Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
2017tut 8 PDF
Загружено:
Swarnava SanyalОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2017tut 8 PDF
Загружено:
Swarnava SanyalАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
PYL 115: Applied Optics
Tutorial Sheet-VIII
Waveguides and Fiber Optics
1. Consider a symmetric planar waveguide shown in Fig. 1. The direction of propagation is z. The waveguide
is excited by a beam from a GaAlAs laser (free space wavelength = 850 nm). What are the guided modes
that could propagate? Draw a labelled approximately scaled diagram of the transverse electric field of each
of these modes.
x
n2 1.50
6 m
Fig. 1 n1 1.51 z y
2. What are the values of U, W and V at cutoff for the all the modes in Problem 1 above?
3. The refractive index variation for pure silica in the wavelength region 0.5 m < 0 < 1.6 m is
approximately described by the following empirical formula
2 2
n( 0 ) C0 a 0 (b 0 )
where C0 1.451, a b 0.003 and 0 is measured in m. Calculate phase velocity vp and group velocity
vg at 0 0.6 m , 0.8 5 m , 1.0 m , 1.2 5 m , 1.4 m and 1.55 m.
Plot vg as a function of 0 and interpret the result physically. Calculate and plot the material dispersion (in
ps/km.nm) in the wavelength domain 0.5 < 0 < 1.6 m.
4. For a step index multimode fiber, n1 = 1.5 and = 0.015. Calculate n2, NA and the maximum acceptance
angle. (Ans: 1.477, 0.26, 15o).
5. Based on the previous problem, consider the same step index fiber immersed in water of refractive index
1.33. Calculate the maximum acceptance angle.
6. The power of a 2 mW laser beam decreases to 15 W after traversing through 25 km of a single mode
optical fiber. Calculate the attenuation of the fiber. (Ans: 0.85 dB/km)
5. A 5 mW laser beam passes through a 26 km fiber of loss 0.2 dB/km. Calculate the power at the output end.
(Ans: 1.5 mW).
6. Consider a step-index fiber with n1 = 1.5, a = 40 m and = 0.015 operating at 850 nm with a spectral
width of 50 nm. (a) Is this a single mode fiber or a multimode fiber? (b) Calculate the material dispersion,
intermodal dispersion and the total pulse dispersion. [Ans. (b) 4.2 ns/km, 75 ns/km, 75.1 ns/km]. Calculate
the same parameters for the same fiber operating at 1.25 m with a source of spectral width 25 nm.
7. Consider a bare fiber with: n1 = 1.46 (pure silica), n2 = 1.0 (air) and core radius a = 30 m.
(a) Show that all rays making an angle < 46.770 with the z –axis will be guided through the fiber.
(b) Assume = 300 and calculate the number of reflections that will occur in propagating through 1 km
length of the fiber. Assume only 0.01% decrease in power at each reflection; calculate the power loss
in propagating through 1 km length of the fiber. [9.6 x 10 6,4179 dB/km]
8. Consider a bare step index fiber with n1 = 1.46, n2 = 1.0 and a = 50 m. Show that the pulse dispersion is
about 2240 ns/km.
9. Consider a step index fiber with n2 = 1.46 and = 0.0015. If the operating wavelength is 1.3 m, show that
it is single moded for a > 6.2 m.
10. Consider a step index fiber with n2 = 1.46 , = 0.0015 and a = 5 m. Show that it is single-moded for 0 >
1.04 m.
11. A step index fiber, n1 = 2, n2 = 3 is placed in air, what is the maximum angle an incident ray can make
with the axis of the fiber at the input end in air, so that it is guided after entering the fiber. [90 o]
Вам также может понравиться
- Sequence Generator FSM Design Lab ExperimentДокумент1 страницаSequence Generator FSM Design Lab ExperimentSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Sheet 7Документ2 страницыTutorial Sheet 7Swarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Lift-Off Techniques for Clean PatterningДокумент4 страницыLift-Off Techniques for Clean PatterningSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 4Документ6 страницTutorial 4Swarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- 4 Orbit SolutionДокумент15 страниц4 Orbit SolutionSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- IIT Delhi Physics Problem Sheet on Classical Mechanics & RelativityДокумент1 страницаIIT Delhi Physics Problem Sheet on Classical Mechanics & RelativitySwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент2 страницыUntitledSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 5Документ6 страницTutorial 5Swarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- AZ nLOF 2000 Series Technical DatasheetДокумент8 страницAZ nLOF 2000 Series Technical DatasheetSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- RBI PublicationДокумент134 страницыRBI PublicationAshok PariharОценок пока нет
- CML100 Ar2a PDFДокумент34 страницыCML100 Ar2a PDFDivyansh GuptaОценок пока нет
- PMT - MCP100 - Sem 2 - 2016-17Документ8 страницPMT - MCP100 - Sem 2 - 2016-17Swarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- AbcdДокумент1 страницаAbcdSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- 4 Orbit SolutionДокумент15 страниц4 Orbit SolutionSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Iisc Physics BSC SyllabusДокумент1 страницаIisc Physics BSC SyllabusSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Exp5 - Polarization of Light PDFДокумент10 страницExp5 - Polarization of Light PDFSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Physics Course OverviewДокумент6 страницPhysics Course OverviewSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Iisc Physics BSC SyllabusДокумент1 страницаIisc Physics BSC SyllabusSwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- CML 100 Lectures 8-9Документ68 страницCML 100 Lectures 8-9Swarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- Course Content For IIT DELHIДокумент2 страницыCourse Content For IIT DELHISwarnava SanyalОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Hollow Prism - Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSEДокумент12 страницHollow Prism - Physics Investigatory Project Class 12 CBSEadityabaweja82% (487)
- EMD Important Questions Unit-III Starting MethodsДокумент9 страницEMD Important Questions Unit-III Starting MethodsJoseph HarindranathОценок пока нет
- G10 Physics CompendiumДокумент41 страницаG10 Physics CompendiumAlodia Carlos PastorizoОценок пока нет
- Intro Optics - PPT V2part 05Документ45 страницIntro Optics - PPT V2part 05buffmomОценок пока нет
- Lab Report For Looking Angle and Matlab CodeДокумент8 страницLab Report For Looking Angle and Matlab Codesathi_toya0% (1)
- Raman Microscopy First Edition PDFДокумент34 страницыRaman Microscopy First Edition PDFGerald See TohОценок пока нет
- BX2M/MX51: Metallurgical MicroscopesДокумент12 страницBX2M/MX51: Metallurgical MicroscopesJackard WuОценок пока нет
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA IISc PHYSICS EXAMДокумент3 страницыKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA IISc PHYSICS EXAMJASWINDER SINGHОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Exam Physics ReviewДокумент9 страницPreliminary Exam Physics ReviewRonak JoshiОценок пока нет
- XII Comparision of Termwise and Full Syllabus 2021-22Документ9 страницXII Comparision of Termwise and Full Syllabus 2021-22Siddharth NayakОценок пока нет
- Ray Optics: Kristine Angela R. RevillaДокумент5 страницRay Optics: Kristine Angela R. RevillaEzekiel BundaОценок пока нет
- Fiber cable testing standardsДокумент3 страницыFiber cable testing standardsYousif_AbdalhalimОценок пока нет
- Measuring Negative Focal LengthsДокумент5 страницMeasuring Negative Focal Lengthswardendavid5591Оценок пока нет
- Demonstration of the First LaserДокумент10 страницDemonstration of the First LaserRanjith R MenonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 AC MachinesДокумент5 страницChapter 9 AC MachinesJACOB MUDONHIОценок пока нет
- Outdoor Workplace Lighting StandardsДокумент17 страницOutdoor Workplace Lighting StandardsRoberto MiletОценок пока нет
- Exp 3 Rahul Singh 2k20-A18-12Документ8 страницExp 3 Rahul Singh 2k20-A18-12Dummy Account-Rahul SinghОценок пока нет
- Light and Sound 1 QPДокумент13 страницLight and Sound 1 QPSumira ZamanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Astronomy LectureДокумент70 страницChapter 5 Astronomy LectureAbdallah AlyОценок пока нет
- Plasmonics Slides PDFДокумент11 страницPlasmonics Slides PDFBugmenot05Оценок пока нет
- Shivani Laser PDFДокумент23 страницыShivani Laser PDFShalini Mahajan100% (1)
- Week 3 A Chapter 10 & 11 X-Ray Production and Emission 79Документ80 страницWeek 3 A Chapter 10 & 11 X-Ray Production and Emission 79bathinsreenivasОценок пока нет
- VerTera Flyer enДокумент2 страницыVerTera Flyer enErcx Hijo de AlgoОценок пока нет
- Vaibhav Project FinalДокумент23 страницыVaibhav Project Finalaroracreation4Оценок пока нет
- BLDC Motor Review: State-of-Art Control Techniques and ApplicationsДокумент40 страницBLDC Motor Review: State-of-Art Control Techniques and Applicationsricmf89Оценок пока нет
- Total Internal Reflection, Optical Fibre, Applications of Total Internal Reflection, Physics Project Report ConvДокумент9 страницTotal Internal Reflection, Optical Fibre, Applications of Total Internal Reflection, Physics Project Report ConvAtharva MaheshwariОценок пока нет
- OC and SC Test ResultsДокумент8 страницOC and SC Test ResultsDhyanОценок пока нет
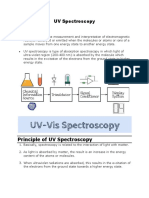
- UV SpectrosДокумент4 страницыUV SpectrosCarlton GrantОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Plane and Spherical Mirrors: Key Optics Concepts ExplainedДокумент9 страницIntroduction to Plane and Spherical Mirrors: Key Optics Concepts Explainedchinkayaby16Оценок пока нет
- A Broadband Low-Reflection Metamaterial AbsorberДокумент6 страницA Broadband Low-Reflection Metamaterial AbsorberRiston SinagaОценок пока нет