Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hot Oil System Control Philosophy
Загружено:
Riyadh SalehИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hot Oil System Control Philosophy
Загружено:
Riyadh SalehАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Process Control Philosophy of
Hot Oil System
The hot oil system is a closed circuit heating system used to deliver heat to process heat
exchangers using hot oil as a heating medium. Hot oil fired heater (H-2701) provided to heat the
hot oil, is designed for 100% heat load. Fired heater will be on line and started manually from
field.
Hot oil fired heater requires a minimum flow of hot oil through the tubes to prevent the
development of hot spots, potentially leading to tube failure, and also to avoid degradation of the
oil.
A Hot Oil Dump Cooler (A-2701) is provided for managing rapid reductions in hot oil demand.
1. Hot Oil Header Pressure Control
1.1 Hot Oil Supply Header (250 °C) Pressure Control
A pressure controller PIC-2701-10 is provided at the hot oil supply header, which would monitor
and control the overall hot oil flow through the fired heater and dump cooler. Heater is started at
minimum load of 40 % heater duty (Turndown Duty). Once heater is taken online, the pressure
controller PIC-2701-10 is switched to auto mode and it will start increasing the hot oil flow through
the heater until the required hot oil flow is met. When demand decreases, the hot oil flow to heater
is reduced first to the minimum load of 40% of the heater duty. If the header pressure is still higher
due to sustained reduction in load of consumers or due to trip of any consumer heat exchanger,
the header pressure controller opens the letdown control valve PV-2701-10 in the dump line to
maintain the pressure of hot oil supply header.
If the heater main burner trip is activated (not due to leakage in tube), then it is not recommended
to stop the hot oil flow immediately. It is recommended to keep the hot oil flow at least higher than
the minimum flow rate until the pilots are also closed or keep the hot oil circulation until the main
burners’ operation is resumed. In the case of both main burners and pilots tripped, continue the
hot oil circulation for five more minutes. Then the hot oil circulation can be stopped.
2. Temperature Control
2.1 Hot Oil Supply Header (250℃) Temperature Control
Each individual consumer heat exchanger has demand control based on a measured process
parameter, temperature. The exchanger outlet process fluid temperature controller controls the
heat input by modulating on temperature control valve at the hot oil outlet. In the event of sudden
drop in flow or trip of the specific heat exchanger the supply header pressure tends to increase
and the corrective action as described under pressure control takes place.
2.2 Hot Oil Return Header (179℃) Temperature Control
Hot Oil Supply Header pressure controller PIC-2701-10 would letdown the excess material into
Hot Oil Dump Cooler, A-2701 in the event of pressure rise due to sudden drop out of some
consumers.
With the Hot Oil Dump Cooler, A-2701 the hot oil is cooled to 179℃ in air coolers prior to send to
hot oil to return header. The temperature of the cooler outlet is controlled by means of temperature
controller (TIC-2701-06) by adjusting fan blade pitch automatically by use of pneumatic actuator
for one fan and the blade pitch control of the second fan shall be manual. Moreover, manual
louver is also provided for further control.
It is recommended that at least one fan be in operation at all times to allow for any sudden
automated demand on the cooler.
3. Heater Controller Configuration
3.1 Flow Controller
The hot oil fired heater is provided with hot oil flow controller FIC-2703-04 for which the pressure
controller PIC-2701-10 provides set point depending on the demand of hot oil to consumers.
However at all the time, hot oil flow through fired heater shall not be less than the minimum flow
recommended by fired heater vendor (82160 kg/hr which is about 107 m3/hr at inlet temperature
of 179℃).
3.2 Temperature Controller
The fired heater hot oil outlet temperature is controlled by temperature controller TIC-2701-106,
which varies the LP fuel gas flow rate to the fired heater by pressure control valve on the LP fuel
gas supply to burners. The heater temperature controller maintains the hot oil outlet temperature
at 250℃.
4. Hot Oil Filtration Stream Control
2% of the overall hot oil circulation flow is filtered to prevent accumulation of solid materials in
the hot oil system and the associated fouling problems.
This slipstream is in parallel to the bypass from the pump discharge header to the hot oil return
header (pump suction) by means of RO. The flow is measured in FI-2701-01A.
5. Hot Oil Equipments Pressure Control
Hot oil expansion vessel (V-2702), Hot oil Drain Vessels (V-2701 & V-2703), Hot Oil Main
Circulation Pumps (P-2703 A/B) form part of the hot oil circulation system. The following section
describes the various control schemes associated with these equipment.
5.1 Vessels Pressure Control
The Hot Oil Expansion Vessel is provided with dedicated pressure control system to maintain
the equipment operating pressure. Self regulated pressure control valves PCV-2702-04 & PCV-
2702-05 are provided for inbreathing / out breathing application. Fuel gas blanketing is provided
for the above equipments to prevent air ingress and consequent flammable mixture of hot oil
vapour and air. The vapour from Expansion Vessel, V-2702, which is mainly fuel gas, is vented
to ground flare.
5.2 Hot Oil Pumps Minimum Flow & Discharge Pressure Control
The Hot Oil Main Circulating Pumps are provided with common minimum flow control FIC-2703-
01, which is cascaded with PIC-2703-03 to control PV-2703-03. This valve ensures that the pump
stable minimum flow is maintained during reduced or blocked Discharge condition.
5.3 Hot Oil Drain Pump Control
Both hot oil drain vessels, V-2701 & V-2703 have been provided to collect the hot oil from the
system in utility area and process area respectively. Both vessels are fitted with pumps, P-2701
& P-2702 respectively.
Вам также может понравиться
- PSV For Distillation GuidelinesДокумент3 страницыPSV For Distillation GuidelinesMubarik AliОценок пока нет
- Depropanizer Startup ProcedureДокумент3 страницыDepropanizer Startup Procedurejayprakash100% (1)
- Kg-Tower ManualДокумент5 страницKg-Tower ManualJohnny50% (2)
- Hot Oil System Design Consideration-LibreДокумент28 страницHot Oil System Design Consideration-LibreAdel Chelba100% (2)
- Wall Metal Temperature During Emergency DepressurizationДокумент7 страницWall Metal Temperature During Emergency Depressurizationmihaileditoiu2010Оценок пока нет
- Jump Start Relief Sizing in Aspen HYSYS and Aspen Plus Temp PDFДокумент35 страницJump Start Relief Sizing in Aspen HYSYS and Aspen Plus Temp PDFMreza JafariОценок пока нет
- Controlled and Non-Controlled Type DepressuringДокумент12 страницControlled and Non-Controlled Type Depressuringgrimdorlf100% (1)
- Amine Processing Unit DEAДокумент9 страницAmine Processing Unit DEAFlorin Daniel AnghelОценок пока нет
- OPERATING MANUALS - Kerosene Hydrotreater Rev 01 - 3Документ13 страницOPERATING MANUALS - Kerosene Hydrotreater Rev 01 - 3MohamadMostafavi100% (1)
- راﺰﻓا مﺮﻧ Flarenet Flarenet: ﯽﺷزﻮﻣآ هرود training courseДокумент26 страницراﺰﻓا مﺮﻧ Flarenet Flarenet: ﯽﺷزﻮﻣآ هرود training courseshin_malaq100% (1)
- Unit 3 Steam GenerationДокумент30 страницUnit 3 Steam GenerationkhalimnОценок пока нет
- De Ethanizer ColumnДокумент24 страницыDe Ethanizer Columnrohit agrawalОценок пока нет
- CET 1112 012 Dynamic Simulation Sweetening Process Natural GasДокумент6 страницCET 1112 012 Dynamic Simulation Sweetening Process Natural GasRebwar Nori JanОценок пока нет
- API - STD - 521 Fire Gas ExpansionДокумент3 страницыAPI - STD - 521 Fire Gas Expansioneliealtawil100% (1)
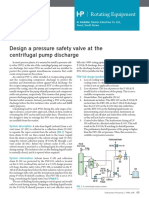
- Design A Pressure Safety Valve at The Centrifugal Pump DischargeДокумент2 страницыDesign A Pressure Safety Valve at The Centrifugal Pump Dischargeroberdani12Оценок пока нет
- Forced Draft Fan Sizing For Fired HeatersДокумент5 страницForced Draft Fan Sizing For Fired Heatersdlalameen4471Оценок пока нет
- Hysys CompressДокумент4 страницыHysys CompressVidyasenОценок пока нет
- Calculate The Wetted Surface Area of Pressure VesselsДокумент7 страницCalculate The Wetted Surface Area of Pressure VesselsHsein WangОценок пока нет
- Supercritical Fluids PSV SizingДокумент5 страницSupercritical Fluids PSV SizingVikram Singh100% (5)
- JEWEL T Hydrocarbon Dew Point ControlДокумент2 страницыJEWEL T Hydrocarbon Dew Point ControljojeecaresОценок пока нет
- UniSim Design TutorialДокумент92 страницыUniSim Design Tutorialsolo660% (1)
- SRU Start-Up Considerations - Shrikant Koli - Black & Veatch PDFДокумент26 страницSRU Start-Up Considerations - Shrikant Koli - Black & Veatch PDFJunghietu DorinОценок пока нет
- Depressuring in Aspen Hysys®: Revised: Nov 27, 2012Документ6 страницDepressuring in Aspen Hysys®: Revised: Nov 27, 2012udokasОценок пока нет
- Fractionation Tower Controls-Part 1Документ38 страницFractionation Tower Controls-Part 1Rebekah Schmidt100% (1)
- Process Safety Analysis - Aspen HysysДокумент51 страницаProcess Safety Analysis - Aspen HysysNadia BahloulОценок пока нет
- Design of Hot Oil SystemДокумент25 страницDesign of Hot Oil SystemVinicius NoronhaОценок пока нет
- Aspen FLARENET Getting Started PDFДокумент62 страницыAspen FLARENET Getting Started PDFPankaj AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Control of Vapor Recovery Units (VRU)Документ8 страницControl of Vapor Recovery Units (VRU)Yasmine ياسمينОценок пока нет
- IPS G ME 200 Fired HeaterДокумент26 страницIPS G ME 200 Fired Heateralizadeh2222100% (1)
- Depressuring - A Practical GuideДокумент30 страницDepressuring - A Practical GuideCastorlexОценок пока нет
- 02 PropaneRefrigerationLoopДокумент26 страниц02 PropaneRefrigerationLoopChristian ChineduОценок пока нет
- Depressuirng Calculation ResultsДокумент6 страницDepressuirng Calculation ResultsIoana PopescuОценок пока нет
- Proii WorkbookДокумент218 страницProii WorkbookJose Marin100% (3)
- PROII 8.1 Getting Started GuideДокумент139 страницPROII 8.1 Getting Started Guidekingcobra008100% (2)
- Setting MDMT Based On Hysys Depressuring ResultsДокумент3 страницыSetting MDMT Based On Hysys Depressuring Resultszubair195Оценок пока нет
- A Technical Report On Design of Hot Oil SystemДокумент25 страницA Technical Report On Design of Hot Oil SystemEvert AlexОценок пока нет
- WP UniSim Design Blowdown Utility PDFДокумент21 страницаWP UniSim Design Blowdown Utility PDFMinh Hoàng NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Flaresim Getting StartedДокумент116 страницFlaresim Getting Startedfiqry DarwansyahОценок пока нет
- Unisim Tutorial - Methanol ProductionДокумент77 страницUnisim Tutorial - Methanol ProductionR-wah LarounetteОценок пока нет
- Flare System Design TipsДокумент5 страницFlare System Design TipsbalajikrishnanОценок пока нет
- Doc. No.: PDG-MUM-XXX Rev. 0 Relief Valve Sizing Philosophy Page 1 of 10Документ10 страницDoc. No.: PDG-MUM-XXX Rev. 0 Relief Valve Sizing Philosophy Page 1 of 10kishna009Оценок пока нет
- HP Fuel Gas SystemДокумент8 страницHP Fuel Gas SystemAnonymous QSfDsVxjZОценок пока нет
- Relief and Blowdown System FlaringДокумент5 страницRelief and Blowdown System FlaringRicardo NapitupuluОценок пока нет
- Optimizing Pressure Relief SystemsДокумент6 страницOptimizing Pressure Relief SystemssgrsthОценок пока нет
- Intrument Air ConsumptionДокумент4 страницыIntrument Air ConsumptionyogacruiseОценок пока нет
- Fire Relief Rate Calculation-Part 2Документ4 страницыFire Relief Rate Calculation-Part 2zubair195Оценок пока нет
- Coolingwater 140301175552 Phpapp01Документ9 страницCoolingwater 140301175552 Phpapp01Vasanth Rajan100% (1)
- Ms9001E Lube Oil System: GeneralДокумент6 страницMs9001E Lube Oil System: Generalferas_elnggarОценок пока нет
- Me SystemsДокумент29 страницMe Systemskarthick_mariner92Оценок пока нет
- Design Consideration of Hot Oil SystemДокумент24 страницыDesign Consideration of Hot Oil SystemOmar EzzatОценок пока нет
- Control Philosophy - UpdatedДокумент13 страницControl Philosophy - UpdatedAlvin SmithОценок пока нет
- Complex InstДокумент13 страницComplex InstJHANSIОценок пока нет
- Systems Description Lubricating Oil System For LM2000Документ3 страницыSystems Description Lubricating Oil System For LM2000KALPUSHОценок пока нет
- 43-4002 - Fuel Oil SupplyДокумент4 страницы43-4002 - Fuel Oil Supplydebu1985Оценок пока нет
- Gas Turbine CourseДокумент54 страницыGas Turbine CourseMgn San100% (1)
- Oil Burner ManualДокумент42 страницыOil Burner Manualguru22100% (1)
- Governing SystemlankoДокумент14 страницGoverning SystemlankoSam100% (2)
- Steam Turbine Maintenance Manual-1Документ244 страницыSteam Turbine Maintenance Manual-1Trie Wahyudi100% (4)
- Lubrication System PDFДокумент10 страницLubrication System PDFHussam Baiee100% (1)
- Turbine Start-Up SOPДокумент17 страницTurbine Start-Up SOPCo-gen ManagerОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics and Energy: Conservation of Energy Principle. It Simply States That DuringДокумент24 страницыThermodynamics and Energy: Conservation of Energy Principle. It Simply States That DuringRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Emergency Response LogДокумент1 страницаEmergency Response LogRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Electrical Training CourseДокумент89 страницElectrical Training CourseRiyadh Saleh100% (1)
- CH 11 Maintenance and RepairДокумент18 страницCH 11 Maintenance and RepairRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Fire Emergency Response in CampДокумент2 страницыFire Emergency Response in CampRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Identification Location: MB Rig-: Inspection of Load Binder Attachment: 2Документ1 страницаIdentification Location: MB Rig-: Inspection of Load Binder Attachment: 2Riyadh Saleh100% (1)
- Load Securing ProcedureДокумент2 страницыLoad Securing ProcedureRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- JHA Vessel EntryДокумент2 страницыJHA Vessel EntryRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- HSE's Procedure: Issued On Revision Date Revision NДокумент3 страницыHSE's Procedure: Issued On Revision Date Revision NRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Insp Load Securing DevicesДокумент5 страницInsp Load Securing DevicesRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Deficiencies: Inspection of Chain Attachment: 1Документ1 страницаDeficiencies: Inspection of Chain Attachment: 1Riyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Closing-In Procedure For Wells: "Hard Shut-In" (Ram Preventer)Документ1 страницаClosing-In Procedure For Wells: "Hard Shut-In" (Ram Preventer)Riyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Cover ProceduresДокумент1 страницаCover ProceduresRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Reactive Chemicals: - at My My ParentsДокумент26 страницReactive Chemicals: - at My My ParentsRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- GOOD... Morning: Welcome TO Isba ChronologyДокумент28 страницGOOD... Morning: Welcome TO Isba ChronologyRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- OSHA's Respiratory Protection Standard 29 CFR 1910.134Документ62 страницыOSHA's Respiratory Protection Standard 29 CFR 1910.134Riyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Electric Safety AwarenessДокумент24 страницыElectric Safety AwarenessRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- QRA Principles Light ColoursДокумент36 страницQRA Principles Light ColoursRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Gtep Iv C04Документ14 страницGtep Iv C04Riyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- New Risk Assessment MatrixДокумент1 страницаNew Risk Assessment MatrixRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Module-18-Design Safety Practices (Petrofac)Документ55 страницModule-18-Design Safety Practices (Petrofac)Riyadh Saleh100% (1)
- Module-18-Design Safety Practices (Petrofac)Документ55 страницModule-18-Design Safety Practices (Petrofac)Riyadh Saleh100% (1)
- Well Services FamiliarisationДокумент59 страницWell Services FamiliarisationRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Mess Check ListДокумент4 страницыMess Check ListRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- HAZOPДокумент35 страницHAZOPRiyadh Saleh100% (1)
- H2S Facts and AwarenessДокумент12 страницH2S Facts and AwarenessRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- RefrigerationДокумент106 страницRefrigerationRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Work PermitДокумент41 страницаWork PermitRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Prepared By: Mueen Hniedy Saleh Abu Assaf Youssef Chalabi Bashar IbrahimДокумент18 страницPrepared By: Mueen Hniedy Saleh Abu Assaf Youssef Chalabi Bashar IbrahimRiyadh SalehОценок пока нет
- Used Oil AnalysisДокумент44 страницыUsed Oil AnalysisRiyadh Saleh100% (1)
- Aermec FCX Technical Manual EngДокумент72 страницыAermec FCX Technical Manual Engzlobcek0% (1)
- Culvert and Septic TankДокумент14 страницCulvert and Septic TankFunny VinesОценок пока нет
- Car LiftДокумент4 страницыCar LiftIrshad KhanОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationДокумент9 страницNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationRAMA MОценок пока нет
- Business Category List PDFДокумент3 страницыBusiness Category List PDFremyboyОценок пока нет
- Qa-Lhb-Lifting-Roller Bearing and Wheel AssemblyДокумент7 страницQa-Lhb-Lifting-Roller Bearing and Wheel AssemblySriram SubramanianОценок пока нет
- 1997jan Util and StruclДокумент4 страницы1997jan Util and Struclcin26Оценок пока нет
- API 650-Impact TestДокумент4 страницыAPI 650-Impact TestBashu PoudelОценок пока нет
- Taliesin West: Assignment 3: Case StudyДокумент17 страницTaliesin West: Assignment 3: Case StudyGeroke SzekeresОценок пока нет
- Concrete Bleeding Good or Bad - tcm45-348530Документ2 страницыConcrete Bleeding Good or Bad - tcm45-348530Chris YangОценок пока нет
- Indian Standard - Septic TanksДокумент19 страницIndian Standard - Septic TankskibzeamОценок пока нет
- Safety Procedures in ConstructionДокумент21 страницаSafety Procedures in ConstructionMalith De Silva100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between Lateral Tee and True WyeДокумент11 страницWhat Is The Difference Between Lateral Tee and True WyeYaneYangОценок пока нет
- TR 43 Post-Tensioned Concrete Floors-Design HandbookДокумент178 страницTR 43 Post-Tensioned Concrete Floors-Design HandbookJaffar Isam Al-Aloosi100% (9)
- Bamboo As A Construction Material Ijariie3659Документ7 страницBamboo As A Construction Material Ijariie3659IT'S MY DREAMОценок пока нет
- Espresso Coffee Machine PDFДокумент104 страницыEspresso Coffee Machine PDFStrugaru GheorgheОценок пока нет
- CSI Codes - Alphabetical 2004Документ10 страницCSI Codes - Alphabetical 2004ritchie_mayoОценок пока нет
- Amanora Township Case StudyДокумент11 страницAmanora Township Case StudyPrasoon G Das82% (11)
- 160.84-AD1-Application Data-YMC2 Refrigerant Relief Valve Vent SizingДокумент6 страниц160.84-AD1-Application Data-YMC2 Refrigerant Relief Valve Vent SizingCarl CrowОценок пока нет
- Effect of Using Saturated Lime Water in The Production of Concrete Using Pozzolanic Cement Cem II B-PДокумент18 страницEffect of Using Saturated Lime Water in The Production of Concrete Using Pozzolanic Cement Cem II B-PKellymax olakitarОценок пока нет
- Annexure 1 - Sample Soil Investigation Reort PDFДокумент121 страницаAnnexure 1 - Sample Soil Investigation Reort PDFHarshrajsinh VaghelaОценок пока нет
- Ductile Iron Pipe Iso en Standards 5c348f95Документ24 страницыDuctile Iron Pipe Iso en Standards 5c348f95elmfp7774676Оценок пока нет
- 20 TMSS 02 R1Документ26 страниц20 TMSS 02 R1Anonymous NrBbhHuZyiОценок пока нет
- HH 102Документ100 страницHH 102ROBERSON ROMERÒ100% (6)
- Unique & Latest Civil Engineering Project, Seminar, Thesis & Presentation Topics - CivilDigital PDFДокумент6 страницUnique & Latest Civil Engineering Project, Seminar, Thesis & Presentation Topics - CivilDigital PDFAlfredo L. PenachosОценок пока нет
- GF Flange PPДокумент8 страницGF Flange PPRosi Nuraeni YusfiОценок пока нет
- Chart of Plastic MaterialsДокумент4 страницыChart of Plastic MaterialsvyakshiОценок пока нет
- Bermad Strainer Model BC-70F-P: Buildings & ConstructionДокумент2 страницыBermad Strainer Model BC-70F-P: Buildings & ConstructionGuillermo GuzmánОценок пока нет
- AbutmentДокумент42 страницыAbutmentinfra120Оценок пока нет
- Construction Document Sheet Numbers and Sheet OrderДокумент5 страницConstruction Document Sheet Numbers and Sheet Orderkajale_shrikant2325Оценок пока нет