSON- Phlebotomist
6.0 PROCEDURE
6.1 Welcome the donor
6.2 Confirm the labels on the vacuitainers, blood bags and master card
6.3 Inspect the bag for any defects and discoloration
6.4 Confirm expiry date on the bag, apply pressure to check for leaks
6.5 Prepare donors arm as follows; Apply tourniquet, identify venipuncture site and clean thoroughly with antiseptic
solution. Cotton swabs are used and wiped inside out in circular movements.
6.6 Position the blood bag below the level of the donors arm; hang on the spring scale at the side of the chair or bed.
6.7 Clip the tubing using the provided clips, remove the needle protection and perform venepuncture with the bevel up,
release the clipping. When the needle position is acceptable and blood is flowing freely into the tubing, tape the
tubing onto the donors arm to hold the needle in place.
6.8 Ask the donor to squeeze the ball slowly every ten to twenty seconds during collection
6.9 Mix blood and anticoagulant gently and periodically (approx. every 45 sec) during collection. Unit should take up to
15 minutes to fill.
6.10 Monitor volume of blood being drawn. Stop bleeding when correct weight is achieved (450mls).
6.11 Clip tubing, remove tourniquet, remove needle from arm, apply pressure over swab and have donor raise arm
over elbow straight and hold swab firmly over phlebotomy site with the other hand.
6.12 Unclip and fill the vacuitainers for blood processing samples without contaminating contents of the bag by
inserting the needles into the vacuitainers one at a time.
6.13 Seal the tube using the hand sealer, cut and discard needle into the biohazard container.
6.14 Place blood unit at an appropriate temp.
6.15 Lower arm and apply pressure dressing.
6.16 Release donor for refreshment and continued post donation care after resting in bed for at least 5 mins.
POST DONATION CARE
1.0 PURPOSE-To provide a procedure for proper post donation care.
2.0 SCOPE-To ensure proper post donation care is given.
3.0 REFERENCE
3.1 AABB Technical Manual, 14th Edition
RESPONSIBLE PERSON -Nurse/Phlebotomist.
4.0 EQUIPEMENT-Not applicable.
5.0 PROCEDURE
5.1 Check arm and apply bandage after bleeding stops.
5.2 Have donor remain reclining on bed or in donor chair for 5-10 minutes under close observation by Phlebotomist.
If the donor gets adverse reaction or faints, refer as per job aide.
5.3 Allow donor to sit up when his/her condition appears satisfactory and monitor as he/she resumes upright
position and walks to refreshment area.
5.4 Allow the donor to sit in a comfortable position for refreshment (fluids).
5.5 Give the donor post donation instruction card before leaving the donation site.
5.6 Thank the donor for an important contribution and encourage him/her to come back after 3-4 months (refer to
SOPs on donor retention).
6 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |7
BLOOD PACKAGING AND TRANSPORTATION
1.0 PURPOSE-To provide an appropriate procedure for packing and transportation of whole blood to the center.
2.0 SCOPE-To ensure that blood units are packed and transported at appropriate temperatures to maintain viability of
components.
3.0 REFERENCE-AABB Technical Manual, 14th Edition
4.0 RESPONSIBLE PERSON-Team Leader.
5.0 PROCEDURE
5.1 Put blood units in a cool box in an upright position allowing room for air circulation.
5.2 Rubber band the minimum and maximum thermometer in between two units of blood (Temperature should be
maintained at between + 2oC - + 10oC.
5.3 Put a piece of carton box on top of units and then place ice packs above avoiding direct contact between the
blood units and ice packs.
5.4 Seal the cool box and transport to the centre within 12 hours of collection.
5.5 Units for Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) preparation to be delivered to the centre within a maximum of 6 hrs. of
collection.
5.6 Units for platelet preparation to be transported in cool boxes without ice packs (between temperatures + 20 - +
24oC) and to be delivered to the centre within a maximum of 6 hrs. of collection.
5.7 Pack the blood into the vehicle and leave the station
5.8 On arrival at the center, unpack the blood and samples from the vehicles
5.8.1 Turn in blood and samples to cold room.
5.8.2 Turn in records to the relevant departments
5.8.3 Turn in supplies and equipment to the store.
5.8.4 Vehicle is packed at the designated packing yard.
6.0 DOCUMENTATION-Temperature Charts
APPENDIX
APPENDIX I
FIRST AID
FAINTING
a. Apply cold compresses to the donors forehead or back of neck.
b. Place donor on their backs and elevate the lower limbs
c. Loosen tight clothing.
d. Be sure donor has an adequate airway
e. Monitor blood pressure, pulse and respiration periodically until donor recovers.
NAUSEA AND VOMITING
a. Make the donor as comfortable as possible.
b. Instruct to breath slowly and deeply.
c. Apply cold compresses to forehead or back of neck.
d. Turn head to side.
e. Provide vomit receptacles.
f. Give water after vomiting has ended to rinse mouth.
TWITCHING AND MUSCULAR SPASMS
a. Divert attention by engaging in conversation.
(To interrupt hyperventilation pattern)
b. Have donor re-breath in paper-bag if symptomatic
7 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |8
HAEMATOMA
a. Remove tourniquet and needle.
b. Place 3 or 4 gauze squares over the site and apply firm digital pressure for 7-10 minutes with arms raised.
c. Apply ice for five minutes if desired.
NB: Convulsions and cardiac difficulties Try to position donor in recovery position and call for help immediately. (Calm and try to
prevent injury to the donor and yourself; use emergency kit).
1. APPENDIX II
CUTTING TABLE
a. Portable table
b. Mackintosh
c. Test tube rack
d. Pair of scissors
e. Sharps container /Safety box
f. Gauze
g. Dsinfectant e.g. 2% glutaraldehyde, savlon, hypochlorite solution, alcohol, etc.
2. APPENDIX III
PHLEBOTOMY TRAY
a. Skin disinfectant
b. Strapping
c. Squeezing balls
d. Tourniquets
e. Dry cotton swabs
f. Blood weighing scales
g. Clips
h. Gloves
i. Pair of scissors.
j. Gauze pads.
3. APPENDIX IV
ADVERSE REACTION REPORT
DATE:________________ INSTITUTION:___________________________
NO NAME DONOR NO. TYPE OF ACTION REMARKS RESPONSIBLE
REACTION TAKEN OFFICER
1
2
3
4
5
8 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Page |9
KENYA NATIONAL BLOOD TRANSFUSION SERVICE-STANDARDS
5.2 Information, Consent and Notification
5.2.1 Donor Identification
Blood collection facilities shall obtain the donors name, date of birth, identification (where
applicable), telephone number (where applicable), and occupation. For repeat donors, the blood
collection facility shall confirm the donors identity and compare current information to existing
records for accuracy.
5.2.2 Donor Education
The blood bank or NBTS shall have procedures to ensure that the following requirements are met
for all prospective donors:
1) Donors are given educational information regarding, donor selection criteria, the donation
process, and infectious diseases transmitted by blood transfusion.
2) Donors acknowledge that the educational information has been received and understood.
5.2.3 Donor Consent
The blood bank shall ensure that donors understand the donation process and agree in writing to
the donation process prior to donation. The following issues shall be addressed in the agreement:
1) What tests will be performed on their donated blood;
2) Under what circumstances they will be informed of test results;
3) Donor specific information shall not be shared with third parties without appropriate consent.
4) Donors shall be provided with appropriate post-donation advice, care, and information about
possible donor adverse events.
5.2.4 Donor Notification of Abnormal Test Results
Donors shall be informed of any medically significant abnormality detected during pre-collection
evaluation or as a result of laboratory testing. Donors shall be entitled to receive testing results
which shall be ready within 30 days of donation.
5.2.4.1 The blood bank shall provide counseling or referral for a
donor who has any positive or confirmed reactive infectious disease marker.
5.2.5 Donor Test Results
Donor test results shall be maintained in a confidential manner and in conformance with the laws
of Kenya.
5.2.6 Information About Donors
The blood bank or transfusion unit shall have a process for managing post-donation information
received from the donor or a third party about a donors suitability.
9 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
P a g e | 10
5.3 Care of Donors
5.3.1 The collection facility shall have a policy to ensure that the donor qualification process is private
and confidential.
5.3.2 The donor shall be observed closely during the donation and for no less than 20 minutes
thereafter.
5.3.2.1 The collection facility shall have a process for the management of donor adverse events
and the provision for availing emergency medical care, as necessary. Immediate assistance
and the necessary equipment and supplies shall be available.
5.4 Donor Qualification
On the day of donation and before collection, the prospective donors history shall be evaluated and the
donor examined to minimize the risk of harm to the donor and the potential recipient. The prospective
donor shall meet all donor qualification criteria. Additional donor qualification procedures (such as those
in the Policy Guidelines on Blood Transfusion in Kenya, 2001) may be incorporated by reference.
5.4.1 Donors shall attest that they have provided accurate information.
5.5 Blood Collection
5.5.1 Methods
Blood shall be collected into a sterile closed system.
5.5.2 Protection against contamination
The venipuncture site shall be prepared so as to minimize risk of bacterial contamination.
5.5.2.1 Every collection site shall have a sharps disposal container.
5.5.3 Samples for Laboratory Tests
At the time of collection or component preparation, the integral donor tubing shall be filled with
anticoagulated blood and sealed in such a manner that it shall be available for subsequent
compatibility testing.
5.5.3.1 The integral donor tubing segments shall be separable from the container without breaking
the sterility of the container.
5.5.3.2 At the time of collection, additional blood may be collected for laboratory tests.
Containers shall be properly labeled at the time of collection, shall accompany the blood
bag and, shall be re-identified with the blood bag immediately after filling.
5.5.3.2 Storage of samples before testing shall meet the requirements stated in the manufacturers
written instructions for the test being performed.
5.5.3.3 Donated blood sample aliquots shall be stored in a stable and retrievable manner for at
least one year to facilitate look-back.
5.5.4 Ratio of Blood to Anticoagulant/Preservative
The volume of blood to be drawn shall be proportional to the amount of
anticoagulant/preservative solution in the collection bag, in accordance with manufacturers
instructions.
5.5.5 Temperature during Transport
If blood is to be transported from the collection site to the component processing laboratory, it
shall be placed in a blood transport box having sufficient refrigeration capacity to cool the blood
continuously toward a temperature range of 2-10o C until it arrives at the processing laboratory.
5.5.5.1 Blood intended for preparation of platelets, shall be transported and stored in a manner
intended to maintain the blood at a temperature range of 20- 24o C. Separation shall be
completed within 6 hours of collection.
5.5.6 Quarantine of Donated Blood
5.5.7 All blood and blood products shall remain quarantined until all laboratory tests have been completed.
10 UNCONTROLLED DOCUMENT-(TEMPORARY)| RBTC-KISUMU-NB-REFERENCE ON BLOOD DONORS
ON POLICY GUIDELINES ON BLOOD TRANSFUSION IN KENYA-PG 13
Вам также может понравиться
- DM 2021-0277 2021 LHS ML Annual Monitoring and Updated LHS ML ToolДокумент43 страницыDM 2021-0277 2021 LHS ML Annual Monitoring and Updated LHS ML Toolmike100% (2)
- IPCRF Supply OffrДокумент9 страницIPCRF Supply OffrBoycie Tarca100% (3)
- Presentation. SPLIT Legal Responsibilities and FormsДокумент47 страницPresentation. SPLIT Legal Responsibilities and FormsMer Cy100% (2)
- RHS Exam OutlineДокумент10 страницRHS Exam Outlinefree booksОценок пока нет
- Perkaba Nomor 3Документ89 страницPerkaba Nomor 3Still WhyОценок пока нет
- Accomplishment Report: For The Month of MAY, 2021Документ3 страницыAccomplishment Report: For The Month of MAY, 2021Lyn Olita100% (1)
- Quality Policy Manual V3 PDF 15 122011Документ82 страницыQuality Policy Manual V3 PDF 15 122011Migori Art100% (5)
- Kenya Revised Code of Regulation 2006Документ230 страницKenya Revised Code of Regulation 2006sise193% (14)
- Hulk Hogan LawsuitДокумент19 страницHulk Hogan LawsuitLegalBlitz100% (1)
- Assessor Non Compliance ObservationДокумент9 страницAssessor Non Compliance ObservationSwati BajpaiОценок пока нет
- 1 No Sop General NformetionДокумент11 страниц1 No Sop General NformetionMANORANJANОценок пока нет
- Nassarawa LG Road Map To Developmental Projects 2024Документ7 страницNassarawa LG Road Map To Developmental Projects 2024ashehusani1Оценок пока нет
- 53797-2000-Bar Matter No. 850 Mandatory ContinuingДокумент6 страниц53797-2000-Bar Matter No. 850 Mandatory ContinuingAyra ArcillaОценок пока нет
- 2003 TESDC ManualДокумент54 страницы2003 TESDC ManualMarigold Cherie100% (1)
- Coconut Seedlings Dispersal Project (CSDP) - Processes and ControlsДокумент6 страницCoconut Seedlings Dispersal Project (CSDP) - Processes and ControlsCarmelaEspinoОценок пока нет
- Attachment D - Focus IndicatorsДокумент4 страницыAttachment D - Focus IndicatorsDILG ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Re: Mandatory Continuing Legal Education (Mcle) : en Banc Bar Matter No. 850Документ9 страницRe: Mandatory Continuing Legal Education (Mcle) : en Banc Bar Matter No. 850Darla GreyОценок пока нет
- Icf 20nov13 F-VerДокумент11 страницIcf 20nov13 F-VerArzo QaderiОценок пока нет
- Pre-Assessment Guidelines and Forms (Hospital/SHCO) : Nabhi-PaДокумент10 страницPre-Assessment Guidelines and Forms (Hospital/SHCO) : Nabhi-PaEka BОценок пока нет
- SOLIDO ESMP (Repair of Health Center)Документ4 страницыSOLIDO ESMP (Repair of Health Center)Fredd Sherwin PanimОценок пока нет
- Scoping Matrix DAO 96-37Документ3 страницыScoping Matrix DAO 96-37Chemtech-tupt EF ClassОценок пока нет
- Final 2019 Indicator Reference For RegionsДокумент6 страницFinal 2019 Indicator Reference For RegionsavaОценок пока нет
- Department of The Interior and Local Government Guidelines Form 4 (Indicator Reference For PCMS)Документ7 страницDepartment of The Interior and Local Government Guidelines Form 4 (Indicator Reference For PCMS)avaОценок пока нет
- CITIZENS CHARTER NO. RO-F-03a. ISSUANCE OF CERTIFICATE OF VERIFICATION COV FOR THE TRANSPORT OF PLANTED TREES WITHIN PRIVATE LAND NON-TIMBER FOREST PRODUCTS EXCEPT RATTAN AND BAMBOOДокумент3 страницыCITIZENS CHARTER NO. RO-F-03a. ISSUANCE OF CERTIFICATE OF VERIFICATION COV FOR THE TRANSPORT OF PLANTED TREES WITHIN PRIVATE LAND NON-TIMBER FOREST PRODUCTS EXCEPT RATTAN AND BAMBOOJimmy JoseОценок пока нет
- IAO FunctionsДокумент11 страницIAO FunctionsVedprilJacky TVОценок пока нет
- 00 SP-DILG-07-Uncontrolled - Client Satisfaction Survey - DILG - ISOДокумент11 страниц00 SP-DILG-07-Uncontrolled - Client Satisfaction Survey - DILG - ISOGodece RosalОценок пока нет
- Monitoring Plan and Standard Operating Procedure: Protocol TitleДокумент5 страницMonitoring Plan and Standard Operating Procedure: Protocol TitleDipeshОценок пока нет
- SV-TEP-001 - Barrier Management Rev.0Документ2 страницыSV-TEP-001 - Barrier Management Rev.0Fiqih MuhammadОценок пока нет
- South Africa Region Metallurgy: Action Manager ProcedureДокумент18 страницSouth Africa Region Metallurgy: Action Manager ProceduregrantОценок пока нет
- Condition Evaluation ELBEДокумент8 страницCondition Evaluation ELBElmОценок пока нет
- POC Performance Audit ManualДокумент20 страницPOC Performance Audit ManualMaria Fiona Duran MerquitaОценок пока нет
- Payment To SuppliersДокумент2 страницыPayment To SuppliersvictorsebstarОценок пока нет
- Action PlanДокумент6 страницAction Planashehusani1Оценок пока нет
- HSSE Standards ProcedureДокумент4 страницыHSSE Standards ProcedureTamara JohnsonОценок пока нет
- 14 - Monitoring - On-Site Monitoring Visit Agenda-ChecklistДокумент1 страница14 - Monitoring - On-Site Monitoring Visit Agenda-ChecklistBouy SokОценок пока нет
- BMB-UWM 2017 - PaPIS &NPDinput - Sept 23 (2) - May 4, 2017Документ44 страницыBMB-UWM 2017 - PaPIS &NPDinput - Sept 23 (2) - May 4, 2017cenro staritaОценок пока нет
- Operations Operations Operations Operations Manual Manual Manual ManualДокумент2 страницыOperations Operations Operations Operations Manual Manual Manual ManualAlimoden Didaagun AnsaryОценок пока нет
- Personnel Actions: Procedure Manual For QMS and ISO 9001:2015Документ4 страницыPersonnel Actions: Procedure Manual For QMS and ISO 9001:2015Aurioule DepaysoОценок пока нет
- AzSPU SSOW Procedure For DeviationsДокумент11 страницAzSPU SSOW Procedure For DeviationsAmir M. ShaikhОценок пока нет
- Covid-19 - Alert Level System An Testing Revolving Fund - 09152021Документ13 страницCovid-19 - Alert Level System An Testing Revolving Fund - 09152021Karen SomcioОценок пока нет
- PolicyPresentation POCAUDIT2022 PDFДокумент148 страницPolicyPresentation POCAUDIT2022 PDFjecyle ludaОценок пока нет
- Format: Pcs Research ProposalДокумент11 страницFormat: Pcs Research ProposalPatrick JohnОценок пока нет
- Cofl GTL Ep 4 4 4 2 RelateДокумент5 страницCofl GTL Ep 4 4 4 2 RelateVictorОценок пока нет
- Weekly Monitoring ReportДокумент2 страницыWeekly Monitoring ReportErshadОценок пока нет
- Participant Transfers and Guest Visits - 11AUG2022Документ12 страницParticipant Transfers and Guest Visits - 11AUG2022Julio OrtizОценок пока нет
- Control of DocumentДокумент7 страницControl of Documentmohd irshahrezal muhamad rasidiОценок пока нет
- Rehabilitation and Recovery Management Service: Revised Guideline in Administration of NDRRM FundДокумент16 страницRehabilitation and Recovery Management Service: Revised Guideline in Administration of NDRRM FundAllinah MagnayeОценок пока нет
- OPA Teacher Sponsor PresentationДокумент15 страницOPA Teacher Sponsor PresentationCarlos Eduardo Hernandez RojasОценок пока нет
- COS Check List Effective January 1 2018-BlankДокумент22 страницыCOS Check List Effective January 1 2018-BlankYukonCorneliousОценок пока нет
- 6 WPP 1Документ4 страницы6 WPP 1Fernand CastroОценок пока нет
- Doj Citizen'S Charter Witness Protection Security and Benefit Program (WPSBP)Документ4 страницыDoj Citizen'S Charter Witness Protection Security and Benefit Program (WPSBP)denver cayagaОценок пока нет
- Audit of Cash LessonДокумент6 страницAudit of Cash LessonRockheart 18Оценок пока нет
- Procedure - CSCДокумент4 страницыProcedure - CSCKim MoritОценок пока нет
- Turn-Over Checklist For CEFДокумент4 страницыTurn-Over Checklist For CEFArnel B. PrestoОценок пока нет
- PM 02 04 Control of Documents ProcedureДокумент5 страницPM 02 04 Control of Documents ProcedureAnnaflor UriarteОценок пока нет
- Control of RecordsДокумент3 страницыControl of Recordschahi100% (1)
- 9.1 Flow Chart RSPДокумент3 страницы9.1 Flow Chart RSPmahal79Оценок пока нет
- Doc.121528-Tracking & Handling of CRFS, MIDFs, DCFs & GAFДокумент6 страницDoc.121528-Tracking & Handling of CRFS, MIDFs, DCFs & GAFerikaoktavianipurbaОценок пока нет
- Bps Citizen's Charter Completed 3.4.15Документ8 страницBps Citizen's Charter Completed 3.4.15lala_omgОценок пока нет
- (Parenthetical Title, If Applicable) Monthly Salary: Duties and ResponsibilitiesДокумент3 страницы(Parenthetical Title, If Applicable) Monthly Salary: Duties and ResponsibilitiesJae WaiОценок пока нет
- Section 4. Matrix of CPD: 1. Professional Track (Training Offered by Accredited CPD Providers, Face To Face, Online)Документ8 страницSection 4. Matrix of CPD: 1. Professional Track (Training Offered by Accredited CPD Providers, Face To Face, Online)Francia Mae BuenoОценок пока нет
- 1last Final ProjДокумент114 страниц1last Final ProjSamuel GetachewОценок пока нет
- Genealogy Standards: Millenium EditionОт EverandGenealogy Standards: Millenium EditionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (19)
- Fees Structure For FreshersДокумент8 страницFees Structure For FreshersMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Active Case FindingДокумент23 страницыActive Case FindingMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- New Jubilee Pre AuthДокумент2 страницыNew Jubilee Pre AuthMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- KMTC 1254Документ1 страницаKMTC 1254Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Objectives-Integrated CurriculumДокумент4 страницыObjectives-Integrated CurriculumMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Advertisement KMTC 2019.2020. CleanedДокумент2 страницыAdvertisement KMTC 2019.2020. CleanedMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Aar Insurance New in Patient Preauthorization Form 2019Документ1 страницаAar Insurance New in Patient Preauthorization Form 2019Migori Art0% (2)
- Introduction & Epidemiology of TBДокумент45 страницIntroduction & Epidemiology of TBMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Optimization of ART RegimenДокумент81 страницаOptimization of ART RegimenMigori Art100% (1)
- PrEP - A Toolkit For Providers - InspectionCopy - March17Документ37 страницPrEP - A Toolkit For Providers - InspectionCopy - March17Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Lab Daily Summary RegisterДокумент130 страницLab Daily Summary RegisterMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Lab Diagnosis of TBДокумент73 страницыLab Diagnosis of TBMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Process MapДокумент1 страницаProcess MapMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- PrEP - A Toolkit For Providers - InspectionCopy - March17Документ37 страницPrEP - A Toolkit For Providers - InspectionCopy - March17Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Kenya Natl Guidelines On MGMT of Sexual Violence 3rd Edition 2014Документ98 страницKenya Natl Guidelines On MGMT of Sexual Violence 3rd Edition 2014Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Disaster Recovery Plan STДокумент14 страницDisaster Recovery Plan STMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- SGBV SopДокумент72 страницыSGBV SopMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Pep Protocol 2016Документ2 страницыPep Protocol 2016Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Accreditation Report.Документ1 страницаAccreditation Report.Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Fighting Pseudoscience Isn't Free: We Believe We Play An Important Role in Defending Truth and ObjectivityДокумент20 страницFighting Pseudoscience Isn't Free: We Believe We Play An Important Role in Defending Truth and ObjectivityMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Co Operative Bank Codes As of April 2014 PDFДокумент29 страницCo Operative Bank Codes As of April 2014 PDFMigori Art0% (2)
- Genetically Modified Organis1Документ17 страницGenetically Modified Organis1Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Counsellingthe Cancerpatient: Surgeon'Scounsel : George T. Pack, M.DДокумент5 страницCounsellingthe Cancerpatient: Surgeon'Scounsel : George T. Pack, M.DMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- TB Microscopy Handbook - FinalДокумент88 страницTB Microscopy Handbook - FinalMigori Art100% (1)
- Counsellingthe Cancerpatient: Surgeon'Scounsel : George T. Pack, M.DДокумент5 страницCounsellingthe Cancerpatient: Surgeon'Scounsel : George T. Pack, M.DMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- Guidelines For The Management of Drug Resistant Tuberculosis in Kenya (2010)Документ88 страницGuidelines For The Management of Drug Resistant Tuberculosis in Kenya (2010)Migori ArtОценок пока нет
- Kenya NationalPolicyoninjectionДокумент18 страницKenya NationalPolicyoninjectionMigori ArtОценок пока нет
- 2,4-Toluene Diisocyanate: Hazard SummaryДокумент4 страницы2,4-Toluene Diisocyanate: Hazard SummaryBeverly RamosОценок пока нет
- Nurse Deployment Program NDP Examination NotesДокумент44 страницыNurse Deployment Program NDP Examination NotesAngelo Quixote100% (1)
- LoperamideДокумент2 страницыLoperamideulerc1100% (1)
- Strolling Match PDFДокумент100 страницStrolling Match PDFHK15100% (1)
- Improper Garbage DisposalДокумент2 страницыImproper Garbage DisposalYo1Оценок пока нет
- 110705494X PDFДокумент1 689 страниц110705494X PDFBenny Chris Tanto100% (3)
- Rare Juvenile Primary Systemic Vasculitis What Is It?: WWW - Pediatric-Rheumathology - Printo.itДокумент7 страницRare Juvenile Primary Systemic Vasculitis What Is It?: WWW - Pediatric-Rheumathology - Printo.itcocoramziОценок пока нет
- Fullerton 2018Документ100 страницFullerton 2018emanuelvelalariosОценок пока нет
- Resume VeronicaДокумент3 страницыResume Veronicajomar_saquingОценок пока нет
- Classical Five-Element Acupuncture: Two More Powerful Treatment StrategiesДокумент10 страницClassical Five-Element Acupuncture: Two More Powerful Treatment StrategiesAОценок пока нет
- Tumbuhan Biji Terbuka (Gymnospermae) Dan Tertutup (Angiospermae)Документ10 страницTumbuhan Biji Terbuka (Gymnospermae) Dan Tertutup (Angiospermae)novianti InnaОценок пока нет
- Seminars in Pediatric SurgeryДокумент6 страницSeminars in Pediatric SurgeryDr Venkatachalapathy T S Ped SurgeonОценок пока нет
- Treatment For Complicated Grief State of The ScienДокумент7 страницTreatment For Complicated Grief State of The SciendfvbnmjkioОценок пока нет
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanДокумент1 страницаGestational Diabetes Mellitus Nursing Care PlanASIS, MARK ANTHONY M.Оценок пока нет
- Core Stability JournalДокумент12 страницCore Stability JournalfricaОценок пока нет
- World Health Champion Game Questions and Answers BRMДокумент18 страницWorld Health Champion Game Questions and Answers BRMNourhan YehiaОценок пока нет
- Pharmabites 9 10 07Документ1 страницаPharmabites 9 10 07api-3707097Оценок пока нет
- Trauma Evaluation and Management: Early Care of The Injured PatientДокумент130 страницTrauma Evaluation and Management: Early Care of The Injured PatienttesfahuntekleОценок пока нет
- Patients Bill of Rights - Nursing JurisprudenceДокумент2 страницыPatients Bill of Rights - Nursing JurisprudenceVia Songcal100% (1)
- Nidcap Vol 11 No1-FinalДокумент26 страницNidcap Vol 11 No1-FinalDaniel MarvasoОценок пока нет
- LO 7 - Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus AureusДокумент7 страницLO 7 - Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus AureusLenovo Legion Y520Оценок пока нет
- Pharmacovigilance For PanamaДокумент24 страницыPharmacovigilance For PanamamagicianchemistОценок пока нет
- Michelle Martin Resume 2021 Final 1pageДокумент1 страницаMichelle Martin Resume 2021 Final 1pageapi-540444992Оценок пока нет
- CAP AlgorithmДокумент1 страницаCAP AlgorithmdamondouglasОценок пока нет
- Group (DSKTJP) Mini Project DPK20073Документ11 страницGroup (DSKTJP) Mini Project DPK20073Keshini RameshОценок пока нет
- Prosthetic Rehabilitation of A Maxillectomy Patient With A Titanium Closed Hollow Bulb Obturator Using Lost Wax Bolus Technique - A Case ReportДокумент8 страницProsthetic Rehabilitation of A Maxillectomy Patient With A Titanium Closed Hollow Bulb Obturator Using Lost Wax Bolus Technique - A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALОценок пока нет
- Breastcrawl PDFДокумент41 страницаBreastcrawl PDFRyan AndarestaОценок пока нет
- Sydney Telischak ResumeДокумент2 страницыSydney Telischak Resumeapi-546817891Оценок пока нет