Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chain Is Hydrogen, Involved in The Formation of The Amide
Загружено:
Kim Ramos0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров2 страницыwe
Оригинальное название
BiochemSMPLX 16-30
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документwe
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
23 просмотров2 страницыChain Is Hydrogen, Involved in The Formation of The Amide
Загружено:
Kim Ramoswe
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
16. Which of the characteristics below apply to amino acid Glycine?
Keywords: Not in L configuration or Not Optically active, side
chain is hydrogen, involved in the formation of the amide
link in an amide linked myristoyl anchored protein
STEMS:
16.a. Of the 20 standard amino acids, only ___________ is not optically active. The reason
is that its side chain ___________.
A) alanine; is a simple methyl group
B) glycine; is a hydrogen atom
C) glycine; is unbranched
D) lysine; contains only nitrogen
16.b. All of the 20 amino acids are of L configuration, EXCEPT:
a. Tyrosine
b. Glycine
c.Valine
d.Prolene
17. What is the net charge of Histidine at pH 8, given that the -
COOH, -NH2, and the imidazole groups have pKa values of 2, 9, &
6, respectively?
18. The member of the Respiratory Chain closely associated with
an enzyme of Kreb’s Cycle:
a. Complex I
b. Complex II
c. Complex III
d. Complex IV
19. The mobile component of the ETC that mediates the electrons
between Complex II and Complex III:
a. Cytochrome c
b. FeS centers
c. Ubiquinone/ Coenzyme Q
d. FAD
20. Significance of electrons entering NAD+:
a. Gives a P:O ration of 2:1
b. 2 protons and 2 electrons are accepted
c. 3 moles of ATP are generated
d. 2 protons and an electron are accepted
21. A characteristic feature of ATP:
a. A common intermediate between energy delivering and energy requiring reactions
b. Carrier of chemical energy between high energy phosphate acceptors and low
energy phosphate donors
c. Has three phosphoanhydride bonds
d. ΔG0 -7300 Cal/mole from the bond between C5’ of ribose and alpha phosphate
1. The interactions between the active site and the substrate are
brought about by the following, EXCEPT:
2. This reaction given is catalyzed by an enzyme that belongs to
what major class:
3. When a molecule similar to the specific substrate interacts with
the active site of an enzyme, the process is called: competitive
inhibition
4. An organic cofactor loosely bound to the apoenzyme: coenzyme
5. The activity of the tandem enzyme that slows down the activity
PFK 1 of glycolysis by hydrolyzing the most important allosteric
regulator of both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis:
6. Where is the major anaplerotic reaction found and catalyzed by
what enzyme?
7. The activities of the branching enzyme of the glycogenesis:
catalyzes formation of (α1 → 6) linkages during glycogen
synthesis.
8. The specific reaction catalyzed by glycogen phosphorylase
breaking down glycogen to glucose 1-PO4:
9. The initial reaction of the major pathway for fructose
metabolism is catalyzed by:
Вам также может понравиться
- SF 25a 98 Payment BondДокумент2 страницыSF 25a 98 Payment Bond123pratus100% (3)
- Fetal Morphological and Physiological Development PDFДокумент10 страницFetal Morphological and Physiological Development PDFKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Separation of Polymers by Solvent FractionationДокумент6 страницSeparation of Polymers by Solvent FractionationSzePT100% (2)
- CH 18 Notes - Glycolysis - BiochemistryДокумент16 страницCH 18 Notes - Glycolysis - Biochemistryjuhi93100% (1)
- 7 - The Biliary TractДокумент48 страниц7 - The Biliary TractKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Debenture and BondДокумент7 страницDebenture and BondPiesie AmponsahОценок пока нет
- FRM Part I - Full Length Test 3Документ37 страницFRM Part I - Full Length Test 3pradeep johnОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding McqsДокумент6 страницChemical Bonding McqsSumera SarwarОценок пока нет
- HarpicДокумент12 страницHarpicreptilia89Оценок пока нет
- Biochemistry-Exam 2 Heinz SchwarzkopfДокумент162 страницыBiochemistry-Exam 2 Heinz SchwarzkopfthomasОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Review Questions Chapter 17 Chapter 18 and Chapter 19Документ5 страницBiochemistry Review Questions Chapter 17 Chapter 18 and Chapter 19Jan Fernan Dela VegaОценок пока нет
- Biochem HomeworkДокумент13 страницBiochem Homeworkfcukingfranztastik50% (2)
- 4 Ob ExamДокумент9 страниц4 Ob ExamKim Ramos100% (1)
- 00018Документ92 страницы00018Fernandez-De Ala NicaОценок пока нет
- Advantages of Prestressed ConcreteДокумент9 страницAdvantages of Prestressed ConcreteKuruОценок пока нет
- (Ob) - 4s-1-Antepartum Surveillance and Intrapartum MonitoringДокумент8 страниц(Ob) - 4s-1-Antepartum Surveillance and Intrapartum MonitoringKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16 Test BankДокумент7 страницChapter 16 Test BankDilla Wulan NingrumОценок пока нет
- 1 - Sampling Methods PDFДокумент35 страниц1 - Sampling Methods PDFKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Biochem Exam4practiceCHE242summer2011Документ12 страницBiochem Exam4practiceCHE242summer2011Praveen TekkaliОценок пока нет
- 'PH Bank Secrecy Laws Strictest in The World Along With LebanonДокумент12 страниц'PH Bank Secrecy Laws Strictest in The World Along With LebanonjealousmistressОценок пока нет
- (Pharm) 1s-2 Ans DrugsДокумент16 страниц(Pharm) 1s-2 Ans DrugsKim Ramos67% (3)
- 1-BIOCHEM-PRELIM-Shiftings-Carbohydrate-Chem-Enzymes-Energy-Metabolism-Porphyrins (1 DC)Документ14 страниц1-BIOCHEM-PRELIM-Shiftings-Carbohydrate-Chem-Enzymes-Energy-Metabolism-Porphyrins (1 DC)MICHAEL DELIVAОценок пока нет
- Exam4 v4 2022KEYДокумент9 страницExam4 v4 2022KEYmostafa dawoudОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Study ProblemsДокумент6 страницFinal Exam Study Problemsaboodh123Оценок пока нет
- Exercise For Signal Transduction, Blood Biochemistry and Liver Biochemistry - 0Документ8 страницExercise For Signal Transduction, Blood Biochemistry and Liver Biochemistry - 0nihadabj2003Оценок пока нет
- Molecular Cell Biology Lodish 7th Edition Test BankДокумент8 страницMolecular Cell Biology Lodish 7th Edition Test BankmarisorbornewwssОценок пока нет
- Glycolysis 1 & 2 (Complete Text With Figures) : K C Q GДокумент25 страницGlycolysis 1 & 2 (Complete Text With Figures) : K C Q GNur SyamimiОценок пока нет
- Amino Acids QuestionsДокумент5 страницAmino Acids QuestionsKrishna KumarОценок пока нет
- Soal Biokim IДокумент9 страницSoal Biokim INuraMalahayatiОценок пока нет
- Quiz-4-Storage Mechanisms and Control in Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент5 страницQuiz-4-Storage Mechanisms and Control in Carbohydrate Metabolismaichiii.bearОценок пока нет
- BCH210 Midterm Exam 2015Документ12 страницBCH210 Midterm Exam 2015Jefin Abraham Mathews100% (1)
- F97 BIOC-3560 FinalДокумент10 страницF97 BIOC-3560 FinalbobОценок пока нет
- Bio ww6Документ2 страницыBio ww6kram ichuОценок пока нет
- Examen de Bioquimica PDFДокумент11 страницExamen de Bioquimica PDFNicolás BeltránОценок пока нет
- Textbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test BankДокумент23 страницыTextbook of Biochemistry With Clinical Correlations 7th Edition Devlin Test Banklovellgwynavo100% (14)
- Enzyme TechnologyДокумент19 страницEnzyme TechnologySusmit NimjeОценок пока нет
- DP1 BioHL - Topic 8 - Revision WorksheetДокумент30 страницDP1 BioHL - Topic 8 - Revision WorksheetlesedimamareganeОценок пока нет
- Practice Questions For The MCB FinalДокумент7 страницPractice Questions For The MCB FinalDrew LorenОценок пока нет
- Reactants Products LN T R - ' G: CHM 232-Exam #4Документ6 страницReactants Products LN T R - ' G: CHM 232-Exam #4John SmithОценок пока нет
- BCH Finals 1Документ12 страницBCH Finals 1roxanne.viriОценок пока нет
- Exam Iii: Only V VДокумент8 страницExam Iii: Only V Vss shinodaОценок пока нет
- 7 Glycolysis Notes GanapathyДокумент16 страниц7 Glycolysis Notes GanapathyAli Ali AliОценок пока нет
- Biochem 3rd ExamДокумент2 страницыBiochem 3rd ExamRex Bryan RanalanОценок пока нет
- Week 2 - NotesДокумент4 страницыWeek 2 - NotesBae SeujiОценок пока нет
- Module 3 t1 2021Документ19 страницModule 3 t1 2021erОценок пока нет
- (BCH) Pokedex FQ Lipid Metabolism - DRAFTДокумент4 страницы(BCH) Pokedex FQ Lipid Metabolism - DRAFTChristiel John MagtibayОценок пока нет
- CHO Metabolism Part 3Документ34 страницыCHO Metabolism Part 3QasmОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 2016 Spring Chapter17 19Документ121 страницаBiochemistry 2016 Spring Chapter17 19krismarie94Оценок пока нет
- OopДокумент9 страницOopakhidenorshekinahОценок пока нет
- 1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - AlmendrasДокумент5 страниц1ST SA BIOCHEMISTRY - AlmendrasCherry DagohoyОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 2018 Mcqs AnswersДокумент5 страницBiochemistry 2018 Mcqs AnswerschibuyeОценок пока нет
- BCH3120 2023 Lecture 20Документ61 страницаBCH3120 2023 Lecture 20Rediet AtnafuОценок пока нет
- Bio Final: Properties of WaterДокумент11 страницBio Final: Properties of WaterebtОценок пока нет
- Biochem Questions 1Документ4 страницыBiochem Questions 1Swapna ChavanОценок пока нет
- Amino Acid SynthesisДокумент3 страницыAmino Acid SynthesismidhunОценок пока нет
- Worksheet Respiration in PlantsДокумент1 страницаWorksheet Respiration in PlantsAakif RazaОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrat McqsДокумент12 страницCarbohydrat McqsMuhammadsiddique khanОценок пока нет
- The Plasma Membrane (Structure) : RB - Soeherman H, DR.,MKДокумент61 страницаThe Plasma Membrane (Structure) : RB - Soeherman H, DR.,MKPrishneesha KalatharanОценок пока нет
- Reactivity of LigninДокумент1 страницаReactivity of Ligninpkjhan1353Оценок пока нет
- Introduction To Biochemistry Exam I: Osmosis Is Movement of AДокумент8 страницIntroduction To Biochemistry Exam I: Osmosis Is Movement of AAlex HoffmanОценок пока нет
- The Are in The For: BIOL 220 - Final (Page 1)Документ14 страницThe Are in The For: BIOL 220 - Final (Page 1)Jad AwadОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Документ6 страницBiochemistry 1st Semester BSN Mcqs For Practice AD, Educational Platform-1Prince Masroor Ali Abro100% (2)
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules AssignmentДокумент6 страницCBSE Class 12 Chemistry - Biomolecules Assignmentsyed0% (1)
- End of Semester I Combined CAT: Involvement in Examination Irregularity Shall Lead To DiscontinuationДокумент10 страницEnd of Semester I Combined CAT: Involvement in Examination Irregularity Shall Lead To DiscontinuationSwabra MbogoОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry 20 MCQs-1Документ6 страницBiochemistry 20 MCQs-1Muhammadsiddique khanОценок пока нет
- MEDE 0001 Assignment 2 Glycan Complexity-1Документ2 страницыMEDE 0001 Assignment 2 Glycan Complexity-1Jeffrey ChanОценок пока нет
- Practice Exam 3A BMB 401Документ6 страницPractice Exam 3A BMB 401rajОценок пока нет
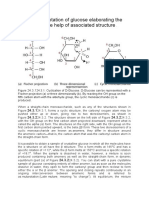
- Explain Mutarotation of Glucose Elaborating The Answer With The Help of Associated StructureДокумент14 страницExplain Mutarotation of Glucose Elaborating The Answer With The Help of Associated StructureMAJJOMAN on fireОценок пока нет
- Click For Larger Image: Introduction To GlycolysisДокумент5 страницClick For Larger Image: Introduction To GlycolysisGil JumagdaoОценок пока нет
- Biochem MidtermsДокумент7 страницBiochem MidtermsRashed Aiman Sameer Alsayyed AlalqamawiОценок пока нет
- Glycolysis and TCA CycleДокумент38 страницGlycolysis and TCA CycleAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dОценок пока нет
- Bio Cel Bank TestДокумент153 страницыBio Cel Bank TestPâmella PicançoОценок пока нет
- Glycoconjugate Research: Proceedings of the Interior Symposium on GlycoconjugatesОт EverandGlycoconjugate Research: Proceedings of the Interior Symposium on GlycoconjugatesОценок пока нет
- Sustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeОт EverandSustainable synthesis of ciclopentene derivatives through multicomponent reactions in continuous flow regimeОценок пока нет
- B. Mayosi PenicllinДокумент31 страницаB. Mayosi PenicllinKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Puerperium and AnalgesiaДокумент12 страницPuerperium and AnalgesiaKim RamosОценок пока нет
- 1 PATHO 2b - Repair - Dr. BailonДокумент9 страниц1 PATHO 2b - Repair - Dr. BailonKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Research On Problems of The Dialysis Patient: FormedДокумент2 страницыResearch On Problems of The Dialysis Patient: FormedKim RamosОценок пока нет
- InstructionsДокумент1 страницаInstructionsKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Reaction Paper On Unethical Experiments' Painful Contributions To Today's MedicineДокумент2 страницыReaction Paper On Unethical Experiments' Painful Contributions To Today's MedicineKim RamosОценок пока нет
- 3rd MNC Meeting, May 3, 2018Документ11 страниц3rd MNC Meeting, May 3, 2018Kim RamosОценок пока нет
- (Pharma-B) 6s-1-Draft - Experiment C & eДокумент3 страницы(Pharma-B) 6s-1-Draft - Experiment C & eKim RamosОценок пока нет
- 5s 4 Draft Opioid AnalgesicsДокумент4 страницы5s 4 Draft Opioid AnalgesicsKim RamosОценок пока нет
- LetterДокумент1 страницаLetterKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Quizzes: Lab. Examsd and F Cardiovascular and Git Expts. On Herbal PlantsДокумент2 страницыQuizzes: Lab. Examsd and F Cardiovascular and Git Expts. On Herbal PlantsKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Surmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Документ18 страницSurmacz Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance1Kim RamosОценок пока нет
- (Patho) 1s-3 Cell Adaptation, Injury and DeathДокумент10 страниц(Patho) 1s-3 Cell Adaptation, Injury and DeathKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Pedia G&DДокумент2 страницыPedia G&DKim RamosОценок пока нет
- A. Endothelium B. Smooth Muscle Cells C. Pericytes D. A & B E. A, B, & CДокумент1 страницаA. Endothelium B. Smooth Muscle Cells C. Pericytes D. A & B E. A, B, & CKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Centro Escolar University: School of Medicine SY 2018-2019 Urinary Tract - Glomerulus October 28, 2018Документ78 страницCentro Escolar University: School of Medicine SY 2018-2019 Urinary Tract - Glomerulus October 28, 2018Kim RamosОценок пока нет
- Physio Gastrointestinal Motility PDFДокумент11 страницPhysio Gastrointestinal Motility PDFKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Customized Geometric Risk Premium EstimatorДокумент43 страницыCustomized Geometric Risk Premium EstimatorMuhammad ShakoorОценок пока нет
- Printed Thinking Map From 5Документ16 страницPrinted Thinking Map From 5Mohd Rizal LakimОценок пока нет
- 4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and AminesДокумент30 страниц4.06 - 4.07 Aromatic Chemistry and AminesAdnan ChowdhuryОценок пока нет
- Alcohols IIДокумент38 страницAlcohols IIRafael G. Garcia SanchezОценок пока нет
- Dyeing With Direct DyesДокумент35 страницDyeing With Direct DyesAkshita BajpaiОценок пока нет
- Biochem - Lec 05Документ3 страницыBiochem - Lec 05Louis FortunatoОценок пока нет
- 2 5 Marking ScheduleДокумент6 страниц2 5 Marking Scheduleapi-218511741Оценок пока нет
- AP Syllabus Only Expanded 2011Документ11 страницAP Syllabus Only Expanded 2011pringlekОценок пока нет
- PDC-001 002 UserManual2014 Final (STD)Документ60 страницPDC-001 002 UserManual2014 Final (STD)Consuelo Rubio De RuizОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 - 542Документ26 страницChapter 6 - 542Nada KhanОценок пока нет
- Markets and Commodity Figures: Total Market Turnover StatisticsДокумент3 страницыMarkets and Commodity Figures: Total Market Turnover StatisticsTiso Blackstar GroupОценок пока нет
- Chemsheets A2 025 (Polymers)Документ3 страницыChemsheets A2 025 (Polymers)lianchen251110Оценок пока нет
- C2HДокумент16 страницC2HLaurenОценок пока нет
- SBI Mutual FundДокумент12 страницSBI Mutual FundSriram MuthuОценок пока нет
- General Chemistry Course v5 PDFДокумент448 страницGeneral Chemistry Course v5 PDFStefan AdrianОценок пока нет
- Credit Transaction Case DigestДокумент10 страницCredit Transaction Case DigestMarco ArponОценок пока нет
- Resonance Test SeriesДокумент19 страницResonance Test SeriesAman Shrivastava0% (1)
- ch5 6 7Документ1 страницаch5 6 7Jeff MartinОценок пока нет
- Litton MIlls Inc. v. Galleon Trader Inc.Документ1 страницаLitton MIlls Inc. v. Galleon Trader Inc.Ron DecinОценок пока нет
- Experiment Report 2Документ12 страницExperiment Report 2Lris Tan100% (1)
- Post Lab 3Документ2 страницыPost Lab 3dave_1128Оценок пока нет
- Icm ScienceДокумент2 страницыIcm Scienceapi-345381848Оценок пока нет