Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
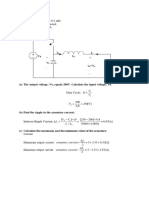
Motor Power Calculation
Загружено:
Mohd Tauffid TawangАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Motor Power Calculation
Загружено:
Mohd Tauffid TawangАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fundamentals of Electricity - Watt's Law - Three Phase http://c03.apogee.net/contentplayer/?coursetype=foe&utilityid=psoklah...
Fundame ntals of Ele ctricity
Rates & Calculations > Watt's Law >
Search
Watt's Law - Three Phase
Contents
Delivery Three phase power is used primarily in commercial and industrial environments, providing power to
Generation motors and equipment. It is more economical to operate large equipment with three phase power. In
Rates & Calculations
order to calculate three-phase wattage, we multiply the average voltage of each phase times the
Basics
Safety
average current of each phase, times the power factor, then multiply by the square root of 3. The
Circuits square root of 3 is equal to 1.732, so the equation is written as shown:
FAQs
Watt's Law: W = V avg. x A avg x p.f. x 1.732
Where:
W = wattage (watts)
Vavg = average voltage of the three separate phases (volts)
Aavg = average current of the three separate phases current (amps)
p.f. = average power factor or the three separate phases
1.732 = a constant necessary with 3 phase.
In a three phase circuit,
the use of the constant
1.732 results from the
fact that not all three
phases are producing the
same amount of power at
the same time. Each
phase's voltage and
current move through
zero at different times.
Suffice it to say that the
correct power from a
three-phase system at
any point in time is found
by multiplying by the square root of 3.
The electrical power input in kilowatts for a three phase motor is calculated by multiplying the average
voltage of all three phases measured at the motor times the average amperage of all three phases
measured at the motor times the average power factor of all three phases measured at the motor times
a constant of 1.732 and dividing the result by 1000.
An operating three phase motor has voltages measured with a voltmeter on each phase of 453, 458,
and 461 volts, amperage measured on each phase with an ammeter are 14.1, 13.9, and 13.8 amps,
power factor was measured as 0.82. The average voltage is 453 plus 458 plus 461 divided by 3 which
equals 457 volts.
The average current is 14.1 plus 13.9 plus 13.8 divided by
3 which equals 13.9 amps.
The electrical
power input to
the motor
equals 457
volts times 13.9 amps times 0.82 power factor divided by 1000 which equals 5.2 kilowatts.
(457V x 13.9A x .082pf x 1.732) / 1000 = 9.02 Kwatts
1 of 1 07-Dec-17, 10:46 AM
Вам также может понравиться
- Electrical Transformers and Rotating Machines 4th Edition Herman Test Bank DownloadДокумент3 страницыElectrical Transformers and Rotating Machines 4th Edition Herman Test Bank DownloadViola Forsberg100% (23)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsОт EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- Grade 9 WorkbookДокумент44 страницыGrade 9 WorkbookMaria Russeneth Joy NaloОценок пока нет
- Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications: Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsДокумент61 страницаDiscrete Mathematics and Its Applications: Basic Structures: Sets, Functions, Sequences, and SumsBijori khanОценок пока нет
- Electrical Engineering Ch2 - Polyphase CircitДокумент31 страницаElectrical Engineering Ch2 - Polyphase CircitIshaОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase LectureДокумент37 страницThree-Phase LectureAlnie Albaran DemoralОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Power: Phase Power Total True Power The Power TriangleДокумент37 страницThree-Phase Power: Phase Power Total True Power The Power TriangleGwenShepherdОценок пока нет
- Electrical Power MeasurementДокумент4 страницыElectrical Power MeasurementSurendra ReddyОценок пока нет
- General Safety Measures of Electromechanical System LabДокумент7 страницGeneral Safety Measures of Electromechanical System LabAbdul HaseebОценок пока нет
- 02 Linear Circuit AnalysisДокумент29 страниц02 Linear Circuit AnalysisAhsan MalikОценок пока нет
- University of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering DepartmentДокумент8 страницUniversity of Tripoli Faculty of Engineering Electrical and Electronics Engineering DepartmentShehab RamadanОценок пока нет
- Correcting Unbalance CurrentДокумент16 страницCorrecting Unbalance CurrentBalaji GurumurthyОценок пока нет
- Britannica Concise EncyclopediaДокумент15 страницBritannica Concise EncyclopediamerusaОценок пока нет
- Electric PowerДокумент12 страницElectric PowerAyodele AdeyonuОценок пока нет
- Power AnalysisДокумент35 страницPower AnalysisSuresh KumarОценок пока нет
- LAB1 RyanKimДокумент4 страницыLAB1 RyanKimRyan Kim PatronОценок пока нет
- Three-Phase Circuits: by Hani YasintaДокумент15 страницThree-Phase Circuits: by Hani YasintaAisyah FitriОценок пока нет
- 13 Power MeasurementДокумент14 страниц13 Power MeasurementSreejithОценок пока нет
- Three Phase MeasurementДокумент26 страницThree Phase MeasurementAnjanaОценок пока нет
- UNIT 5 Current and Resistance 12ADVДокумент17 страницUNIT 5 Current and Resistance 12ADVhamdaalali2006Оценок пока нет
- Enc Encoded E99PKQj6R0fd2aAqtC B2psxn2h9uyB1sdfjlXe0qRJAKGBzaByJFioQetxEV kl5SEFДокумент15 страницEnc Encoded E99PKQj6R0fd2aAqtC B2psxn2h9uyB1sdfjlXe0qRJAKGBzaByJFioQetxEV kl5SEFAmal MonichanОценок пока нет
- ES Unit-4Документ18 страницES Unit-4Mazin VoraОценок пока нет
- Science Section 9.2Документ20 страницScience Section 9.2levyОценок пока нет
- 3 Phase Power CalculationДокумент5 страниц3 Phase Power CalculationChris Osea AlvarezОценок пока нет
- DET50083 Topic 3 Fault Current CalculationДокумент19 страницDET50083 Topic 3 Fault Current Calculation25det20f1062Оценок пока нет
- Ch-2 Electrical Circuit Anlysis-PART 1Документ44 страницыCh-2 Electrical Circuit Anlysis-PART 1temesgen adugnaОценок пока нет
- Analysing Three Phase Circuits PDFДокумент16 страницAnalysing Three Phase Circuits PDFsenthilОценок пока нет
- Performance Analysis of Three Phase Induction Motor Under Balance and Unbalance Voltage ConditionsДокумент3 страницыPerformance Analysis of Three Phase Induction Motor Under Balance and Unbalance Voltage ConditionsAnonymous VIwdTViYIОценок пока нет
- ESO 210 Lecture-15 - 2014Документ21 страницаESO 210 Lecture-15 - 2014Amit MondalОценок пока нет
- 3.8 Power in Three-Phase AC Circuits: Per-Phase Powers in (A) A Delta-Connected Load and (B) A Star-Connected LoadДокумент16 страниц3.8 Power in Three-Phase AC Circuits: Per-Phase Powers in (A) A Delta-Connected Load and (B) A Star-Connected LoadBaquiran John Paul BaquiranОценок пока нет
- Iee Unbalanced PDFДокумент5 страницIee Unbalanced PDFDery TriОценок пока нет
- Three Phase ReportДокумент7 страницThree Phase ReportMohamed KamilОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1A (1) Phys203Документ11 страницExperiment 1A (1) Phys203Namık Cem BaydarОценок пока нет
- Per Unit CalculationsДокумент3 страницыPer Unit CalculationssupernaenergyОценок пока нет
- Transient AnalysisДокумент16 страницTransient Analysisdr_biltОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Three Single Phases Power AdditionДокумент9 страницSimulation of Three Single Phases Power Additionmaha malikОценок пока нет
- Universidad Nacional de IngenieríaДокумент14 страницUniversidad Nacional de IngenieríaRenzo UPОценок пока нет
- Trofazni Motor Na Jednofaznoj MreziДокумент7 страницTrofazni Motor Na Jednofaznoj Mrezialmen_matanovic1675Оценок пока нет
- Short Circuit Calculations Made EasyДокумент18 страницShort Circuit Calculations Made EasyBong Oliveros100% (1)
- Star and Delta SystemДокумент7 страницStar and Delta Systemjagadeeshkumar116Оценок пока нет
- Three Phase Electric Power SystemДокумент5 страницThree Phase Electric Power SystemJarah GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Module 1 ELCT110 Lesson 3Документ9 страницModule 1 ELCT110 Lesson 3Xyrozin BalangueОценок пока нет
- Analisis Perencanaan Pembagian Beban Dan Instalasi Listrik Pada Hotel Golden Tulip Di Kota PontianakДокумент8 страницAnalisis Perencanaan Pembagian Beban Dan Instalasi Listrik Pada Hotel Golden Tulip Di Kota PontianakMuhammad FaruqОценок пока нет
- Wattmeter PresentationДокумент14 страницWattmeter Presentationkiran392Оценок пока нет
- A Report On Electrical CircuitsДокумент8 страницA Report On Electrical CircuitsZayn AhmedОценок пока нет
- 3-Phase Power CalculationДокумент2 страницы3-Phase Power CalculationMD. Mahfuj RahmanОценок пока нет
- Assignment Be&e TransformerДокумент17 страницAssignment Be&e TransformerAbbyОценок пока нет
- 3 Phase Power MeasurementДокумент6 страниц3 Phase Power MeasurementAnthony GregoryОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Electrical FundaeДокумент58 страниц2.1 Electrical FundaeMr TrupenОценок пока нет
- L3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 2 PDFДокумент9 страницL3-BEKG2433-Three Phase Part 2 PDFVievie Le BluewberrietrufflesОценок пока нет
- Syllabus:: Electrical Dept. Electrical Power III Dr. Omar AlazzawiДокумент97 страницSyllabus:: Electrical Dept. Electrical Power III Dr. Omar AlazzawiAkram KhasheaОценок пока нет
- AC Circuits Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Congson, Krizia Dianne NДокумент3 страницыAC Circuits Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Congson, Krizia Dianne NGillian Claire CancioОценок пока нет
- Power Supply For Asynchronous Motors: White PaperДокумент16 страницPower Supply For Asynchronous Motors: White PaperLewis HamiltonОценок пока нет
- C2-3 PH ckts-S1Документ31 страницаC2-3 PH ckts-S1mhmd.akzrОценок пока нет
- Week 4Документ18 страницWeek 4Syed Faras HaiderОценок пока нет
- Analisis Perencanaan Pembagian Beban Dan Instalasi Listrik Pada Hotel Golden Tulip Di Kota PontianakДокумент8 страницAnalisis Perencanaan Pembagian Beban Dan Instalasi Listrik Pada Hotel Golden Tulip Di Kota Pontianakbrian yudhaОценок пока нет
- Drive Lab ManualДокумент94 страницыDrive Lab ManualKeerthana SahadevanОценок пока нет
- AC Circuits Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Verallo, Rhea Ann RДокумент3 страницыAC Circuits Laboratory Report: Submitted By: Verallo, Rhea Ann RGillian Claire CancioОценок пока нет
- E 344 ContentДокумент69 страницE 344 ContentzebidiansОценок пока нет
- On The Natural Frequency of Oscillations of Induction MotorsДокумент11 страницOn The Natural Frequency of Oscillations of Induction MotorsIEREKPRESSОценок пока нет
- Power Elect3 2011Документ3 страницыPower Elect3 2011NGOUNEОценок пока нет
- Power Measurements Under Nonsinusoidal Conditions : A Thesis in Electrical EngineeringОт EverandPower Measurements Under Nonsinusoidal Conditions : A Thesis in Electrical EngineeringОценок пока нет
- F5 Chem Rusting ExperimentДокумент9 страницF5 Chem Rusting ExperimentPrashanthini JanardananОценок пока нет
- A Junk Project - An Income Generating ProjectДокумент2 страницыA Junk Project - An Income Generating ProjectHercules Verdeflor ValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- Homework 1Документ8 страницHomework 1Yooncheul JeungОценок пока нет
- Buildingawinningsalesforce WP DdiДокумент14 страницBuildingawinningsalesforce WP DdiMawaheb ContractingОценок пока нет
- IFR CalculationДокумент15 страницIFR CalculationSachin5586Оценок пока нет
- Assignment Csi104Документ11 страницAssignment Csi104Minh Lê KhảiОценок пока нет
- Formal Letter LPДокумент2 страницыFormal Letter LPLow Eng Han100% (1)
- 01 - A Note On Introduction To E-Commerce - 9march2011Документ12 страниц01 - A Note On Introduction To E-Commerce - 9march2011engr_amirОценок пока нет
- Business CombinationsДокумент18 страницBusiness Combinationszubair afzalОценок пока нет
- Pricing of A Revolutionary ProductДокумент22 страницыPricing of A Revolutionary ProductiluvparixitОценок пока нет
- Personal Finance Kapoor 11th Edition Solutions ManualДокумент26 страницPersonal Finance Kapoor 11th Edition Solutions Manualsiennamurielhlhk100% (28)
- IMC - BisleriДокумент8 страницIMC - BisleriVineetaОценок пока нет
- Laboratorio 1Документ6 страницLaboratorio 1Marlon DiazОценок пока нет
- Historical Exchange Rates - OANDA AUD-MYRДокумент1 страницаHistorical Exchange Rates - OANDA AUD-MYRML MLОценок пока нет
- DxDiag Copy MSIДокумент45 страницDxDiag Copy MSITạ Anh TuấnОценок пока нет
- MV Lec PDFДокумент102 страницыMV Lec PDFJonas Datu100% (1)
- Ed Post Lab Heat of Formation of NaClДокумент4 страницыEd Post Lab Heat of Formation of NaClEdimar ManlangitОценок пока нет
- Information Technology Project Management: by Jack T. MarchewkaДокумент44 страницыInformation Technology Project Management: by Jack T. Marchewkadeeps0705Оценок пока нет
- Dissertation 7 HeraldДокумент3 страницыDissertation 7 HeraldNaison Shingirai PfavayiОценок пока нет
- ATADU2002 DatasheetДокумент3 страницыATADU2002 DatasheethindОценок пока нет
- GTA IV Simple Native Trainer v6.5 Key Bindings For SingleplayerДокумент1 страницаGTA IV Simple Native Trainer v6.5 Key Bindings For SingleplayerThanuja DilshanОценок пока нет
- Lateritic NickelДокумент27 страницLateritic NickelRAVI1972100% (2)
- Water Tanker Check ListДокумент8 страницWater Tanker Check ListHariyanto oknesОценок пока нет
- Health and Safety For The Meat Industry: Guidance NotesДокумент198 страницHealth and Safety For The Meat Industry: Guidance NotesPredrag AndjelkovicОценок пока нет
- FSM Syllabus20071228 1Документ3 страницыFSM Syllabus20071228 1Institute of Fengshui BaziОценок пока нет
- Bajaj CNSДокумент3 страницыBajaj CNSAbhijit PaikarayОценок пока нет
- Vernacular ArchitectureДокумент4 страницыVernacular ArchitectureSakthiPriya NacchinarkiniyanОценок пока нет
- 1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDДокумент81 страница1"a Study On Employee Retention in Amara Raja Power Systems LTDJerome Samuel100% (1)