Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
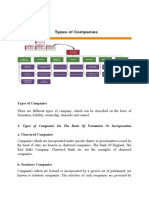
Kinds of Companies Under Companies Act
Загружено:
Soumo DasОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kinds of Companies Under Companies Act
Загружено:
Soumo DasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Kinds of Companies under Companies Act, 2013
According to sec 2(20) of the companies act, 2013 A company is a company
formed under the companies Act 2013 or under any of the previous acts relating
to companies.
A company may be defined as an incorporated association which is an artificial
person, having a separate legal entity, with a perpetual succession, a common seal,
a common capital compromised of transferable shares and limited liability.
Royal Chartered Company These are companies formed under the Royal
Charter of a company or by a special order of king or queen.
Eg. East India Company formed by the Royal Charter of Great Britain. Such a
company derives its nature on the basis of the charter under which they are formed.
Statutory Company It is incorporated by a special Act passed either by the
Central or State legislature. Companies intended to carry on some business of
national importance are formed this way to provide a service to its citizens. Eg. RBI
formed under RBI Act 1934.
Registered Companies A company registered under the companies Act 2013 or
any other existing Act. It is governed by the companies Act 2013.
Company limited by shares It is a company in which the liability of the members
(shareholders) limited i.e. they are only liable for the unpaid value of shares held by
the member. The unpaid amount can be called upon any time
during the life time or winding up of the company. If the shares of a member are fully
paid up then his liability will be nil.
Company limited by Guarantee In such a company the Liability of shareholders
is limited up to the amount guaranteed or invested by the shareholder towards the
assets of the company in the event of its being wound up. The amount guaranteed
can be only demanded at the time of
its wound up, hence it is a reserve capital. Such companies are generally formed to
promote art, science, commerce, sports etc. and are not for profit making.
Unlimited companies A company having no limit on the liability of its
Shareholders is an unlimited company. Thus the liability mayextend to the personal
property of the Shareholders in case the company is not able to
satisfy its claims at the time of winding up. This liability of members is like a
partnership where they have to contribute according to the ratio of amount invested
in the company.
Holding and Subsidiary company Where one company controls the
management of another company, the former is called the holding company and the
later over which the control is exercised is termed as a subsidiary company.
1. A company shall deemed to be a holding company of another, if that other is a
subsidiary.
2. A company shall be deemed to be subsidiary of another company if the other
company.
o Controls the composition of its Board of Directors.
o Holds more than half of nominal value of equity share capital.
o It is a subsidiary of another company which is another companys subsidiary.
o If it holds more than 50% of the total voting rights of the company.
Private Company The term private company has been de ned under section
2(68) of Companies act 2013. A private company means a company, which has a
minimum paid up share capital of Rs. 1 lakh and which provides the following
restrictions through its Articles of Association and Memorandum
o Restricts the transfer of shares by its members
o Limits the maximum number of members to 200
o Prohibits any invitation or acceptance of public deposits
o Prohibits invitation to public for debentures of the company
It enjoys special privileges also-
o It can be started with only 2 members
o It is not required to prepare a prospectus and it can start its operations
immediately after receiving the certificate of incorporation.
Public company The term public company has
been de ned under section 2(71)of Companie act 2013. A public company means a
company which has minimum paid up share capital of Rs. 5 lakh and which is not a
private company. It has the following features
o It does not restrict transferability of shares
o It does not limit maximum members to 50
o At least 7 members are required to form a public company
o It has at least 3 directors
o Its name end with the word limited
o It can accept public deposits and invite public for subscription of its shares
and debentures
A private company which is a subsidiary of a public company will also be
considered a public company under this Act
Domestic company A company which is based in India registered under the
Companies Act 2013. The head Office and its business operations are conducted
within the country. It can either be private or public.
Foreign company A Foreign Company is a company incorporated outside India
which establishes its business operations within India under the Companies Act
2013. Within 30 days of its establishment, it has to furnish important documents to
the registrar as per Sec 380. They are:
o A certified copy of the charter of the company
o Memorandum and Articles of Association of the company
o Address of the registered office
o List of directors and secretary
o Full address of the principle place of business in India
o Name and address of the authorised person to do business on behalf of the
company in India.
One Man Company Where one man holds practically the whole of the share
capital of a company and takes a few more dummy members simply to meet the
statutory requirements of the minimum number of persons such a company is one
man company. A one man company can be incorporated under sec 2(62) of the
Companies Act, 2013. In such a company the principle shareholder is the virtual
owner running the business with limited liability and other members may have even
one share.
Companies not for profit These companies must obtain a license from the central
government before they are registered. They are limited liability but are not required
to use the word Limited or private with their names.
They are formed promoting art, science, commerce, sports etc. Profits are applied
towards its objective and cannot be distributed among its members.
1. It enjoys various exemptions on registration.
2. It does not pay stamp duty for registration of Memorandum and Articles of
Association.
3. It can be formed without share capital
4. Government can revoke license any time by giving a notice
Вам также может понравиться
- Types of Companies and OPC - NotesДокумент8 страницTypes of Companies and OPC - Notes23Mansi JainIОценок пока нет
- Salient Features of The Companies Act 2013Документ24 страницыSalient Features of The Companies Act 2013Ajay RoyОценок пока нет
- Unit - 1 Corporate LawДокумент44 страницыUnit - 1 Corporate LawSanthosh SanthuОценок пока нет
- Legal Aspects of Business Unit 4 Ms Neha RaniДокумент123 страницыLegal Aspects of Business Unit 4 Ms Neha Ranihari haranОценок пока нет
- Contacts DetailsДокумент33 страницыContacts DetailsviswaОценок пока нет
- White Label Travel Portal DevelopmentДокумент5 страницWhite Label Travel Portal DevelopmentwhitelabeltravelportalОценок пока нет
- The Company Act, 1956 PDFДокумент34 страницыThe Company Act, 1956 PDFSahitya SoniОценок пока нет
- Company Law 2013Документ191 страницаCompany Law 2013Vetri VelanОценок пока нет
- Module HandbookДокумент307 страницModule HandbookHenry So E DiarkoОценок пока нет
- Section 138 NIДокумент19 страницSection 138 NINagmani Kumar100% (1)
- Financial Accounting Reviewer - Chapter 60Документ15 страницFinancial Accounting Reviewer - Chapter 60Coursehero Premium100% (1)
- Law of Contract: Prepared ByДокумент50 страницLaw of Contract: Prepared Bymusbri mohamed98% (44)
- Company LawsДокумент31 страницаCompany LawsRahul GandhiОценок пока нет
- Quantitative TechiniquesДокумент38 страницQuantitative TechiniquesJohn Nowell Diestro100% (3)
- Msop Project PDFДокумент40 страницMsop Project PDFshahabanooОценок пока нет
- DocumentДокумент2 страницыDocumentJhazreel BiasuraОценок пока нет
- National Cardiovascular Centre Harapan Kita JULY, 15, 2019Документ30 страницNational Cardiovascular Centre Harapan Kita JULY, 15, 2019Aya BeautycareОценок пока нет
- Abm 115 TRMДокумент329 страницAbm 115 TRMgurubabОценок пока нет
- CompaniesДокумент7 страницCompaniesShruti DedhiaОценок пока нет
- Company LawДокумент15 страницCompany Lawramesh.kОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 Company LawДокумент5 страницUnit-1 Company LawVishi AwasthiОценок пока нет
- Companies ActДокумент47 страницCompanies Actashmit.5217Оценок пока нет
- Company Law: Holding and Subsidiary Company - Tata CompanyДокумент41 страницаCompany Law: Holding and Subsidiary Company - Tata CompanyVanshdeep Singh SamraОценок пока нет
- C A A "By A Company Is Meant An Association of Persons WhoДокумент7 страницC A A "By A Company Is Meant An Association of Persons WhoUma MurugananthamОценок пока нет
- Classification of CompaniesДокумент3 страницыClassification of CompaniesPriyanshu GuptaОценок пока нет
- Company LawДокумент12 страницCompany LawGajendraОценок пока нет
- Company LawДокумент37 страницCompany LawHardik KothiyalОценок пока нет
- 1.introduction, Features & Formation of CopaniesДокумент35 страниц1.introduction, Features & Formation of CopaniesIshan GuptaОценок пока нет
- Indian Companies ActДокумент25 страницIndian Companies ActswesiОценок пока нет
- Companies Act 2013: Meaning of A CompanyДокумент7 страницCompanies Act 2013: Meaning of A CompanyMohit RanaОценок пока нет
- Kinds of CompaniesДокумент3 страницыKinds of CompaniesPadmasree HarishОценок пока нет
- Company Law FinalДокумент95 страницCompany Law Finalthakur_arunsinghОценок пока нет
- The Companies Act 1956Документ77 страницThe Companies Act 1956Varun JainОценок пока нет
- B Company LAW - StudentДокумент61 страницаB Company LAW - StudentSudipta SarangiОценок пока нет
- Company Law: Nature of A CompanyДокумент151 страницаCompany Law: Nature of A Companychangumangu100% (1)
- Company Under The Companies Act 2013Документ14 страницCompany Under The Companies Act 2013Shubham saxenaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Company LawДокумент34 страницыUnit 2 Company LawPriya SekarОценок пока нет
- Separate Legal Identity: Section 34 (2) of The Companies Act, 2013Документ16 страницSeparate Legal Identity: Section 34 (2) of The Companies Act, 2013Manju SujayОценок пока нет
- Unit 3-Part 1Документ17 страницUnit 3-Part 1Aman RaiОценок пока нет
- Company Law - Unit IДокумент61 страницаCompany Law - Unit IHarsh ThakurОценок пока нет
- Calcutta Business School: Legal Aspect of Business Law and Corporate Social ResponsibilityДокумент15 страницCalcutta Business School: Legal Aspect of Business Law and Corporate Social ResponsibilitySoumo DasОценок пока нет
- The Company Law in India: Urvi Shah Assistant Professor of Law Unitedworld School of LawДокумент48 страницThe Company Law in India: Urvi Shah Assistant Professor of Law Unitedworld School of LawSunil ShawОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ41 страницаUnit 1anuragОценок пока нет
- Companies ActДокумент45 страницCompanies ActJanavi KalekarОценок пока нет
- Kinds of CompanyДокумент9 страницKinds of CompanySupriya Prakash LimanОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 - Part 2Документ13 страницUnit 1 - Part 2Ridhima AggarwalОценок пока нет
- Lectures On Company Law-FullДокумент73 страницыLectures On Company Law-FullshakilhmОценок пока нет
- Company Law NotesДокумент95 страницCompany Law NotesAakriti BaderiaОценок пока нет
- Company Lawbba 5TH SemДокумент29 страницCompany Lawbba 5TH SemAB ROCKSОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Forms of CompaniesДокумент12 страницPresentation On Forms of CompaniesJappanJyot KalraОценок пока нет
- Company LawДокумент34 страницыCompany LawShaun LewОценок пока нет
- Unit IДокумент13 страницUnit IJ.SreenivasanОценок пока нет
- Legal and Business Environment - Company Law MaterialДокумент36 страницLegal and Business Environment - Company Law MaterialSai Krishna LinguntlaОценок пока нет
- Companies ActДокумент9 страницCompanies ActSnigdhangshu BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- MBA Notes - Company LawДокумент9 страницMBA Notes - Company LawAnonymous uxd1yd100% (2)
- Company Law UpДокумент95 страницCompany Law UpAshesh DasОценок пока нет
- COMPANY LAW UpДокумент95 страницCOMPANY LAW UpAshesh DasОценок пока нет
- Company Law Unit - 1Документ22 страницыCompany Law Unit - 1Anjali ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Company LawДокумент86 страницCompany Lawthalapathy.7502Оценок пока нет
- Lab Study Note-2021Документ78 страницLab Study Note-2021elizabeth shrutiОценок пока нет
- Company Law NotesДокумент10 страницCompany Law NotesAmi KolkОценок пока нет
- Corporate AccountingДокумент14 страницCorporate AccountingMohammad AzanОценок пока нет
- Essential Features of A CompanyДокумент17 страницEssential Features of A CompanySujata MansukhaniОценок пока нет
- 20.types of CompanyДокумент20 страниц20.types of CompanyHemanta PahariОценок пока нет
- Types of Companies Under Companies Act, 2013 (Https://taxguru - In/company-Law/types-Companies-Companies-Act-2013.html)Документ13 страницTypes of Companies Under Companies Act, 2013 (Https://taxguru - In/company-Law/types-Companies-Companies-Act-2013.html)rajneeshkarloopiaОценок пока нет
- Business Law Unit-3 NotesДокумент32 страницыBusiness Law Unit-3 NoteskartikОценок пока нет
- Classification of Companies (Part-Ii)Документ16 страницClassification of Companies (Part-Ii)Tania MajumderОценок пока нет
- Assignment of CLLДокумент6 страницAssignment of CLLAbdulhadi MaiwandОценок пока нет
- Apollo Tyres IMДокумент5 страницApollo Tyres IMSoumo DasОценок пока нет
- Debayan Ghosh 16004 PGDM 2016-2018 MGLO AssignmentДокумент3 страницыDebayan Ghosh 16004 PGDM 2016-2018 MGLO AssignmentSoumo DasОценок пока нет
- Selective PerceptionДокумент1 страницаSelective PerceptionSoumo DasОценок пока нет
- Calcutta Business School: Legal Aspect of Business Law and Corporate Social ResponsibilityДокумент15 страницCalcutta Business School: Legal Aspect of Business Law and Corporate Social ResponsibilitySoumo DasОценок пока нет
- Vault Guide To The Top Financial Services EmployersДокумент385 страницVault Guide To The Top Financial Services EmployersPatrick AdamsОценок пока нет
- Asian Paints Expansion Strategy in South PacificДокумент5 страницAsian Paints Expansion Strategy in South PacificKshitij JindalОценок пока нет
- PostgraduateДокумент2 страницыPostgraduatelegendОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Answers To Homework AssignmentsДокумент13 страницCH 5 Answers To Homework AssignmentsJan Spanton100% (1)
- Business Tour, DubaiДокумент12 страницBusiness Tour, DubaiVIVEKОценок пока нет
- JDEtips Article E1PagesCreationДокумент20 страницJDEtips Article E1PagesCreationValdir AraujoОценок пока нет
- B. MG Buys One Month Futures Where It Agrees To Buy, in One Month's Time The SameДокумент7 страницB. MG Buys One Month Futures Where It Agrees To Buy, in One Month's Time The Samemegha sharmaОценок пока нет
- TABB Group Report - Institutional Brokerage ProfitabilityДокумент21 страницаTABB Group Report - Institutional Brokerage ProfitabilityMarlon WeemsОценок пока нет
- Nyept Code:-Pt122: 2. For Export of Data From Company To Company Tally UsesДокумент11 страницNyept Code:-Pt122: 2. For Export of Data From Company To Company Tally UsesSumit PandyaОценок пока нет
- 1.1 World Class DC Start Up (MWDC)Документ36 страниц1.1 World Class DC Start Up (MWDC)Adicipto UtomoОценок пока нет
- Steel Joists and Joist GirdersДокумент26 страницSteel Joists and Joist Girderskienking80Оценок пока нет
- NAB Satellite Uplink Operators Training SeminarДокумент5 страницNAB Satellite Uplink Operators Training SeminarChucx I. ChucxОценок пока нет
- Airarabia FundamentalsДокумент11 страницAirarabia FundamentalsallenОценок пока нет
- Fco - 63 - 61 - Alim-AiiДокумент2 страницыFco - 63 - 61 - Alim-AiiAmiОценок пока нет
- Audit Planning and Analytical Procedures ADJUSTED CH 8Документ23 страницыAudit Planning and Analytical Procedures ADJUSTED CH 8alghanmi1411Оценок пока нет
- Small Medium Enterprise (SME) PositioningДокумент31 страницаSmall Medium Enterprise (SME) Positioningnitish110009Оценок пока нет
- BUS 206 Milestone OneДокумент3 страницыBUS 206 Milestone OneTrish FranksОценок пока нет
- TOYOTA - Automaker Market LeaderДокумент26 страницTOYOTA - Automaker Market LeaderKhalid100% (3)
- FBI Interview Excerpts WhalenДокумент11 страницFBI Interview Excerpts WhalenTeej NeffОценок пока нет
- Disadvantages of TriggersДокумент1 страницаDisadvantages of Triggerssanand11Оценок пока нет