Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Crayfish Table
Загружено:
api-3529269870 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
223 просмотров3 страницыОригинальное название
crayfish table
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
223 просмотров3 страницыCrayfish Table
Загружено:
api-352926987Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
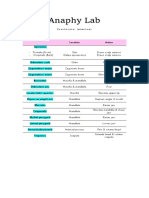
External Anatomy
Appendage Function Location Draw Appendage
Here
Antennules Senses touch & in front of the .
taste; helps mouth
crayfish maintain
balance
Antenna Senses touch and in front of the .
taste mouth
Mandible or jaw Crushes food mouth .
First Maxilla Moves food to the behind the .
mouth mandibles
second maxilla moves water in behind the .
the gill chamber mandibles
First maxilliped Holds food; at ventral and .
Senses touch and forward part of
taste the thorax region
Second Holds food; at ventral and .
maxilliped Senses touch and forward part of
taste the thorax region
Third maxilliped Holds food; at ventral and .
Senses touch and forward part of
taste the thorax region
Cheliped Grasps food at ventral part of .
thorax-posterior
to the
maxillipeds
walking leg Locomotion at ventral part of .
thorax-posterior
(walking) to the
maxillipeds
Swimmeret 1st swimmeret in abdominal region .
males transfers on the ventral
sperm to female; side
females use the
2nd-5th
swimmerets to
hold eggs &
young;
locomotion
uropod swimming posterior or tail .
end
telson swimming posterior or tail .
end
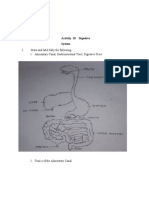
Internal Anatomy
Green Gland: This organ acts like the human kidney. It filters the blood of the crayfish to
take out wastes. The waste is then excreted (lost) through pores in the body of the
crayfish.
Ventral Nerve Cord: This long nerve is like the human spinal cord. It sends signals to all
parts of the crayfish (muscles and appendages) from the brain.
Gastric Mill: Inside the stomach, teeth made of chitin grind food into smaller pieces
Chitin: A hard structural material that makes up exoskeletons of insects and the cell
walls of fungi. This also makes up the teeth in the stomach of a crayfish.
Be able to label the internal and external parts of a crayfish for your quiz!
Вам также может понравиться
- Earths Structure WorksheetДокумент2 страницыEarths Structure Worksheetapi-35292698791% (11)
- AnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyДокумент5 страницAnaPhy 1 - Unit 1 - Language of AnatomyAndrea JiongcoОценок пока нет
- Digestion Absorption MetabolismДокумент12 страницDigestion Absorption MetabolismEunice Villa CuñadaОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Questions & AnswersДокумент161 страницаMechanical Questions & AnswersTobaОценок пока нет
- 2 - Stretching of The Trigger PointДокумент17 страниц2 - Stretching of The Trigger PointLolyОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент10 страницDigestive SystemSweets Jar80% (5)
- D257272 1200 FDD 002 R1 PDFДокумент420 страницD257272 1200 FDD 002 R1 PDFTap Toan100% (1)
- Oracle Fusion Financials Book Set Home Page SummaryДокумент274 страницыOracle Fusion Financials Book Set Home Page SummaryAbhishek Agrawal100% (1)
- Carolina Rabbit Dissection Guide PDFДокумент26 страницCarolina Rabbit Dissection Guide PDFclairosusОценок пока нет
- LLM DissertationДокумент94 страницыLLM Dissertationjasminjajarefe100% (1)
- GRACE 8 Quarter 4 Lesson 1Документ32 страницыGRACE 8 Quarter 4 Lesson 1Mary Dianne BelgaОценок пока нет
- MKT-case StudyДокумент7 страницMKT-case StudyJoe Thampi KuruppumadhomОценок пока нет
- Compilation Medsurg PrelimsДокумент29 страницCompilation Medsurg PrelimsEunice CuñadaОценок пока нет
- Group 5 Dissecting ActivityДокумент10 страницGroup 5 Dissecting Activityvincentelijah2911Оценок пока нет
- The Digestive System and Body MetabolismДокумент5 страницThe Digestive System and Body MetabolismGlen DaleОценок пока нет
- MetabolismДокумент3 страницыMetabolismElsie CarbonОценок пока нет
- Differences between Turbellaria, Trematoda and CestodaДокумент3 страницыDifferences between Turbellaria, Trematoda and CestodaRio YuhanataОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент3 страницыDigestive SystemElene PerfasОценок пока нет
- Animal Digestive Systems ExplainedДокумент70 страницAnimal Digestive Systems ExplainedAnnaGuese100% (1)
- Chapter 12: Digestive SystemДокумент17 страницChapter 12: Digestive SystemTricia BarotОценок пока нет
- Anaphy Lab: Location Action EpicraniusДокумент3 страницыAnaphy Lab: Location Action EpicraniusAndrea BurnotОценок пока нет
- 1 Human OrganismДокумент5 страниц1 Human OrganismEly Fructuoso100% (1)
- Digestive System 16 18Документ11 страницDigestive System 16 18riguel222Оценок пока нет
- PRINTED Digestive System HandoutsДокумент8 страницPRINTED Digestive System HandoutsKate GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Digestive system anatomy and functionsДокумент13 страницDigestive system anatomy and functionsMarija OreškovićОценок пока нет
- VisibleBody Digestive SystemДокумент13 страницVisibleBody Digestive SystemcascaveletteОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal TractДокумент5 страницGastrointestinal TractMalayao, Philip Jude M.Оценок пока нет
- Muscles of The Head Origin Insertion ActionДокумент4 страницыMuscles of The Head Origin Insertion Actionanon ymousОценок пока нет
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEMДокумент3 страницыDIGESTIVE SYSTEMkhakimagdalenaОценок пока нет
- Nutrition in Humans: Peristalsis Process of Digestion Absorption Assimilation The LiverДокумент55 страницNutrition in Humans: Peristalsis Process of Digestion Absorption Assimilation The LiverAli Zain BhattiОценок пока нет
- Exercise 2 UnfinishedДокумент7 страницExercise 2 UnfinishedMaureen LauzonОценок пока нет
- Anatomical TermsДокумент7 страницAnatomical TermsKathleenJoyGalAlmasinОценок пока нет
- Cranial NervesДокумент2 страницыCranial NervesDomalaon, Princess Sophia B.Оценок пока нет
- Bio FrogДокумент9 страницBio FrogMARK JIRON ROTONIОценок пока нет
- Laboratory Worksheet # 14 & 15 - Digestive and Respiratory SystemДокумент14 страницLaboratory Worksheet # 14 & 15 - Digestive and Respiratory SystemAtasha GeronimoОценок пока нет
- THE Disgestive System: by Second GroupДокумент17 страницTHE Disgestive System: by Second GroupAuliya AlfaОценок пока нет
- Vocabulary of Invertebrates PDFДокумент2 страницыVocabulary of Invertebrates PDFnatalescorОценок пока нет
- Animal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionДокумент53 страницыAnimal Nutrition: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionAfifaОценок пока нет
- RT 204 Prefinal TransesДокумент22 страницыRT 204 Prefinal TransesLouise0% (1)
- UntitledДокумент9 страницUntitledLeyluhgheylОценок пока нет
- GZ Lab Finals RevДокумент5 страницGZ Lab Finals Revgerlyn duranОценок пока нет
- Muscular System of FrogДокумент3 страницыMuscular System of FrogBanana LatteОценок пока нет
- Results Anatomy Shellfish LabДокумент17 страницResults Anatomy Shellfish LabSyafiqa UmairahОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Handbook-CodeworksДокумент171 страницаAnatomy Handbook-CodeworksBe GameОценок пока нет
- The Pancreas - Anatomy - Duct System - Vasculatur 5Документ1 страницаThe Pancreas - Anatomy - Duct System - Vasculatur 5KC Dela RosaОценок пока нет
- The Ruminant Digestive System Day 2Документ18 страницThe Ruminant Digestive System Day 2Yanyan PaydaОценок пока нет
- Resume Anatomy. Intestines & Peritoneum. Melissa AlvarezДокумент2 страницыResume Anatomy. Intestines & Peritoneum. Melissa AlvarezJhon Cusme (jhoncusme)Оценок пока нет
- External Anatomy of The FrogДокумент19 страницExternal Anatomy of The Frogabigail_estrecho83% (6)
- Presentation in Health Science: By: Benjie Lachica Jerlyn AriesДокумент17 страницPresentation in Health Science: By: Benjie Lachica Jerlyn AriesJerlyn AriesОценок пока нет
- Gastrointestinal System: AnatomyДокумент7 страницGastrointestinal System: AnatomyMYKRISTIE JHO MENDEZОценок пока нет
- BIOL 546 DigestionДокумент71 страницаBIOL 546 DigestiontОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент15 страницDigestive SystemHenry BuñagОценок пока нет
- Activity-10-Digestive-System - PERALTAДокумент12 страницActivity-10-Digestive-System - PERALTACogie PeraltaОценок пока нет
- Digeestive System Structures and FunctionsДокумент3 страницыDigeestive System Structures and FunctionsyeshenbehariОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент3 страницыDigestive SystemJheinafaye ValienteОценок пока нет
- A&P - Muscle WorksheetДокумент4 страницыA&P - Muscle WorksheetJerry GОценок пока нет
- Vertebrates Digestive structureFINALДокумент74 страницыVertebrates Digestive structureFINALdaryllashleictevesОценок пока нет
- Vertebrate Animal AnatomyДокумент8 страницVertebrate Animal AnatomynurОценок пока нет
- Anaphy FinalsДокумент20 страницAnaphy FinalsHazel Anne Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Muscles of Leg2003Документ11 страницMuscles of Leg2003mosesjc07Оценок пока нет
- I. Facial MusclesДокумент5 страницI. Facial MusclesAnya RamosОценок пока нет
- Frog S Muscular System PDFДокумент9 страницFrog S Muscular System PDFVia CabardaОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент12 страницDigestive SystemJen SmithОценок пока нет
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesДокумент4 страницыPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaОценок пока нет
- Nutrition&DietTherapy (LAB) - Functions of The Digestive SystemДокумент14 страницNutrition&DietTherapy (LAB) - Functions of The Digestive SystemkappaОценок пока нет
- Natural Hazards Study GuideДокумент5 страницNatural Hazards Study Guideapi-352926987100% (1)
- Energy and Forces Study GuideДокумент6 страницEnergy and Forces Study Guideapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- DC 10642Документ2 страницыDC 10642api-353250460Оценок пока нет
- Preservation ProposalДокумент1 страницаPreservation Proposalapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Natural Hazards BrochureДокумент3 страницыNatural Hazards Brochureapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Science Fair ExplanationsДокумент8 страницScience Fair Explanationsapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- HomeroomДокумент1 страницаHomeroomapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Answer Key To Forces and Energy SGДокумент6 страницAnswer Key To Forces and Energy SGapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- CalendarsДокумент1 страницаCalendarsapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Crayfish TableДокумент3 страницыCrayfish Tableapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Earthquake BuildingsДокумент5 страницEarthquake Buildingsapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Retake Form 1Документ1 страницаRetake Form 1api-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Plate TectonicsДокумент2 страницыPlate Tectonicsapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Science Fair DeadlinesДокумент1 страницаScience Fair Deadlinesapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Science SyllabusДокумент4 страницыScience Syllabusapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Isle RoyaleДокумент1 страницаIsle Royaleapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Plate Tectonics ActivityДокумент2 страницыPlate Tectonics Activityapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- UnitoverviewДокумент4 страницыUnitoverviewapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Math Sample LessonsДокумент3 страницыMath Sample Lessonsapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Social Studies Lesson ExampleДокумент5 страницSocial Studies Lesson Exampleapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- MathunitoverviewДокумент3 страницыMathunitoverviewapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- 3 23 17punnettsquaresДокумент3 страницы3 23 17punnettsquaresapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Electricityunitoverview 1Документ6 страницElectricityunitoverview 1api-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Unitoverview SsДокумент6 страницUnitoverview Ssapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Resume PDFДокумент1 страницаResume PDFapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Electricity SampleДокумент5 страницElectricity Sampleapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Unit OverviewДокумент4 страницыUnit Overviewapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- Gibbs Erin MidtermДокумент6 страницGibbs Erin Midtermapi-352926987Оценок пока нет
- 153C Final Exam Study Guide-2Документ6 страниц153C Final Exam Study Guide-2Soji AdimulaОценок пока нет
- A Woman's Talent Is To Listen, Says The Vatican - Advanced PDFДокумент6 страницA Woman's Talent Is To Listen, Says The Vatican - Advanced PDFhahahapsuОценок пока нет
- Flexible AC Transmission SystemsДокумент51 страницаFlexible AC Transmission SystemsPriyanka VedulaОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 2018-2019 Term 1Документ205 страницLesson Plan 2018-2019 Term 1Athlyn DurandОценок пока нет
- EQ - Module - Cantilever MethodДокумент17 страницEQ - Module - Cantilever MethodAndrea MalateОценок пока нет
- Product Catalog 2016Документ84 страницыProduct Catalog 2016Sauro GordiniОценок пока нет
- EE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherДокумент23 страницыEE-434 Power Electronics: Engr. Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherMirza Azhar HaseebОценок пока нет
- EPF Passbook Details for Member ID RJRAJ19545850000014181Документ3 страницыEPF Passbook Details for Member ID RJRAJ19545850000014181Parveen SainiОценок пока нет
- Presentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToДокумент79 страницPresentation On Ich Topics & Guidelines With A Special Reference ToVidyaОценок пока нет
- Assessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistДокумент7 страницAssessing Eyes NCM 103 ChecklistNicole NipasОценок пока нет
- Application Programming InterfaceДокумент12 страницApplication Programming InterfacesorinproiecteОценок пока нет
- Trove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Документ51 страницаTrove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Ceren ArkancanОценок пока нет
- ASD Manual and AISC LRFD Manual For Bolt Diameters Up To 6 Inches (150Документ1 страницаASD Manual and AISC LRFD Manual For Bolt Diameters Up To 6 Inches (150rabzihОценок пока нет
- Tugas B InggrisДокумент6 страницTugas B Inggrisiqbal baleОценок пока нет
- SOP for Troubleshooting LT ACB IssuesДокумент9 страницSOP for Troubleshooting LT ACB IssuesAkhilesh Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Choose the Best WordДокумент7 страницChoose the Best WordJohnny JohnnieeОценок пока нет
- Mark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'Документ5 страницMark Dean GR6211 Fall 2018 Columbia University: - Choice Theory'bhaskkarОценок пока нет
- Revised Man As A Biological BeingДокумент8 страницRevised Man As A Biological Beingapi-3832208Оценок пока нет
- Manual - Sentron Pac Profibus Do Modul - 2009 02 - en PDFДокумент106 страницManual - Sentron Pac Profibus Do Modul - 2009 02 - en PDFDante Renee Mendoza DelgadoОценок пока нет
- Long Run Average Cost (LRAC) : Economies of ScaleДокумент3 страницыLong Run Average Cost (LRAC) : Economies of ScaleA PОценок пока нет
- ChE 135 Peer Evaluation PagulongДокумент3 страницыChE 135 Peer Evaluation PagulongJoshua Emmanuel PagulongОценок пока нет
- 9 - NCP Computer Science PGДокумент19 страниц9 - NCP Computer Science PGM AmbreenОценок пока нет
- Critique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityДокумент2 страницыCritique On A Film Director's Approach To Managing CreativityDax GaffudОценок пока нет
- DAT MAPEH 6 Final PDFДокумент4 страницыDAT MAPEH 6 Final PDFMARLYN GAY EPANОценок пока нет
- Merchandise Floor Ready Standards - Supplier InformationДокумент46 страницMerchandise Floor Ready Standards - Supplier InformationGarmentLearner100% (1)