Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
List of Exercises: Computer Integrated Manufacturing & Technology Driven Practices
Загружено:
navneetkpatil8409Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
List of Exercises: Computer Integrated Manufacturing & Technology Driven Practices
Загружено:
navneetkpatil8409Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Computer Integrated Manufacturing & Technology Driven Practices
Introduction, Evolution, Objectives, CIM Hardware and Software, CIM
Benefits, Nature and role of the elements of CIM, Identifying CIM needs,
05 Data base requirements of CIM, Role of CAD/CAM in CIM, Obstacles to 08
Computer Integrated Manufacturing, Concept of the future CIM systems,
Socio -techno- economic aspects of CIM.
Rapid Prototyping and Tooling
Introduction to RP, Technology Description, Overview of RP, Benefits
and Application. RP Processes: Process overviews, STL file Generation,
Classes of RP systems: Stereo-lithography Approach (SLA), SLA with
photo-polymerization (mathematical modelling of the process), SLA with
liquid thermal polymerization, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Fused
deposition modelling, Laminated object manufacturing, Laser powder
06 forming. Prototype properties: Material properties, colour, dimensional 08
accuracy, stability, surface finish, machinability, environmental
resistance, operational properties.
RP Applications: Design, Concept Models, Form & fit checking,
Functional testing, CAD data verification, Rapid Tooling, Rapid
manufacturing, Science & Medicine, RP processes for MEMS,
Photolithography, Direct Laser Writer, Bulk Lithography for 3D micro
fabrication (Modelling of beam propagation and curing in resin system).
List of Exercises
1. Programming for transformations,
2. Solid modeling using any 3D modeling software
3. Part programming and part fabrication on CNC trainer (Turning / Milling)
4. Geometrical optimization of any mechanical component using computer aided
engineering concepts.
5. Development of physical 3D mechanical structure using any one of the rapid
prototyping processes.
6. Rapid tooling for any one of the engineering or medical applications.
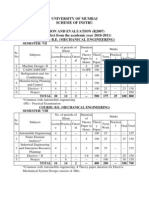
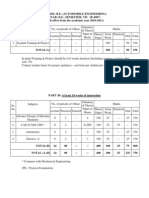
Term Work
Term work shall consist of any three exercises from the above list and a course project in a
group of not more than three (3) students on either computer aided engineering or rapid
prototyping and tooling
The distribution of marks for term work shall be as follows:
Exercises : 15 Marks
Course Project : 05 Marks
Attendance (Theory & Practical) : 05 Marks
The final certification and acceptance of term work ensures the satisfactory performance of
laboratory work and minimum passing in the term work.
Internal Assessment
Assessment consists of two tests out of which; one should be compulsory class test (on minimum
40% of curriculum) and the other is either a class test (on minimum 70% of curriculum) or
assignment on live problems.
44/113
University of Mumbai, Mechanical Engineering (Third and Final Year) Revised Course (Rev-2012)
Вам также может понравиться
- Gujarat Technological University: Mechanical (Cad/Cam) (08) / Mechanical (Machine Design) (09) SUBJECT CODE: 2740801Документ3 страницыGujarat Technological University: Mechanical (Cad/Cam) (08) / Mechanical (Machine Design) (09) SUBJECT CODE: 2740801Ravi ParikhОценок пока нет
- Question Bank - Cad Cam CaeДокумент12 страницQuestion Bank - Cad Cam CaePravin DahalkeОценок пока нет
- RPTДокумент4 страницыRPTSARAN PRASANTHОценок пока нет
- Syllabus AMTДокумент2 страницыSyllabus AMTSyed Farooq PatilОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Документ3 страницыGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Divyeshkumar MorabiyaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 ADMДокумент43 страницыUnit 1 ADMCHINTAKINDI VENKATAIAH RAGHUVAMSHIОценок пока нет
- Lecture01 - CAD CAM - CAE - Introduction of The CourseДокумент21 страницаLecture01 - CAD CAM - CAE - Introduction of The CourseSameer shaikhОценок пока нет
- 19ME307 Rapid Product DevelopmentДокумент2 страницы19ME307 Rapid Product DevelopmentsahilОценок пока нет
- Additive MFGДокумент18 страницAdditive MFGEmerald InnovatesОценок пока нет
- MEE2016 Rapid-Manufacturing-Technologies ETH 1 AC40Документ2 страницыMEE2016 Rapid-Manufacturing-Technologies ETH 1 AC40HarishVenkatesanОценок пока нет
- B.Tech. (Mech.) Fourth Year Syllabus (REVISED)Документ64 страницыB.Tech. (Mech.) Fourth Year Syllabus (REVISED)bawincipetОценок пока нет
- MEE80212 Digital Prototyping For Product Design - II 3+1Документ1 страницаMEE80212 Digital Prototyping For Product Design - II 3+1Honey SinghОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological UniversityДокумент5 страницGujarat Technological Universitychirag khokhriОценок пока нет
- University of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation for B.E. Mechanical EngineeringДокумент82 страницыUniversity of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation for B.E. Mechanical EngineeringJayesh NavareОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент3 страницыSyllabusDishank UpadhyayОценок пока нет
- 6th Sem SyllabusДокумент16 страниц6th Sem SyllabusSOUMIK DASОценок пока нет
- Additive Manufacturing Student NotesДокумент90 страницAdditive Manufacturing Student NotesUdayaKumar100% (1)
- MtvsemДокумент24 страницыMtvsemEnemyОценок пока нет
- Rapid Prototyping Notes by Shashidhar 2Документ132 страницыRapid Prototyping Notes by Shashidhar 2sharma devarajuОценок пока нет
- 0 Productlifecycle PDFДокумент40 страниц0 Productlifecycle PDFCharith ReddyОценок пока нет
- Mechanical - VI. Sem Syllabus GtuДокумент115 страницMechanical - VI. Sem Syllabus GtukishormechОценок пока нет
- CADCAM Course OutlineДокумент9 страницCADCAM Course OutlineJibril JundiОценок пока нет
- Rapid Prototyping IntroductionДокумент90 страницRapid Prototyping Introductionharsh vaghelaОценок пока нет
- Rapid PrototypingДокумент22 страницыRapid PrototypingMohammed SameelОценок пока нет
- Cam 25062016 030053amДокумент4 страницыCam 25062016 030053amRemi KwetchaОценок пока нет
- The Integration of CAD/CAM and Rapid Prototyping in Product Development: A ReviewДокумент8 страницThe Integration of CAD/CAM and Rapid Prototyping in Product Development: A ReviewWangi Pandan SariОценок пока нет
- Rapid PrototypingДокумент123 страницыRapid PrototypingSyed irfan100% (2)
- Unit - 1Документ44 страницыUnit - 1rajeshОценок пока нет
- Maulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West BengalДокумент32 страницыMaulana Abul Kalam Azad University of Technology, West BengalarindamckbtОценок пока нет
- Selected Engineering ProblemsДокумент6 страницSelected Engineering ProblemsDiscord YtОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engg 19Документ115 страницMechanical Engg 19Harshul BrahmbhattОценок пока нет
- Cad BookДокумент86 страницCad BookGopi RaguОценок пока нет
- Operation Research NotesДокумент98 страницOperation Research Notessagar kadam100% (2)
- Additive Manufacturing Processes and ApplicationsДокумент3 страницыAdditive Manufacturing Processes and ApplicationsNishant MayekarОценок пока нет
- B.E. Automobile Engineering Course DocumentsДокумент73 страницыB.E. Automobile Engineering Course Documentssss0987654321Оценок пока нет
- What is a prototypeДокумент5 страницWhat is a prototypeanimeshkumarvermaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ56 страницChapter 1om navadiyaОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University Mechanical (Cad/Cam) (08) : Computer Aided Process Planning 2720813 Semester: IiДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological University Mechanical (Cad/Cam) (08) : Computer Aided Process Planning 2720813 Semester: IiGeorge CamachoОценок пока нет
- 3D Printing BasicsДокумент40 страниц3D Printing BasicsBalaji VasudevanОценок пока нет
- 18me4105 - Additive Manufacturing Key & Scheme of Evaluation Dec-2022Документ13 страниц18me4105 - Additive Manufacturing Key & Scheme of Evaluation Dec-2022srinivas kanakalaОценок пока нет
- The Importance of Additive ManufacturingДокумент9 страницThe Importance of Additive ManufacturingraviОценок пока нет
- Home About Us Manufacturing Courses Photo Gallery Contact Us Result WebmailДокумент6 страницHome About Us Manufacturing Courses Photo Gallery Contact Us Result WebmailudaygwlОценок пока нет
- CAD Exrecise BookДокумент90 страницCAD Exrecise BookPrashant NarwadeОценок пока нет
- 5.syllabus Copy and Brief On PrerequisitesДокумент3 страницы5.syllabus Copy and Brief On PrerequisitesSreedhar MОценок пока нет
- UNIT1,3Документ14 страницUNIT1,3Sagar BatraОценок пока нет
- Unit - 1Документ40 страницUnit - 1rajeshОценок пока нет
- MIni Project Report Batch-12Документ42 страницыMIni Project Report Batch-12Rakshith B Industrial EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Application of Reverse Engineering Techniques in Mechanics System ServicesДокумент9 страницApplication of Reverse Engineering Techniques in Mechanics System ServicesRaul AndresОценок пока нет
- CADCAM-minДокумент91 страницаCADCAM-minBandi KumarreddyОценок пока нет
- Basics of Mechanical Engineering Drawing and Digital FabricationДокумент20 страницBasics of Mechanical Engineering Drawing and Digital FabricationVivek SharmaОценок пока нет
- Parametric Process Optimization To Improve The Accuracy of Rapid Prototyped Stereolithography PartsДокумент23 страницыParametric Process Optimization To Improve The Accuracy of Rapid Prototyped Stereolithography Partsasdada1428Оценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3Документ3 страницыGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 3ashish patelОценок пока нет
- Rapid Prototyping TechniqueДокумент35 страницRapid Prototyping TechniquekajavarunОценок пока нет
- Engineering Principles of Combat Modeling and Distributed SimulationОт EverandEngineering Principles of Combat Modeling and Distributed SimulationОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Engineers' Handbook, Volume 2: Design, Instrumentation, and ControlsОт EverandMechanical Engineers' Handbook, Volume 2: Design, Instrumentation, and ControlsОценок пока нет
- Implementing the Stakeholder Based Goal-Question-Metric (Gqm) Measurement Model for Software ProjectsОт EverandImplementing the Stakeholder Based Goal-Question-Metric (Gqm) Measurement Model for Software ProjectsОценок пока нет
- Software Engineering New Approach (Traditional and Agile Methodologies)От EverandSoftware Engineering New Approach (Traditional and Agile Methodologies)Оценок пока нет
- Software Engineering: Architecture-driven Software DevelopmentОт EverandSoftware Engineering: Architecture-driven Software DevelopmentРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- 2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering StructureДокумент11 страниц2018-19 F.E. To B.E. Mechanical Engineering Structurenavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- 2020engg Cap1 CutoffДокумент1 326 страниц2020engg Cap1 Cutofframeshdorage12Оценок пока нет
- KC I Il Call For ProposalДокумент2 страницыKC I Il Call For Proposalnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- NAAC Criteria IV ChecklistДокумент1 страницаNAAC Criteria IV Checklistnavneetkpatil8409100% (1)
- Measurement of Screw ParametersДокумент2 страницыMeasurement of Screw Parametersnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Nmu at ExaminerДокумент6 страницNmu at Examinernavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Applied Thermodynamics Course OutlineДокумент4 страницыApplied Thermodynamics Course Outlinenavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Colleges Cut Off's HNHNДокумент1 страницаColleges Cut Off's HNHNnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Ethics and Professional Skills Module: SyllabusДокумент9 страницEthics and Professional Skills Module: SyllabusNebiyuОценок пока нет
- Appendix2 Model Workshop Evaluation FormДокумент3 страницыAppendix2 Model Workshop Evaluation FormMaricris ChavezОценок пока нет
- 2 Dse Cutoff PDFДокумент1 859 страниц2 Dse Cutoff PDFnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Star BurnДокумент1 страницаStar BurnJ SELVA ANTONY SANTOSHОценок пока нет
- Report On Sports and Cultural ActivitiesДокумент2 страницыReport On Sports and Cultural Activitiesnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Last Page PDFДокумент2 страницыLast Page PDFnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Applied Thermodynamics LabДокумент3 страницыApplied Thermodynamics Labnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- TCS On Line TestДокумент6 страницTCS On Line TestMohanОценок пока нет
- EEДокумент7 страницEEnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- TCS On Line TestДокумент6 страницTCS On Line TestMohanОценок пока нет
- Registration Sheet MechДокумент1 страницаRegistration Sheet Mechnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- T 1Документ1 страницаT 1navneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- COДокумент7 страницCOnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- I SchemeДокумент7 страницI SchemeAmit GhadeОценок пока нет
- Statement of Grades: (100007) SSBT College of Engineering & Technology, Bambhori, JalgaonДокумент1 898 страницStatement of Grades: (100007) SSBT College of Engineering & Technology, Bambhori, Jalgaonnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- CEДокумент8 страницCEnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Plans and Drawings Checklist For Planning ApplicationsДокумент7 страницPlans and Drawings Checklist For Planning Applicationsnavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Winter 2013 Question PaperДокумент5 страницWinter 2013 Question Papernavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- 12186Документ2 страницы12186Harsh BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Summer 2014 Model Answer PaperДокумент42 страницыSummer 2014 Model Answer Papernavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Seat No.: Instructions: (1) All Questions Are CompulsoryДокумент4 страницыSeat No.: Instructions: (1) All Questions Are Compulsorynavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- 4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat NoДокумент5 страниц4 Hours / 100 Marks: Seat Nonavneetkpatil8409Оценок пока нет
- Mechanical equipment schedule and legendДокумент2 страницыMechanical equipment schedule and legendarief bahtiarОценок пока нет
- Mmaw QДокумент9 страницMmaw Qf_behdadОценок пока нет
- Henderson, Julian - Glass Production and Bronze Age EuropeДокумент17 страницHenderson, Julian - Glass Production and Bronze Age EuropeHelena HrdličkováОценок пока нет
- PKG 5 Customer List in IndiaДокумент5 страницPKG 5 Customer List in IndiaGiri DharОценок пока нет
- Engineering Disasters - Alexander L. KiellandДокумент8 страницEngineering Disasters - Alexander L. KiellandAnonymous ka2kX4jNОценок пока нет
- Coatings Non-ITAR Product and Specification GuideДокумент16 страницCoatings Non-ITAR Product and Specification GuideCarlos Alberto Rozo R.Оценок пока нет
- Genkem Contact AdhesiveДокумент3 страницыGenkem Contact AdhesiveSirGawain9950% (2)
- Διατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήДокумент1 страницаΔιατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήjojogarciaОценок пока нет
- GenSet Wattage WorksheetДокумент2 страницыGenSet Wattage Worksheetjdc_1811654Оценок пока нет
- Materials System SpecificationДокумент13 страницMaterials System Specificationnadeem shaikhОценок пока нет
- TP16-2-Appearance of Embellishment & Trims After A Durability Wash TestДокумент4 страницыTP16-2-Appearance of Embellishment & Trims After A Durability Wash TestSazzad Hossain Hossain100% (1)
- 1807 VS 1 Performance SpecificationsДокумент89 страниц1807 VS 1 Performance SpecificationsNiko TassigiannakisОценок пока нет
- Foerster Circograph 2014 enДокумент6 страницFoerster Circograph 2014 enTiến NguyễnОценок пока нет
- The Fundamentals of Fire ExtinguishmentДокумент0 страницThe Fundamentals of Fire ExtinguishmentjohnzepolОценок пока нет
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Chiller Vs VRF PDFДокумент23 страницыMicrosoft PowerPoint - Chiller Vs VRF PDFcalvin.bloodaxe44780% (2)
- Design - Pinned - Column Base-PlatesДокумент61 страницаDesign - Pinned - Column Base-PlatesYoshua YangОценок пока нет
- Nitric Acid Chematur WheaterlyДокумент4 страницыNitric Acid Chematur WheaterlyAnonymous 1XHScfCI100% (1)
- Rochor Station Pile Design CalculationsДокумент15 страницRochor Station Pile Design CalculationsDifa LiuОценок пока нет
- MSE Wall Shop Drawing Checklist (Rev 3)Документ3 страницыMSE Wall Shop Drawing Checklist (Rev 3)lcruz117Оценок пока нет
- Thermal Mass Flow Controller Scaling RelationsДокумент13 страницThermal Mass Flow Controller Scaling Relationsccwang100% (1)
- Dando Mintec 9000 (Dando Drilling Indonesia)Документ2 страницыDando Mintec 9000 (Dando Drilling Indonesia)Dando Drilling Indonesia100% (2)
- Program of NEWCA Workshop (V27-04)Документ2 страницыProgram of NEWCA Workshop (V27-04)Queiroz PortorrealОценок пока нет
- Lab Test: Fakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Dan Pembuatan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia MelakaДокумент6 страницLab Test: Fakulti Teknologi Kejuruteraan Mekanikal Dan Pembuatan Universiti Teknikal Malaysia MelakaHairul Effendy Ab MaulodОценок пока нет
- One Off Fiberglass Foam Core BoatДокумент15 страницOne Off Fiberglass Foam Core Boatsjdarkman1930100% (2)
- Motovario MaintenanceДокумент72 страницыMotovario Maintenancearachman297988Оценок пока нет
- Dummy Loads - Load Bank Technology - Sephco IndustriesДокумент1 страницаDummy Loads - Load Bank Technology - Sephco IndustriesFELIXDEJОценок пока нет
- S154-1209 IomДокумент66 страницS154-1209 IomAlfredo GodinezОценок пока нет
- Acetone MsdsДокумент4 страницыAcetone MsdsRidwan RifaiОценок пока нет
- Uniclass2015 PR v1 18Документ229 страницUniclass2015 PR v1 18abdullah sahibОценок пока нет
- Pages From Asme Sec Ix 2017-4Документ1 страницаPages From Asme Sec Ix 2017-4Akhtar AnsariОценок пока нет