Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Indapamide
Загружено:
Novi YulianaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Indapamide
Загружено:
Novi YulianaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/indapamide 02/14/2014 03:36PM Plate # 0-Composite pg 1 # 1
1 Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
CNS: dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy. CV: arrhythmias, hypotension. GI: anorexia, PDF Page #1
indapamide (in-dap-a-mide) cramping, nausea, vomiting. Derm: photosensitivity, rashes. Endo: hyperglycemia.
Lozol, Lozide F and E: hypokalemia, dehydration, hypochloremic alkalosis, hyponatremia, hypo-
Classification volemia. Metab: hyperuricemia. MS: muscle cramps.
Therapeutic: antihypertensives, diuretics Interactions
Pharmacologic: thiazide-like diuretics Drug-Drug: Additive hypotension with other antihypertensives, nitrates, or
Pregnancy Category B acute ingestion of alcohol. Additive hypokalemia with corticosteroids, ampho-
tericin B, piperacillin, or ticarcillin.pexcretion of lithium; may cause toxicity.
Indications Hypokalemia mayqrisk of digoxin toxicity.
Mild to moderate hypertension. Edema associated with HF and other causes. Drug-Natural Products: Licorice and stimulant laxative herbs (aloe,
senna) mayqrisk of potassium depletion.
Action
Increases excretion of sodium and water by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the Route/Dosage
distal tubule. Promotes excretion of chloride, potassium, magnesium, and bicarbon- PO (Adults): Hypertension 1.25 5 mg once daily in the morning; may beqat 4-
ate. May produce arteriolar dilation. Therapeutic Effects: Lowering of BP in hy- wk intervals up to 5 mg/day. Edema secondary to HF 2.5 mg once daily in the
pertensive patients and diuresis with subsequent mobilization of edema. morning; may beqafter 1 wk to 5 mg/day.
Pharmacokinetics NURSING IMPLICATIONS
Absorption: Well absorbed from the GI tract after oral administration. Assessment
Distribution: Widely distributed. Monitor BP, intake and output, and daily weight and assess feet, legs, and sacral
Metabolism and Excretion: Mostly metabolized by the liver. Small amounts area for edema daily.
(7%) excreted unchanged by the kidneys. Assess patient, especially if taking digoxin, for anorexia, nausea, vomiting, muscle
Half-life: 14 18 hr. cramps, paresthesia, and confusion; report signs of electrolyte imbalance. Pa-
TIME/ACTION PROFILE (antihypertensive effect) tients taking digoxin have an increased risk of digitalis toxicity due to the potas-
ROUTE ONSET PEAK DURATION
sium-depleting effect of the diuretic.
Assess patient for allergy to sulfonamides.
PO (single dose) unknown 24 hr unknown Lab Test Considerations: Monitor electrolytes (especially potassium), blood
PO (multiple dose) 12 wk 812 wk up to 8 wk glucose, BUN, serum creatinine, and uric acid levels periodically during therapy.
May causeppotassium, sodium, and chloride concentrations. Mayqserum glu-
Contraindications/Precautions cose; diabetic patients may requireqoral hypoglycemic or insulin dose.quric
Contraindicated in: Hypersensitivity; Cross-sensitivity with sulfonamides may oc- acid level an average of 1.0 mg/100 mL; may precipitate an episode of gout.
cur; Anuria.
Use Cautiously in: Renal or severe hepatic impairment; Lactation: May be Potential Nursing Diagnoses
taken while breast feeding although higher doses followed by significant diuresis may Excess fluid volume (Indications)
pmilk production; Pedi: Safety not established; Geri:qsensitivity to drug effects. Risk for deficient fluid volume (Side Effects)
Canadian drug name. Genetic Implication. CAPITALS indicate life-threatening, underlines indicate most frequent. Strikethrough Discontinued.
Name /bks_53161_deglins_md_disk/indapamide 02/14/2014 03:36PM Plate # 0-Composite pg 2 # 2
2
Implementation PDF Page #2
Administer in the morning to prevent disruption of sleep cycle.
PO: May be given with food or milk to minimize GI irritation.
Patient/Family Teaching
Instruct patient to take this medication at the same time each day. Take missed
doses as soon as remembered but not just before next dose is due. Do not double
doses. Advise patients using indapamide for hypertension to continue taking the
medication even if feeling well. Indapamide controls but does not cure hyperten-
sion.
Caution patient to change positions slowly to minimize orthostatic hypotension.
This may be potentiated by alcohol.
Advise patient to use sunscreen (avoid those containing PABA) and protective
clothing when in the sun to prevent photosensitivity reactions.
Instruct patient to follow a diet high in potassium.
Advise patient to report muscle weakness, cramps, nausea, or dizziness to health
care professional.
Instruct patient to notify health care professional of all Rx or OTC medications, vi-
tamins, or herbal products being taken and to consult health care professional be-
fore taking other Rx, OTC, or herbal products.
Emphasize the importance of routine follow-up exams.
Hypertension: Instruct patient and family on proper technique of BP monitor-
ing. Advise them to check BP at least weekly and to report significant changes.
Encourage patient to comply with additional interventions for hypertension
(weight reduction, low-sodium diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, moder-
ation of alcohol consumption, and stress management).
Evaluation/Desired Outcomes
Control of hypertension.
Decrease in edema secondary to HF.
Why was this drug prescribed for your patient?
2015 F.A. Davis Company
Вам также может понравиться
- Drug LisinoprilДокумент1 страницаDrug LisinoprilSrkocherОценок пока нет
- LabetalolДокумент3 страницыLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- Glipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardДокумент1 страницаGlipizide Glucotrol XL Drug CardSheri490Оценок пока нет
- Methocarbamol (Robaxin)Документ1 страницаMethocarbamol (Robaxin)EОценок пока нет
- Terazosin Hytrin Drug CardДокумент1 страницаTerazosin Hytrin Drug CardSheri490Оценок пока нет
- Escitalopram OxalateДокумент3 страницыEscitalopram Oxalateapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- OfloxacinДокумент2 страницыOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug Card BenadrylДокумент1 страницаDrug Card BenadrylAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Atropine Drug ProfileДокумент2 страницыAtropine Drug ProfileShahpmdОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - AmlodipineДокумент1 страницаDrug Study - AmlodipineDanielle Marie SamblacenoОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Basic Pharmacology For Nursing 17th EditionДокумент10 страницTest Bank For Basic Pharmacology For Nursing 17th EditionUsman HaiderОценок пока нет
- MethylprednisoloneДокумент4 страницыMethylprednisoloneadryananestesiОценок пока нет
- Lyrica (Pregabalin)Документ2 страницыLyrica (Pregabalin)Laromac RolandОценок пока нет
- Filgastrim (GCSF)Документ3 страницыFilgastrim (GCSF)Kyla Barrera TabungarОценок пока нет
- Act Rapid 2Документ2 страницыAct Rapid 2Leah Torcelino-InfanteОценок пока нет
- NeostigmineДокумент4 страницыNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonОценок пока нет
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityДокумент5 страницCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityChelsea WuОценок пока нет
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Документ4 страницыChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliОценок пока нет
- EsmololДокумент2 страницыEsmololtherock316_995149Оценок пока нет
- THEOPHYLLINE - Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыTHEOPHYLLINE - Drug Studyeric macabiogОценок пока нет
- LidocaineДокумент2 страницыLidocaineAhprelle Quiring Rodiel100% (1)
- Pseudoephedrine HydrochlorideДокумент6 страницPseudoephedrine HydrochlorideAbdelrhman AboodaОценок пока нет
- Tinidazole Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыTinidazole Drug StudyEmagra AzilОценок пока нет
- AcetazolamideДокумент2 страницыAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- DapagliflozinДокумент1 страницаDapagliflozinAusaf AhmadОценок пока нет
- Methyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidДокумент4 страницыMethyldopa, Losartan K, Ascorbic AcidRico Mae ValenciaОценок пока нет
- Drug Study - BaclofenДокумент5 страницDrug Study - BaclofenRocco WalksОценок пока нет
- Drug Study...Документ5 страницDrug Study...Ezra Dizon ManzanoОценок пока нет
- Doxazosin MesylateДокумент2 страницыDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941Оценок пока нет
- EsmololДокумент3 страницыEsmololTri Purma SariОценок пока нет
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyArdrina SappariОценок пока нет
- Phenergan (Promethazine)Документ1 страницаPhenergan (Promethazine)E100% (1)
- AMINOPHYLLINEДокумент2 страницыAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Case Pre Drug StudyДокумент5 страницCase Pre Drug StudyJoule PeirreОценок пока нет
- Valproic AcidДокумент4 страницыValproic Acidapi-3797941100% (2)
- Miglitol (Glyset)Документ1 страницаMiglitol (Glyset)EОценок пока нет
- Duty Drug Study'sДокумент7 страницDuty Drug Study'sGrape JuiceОценок пока нет
- DrugДокумент4 страницыDrugVANNEZA TRIXZY TAMPARONGОценок пока нет
- Lyrica Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыLyrica Drug StudydyndzОценок пока нет
- SimethiconeДокумент1 страницаSimethiconeDivine Dela PenaОценок пока нет
- AlprazolamДокумент3 страницыAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- AcetazolamideДокумент2 страницыAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOОценок пока нет
- DRug Study PhenytoinДокумент1 страницаDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezОценок пока нет
- Drug Study Table 3Документ5 страницDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Drug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToДокумент2 страницыDrug - Htm#description.: Reference: Submitted By: Date Submitted: Submitted ToSHEILA MAE SACLOTОценок пока нет
- Chloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Документ3 страницыChloral Hydrate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Оценок пока нет
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Документ2 страницыFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaОценок пока нет
- Carbidopa Levodopa SinemetДокумент3 страницыCarbidopa Levodopa SinemetTodd ColeОценок пока нет
- Ditropan Drug CardДокумент2 страницыDitropan Drug CardBenОценок пока нет
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыMagnesium Sulfate Drug StudyMonica Lyka BancaleОценок пока нет
- AminophyllineДокумент9 страницAminophyllineZaira BataloОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsДокумент2 страницыGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsОценок пока нет
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideДокумент3 страницыLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- PiroxicamДокумент2 страницыPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezОценок пока нет
- GlipizideДокумент2 страницыGlipizideFeliciaDorghamОценок пока нет
- BisoprololДокумент2 страницыBisoprololNovi YulianaОценок пока нет
- Hydralazine.1 3Документ1 страницаHydralazine.1 3SОценок пока нет
- AmlodipineДокумент2 страницыAmlodipineAnonymous QqyLDoW1Оценок пока нет
- Med Surg Medication Study GuideДокумент8 страницMed Surg Medication Study Guidetina100% (1)
- Drug StudyДокумент33 страницыDrug Studyjefwy8Оценок пока нет
- CaptoprilДокумент3 страницыCaptoprilNovi YulianaОценок пока нет
- BisoprololДокумент2 страницыBisoprololNovi YulianaОценок пока нет
- NifedipineДокумент3 страницыNifedipineNovi YulianaОценок пока нет
- RamiprilДокумент3 страницыRamiprilNovi YulianaОценок пока нет
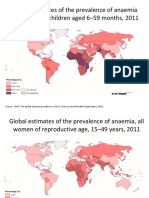
- Global Estimates of The Prevalence of Anaemia in Infants and Children Aged 6 59 Months, 2011Документ4 страницыGlobal Estimates of The Prevalence of Anaemia in Infants and Children Aged 6 59 Months, 2011Novi YulianaОценок пока нет
- Infectious Agents and Cancer: Antiviral Therapy in Acute Viral Hepatitis B: Why and WhenДокумент2 страницыInfectious Agents and Cancer: Antiviral Therapy in Acute Viral Hepatitis B: Why and WhenNovi YulianaОценок пока нет
- Farmakoterapi Coagulation DisorderДокумент55 страницFarmakoterapi Coagulation DisorderNur Astuty PurnamasariОценок пока нет
- WA Health Consent To Treatment Policy: Better Health Better Care Better ValueДокумент42 страницыWA Health Consent To Treatment Policy: Better Health Better Care Better ValueprabhaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry ProjectДокумент13 страницChemistry ProjectPranjal GiriОценок пока нет
- Toc PDFДокумент12 страницToc PDFraviraja moduguОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Tablet PDFДокумент2 страницыEvaluation of Tablet PDFKim50% (2)
- Cirrhosis and Its Complications Evidence Based TreatmentДокумент20 страницCirrhosis and Its Complications Evidence Based TreatmentSucii Sekar NingrumОценок пока нет
- Howtousea Nebulizer in Pediatric ClientsДокумент11 страницHowtousea Nebulizer in Pediatric ClientsAngelina Nicole G. TungolОценок пока нет
- Efficacy of Ethanol Against Viruses in Hand DisinfectionДокумент9 страницEfficacy of Ethanol Against Viruses in Hand DisinfectionImaec LimitedОценок пока нет
- DR Craig WeilДокумент14 страницDR Craig WeilPaula OwensОценок пока нет
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeДокумент4 страницыNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06Оценок пока нет
- LAP DirectoryДокумент36 страницLAP Directorydolly wattaОценок пока нет
- ORAL CANCER - Edited by Kalu U. E. OgburekeДокумент400 страницORAL CANCER - Edited by Kalu U. E. Ogburekeعبد المنعم مصباحيОценок пока нет
- SyphilisДокумент54 страницыSyphilisYeyeh SantosОценок пока нет
- The Therapy BookДокумент398 страницThe Therapy BookAbdelrahman Mamdouh90% (10)
- Hypovolemic Shock Concept MapДокумент1 страницаHypovolemic Shock Concept MapJM AsentistaОценок пока нет
- Case PresДокумент22 страницыCase Presandrei jinОценок пока нет
- 136 AДокумент5 страниц136 AMarcelitaTaliaDuwiriОценок пока нет
- PHARMEVOДокумент3 страницыPHARMEVOFariha AnsariОценок пока нет
- Chorionic Bump in First-Trimester Sonography: SciencedirectДокумент6 страницChorionic Bump in First-Trimester Sonography: SciencedirectEdward EdwardОценок пока нет
- DR Adedayo OSHOLOWU - Clinical Director - Special Olympics - NIGERIAДокумент3 страницыDR Adedayo OSHOLOWU - Clinical Director - Special Olympics - NIGERIAAdedayo OsholowuОценок пока нет
- Neolus: Single Use Hypodermic NeedlesДокумент2 страницыNeolus: Single Use Hypodermic Needlesmiumau3Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisДокумент5 страницPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15Оценок пока нет
- Importance and Purposes of ResearchДокумент3 страницыImportance and Purposes of ResearchKarl Kiw-isОценок пока нет
- Sandra John - Case Scenario On Bulimia NervosaДокумент7 страницSandra John - Case Scenario On Bulimia Nervosasandra0% (1)
- ACUTE ABDOMEN Systemic SonographicДокумент6 страницACUTE ABDOMEN Systemic SonographiciwanОценок пока нет
- Medsave - Claim Form For MediclaimДокумент1 страницаMedsave - Claim Form For Mediclaimpawan1501Оценок пока нет
- Revie Jurnal Sources of Stress and Coping StrategiesДокумент7 страницRevie Jurnal Sources of Stress and Coping StrategiesAmieОценок пока нет
- Rash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: EmergencyДокумент1 страницаRash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: Emergencykdlsfk kajjksolsОценок пока нет
- 2023 Music Therapy & NICUДокумент36 страниц2023 Music Therapy & NICUMohammad Izaan TahirОценок пока нет