Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 6
Загружено:
api-3044860520 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров2 страницыОригинальное название
chapter 6
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров2 страницыChapter 6
Загружено:
api-304486052Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Term Definition
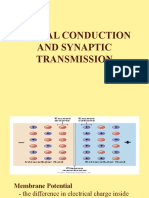
Resting potential The neuron is not conducting an impulse and inside of neuron has a negative
charge of -70mV compared to outside
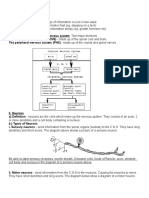
Outline the general organisation of the nervous system
- Formed of central nervous system, brain and spinal cord
- Peripheral nervous system divided into voluntary and automatic nervous system
- Autonomic nervous system consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system
- Voluntary nervous system has motor and sensory neurons
Outline functions of motor neuron
- It carries electrical signals from the brain to effectors
- It causes muscles to contract
Draw a labelled diagram of a motor neuron
Outline movement of ions across membrane of axon
- To establish resting potential, Na-K pump pumps sodium out and potassium in through active
transport which energy is supplied to the pump as ATP
- When the potassium channel opens, it allows only K+ to diffuse out of the axon through
facilitated diffusion
- When the sodium channel opens, it allows only Na+ to diffuse into the axon through facilitated
diffusion
Explain the effect of neonicotinoid pesticides in insects synapses in the
- Neonicotinoid pesticides are similar to nicotine
- Binds to acetylcholine receptors
- Binding is irreversible
- Prevents acetylcholine binding
- Blocks transmission from CNS
Explain how nerve impulses travel along a neuron
- Resting potential of -70mV
- Na/K pump maintains the resting potential
- More sodium outside than inside, more potassium inside than outside
- Nerve impulse is an action potential that stimulates a depolarisation along the axon
- If neuron is stimulated, sodium ion channel opens
- Sodium ions diffuse in
- Na+ move in causing depolarisation
- Potassium ion channel open
- Depolarising in one area triggers depolarisation in neighbouring region
Outline the factors affecting speed of an action potential
- Diameter of axon: Larger diameter
- Myelination of axon: Myelinated sheath
- Temperature: Higher temperature
- Concentration of Na+ ions: More Na+ ions
- Number of synapses involved: Lower number of neurons
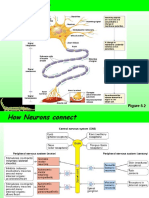
Explain how a nerve message passes from one neuron to another
- Nerve impulse reaches the end of presynaptic neuron
- Depolarisation causes calcium channels in membrane to open
- Calcium diffuses into the presynaptic neuron
- Vesicles containing neurotransmitter move to and fuse with presynaptic membrane
- Neurotransmitter released by exocytosis into synaptic cleft
- Neurotransmitter diffuses across the synapse
- Neurotransmitter attaches to receptors on postsynaptic neuron
- Receptors cause ion channels to open and sodium diffuse into the postsynaptic neuron
- The postsynaptic neuron is depolarised
- Causes a new action potential
- Neurotransmitter on postsynaptic membrane is broken down
- Neurotransmitter is reabsorbed into the presynaptic neuron
Outline the role of calcium ions in the transmission of nerve impulses
- Calcium ions diffuses into presynaptic neuron
- Causing vesicles to move to and fuse with pre synaptic membrane
- Leading to exocytosis
Вам также может понравиться
- Design Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachОт EverandDesign Development and Analysis of a Nerve Conduction Study System An Auto Controlled Biofeedback ApproachОценок пока нет
- Nervous System NotesДокумент16 страницNervous System NotesmorganicalОценок пока нет
- Nervous System NotesДокумент8 страницNervous System NotesGina ChunОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsДокумент25 страницUnit 8 Learning Guide Name: Brandon Au-Young: InstructionsBrandonОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент23 страницыNervous SystemMartyn PereiraОценок пока нет
- Topic 15 Nervous Coordination AO1 QuizДокумент8 страницTopic 15 Nervous Coordination AO1 QuizatemisgoddesofhuntОценок пока нет
- Chapter 48 ReviewДокумент5 страницChapter 48 ReviewamtholeОценок пока нет
- 5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTДокумент55 страниц5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTsohailnoreen5062Оценок пока нет
- Control and Coordination PDFДокумент14 страницControl and Coordination PDFmobasser sikderОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - CNS Structure PhysДокумент66 страницLecture 2 - CNS Structure PhysJB ReyesОценок пока нет
- Neuronal Communication 5.3Документ8 страницNeuronal Communication 5.3bexОценок пока нет
- Bio Psy NotesДокумент44 страницыBio Psy NotesKary ChengОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesДокумент21 страницаThe Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesPrabhathОценок пока нет
- TOPIC 9 NERVOUS CONTROL My Notes 1Документ11 страницTOPIC 9 NERVOUS CONTROL My Notes 1shealtielchigariso06Оценок пока нет
- Crash CourseДокумент4 страницыCrash CourseLya StiubeiОценок пока нет
- A2 Level Biology Coordination and Control - Animals - NeuronesДокумент38 страницA2 Level Biology Coordination and Control - Animals - NeuronesFatma Zorlu100% (1)
- STPM BIOLOGY Nervous SystemДокумент21 страницаSTPM BIOLOGY Nervous Systemwkwhui83% (6)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemДокумент19 страницAutonomic Nervous SystemAnuvabОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент34 страницыNervous SystemKoimahОценок пока нет
- Biological Foundations of BehaviorДокумент39 страницBiological Foundations of BehaviorMaja FranciscoОценок пока нет
- SynapsesДокумент46 страницSynapseshan abuur ahmedОценок пока нет
- The Nervous SystemДокумент6 страницThe Nervous SystemRokas Kibelis100% (1)
- CAPE Nervous Coordination NotesДокумент24 страницыCAPE Nervous Coordination NotesSharina GeraldОценок пока нет
- Nerve Physiology: Mark Jay B. Atizado Jean Kerstin S. PasardozaДокумент30 страницNerve Physiology: Mark Jay B. Atizado Jean Kerstin S. PasardozaRuby CocalОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System & Nerve ImpulsesДокумент22 страницыThe Nervous System & Nerve Impulsestas xoОценок пока нет
- Nervous System Lecture 2Документ12 страницNervous System Lecture 2Thomas Amara KamaraОценок пока нет
- 8A The Nervous System and Neurones 8A CheckpointДокумент8 страниц8A The Nervous System and Neurones 8A CheckpointsalmaОценок пока нет
- 3.8. The Nervous SystemДокумент6 страниц3.8. The Nervous SystemGentiana GashiОценок пока нет
- Neurohormonal Regulation of Body FunctionsДокумент34 страницыNeurohormonal Regulation of Body FunctionsjimmyОценок пока нет
- Nervou YtemДокумент22 страницыNervou YtemShreya AnandОценок пока нет
- NeuronДокумент4 страницыNeuronJohanne May Capitulo LopezОценок пока нет
- Neuromuscular PhysiologyДокумент44 страницыNeuromuscular PhysiologyAnkita NigamОценок пока нет
- K7. The Transmission of Nervous Impulses - Biokim.joko - Blok 1.4.nop 2015Документ95 страницK7. The Transmission of Nervous Impulses - Biokim.joko - Blok 1.4.nop 2015Radian Dipta PОценок пока нет
- 7.neural Control of Exercising MuscleДокумент42 страницы7.neural Control of Exercising MusclehazimeliasОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент13 страницNervous SystemEmman Acosta DomingcilОценок пока нет
- SynapsesДокумент6 страницSynapsesJeff ParkОценок пока нет
- RSC Nervous SystemДокумент5 страницRSC Nervous SystemDurre shahwarОценок пока нет
- 3-4. Nerve and Synaptic PhysiologyДокумент70 страниц3-4. Nerve and Synaptic Physiologycongresarad2022Оценок пока нет
- Nervous System 2016Документ31 страницаNervous System 2016api-277471896Оценок пока нет
- Synapse: I. Anatomical TypesДокумент5 страницSynapse: I. Anatomical TypesAswin AjayОценок пока нет
- Action PotentialДокумент53 страницыAction PotentialHusna Amalia100% (2)
- Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionДокумент87 страницNeural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionRose BernardoОценок пока нет
- Nerve Physiology PDFДокумент31 страницаNerve Physiology PDFJunior AbdulcaderОценок пока нет
- BBS1-FL-K5 2020 SinapsДокумент36 страницBBS1-FL-K5 2020 SinapsVania IlmiОценок пока нет
- Topic 6.5: Nervous System: NameДокумент10 страницTopic 6.5: Nervous System: NameJimena AguilarОценок пока нет
- Neural Control and Coordination-1 PDFДокумент34 страницыNeural Control and Coordination-1 PDFAОценок пока нет
- Unit 9A Improved Unit 9A Biology - Human Regulation and ReproductionДокумент10 страницUnit 9A Improved Unit 9A Biology - Human Regulation and ReproductionNellОценок пока нет
- Neuromuscular TransmissionДокумент45 страницNeuromuscular TransmissionparuОценок пока нет
- AQA A Level Biology Unit 5Документ33 страницыAQA A Level Biology Unit 5Muadh Chati100% (1)
- A&P - 3. Neurotransmission (10p)Документ10 страницA&P - 3. Neurotransmission (10p)Gabriel StratulatОценок пока нет
- Divisi Fisiologi FK Unswagati Divisi Fisiologi FK UnswagatiДокумент53 страницыDivisi Fisiologi FK Unswagati Divisi Fisiologi FK UnswagatiRizky PebryanОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System - Docx6-7Документ19 страницThe Nervous System - Docx6-7aboody62621Оценок пока нет
- Coordination, Response and Gene TechnologyДокумент13 страницCoordination, Response and Gene Technologymii chanrОценок пока нет
- 2 - Communication of A Neuron Part C & DДокумент24 страницы2 - Communication of A Neuron Part C & DRukhsarОценок пока нет
- Lesson# 10 - Synaptic TransmissionДокумент2 страницыLesson# 10 - Synaptic TransmissionSmith PennanОценок пока нет
- 5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTДокумент58 страниц5.3 Neuronal Communication POWERPOINTLisa MillardОценок пока нет
- NeuronsДокумент32 страницыNeuronsDesadaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NeuronДокумент80 страницAnatomy and Physiology of The NeuronFelix LupulescuОценок пока нет
- Nerve ImpulseДокумент26 страницNerve ImpulseAnonymous hYMWbAОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ1 страницаChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ1 страницаChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ2 страницыChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ2 страницыChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ2 страницыChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ2 страницыChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ2 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ2 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ3 страницыChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ3 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ3 страницыChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ1 страницаChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ2 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ2 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ4 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ6 страницChapter 6api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Malaysia Is A Major Producer of Ammonia Which Is Mainly Controlled by PETRONAS Chemical Group BerhadДокумент3 страницыMalaysia Is A Major Producer of Ammonia Which Is Mainly Controlled by PETRONAS Chemical Group BerhadgongweejieОценок пока нет
- Biodegradable Polymers, Current Trends of Research and Their Applications, A ReviewДокумент43 страницыBiodegradable Polymers, Current Trends of Research and Their Applications, A ReviewShiji BalesОценок пока нет
- A-Level: Chemistry 7405/2Документ30 страницA-Level: Chemistry 7405/2Rihla Media91% (11)
- Ch5. ST - Lecture4 FunctionДокумент50 страницCh5. ST - Lecture4 Functionsultan khabeebОценок пока нет
- Health Care Waste Managementan Advocacypaper For Final RevisionДокумент62 страницыHealth Care Waste Managementan Advocacypaper For Final RevisionNikki BarenaОценок пока нет
- 10 Chapter 1Документ44 страницы10 Chapter 1Abeera Hassan ChohanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7Документ56 страницChapter 7itsjc0% (1)
- Elements of Agricultural Chemistry by Anderson, ThomasДокумент196 страницElements of Agricultural Chemistry by Anderson, ThomasGutenberg.orgОценок пока нет
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesДокумент14 страницHaloalkanes and HaloarenesKalpesh BishnoiОценок пока нет
- Organic Syntheses 031814 MBPДокумент137 страницOrganic Syntheses 031814 MBPglodovichiОценок пока нет
- Lorenz2012 PDFДокумент15 страницLorenz2012 PDFCatherine Cinthya RIMAC PANEZОценок пока нет
- Medicinal Ligand Synthesis PDFДокумент71 страницаMedicinal Ligand Synthesis PDFmbugua simon ngigiОценок пока нет
- Tegomer Dispersing at Its BestДокумент32 страницыTegomer Dispersing at Its BestHiếu Mai ĐứcОценок пока нет
- Fuels and Lubricants PDFДокумент20 страницFuels and Lubricants PDFkamaldeshapriyaОценок пока нет
- Environmental PollutionДокумент22 страницыEnvironmental PollutionMahir PembeОценок пока нет
- Smart Udyojak January 2022 Digital EditionДокумент56 страницSmart Udyojak January 2022 Digital EditionGОценок пока нет
- Phosphatase, Alkaline: 1,000 U (1 U/ L) 1,000 U (20 U/ L)Документ1 страницаPhosphatase, Alkaline: 1,000 U (1 U/ L) 1,000 U (20 U/ L)hermannОценок пока нет
- Pre Ph.D. Exam 2019-20: 9009-Ruhs PHD Exam (Pharmaceutical Chemistry) Question Paper With Answer Key Common SectionДокумент20 страницPre Ph.D. Exam 2019-20: 9009-Ruhs PHD Exam (Pharmaceutical Chemistry) Question Paper With Answer Key Common SectionFarhadz Sailama BarahamaОценок пока нет
- Polyester - WikipediaДокумент9 страницPolyester - WikipediasachinОценок пока нет
- Etest ReadingДокумент68 страницEtest ReadingAnan ChongthaleongОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15Документ43 страницыChapter 15bunnyОценок пока нет
- J Parenter Enteral Nutr - 2021 - Boullata - Parenteral Nutrition Compatibility and Stability A Comprehensive ReviewДокумент27 страницJ Parenter Enteral Nutr - 2021 - Boullata - Parenteral Nutrition Compatibility and Stability A Comprehensive ReviewSamaria CruzОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Carbon DioxideДокумент25 страницManufacturing Carbon DioxideMichael Mthulisi NgwenyaОценок пока нет
- Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, HisarДокумент42 страницыGuru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, HisarSwati SharmaОценок пока нет
- Scimich WQ TestДокумент12 страницScimich WQ TestShita AlemieОценок пока нет
- Plant EcologyДокумент22 страницыPlant EcologyAtika ZulfiqarОценок пока нет
- Chem Cuprammonium RayonДокумент6 страницChem Cuprammonium RayonAnjali MenonОценок пока нет
- What Is A CellДокумент2 страницыWhat Is A CellJocelinyenОценок пока нет
- Capstone Challenge 2022/2023 Grade 10 - Semester 1 Mostafa Shawky Abdel MoezДокумент10 страницCapstone Challenge 2022/2023 Grade 10 - Semester 1 Mostafa Shawky Abdel MoezSpidy MoveОценок пока нет
- Chemistry SCIENCE Paper - 2: (Two Hours)Документ9 страницChemistry SCIENCE Paper - 2: (Two Hours)Puja AgarwalОценок пока нет