Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
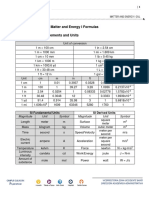
Base Quantities & Derived Quantities
Загружено:
jgd2080Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Base Quantities & Derived Quantities
Загружено:
jgd2080Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
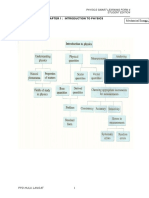
Chapter 1
Transparency
1
Introduction To Physics
Base Quantities & Derived Quantities
Base Quantities
Measuring
Instruments
Length Mass Time Temperature Electric Current
l m t T I
meter kilogram second kelvin ampere
SI Unit
m kg s K A
Derived Quantities
Quantity Relationship Derived unit
Volume Length × Breadth × Height m3
Mass
Density Volume kg m–3
Acceleration Change of velocity m s–2
Time taken
Momentum Mass × Velocity kg m s–1
SI Prefixes & Symbols
Prefix tera giga mega kilo hecto deca deci centi milli micro nano pico
Symbol T G M k h da d c m μ n p
Value 1012 109 106 103 102 101 10–1 10–2 10–3 10–6 10–9 10–12
Example 1 19.2 nanometer = 19.2 nm (Scientific notation)
= 19.2 × 10–9 m (Conversion to SI unit)
= 1.92 × 10–8 m (Standard form)
52.8
Example 2 gram = 52.8 × 105 g (Scientific notation)
10−5
= 52.8 × 105 × 10–3 kg (Conversion to SI unit)
= 5.28 × 103 kg (Standard form)
© Marshall Cavendish ( Malaysia ) Sdn. Bhd.
Вам также может понравиться
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Документ45 страницChapter 1 Physical Quantities and Measurement Lecturer Only1Jerome FizzowОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 1 - Chemical HistoryДокумент9 страницLecture Notes 1 - Chemical HistoryannmarieОценок пока нет
- Conversion of UnitsДокумент3 страницыConversion of UnitsJonn Jhasmir MirОценок пока нет
- Topic 2. Measurements and Units: Matter and Energy I FormulasДокумент5 страницTopic 2. Measurements and Units: Matter and Energy I FormulasGaelОценок пока нет
- Genchem Lesson 2Документ4 страницыGenchem Lesson 2Joeleo Aldrin SupnetОценок пока нет
- Understanding Physics: Study of All Natural PhenomenonДокумент14 страницUnderstanding Physics: Study of All Natural PhenomenonbatrisyiaОценок пока нет
- Unit I: Resultant and Equilibrium of ForcesДокумент140 страницUnit I: Resultant and Equilibrium of ForcesSai AmithОценок пока нет
- Quantities and Units: Ditta Kharisma Yolanda Putri, S.T., M.T. NIP. 199412212019032018Документ11 страницQuantities and Units: Ditta Kharisma Yolanda Putri, S.T., M.T. NIP. 199412212019032018Malik KarimОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ17 страницModule 1Kenth Godfrei DoctoleroОценок пока нет
- Here are the conversions:i) 45.7 mm = 0.0457 mii) 2130 cm2 = 0.2130 m2 iii) 150 cm3 = 0.150 m3iv) 72 km/h = 20 m/sv) 9.8 g/cm3 = 9800 kg/m3Документ16 страницHere are the conversions:i) 45.7 mm = 0.0457 mii) 2130 cm2 = 0.2130 m2 iii) 150 cm3 = 0.150 m3iv) 72 km/h = 20 m/sv) 9.8 g/cm3 = 9800 kg/m3RN Builder IpohОценок пока нет
- HBSC4103 Topic 1Документ41 страницаHBSC4103 Topic 1atun28Оценок пока нет
- INTROДокумент2 страницыINTROPrincess kc DocotОценок пока нет
- Fundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditДокумент19 страницFundamental Concept of ThermodynamicseditMohamad Radhahudin100% (1)
- General Physics 1: Units, Quantities, and MeasurementДокумент33 страницыGeneral Physics 1: Units, Quantities, and MeasurementShernanОценок пока нет
- 4.1 Intro To PhysicsДокумент6 страниц4.1 Intro To PhysicsvelavanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.0: Introduction To PhysicsДокумент13 страницChapter 1.0: Introduction To PhysicsshahidaОценок пока нет
- 03 - ICSE9th - Physics BookLet 27 May 21Документ99 страниц03 - ICSE9th - Physics BookLet 27 May 21Vivaan GandhiОценок пока нет
- Understanding Base QuantitiesДокумент18 страницUnderstanding Base QuantitiesAnnie IbrahimОценок пока нет
- SM-Intro To CE CalculationsДокумент25 страницSM-Intro To CE CalculationsAzlina LamajidОценок пока нет
- Understanding Units of Measurement in ChemistryДокумент16 страницUnderstanding Units of Measurement in ChemistryAdib azahariОценок пока нет
- Measurement SI Units GuideДокумент2 страницыMeasurement SI Units GuideDane BosevОценок пока нет
- Double Physics NOTES - Copy - Copy (4)Документ161 страницаDouble Physics NOTES - Copy - Copy (4)yaonekarenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.1-Physical Quantities (Student) PDFДокумент19 страницChapter 1.1-Physical Quantities (Student) PDFdhanisaaОценок пока нет
- Physics NotesДокумент2 страницыPhysics Notesredz45Оценок пока нет
- LAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesДокумент19 страницLAS 1 Units Physical Quantities Measurement Errors and UncertaintiesFlor de AldaОценок пока нет
- 1.1 & 1.3 Length & Time - Mass & Weight 2Документ9 страниц1.1 & 1.3 Length & Time - Mass & Weight 2Haniya NadeemОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ12 страницLecture 1alyssaОценок пока нет
- SI Units - Chemistry LibreTextsДокумент3 страницыSI Units - Chemistry LibreTextsBabalola TomisinОценок пока нет
- Session 1Документ20 страницSession 1THE SEZARОценок пока нет
- What I Need To Know: System of MeasurementДокумент9 страницWhat I Need To Know: System of Measurementzest ishuriОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Units and MeasuremntsДокумент31 страницаChapter 1 Units and MeasuremntsAiman HakimОценок пока нет
- 5054 Topic 1 - Motion, Forces and EnergyДокумент9 страниц5054 Topic 1 - Motion, Forces and EnergyNayeem HakimОценок пока нет
- AS Physics Summer ProjectДокумент22 страницыAS Physics Summer ProjectBrandon LarmondОценок пока нет
- Module Chapter 1 TeacherДокумент26 страницModule Chapter 1 TeacherhidayahnurulОценок пока нет
- Units of Measurement: LessonДокумент26 страницUnits of Measurement: Lessongavint skynardОценок пока нет
- Gen Chem ReviewerДокумент4 страницыGen Chem ReviewerAvegaile PaduaОценок пока нет
- Units of Measurement ObjectivesДокумент6 страницUnits of Measurement ObjectivesErienne IbanezОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Physics 1 PDFДокумент27 страницIntroduction To Physics 1 PDFjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- General Physics ReviewerДокумент12 страницGeneral Physics ReviewerfelixiefairyОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент33 страницыUntitledmuhammad sallehuddin ismailОценок пока нет
- 1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsДокумент49 страниц1 - Physical Quantities and MeasurementsPunitha MarimuthooОценок пока нет
- METRIC MEASUREMENT MASTERYДокумент2 страницыMETRIC MEASUREMENT MASTERYEarl CalingacionОценок пока нет
- Week 1 Phy 1 MeasurementДокумент22 страницыWeek 1 Phy 1 MeasurementAngelica Marie DiegoОценок пока нет
- UNITS AND MEASUREMENT (NOTES)Документ12 страницUNITS AND MEASUREMENT (NOTES)ruchihonaleОценок пока нет
- General ChemistryДокумент101 страницаGeneral ChemistryNohelia Fer GavОценок пока нет
- CH 1 IntroДокумент19 страницCH 1 Introalexander duncanОценок пока нет
- General-Physics-1 Q1 W1 M1 LDS Measurements ALG RTPДокумент13 страницGeneral-Physics-1 Q1 W1 M1 LDS Measurements ALG RTPKaye Cee GonzaloОценок пока нет
- Accurate PreciseДокумент27 страницAccurate PreciseAngeline Mae RomagosОценок пока нет
- Units and Conversions PDFДокумент33 страницыUnits and Conversions PDFiayamaeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement - Nov 2015.docx UpdatedДокумент26 страницChapter 1 - Physical Quantities and Measurement - Nov 2015.docx Updateddannypro13Оценок пока нет
- Senior High School Department: Physical QuantitiesДокумент6 страницSenior High School Department: Physical Quantitiessherwin dela cruzОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Notes: Physical Quantities, Units & MeasurementДокумент8 страницChapter 1 Notes: Physical Quantities, Units & MeasurementterrygohОценок пока нет
- Cainta Catholic College: Academic Year 2021 - 2022Документ3 страницыCainta Catholic College: Academic Year 2021 - 2022Angelo lacandiliОценок пока нет
- Unit 1 AДокумент18 страницUnit 1 Aapi-3699866100% (1)
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresОт EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Handbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningОт EverandHandbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- DIAGRAM SUHUДокумент9 страницDIAGRAM SUHUjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Form 4 Physics Graph Plotting TechniquesДокумент9 страницForm 4 Physics Graph Plotting Techniquesjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Rajah 8.2 Menunjukkan Satu Cawan Bertutup. Cawan Ini Tidak Sesuai Untuk Mengekalkan Suhu Bagi Minuman Panas Dalam Masa Yang LamaДокумент10 страницRajah 8.2 Menunjukkan Satu Cawan Bertutup. Cawan Ini Tidak Sesuai Untuk Mengekalkan Suhu Bagi Minuman Panas Dalam Masa Yang Lamajgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Link Kuiz 24 April 2020Документ1 страницаLink Kuiz 24 April 2020jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Exercises 1.1.1 & 1.1.2 Physical Quantities & SI UnitsДокумент1 страницаExercises 1.1.1 & 1.1.2 Physical Quantities & SI Unitsjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- JWPN Soalan F4 Fasa 4 Bil 1Документ3 страницыJWPN Soalan F4 Fasa 4 Bil 1jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.1.3. TEACHERSДокумент3 страницыChapter 1.1.3. TEACHERSjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- 1.1.4 Scalar and Vector QuantityДокумент2 страницы1.1.4 Scalar and Vector Quantityjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Respiration 1Документ3 страницыRespiration 1jgd20800% (1)
- Key inДокумент3 страницыKey injgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Soalan F4 PKP 3Документ1 страницаSoalan F4 PKP 3jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- ANSWERS - Latihan 1 RespirationДокумент1 страницаANSWERS - Latihan 1 Respirationjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Science Pt3: 3 Ibnu Batutta (Pn. Norita)Документ1 страницаScience Pt3: 3 Ibnu Batutta (Pn. Norita)jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.1.3Документ3 страницыChapter 1.1.3jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Respiration 1Документ3 страницыRespiration 1jgd20800% (1)
- Tag Tali Pinggang ExamДокумент1 страницаTag Tali Pinggang Examjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Try 1Документ1 страницаTry 1jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- En. Rasidi Bin Mohamed Zain: 3 OGOS 2018Документ1 страницаEn. Rasidi Bin Mohamed Zain: 3 OGOS 2018jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Sekolah Menengah KebangsaanДокумент2 страницыSekolah Menengah Kebangsaanjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Topic That Will Be Tested Science Form 3 (Pt3) Standardized Test 1, SEMESTER 2, 2018Документ1 страницаTopic That Will Be Tested Science Form 3 (Pt3) Standardized Test 1, SEMESTER 2, 2018jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Topic That Will Be Tested Science Form 3 (Pt3) Standardized Test 1, SEMESTER 2, 2018Документ1 страницаTopic That Will Be Tested Science Form 3 (Pt3) Standardized Test 1, SEMESTER 2, 2018jgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Table of Test SpecificationДокумент2 страницыTable of Test Specificationjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Pdfa1 3Документ1 страницаPdfa1 3aizatОценок пока нет
- Tag Tali Pinggang ExamДокумент1 страницаTag Tali Pinggang Examjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Cash ReceiptДокумент4 страницыCash Receiptjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- How to Create a Blog and Add Basic ElementsДокумент77 страницHow to Create a Blog and Add Basic Elementsjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Pdfa1 2Документ1 страницаPdfa1 2aizatОценок пока нет
- Table of Test SpecificationДокумент2 страницыTable of Test Specificationjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Form 5 Physics Standardised Test 1 TopicsДокумент1 страницаForm 5 Physics Standardised Test 1 Topicsjgd2080Оценок пока нет
- Celestial Navigation Made SimpleДокумент32 страницыCelestial Navigation Made Simplejbtam99Оценок пока нет
- Metric and Standard Units of MeasureДокумент20 страницMetric and Standard Units of Measureapi-302577842Оценок пока нет
- ED-ME111 ScalesДокумент29 страницED-ME111 Scaleskiran kumarОценок пока нет
- BetzДокумент4 страницыBetzjoaquim serroteОценок пока нет
- Tidal Predictions For Georgetown GuyanaДокумент7 страницTidal Predictions For Georgetown GuyanahutsonianpОценок пока нет
- Experiment On Bore Dial GaugeДокумент4 страницыExperiment On Bore Dial Gaugevipsdgr8100% (4)
- 49 Baklad - Tinoto - Mangrove PDFДокумент1 страница49 Baklad - Tinoto - Mangrove PDFCirilo Jr. LagnasonОценок пока нет
- Calibration of Thermocouples and Temperature InstrumentsДокумент24 страницыCalibration of Thermocouples and Temperature InstrumentsLim ChsОценок пока нет
- Venire CaliperДокумент4 страницыVenire CaliperAdnan QureshiОценок пока нет
- Moon, Planets and Polaris-08iДокумент14 страницMoon, Planets and Polaris-08iMarshn manОценок пока нет
- Automatic Electric Ltd. Instrument Division CatalogДокумент27 страницAutomatic Electric Ltd. Instrument Division CatalogpbiplОценок пока нет
- The Astrolabe in Theory and Practice: Master Richard WymarcДокумент47 страницThe Astrolabe in Theory and Practice: Master Richard Wymarcl30N4r100% (1)
- A Short Guide To Celestial Navigation - UmlandДокумент98 страницA Short Guide To Celestial Navigation - UmlandEnrico PieroniОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0021967317304909 MainДокумент5 страниц1 s2.0 S0021967317304909 MaineducobainОценок пока нет
- Measurement of Angles and DirectionsДокумент73 страницыMeasurement of Angles and DirectionsSHEAN GAYLE ANGОценок пока нет
- Accounting For Measurement Uncertainty in The SRM-3000Документ4 страницыAccounting For Measurement Uncertainty in The SRM-3000salekojic5332Оценок пока нет
- Seametrics WMX104 Flanged Electromagnetic Flowmeter ModelsДокумент81 страницаSeametrics WMX104 Flanged Electromagnetic Flowmeter ModelsPromagEnviro.comОценок пока нет
- pH Buffer Certificate Nominal Spec 7.00Документ1 страницаpH Buffer Certificate Nominal Spec 7.00Jose Manuel Mejia CañasОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Sains Dan KesehatanДокумент8 страницJurnal Sains Dan Kesehatanrevita dwiОценок пока нет
- Mordern Surveying InstrumentДокумент22 страницыMordern Surveying InstrumentAbhishek NpcОценок пока нет
- Standard Specification For Survey WorkДокумент14 страницStandard Specification For Survey WorkKS&TAN sdn bhd100% (1)
- Latitude and LongitudeДокумент13 страницLatitude and LongitudeAfza KhalidОценок пока нет
- Celso Gen Chem m1 ActivitiesДокумент7 страницCelso Gen Chem m1 ActivitiesRaine Gabrielle CelsoОценок пока нет
- Metric and Imperial Linear ConversionsДокумент4 страницыMetric and Imperial Linear ConversionsJoselyn MessinaОценок пока нет
- SI Conversions PDFДокумент1 страницаSI Conversions PDFRonОценок пока нет
- MODULE-2 - CE-214-Fundamentals-of-SurveyingДокумент5 страницMODULE-2 - CE-214-Fundamentals-of-SurveyingJake Ryan Belen BuanОценок пока нет
- E578-07 (2013) Standard Test Method For Linearity of Fluorescence Measuring SystemsДокумент3 страницыE578-07 (2013) Standard Test Method For Linearity of Fluorescence Measuring SystemsislamakthamОценок пока нет
- Wavelength Selectors For IR SpectrophotometryДокумент2 страницыWavelength Selectors For IR SpectrophotometrySean CollinsОценок пока нет
- Fabric Weight Conversion Chart: gsm to oz/yd2Документ2 страницыFabric Weight Conversion Chart: gsm to oz/yd2Anuruddha Jayasena75% (12)
- Lesson 21 Reciprocal Leveling and Trigonometric Leveling: Fundamental of Surveying Engr. Richard VillamoraДокумент18 страницLesson 21 Reciprocal Leveling and Trigonometric Leveling: Fundamental of Surveying Engr. Richard VillamoraHernan BeñabonОценок пока нет