Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Test Proceudre For Determination of Total Hardness in Water
Загружено:
Suraj RawatОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Test Proceudre For Determination of Total Hardness in Water
Загружено:
Suraj RawatАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
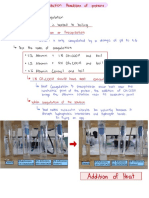
Determination of Total Hardness in water:
Total hardness of water is determined by titrating known quantity of sample with std. EDTA solution
using Eriochrome black T indicator.
1. Principle: this method is based on the ability of EDTA or its disodium salt to form a soluble
complex with calcium and magnesium ions. When dye EBT is added to a solution
containing calcium and magnesium ions at ph 10.0, a wine red complex is formed. This
solution is titrated with std. Solution of EDTA, which extract calcium and magnesium from
dye complex and colour changes to blue. (Original colour of indicator.)
2. Reagents:
1. 0.01 M EDTA: - 3.7224 gms of di-sodium salt of EDTA is dissolved in 1 ltr. Distilled water.
Standardisation of EDTA: -- Weigh 0.2 to 0.4 gm of pure zinc metal, dissolve it in 2ml of
HNO3. Dilute to 100 ml using distilled water in a volumetric flask. Pipette out 5 ml of this
soln. Add NaOH till soln becomes turbid. Add 5 ml of buffer soln, 2 drops of EBT indicator
and titrate against prepared EDTA soln. Colour changes from wine red to blue.
Calculation: - 1ml of 0.01m EDTA = 0.0006538 gm of Zinc
molarity of EDTA = weight of Zn x 0.05 x 0.01
B.R. X 0.0006538
2. Buffer solution - 17.5 gms of NH4Cl is dissolved in 142 ml of liquor ammonia and 108
distilled water.
3. Eriochrome black T :- 1 gm EBT indicator + 75 ml triethanolamine + 15 ml isopropyl
alcohol.
Procedure:
1. Take 25 ml of sample in a conical flask.
2. Add 10 ml of buffer solution.
3. Add 1 - 2 drops of EBT indicator.
4. Titrate with std. EDTA solution.
5. The colour changes from wine red to blue.
6. Note down the burette reading.
Calculations: burette reading x 1000
Total hardness as CaCO3 = -------------------------------
sample taken
Reference : Quantitative Inorganic Analysis by Arthur I Vogel.
Determination of Calcium hardness in water:
Calcium hardness of water is determined by titrating known volume of sample with std. EDTA solution using
murexide indicator at pH 12 - 13. The colour change is pink to purple.
1. Principle:
This method is based on the ability of EDTA or its disodium salt to form a soluble complex with calcium at
pH 12-13. The Magnesium ions at high pH precipitate as Mg(OH)2.
2. Reagents:
1. 0.01 M EDTA = 3.7224 gms EDTA in 1 ltr. D.W.
2. 4 N NaOH (16% NaOH )
3. Murexide indicator. (powder )
3. Procedure:
1. Take 25 ml sample in a conical flask.
2. Add 1 ml of 4 N NaOH and starr. ( pH 12 -13 ).
3. Add murexide indicator.
4. Titrate with std. EDTA solution till the colour changes to purple.
5. Record the volume of EDTA reqd. for the end point.
4. Calculation:
Burette reading x 1000
Calcium hardness as CaCO3 = -------------------------------
Sample Taken
Reference : Quantitative Inorganic Analysis by Arthur I Vogel.
Вам также может понравиться
- Determination of Mg by EDTA TitrationДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Mg by EDTA TitrationJinete EleganteОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Lab ManualДокумент24 страницыChemistry Lab ManualSandeep Singh CharanОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Experiment ManualsДокумент34 страницыChemistry Experiment Manualsmnasir328115Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry LabДокумент49 страницChemistry LabVishwas VermaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry PracticalДокумент38 страницChemistry PracticalMukhtar MalikОценок пока нет
- Experiment 1 Determination of Water Hardness by EDTAДокумент2 страницыExperiment 1 Determination of Water Hardness by EDTAizz isalahОценок пока нет
- Session: 3 Engineering ChemistryДокумент17 страницSession: 3 Engineering ChemistryDUE DATEОценок пока нет
- Determination of Hardness of Water (Step-By-Step Plan)Документ6 страницDetermination of Hardness of Water (Step-By-Step Plan)ravenheart90Оценок пока нет
- Water Analysis PrtocolДокумент29 страницWater Analysis PrtocolRajSharmaОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual For IT (16 TH Dec)Документ52 страницыLab Manual For IT (16 TH Dec)aattishОценок пока нет
- Experiment IДокумент7 страницExperiment ILakshitaОценок пока нет
- Short Procedure - 2022-2024 I-SEM - 231102 - 142651Документ6 страницShort Procedure - 2022-2024 I-SEM - 231102 - 142651AkshayaОценок пока нет
- 2 ZN ExperimentДокумент3 страницы2 ZN ExperimentSanyamkumar HansdahОценок пока нет
- Magnesium Oxide AnalysisДокумент3 страницыMagnesium Oxide AnalysisAnupriya Oberoi100% (1)
- Chemistry 3200 Complexometric Titration With EDTA: ProcedureДокумент5 страницChemistry 3200 Complexometric Titration With EDTA: Proceduretaysi tafriОценок пока нет
- Engineering Chemistry Lab Manual PDFДокумент25 страницEngineering Chemistry Lab Manual PDFmayukrijuОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposeДокумент4 страницыChemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposekuochsochinОценок пока нет
- Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationДокумент4 страницыWater Hardness by EDTA TitrationHanna ShairaОценок пока нет
- Chem FileДокумент60 страницChem FileGaurang GoelОценок пока нет
- NEET Important Catalogues PDFДокумент4 страницыNEET Important Catalogues PDFfepedo3111Оценок пока нет
- ION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralДокумент50 страницION EXCHANGE Analysis Testing Procedures GeneralJinalОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 02: (Metal Ion) + Edta M-EDTA (Colorless) Edta M-EDTA + Free Eriochrome Black TДокумент2 страницыExperiment No. 02: (Metal Ion) + Edta M-EDTA (Colorless) Edta M-EDTA + Free Eriochrome Black Tsam musicОценок пока нет
- CalciumДокумент3 страницыCalciumMuhammad Amir AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Alkalinity Hardness &chlorideДокумент34 страницыAlkalinity Hardness &chloridelhkooОценок пока нет
- FInal Chemistry Sessional ReportДокумент11 страницFInal Chemistry Sessional ReportSyed M IslamОценок пока нет
- CHE551A Practicals (1) - DДокумент4 страницыCHE551A Practicals (1) - DGollum LОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 185H Lab #1: Determining Water HardnessДокумент5 страницChemistry 185H Lab #1: Determining Water HardnessOmSilence2651Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual CHE102 Chemistry LabДокумент41 страницаLaboratory Manual CHE102 Chemistry LabSushil KumarОценок пока нет
- Problems On EDTAДокумент4 страницыProblems On EDTAAniket Kundu100% (1)
- 09.11.2010 MethodologyДокумент16 страниц09.11.2010 MethodologyavvaimsvijayaОценок пока нет
- Gpch1997 Hardness AcmkiyДокумент5 страницGpch1997 Hardness AcmkiyAparna KadamОценок пока нет
- SOL 6 Water HardnessДокумент3 страницыSOL 6 Water HardnessRahimi ShahimiОценок пока нет
- Editable Experiment Record TemplateДокумент5 страницEditable Experiment Record TemplateNemalnath reddy KasarapuОценок пока нет
- Determination of Ca and MG ConcentrationДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Ca and MG ConcentrationRhea TalibОценок пока нет
- SOP For Water TestingДокумент50 страницSOP For Water Testinggreen solutionОценок пока нет
- Deionized Water: Experiment. Edta Titration of Ba2+ of A) Unknown Metal Sulfate and B) Unknown BaclДокумент6 страницDeionized Water: Experiment. Edta Titration of Ba2+ of A) Unknown Metal Sulfate and B) Unknown Bacljohn pibОценок пока нет
- EDTA Titration of Calcium and Magnesium IonsДокумент3 страницыEDTA Titration of Calcium and Magnesium IonsAnonymous NxpnI6jC67% (3)
- Eng - Chemsitry LabmanualДокумент41 страницаEng - Chemsitry Labmanualengineeringchemistry100% (1)
- Experiment IC 2.2Документ5 страницExperiment IC 2.2Cresher SimaОценок пока нет
- 3500-Ca Calcium : 1. Occurrence and SignificanceДокумент2 страницы3500-Ca Calcium : 1. Occurrence and SignificanceAndrés Osorio100% (1)
- Calcium by Titrametric MethodДокумент4 страницыCalcium by Titrametric MethodRajeev ChandОценок пока нет
- 3500-Ca Calcium 3500-Ca A.: 500 Mg/l. The Most CommonДокумент2 страницы3500-Ca Calcium 3500-Ca A.: 500 Mg/l. The Most CommonElard Vilca CutimboОценок пока нет
- EDTA ExperimentДокумент5 страницEDTA ExperimentMahmoud MahmoudmОценок пока нет
- Determining The Hardness of Water Via EDTA-TitrationДокумент2 страницыDetermining The Hardness of Water Via EDTA-Titrationstudent_4_eva0% (1)
- Determination of Total, Temporary and Permanent Hardness in Water Sample Using EDTA MethodДокумент8 страницDetermination of Total, Temporary and Permanent Hardness in Water Sample Using EDTA MethodNaresh kumarОценок пока нет
- A-MDEA Analytical MethodsДокумент8 страницA-MDEA Analytical MethodsSHYAMKANHAIYA100% (3)
- Ni in SteelДокумент3 страницыNi in Steelpayal_joshi_14Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Chem 24092009Документ34 страницыEngineering Chem 24092009Srinivas BoddupallyОценок пока нет
- Standard Methods For The Examination of Water and WastewaterДокумент4 страницыStandard Methods For The Examination of Water and WastewaterMarianita GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Determine Total Hardness of WaterДокумент24 страницыDetermine Total Hardness of Watersiddharth jugaleОценок пока нет
- Calcium-Magnesium by EDTA TitrationДокумент5 страницCalcium-Magnesium by EDTA TitrationnisscriОценок пока нет
- Experiment #8 (Formal Report)Документ5 страницExperiment #8 (Formal Report)Nathan Veracruz100% (1)
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisОт EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresОт EverandThe Chemistry of Fertilisers and Manure - Including Information on the Chemical Constituents and Types of Fertilisers and ManuresРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Fourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974От EverandFourth International Conference on Non-Aqueous Solutions: Vienna 1974V. GutmannОценок пока нет
- Bio-Based SolventsОт EverandBio-Based SolventsFrançois JérômeОценок пока нет
- Cycle Count Process StepsДокумент3 страницыCycle Count Process StepsSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- FT 35 DC D10447340A Setup ApprovalДокумент7 страницFT 35 DC D10447340A Setup ApprovalSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Fuel Bill Template 3Документ1 страницаFuel Bill Template 3Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- NT-EHS-SOP04 SOP For Communication - EMSДокумент3 страницыNT-EHS-SOP04 SOP For Communication - EMSSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Control Plan for Flywheel Assembly CastingДокумент24 страницыControl Plan for Flywheel Assembly CastingSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Training Module and Training SheetДокумент6 страницTraining Module and Training SheetSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- In-Process Inspection Report: Date: - / - / - Rev. No.: 01 (11/05/2016)Документ4 страницыIn-Process Inspection Report: Date: - / - / - Rev. No.: 01 (11/05/2016)Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- FT 35 DC D10447340A Process SheetДокумент7 страницFT 35 DC D10447340A Process SheetSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Time PlotДокумент1 страницаTime PlotSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- .Builds Relations: Awards & CitationsДокумент15 страниц.Builds Relations: Awards & CitationsSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Prueba de Hipotesis para MediasДокумент6 страницPrueba de Hipotesis para MediasMarilyn Depaz GomezОценок пока нет
- Push Pull Meter - Act - 1000n PDFДокумент7 страницPush Pull Meter - Act - 1000n PDFSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Process Sheet: Part No.: Hub 1500629 (Annexure 1 To PCP 1500629E CP-08)Документ5 страницProcess Sheet: Part No.: Hub 1500629 (Annexure 1 To PCP 1500629E CP-08)Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- No. of EmployeesДокумент3 страницыNo. of EmployeesSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Capacity ManagementДокумент2 страницыCapacity ManagementSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Rev 02Документ3 страницыRev 02Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Preventive Maintenance SystemДокумент3 страницыPreventive Maintenance SystemSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Process Sheet: Rev. No. 01 (19/10/2015)Документ6 страницProcess Sheet: Rev. No. 01 (19/10/2015)Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Testing FacilitiesДокумент5 страницTesting FacilitiesSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Contingency plan for manufacturing operationsДокумент1 страницаContingency plan for manufacturing operationsSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Rev 03Документ5 страницRev 03Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Process Sheet: 9 Inner Diameter Ø 95.21/ 95.31 MM 100% 20th PC 10 Inner Diameter Ø 89.934/ 89.957 MM 100% 10th PCДокумент5 страницProcess Sheet: 9 Inner Diameter Ø 95.21/ 95.31 MM 100% 20th PC 10 Inner Diameter Ø 89.934/ 89.957 MM 100% 10th PCSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- D10414410a PFD Casting Rev 00Документ1 страницаD10414410a PFD Casting Rev 00Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- D10414410A CP Rev 00Документ21 страницаD10414410A CP Rev 00Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- D10414410a PFD Pattern Rev 00Документ1 страницаD10414410a PFD Pattern Rev 00Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- FMEA analysis of flywheel casting process failuresДокумент7 страницFMEA analysis of flywheel casting process failuresSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- D10414410a Fmea MachiningДокумент13 страницD10414410a Fmea MachiningSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- D10414410a PFD Machining Rev 00Документ2 страницыD10414410a PFD Machining Rev 00Suraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Machining PFMEAДокумент8 страницMachining PFMEASuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- Fmea CastingДокумент4 страницыFmea CastingSuraj RawatОценок пока нет
- CHEM 238 Experiment #4: Formal Lab Report: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution-The Nitration of Methyl BenzoateДокумент18 страницCHEM 238 Experiment #4: Formal Lab Report: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution-The Nitration of Methyl Benzoateapi-592105594Оценок пока нет
- 3M FlexoДокумент8 страниц3M FlexoHafiani HichamОценок пока нет
- Determination of Niacin in Food Materials by Liquid Chromatography Using Isotope Dilution Mass SpectrometryДокумент6 страницDetermination of Niacin in Food Materials by Liquid Chromatography Using Isotope Dilution Mass SpectrometryMonica chavez escamОценок пока нет
- s2 Eoy Chem Shapta Assessments 2023 OriginalДокумент11 страницs2 Eoy Chem Shapta Assessments 2023 OriginalUV Vïpêr UnïcôrnОценок пока нет
- Does Lactic Fermentation Influence Soy Yogurt Protein Digestibility A Comperative Study Between Soymilk and Soy Yoghurt at Different PHДокумент33 страницыDoes Lactic Fermentation Influence Soy Yogurt Protein Digestibility A Comperative Study Between Soymilk and Soy Yoghurt at Different PHNabilaОценок пока нет
- Representative Laboratory Reference Values: Blood, Plasma, and SerumДокумент22 страницыRepresentative Laboratory Reference Values: Blood, Plasma, and SerumKubra ĖdrisОценок пока нет
- Work Sheet-8 PDFДокумент4 страницыWork Sheet-8 PDFKesanam SpОценок пока нет
- Rotamass Yokogawa PDFДокумент24 страницыRotamass Yokogawa PDFbambang ismailОценок пока нет
- Formation and Types of Covalent BondsДокумент55 страницFormation and Types of Covalent Bonds陈凯雯Оценок пока нет
- Synthesis of Benzyl Acetate Through Fischer Esterification ReactionДокумент10 страницSynthesis of Benzyl Acetate Through Fischer Esterification ReactionAnonymous GO6JVW9Wud100% (4)
- Experiment 3 PDFДокумент7 страницExperiment 3 PDFKami TazuОценок пока нет
- Vitamin C Experiment Literature ReviewДокумент5 страницVitamin C Experiment Literature Reviewaflsjcibl100% (1)
- ElectrodosДокумент20 страницElectrodosRuben Dario Mamani ArellanoОценок пока нет
- Continuous CrystallizersДокумент22 страницыContinuous CrystallizersAravind Vicky0% (1)
- Hardness, Water Softening - Lime-Soda Ash ProcessДокумент22 страницыHardness, Water Softening - Lime-Soda Ash ProcessDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy100% (8)
- Rubber Properties Chart PDFДокумент1 страницаRubber Properties Chart PDFshalabh.g864177Оценок пока нет
- SF - Miscellaneous Cast-In-Place ConcreteДокумент7 страницSF - Miscellaneous Cast-In-Place ConcreteMuwafaq_mibОценок пока нет
- Vidya ThermoДокумент44 страницыVidya ThermoNarendraОценок пока нет
- MSDS Material Safety Data SheetДокумент5 страницMSDS Material Safety Data Sheethhnp204Оценок пока нет
- Mole Concept WorksheetДокумент3 страницыMole Concept WorksheetRoland SocoОценок пока нет
- Alpacon Altreat 400Документ12 страницAlpacon Altreat 400EmadОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 General Chemistry PDFДокумент29 страницUnit 1 General Chemistry PDFchuchu maneОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Ut2Документ8 страницChemistry Ut2vedantbaraskarОценок пока нет
- ConstantsДокумент2 страницыConstants3 stacksОценок пока нет
- PNH Aromaticity and Naphthalene StructureДокумент36 страницPNH Aromaticity and Naphthalene StructureSnuggy SnufОценок пока нет
- Hollow Rivet Manufacturing ProcessДокумент28 страницHollow Rivet Manufacturing ProcessRachel HasibuanОценок пока нет
- Astm D3695 - 1 (En)Документ5 страницAstm D3695 - 1 (En)MilonОценок пока нет
- Fluids Chart: Safety Data Sheets (SDS) AvailableДокумент1 страницаFluids Chart: Safety Data Sheets (SDS) AvailableViktorija GaradauskieneОценок пока нет
- CHE/CHS 2515 CHE/CHS 2516 CHE/CHS 3515 CHE/CHS 3516: Physical ChemistryДокумент11 страницCHE/CHS 2515 CHE/CHS 2516 CHE/CHS 3515 CHE/CHS 3516: Physical ChemistryChristopher JeyakumarОценок пока нет
- MasterRoc HCA 10 safety data sheetДокумент10 страницMasterRoc HCA 10 safety data sheetabukayes.abdinОценок пока нет