Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 2
Загружено:
api-3044860520 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
24 просмотров2 страницыОригинальное название
chapter 2
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
24 просмотров2 страницыChapter 2
Загружено:
api-304486052Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Term Definition
Degenerate More than one codon for an amino acid
Universal All living organisms have this code
Explain the replication of DNA
- Production of DNA is semi-conservative
- One old strand and one new strand
- Double helix separated by breaking H-bonds by helicase
- Leading strand acts as template
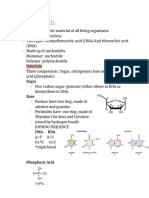
- A with T, C with G
- Nucleotides linked by DNA polymerase
- Daughter DNA molecules rewind
- Daughter stand identical to parent strand
Explain how the base sequence of DNA is conserved during replication
- DNA replication is semi-conservative
- DNA is split into two strands
- Nucleotides are assembled on template stand by complementary base pairing
- A with T and C with G
- Strands newly formed on each stand is identical to other template strand
- DNA polymerase used
- Base pairing ensures that the information encoded in one DNA molecule is passed to others
Explain the process of translation in cells
- Translation is the process to convert base sequence on mRNA into an amino acid sequence
- mRNA attaches to ribosome
- Many ribosomes bind to the same mRNA
- mRNA carries codons each coding for one amino acid
- tRNA each have specific anticodon
- tRNA carries specific amino acid
- tRNA anticodon binds to codon in the mRNA by complementary base pairing
- A second tRNA binds to next codon
- Two amino acids bind together
- first tRNA detaches
- ribosome moves along mRNA
- another tRNA binds to next codon
- continues until stop codon is reached
- stop codon has no corresponding tRNA, causes release of polypeptide
Compare DNA transcription with translation
- Both in 5’ to 3’ direction
- Both require ATP
- DNA is transcribed and mRNA is translated
- Transcription produces RNA and translation produces polypeptides
- RNA polymerase for transcription and ribosome for translation
- Transcription in the nucleus, translation in the cytoplasm
- tRNA needed for translation but not transcription
Explain the relationship between polypeptide and genes
- Genes contain information for making polypeptides
- Genes also contain information to make mRNA
- Stored as codon sequences
- Genetic information is transcribed to mRNA
- mRNA needed to carry genetic message out of nucleus
- Ribosomes are sites for polypeptide synthesis
- mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes essential for translation
- Translation links amino acids to make polypeptide
- Genes can be mutated and result in synthesis of wrong polypeptide
- Universality of genetic code means all organisms show same relationship between polypeptides
and genes
Вам также может понравиться
- AP Biology Unit 6 GuideДокумент7 страницAP Biology Unit 6 Guidelolo2212008Оценок пока нет
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiДокумент27 страницCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaОценок пока нет
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinДокумент16 страницCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinJessa Lynn E. AcalaОценок пока нет
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinДокумент16 страницCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA Proteinmungil_alifОценок пока нет
- Topic 15-18 Content AДокумент28 страницTopic 15-18 Content ALeanne Krystel CastroОценок пока нет
- Genbio Lesson 1 4Документ26 страницGenbio Lesson 1 4Greenard Imperial GualbertoОценок пока нет
- Nucleic AcidsДокумент46 страницNucleic AcidsM. MalonesОценок пока нет
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiДокумент27 страницCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyДокумент30 страницCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyAlthea Mandal100% (1)
- Central Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA ProteinДокумент20 страницCentral Dogma of Biology: DNA RNA Proteinjohn paul.jaisonОценок пока нет
- NA Structure - Central DogmaДокумент47 страницNA Structure - Central DogmaJomar IsonОценок пока нет
- Bio ReviewerДокумент11 страницBio ReviewerAbby de LeonОценок пока нет
- Protein Synthesis NotesДокумент6 страницProtein Synthesis NotesRokunuz Jahan RudroОценок пока нет
- Expression of Genetic Information (Part I)Документ8 страницExpression of Genetic Information (Part I)krittikaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisДокумент34 страницыChapter 4A: DNA Replication & Protein SynthesisPikuОценок пока нет
- Genetics 1Документ7 страницGenetics 1Kaye CampbellОценок пока нет
- Study Dna DnaДокумент45 страницStudy Dna DnaKrystel BeltranОценок пока нет
- Paper TwoДокумент21 страницаPaper TwoSafder AliОценок пока нет
- Transcription and TranslationДокумент16 страницTranscription and TranslationParth MishraОценок пока нет
- 5 11transcription-2013Документ30 страниц5 11transcription-2013jernsssОценок пока нет
- Bio ReviewerДокумент5 страницBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoОценок пока нет
- Nucleic Acids: Adopted From: Francine Williams Excelsior Community CollegeДокумент46 страницNucleic Acids: Adopted From: Francine Williams Excelsior Community CollegeGarnetОценок пока нет
- Unit C Chap 18 Cell DivisionДокумент9 страницUnit C Chap 18 Cell DivisionJane XuОценок пока нет
- BIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinДокумент47 страницBIO121 Chapter 9 From DNA To ProteinggttettanОценок пока нет
- MODULE 1 BIO1007 NotesДокумент10 страницMODULE 1 BIO1007 NotesMuskaan SharmaОценок пока нет
- Sci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationДокумент7 страницSci Q3 Protein Synthesis and MutationMel GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Dna and Rna: Molecule of HeredityДокумент74 страницыDna and Rna: Molecule of Heredityalfani wahyuОценок пока нет
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityДокумент5 страницHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- 2006 CHM6108 L9L10 SlidesДокумент40 страниц2006 CHM6108 L9L10 Slidesaidar.seralinОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of DNAДокумент29 страницStructure and Function of DNAMatthew Justin Villanueva GozoОценок пока нет
- CMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationДокумент22 страницыCMB MODULE IV SEC 3 Gene Expression RegulationTanalgo JPОценок пока нет
- Genetics Lesson 10 OnwardsДокумент18 страницGenetics Lesson 10 OnwardsMa. Joy JocosolОценок пока нет
- DNA, RNA and ProteinsДокумент47 страницDNA, RNA and ProteinsShanice RhuleОценок пока нет
- Biology Lesson 1.1Документ16 страницBiology Lesson 1.1Crystal Joy BondadОценок пока нет
- Q3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisДокумент65 страницQ3 WEEK 4 Protein SynthesisAdonis SanielОценок пока нет
- PK Bio Nucliec AcidsДокумент36 страницPK Bio Nucliec Acidsvinaya raviОценок пока нет
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticДокумент37 страницIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticClàudia VicenteОценок пока нет
- Transcription NotesДокумент16 страницTranscription NotesArathi PillaiОценок пока нет
- Transcription and TranslationДокумент42 страницыTranscription and TranslationConnor EnglandОценок пока нет
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaДокумент43 страницыTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- DNA The Genetic Material Lecture 2 1630394192851Документ21 страницаDNA The Genetic Material Lecture 2 1630394192851The RevolutionОценок пока нет
- Binder Key 2010-DnaДокумент15 страницBinder Key 2010-Dnaapi-292000448Оценок пока нет
- CAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 6 - Nucleic Acids and Protein SynthesisДокумент4 страницыCAIE Biology A-Level: Topic 6 - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesisstephen areriОценок пока нет
- RNA Transcription and TranslationДокумент11 страницRNA Transcription and TranslationMaiSakurajimaОценок пока нет
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFДокумент55 страницNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- Unit 3 - Molecular GeneticsДокумент10 страницUnit 3 - Molecular GeneticsKezia BijuОценок пока нет
- Replikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)Документ62 страницыReplikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)adinda tyasprabandariОценок пока нет
- Central Dogma: Dna ReplicationДокумент18 страницCentral Dogma: Dna ReplicationAkhil KumarОценок пока нет
- DNA Structure, Transcription, TranslationДокумент10 страницDNA Structure, Transcription, TranslationSajanMaharjanОценок пока нет
- Biochem QuinДокумент4 страницыBiochem QuinKingОценок пока нет
- DNA and RNA PracticeДокумент4 страницыDNA and RNA PracticeLaya ShrbagiОценок пока нет
- DNA Overview Central DogmaДокумент56 страницDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaОценок пока нет
- Mol Basis of InheritanceДокумент74 страницыMol Basis of InheritanceNishita BharaliОценок пока нет
- Gene ExpressionДокумент2 страницыGene Expressionvuminhtut66Оценок пока нет
- Transcription Is The Synthesis of Messenger RNA (mRNA) Using Info in DNAДокумент8 страницTranscription Is The Synthesis of Messenger RNA (mRNA) Using Info in DNASarita TelhanОценок пока нет
- Inheritance Slo # 15Документ4 страницыInheritance Slo # 15Aniqa HibbaОценок пока нет
- Module 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaДокумент52 страницыModule 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaPauline Grace CadusaleОценок пока нет
- Genetics 2Документ52 страницыGenetics 2Le Phuong LyОценок пока нет
- How Cells Work CompilationДокумент18 страницHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ1 страницаChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ2 страницыChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ1 страницаChapter 1api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ2 страницыChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ2 страницыChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ2 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ2 страницыChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ1 страницаChapter 2api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ2 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ2 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ3 страницыChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ1 страницаChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ3 страницыChapter 4api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3Документ4 страницыChapter 3api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ3 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ4 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ2 страницыChapter 5api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ2 страницыChapter 6api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ6 страницChapter 6api-304486052Оценок пока нет
- Topic: Base Pair: Hydrogen Bonding and StabilityДокумент5 страницTopic: Base Pair: Hydrogen Bonding and StabilityVINDHYA SHANKERОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Building DNAДокумент5 страницStudent Exploration: Building DNAGGОценок пока нет
- DNA ReplicationДокумент3 страницыDNA ReplicationChenra Missei YoroОценок пока нет
- List of AbbreviationsДокумент3 страницыList of Abbreviationsjuwita latiefahОценок пока нет
- Khan Et Al 2016 rbm20 Regulates Circular Rna Production From The Titin GeneДокумент8 страницKhan Et Al 2016 rbm20 Regulates Circular Rna Production From The Titin GeneAnkurОценок пока нет
- Protein Synthesis PPQ'sДокумент25 страницProtein Synthesis PPQ'sAnthony MoloneyОценок пока нет
- DNA ReplicationДокумент13 страницDNA ReplicationJoanne NgauОценок пока нет
- Daily Lesson Plan in Science 10.rnaДокумент7 страницDaily Lesson Plan in Science 10.rnaJsah Myrl HumpayОценок пока нет
- Nuceic Acid ProjectДокумент2 страницыNuceic Acid ProjectCaryl Alvarado SilangОценок пока нет
- RNA - WikipediaДокумент11 страницRNA - WikipediaAmit KaushikОценок пока нет
- Nucleic AcidsДокумент5 страницNucleic Acidsapi-308598460Оценок пока нет
- Workshop PresentationДокумент24 страницыWorkshop Presentationhuang SteffiОценок пока нет
- General Biology 2: Course Outcome 1Документ6 страницGeneral Biology 2: Course Outcome 1Erin Kyle SolivenОценок пока нет
- Nucleotide Metabolism PPДокумент65 страницNucleotide Metabolism PPCLEMENTОценок пока нет
- Molbio HandoutДокумент29 страницMolbio HandoutHazel FlorentinoОценок пока нет
- Binas 6e Druk 68BДокумент1 страницаBinas 6e Druk 68BGwen Van de WallОценок пока нет
- 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis: 1 FocusДокумент7 страниц12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis: 1 FocusMark HortizuelaОценок пока нет
- Biology Dna Worksheet Answer KeyДокумент4 страницыBiology Dna Worksheet Answer KeyElena abigail silva vallecilloОценок пока нет
- Assignment Topic: Difference Between DNA and RNA DNA RNAДокумент2 страницыAssignment Topic: Difference Between DNA and RNA DNA RNASamra ButtОценок пока нет
- Basic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureДокумент36 страницBasic Molecular Biology: Gene StructureLutfil HadiОценок пока нет
- 02 DNA Replication ReadingДокумент1 страница02 DNA Replication Readinglightning TigerОценок пока нет
- 3 Transcription-From - DNA - To - RNAДокумент7 страниц3 Transcription-From - DNA - To - RNACHIARA ANDREINA ALFARO PURISACAОценок пока нет
- Checkpoint QuestionsДокумент13 страницCheckpoint QuestionsSaheed AbdulkarimОценок пока нет
- Practice Worksheet For SBQ1-AKДокумент17 страницPractice Worksheet For SBQ1-AKShamma AhmedОценок пока нет
- DNA StructureДокумент31 страницаDNA Structuremohammed aliОценок пока нет
- Science 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyДокумент3 страницыScience 10 Summative Test 2 Quarter 3 With Answer KeyRowena Nim100% (2)
- Transcription & Translation ColoringДокумент2 страницыTranscription & Translation ColoringKristen LindstromОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry AssignmentДокумент6 страницBiochemistry AssignmentBizuayehu Ze GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Modelling DNAДокумент6 страницModelling DNADaniel BerryОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics - Notes - KeyДокумент6 страницLesson 1 - 1A - Introduction To Genetics - Notes - Key宋臻若Оценок пока нет