Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CH 8 Test Bank
Загружено:
Vanessa JamesОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CH 8 Test Bank
Загружено:
Vanessa JamesАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CHAPTER 8—HALOALKANES, HALOGENATION, AND RADICAL REACTIONS
MULTIPLE CHOICE
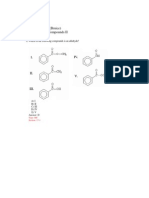
1. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
a. (R)-1-chloro-3-methyl-2-cyclohexene
b. (S)-1-chloro-3-methyl-2-cyclohexene
c. (R)-3-chloro-1-methylcyclohexene
d. (S)-3-chloro-1-methylcyclohexene
ANS: C
2. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
a. (R)-2-bromo-2-vinylpentane
b. (S)-2-bromo-2-vinylpentane
c. (S)-3-bromo-3-propyl-1-butene
d. (R)-3-bromo-3-methyl-1-hexene
ANS: D
3. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound?
a. (E)-1-chloro-1,2,3-trimethyl-1-butene
b. (Z)-1-chloro-1,2,3-trimethyl-1-butene
c. (E)-2-chloro-3,4-dimethyl-2-pentene
d. (Z)-2-chloro-3,4-dimethyl-2-pentene
ANS: D
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 1
4. What is the correct assignment of the names of the following compounds?
1. CH3Cl
2. CH2Cl2
3. CHCl3
a. 1 = methyl chloride; 2 = chloroform; 3 = methylene chloride
b. 1 = trichlor; 2 = chloroform; 3 = methylene chloride
c. 1 = methyl chloride; 2 = methylene chloride; 3 = chloroform
d. 1 = chloroform; 2 = methylene chloride; 3 = trichlor
ANS: C
5. Which of the following has the list of compounds in the correct order of decreasing boiling point
(higher boiling point > lower boiling point)?
a. chloromethane > chloroethane > 2-chloropropane > 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
b. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane > 2-chloropropane > chloroethane > chloromethane
c. chloroethane > chloromethane > 2-chloro-2-methylpropane > 2-chloropropane
d. chloromethane > 2-chloro-2-methylpropane > 2-chloropropane > chloroethane
ANS: B
6. Which of the following has the list of compounds in the correct order of decreasing boiling point
(higher boiling point > lower boiling point)?
a. 2-fluoropropane > 2-chloropropane > 2-bromopropane > 2-iodopropane
b. 2-chloropropane > 2-iodopropane > 2-fluoropropane > 2-bromopropane
c. 2-iodopropane > 2-chloropropane > 2-fluoropropane > 2-bromopropane
d. 2-iodopropane > 2-bromopropane > 2-chloropropane > 2-fluoropropane
ANS: D
7. Which of the following has the list of compounds in the correct order of decreasing density (higher
density > lower density)?
a. CH2Cl2 > CH2Br2 > CH2I2
b. CH2Cl2 > CH2I2 > CH2Br2
c. CH2I2 > CH2Br2 > CH2Cl2
d. CH2I2 > CH2Cl2 > CH2Br2
ANS: C
8. Which of the following has the list of compounds in the correct order of decreasing polarity (more
polar > less polar)?
a. CCl4 > CHCl3 > CH2Cl2
b. CH2Cl2 > CHCl3 > CCl4
c. CCl4 > CH2Cl2 > CHCl3
d. CHCl3 > CCl4 > CH2Cl2
ANS: B
9. Which of the following has the list of compounds in the correct order of decreasing molecular polar
(more polar > less polar)?
a. CH3I > CH3Br > CH3Cl > CH3F
b. CH3F > CH3Cl > CH3Br > CH3I
c. CH3Cl > CH3F > CH3Br > CH3I
d. CH3Cl > CH3I > CH3F > CH3Cl
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 2
ANS: C
10. Which of the following bonds has the lowest bond dissociation enthalpy?
a. CH
b. CF
c. CBr
d. CI
ANS: D
11. Which of the following statements is not true?
a. homolytic cleavage of a bond in a neutral molecule gives two radicals
b. radicals have one or more unpaired electrons
c. movement of single electrons is depicted using a "fishhook arrow"
d. the CF bond is the weakest bond between carbon atom and a halogen
ANS: D
12. Which halogen is most useful in the regioselective radical halogenation of alkenes??
a. fluorine
b. chlorine
c. bromine
d. iodine
ANS: C
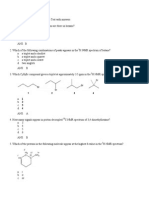
13. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: B
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 3
14. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: B
15. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: A
16. What are the major organic products obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1 and 2
b. 3 and 4
c. 1 and 3
d. 2 and 4
ANS: C
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 4
17. What is the correct order of stability of the following radicals (more stable > less stable)?
a. 1>2>3
b. 1>3>2
c. 3>1>2
d. 3>2>1
ANS: D
18. What is the correct order of stability of the following radicals (more stable > less stable)?
a. 1>2>3
b. 2>1>3
c. 2>3>1
d. 3>2>1
ANS: C
19. What is the characteristic of a radical chain initiation step?
a. radicals are formed
b. substitution products are formed
c. a radical reacts with a molecule to give a new radical and a new molecule
d. two radicals combine to give a molecule
ANS: A
20. What is the characteristic of a radical chain propagation step?
a. radicals are formed
b. byproducts are formed
c. a radical reacts with a molecule to give a new radical and a new molecule
d. two radicals combine to give a molecule
ANS: C
21. What is the characteristic of a radical chain termination step?
a. radicals are formed
b. substitution products are formed
c. a radical reacts with a molecule to give a new radical and a new molecule
d. two radicals combine to give a molecule
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 5
ANS: D
22. What type of reactive intermediate is formed in the reaction of propene with N-bromosuccinimide to
give 3-bromo-1-propene?
a. allylic carbocation
b. allylic carbanion
c. allylic radical
d. cyclic bromonium ion
ANS: C
23. What type of reactive intermediate is formed upon irradiation of a solution of toluene (Ph-CH3) and
bromine?
a. benzylic carbocation
b. benzylic carbanion
c. benzylic radical
d. cyclic bromonium ion
ANS: C
24. Which of the following alkanes does not undergo monobromination to form a single bromoalkane as
the major product?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: D
25. Which of the following alkenes undergoes allylic bromination to form a single monobrominated
product?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: A
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 6
26. What is the major product formed upon radical bromination of (S) 3-methylhexane?
a. (S) 3-bromo-3-methylhexane
b. (R) 3-bromo-3-methylhexane
c. a mixture of (R) and (S) 3-bromo-3-methylhexane
d. (3R) 1-bromo-3-methylhexane
ANS: C
27. What is the geometry of the central carbon atom of a tert-butyl radical?
a. tetrahedral
b. trigonal planar
c. trigonal pyramidal
d. square planar
ANS: B
28. Which of the following statements is not true about the allyl radical
a. the carbon-carbon bond lengths are identical
b. the unpaired electron density is shared between carbons 1 and 2.
c. it undergoes reaction with bromine to give a single product
d. it is formed by abstraction of a hydrogen atom from the methyl group of propene
ANS: B
29. How many electrons does the allyl radical have in p orbitals
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: C
30. How many -bonding, non-bonding, and antibonding orbitals does the allyl radical possess?
a. one bonding, one nonbonding, and one antibonding
b. two bonding, no nonbonding, and no antibonding
c. two bonding, one nonbonding, and no antibonding
d. three bonding, no nonbonding, and no antibonding
ANS: A
31. What type of orbitals overlap to provide stability to the tert-butyl radical by hyperconjugation?
a. 3 C 2p atomic orbital + 3 C sp2 atomic orbital
b. 3 C 2p atomic orbital + methyl CH molecular orbital
c. 3 C sp2 atomic orbital + methyl CH molecular orbital
d. 3 C 2p atomic orbital + methyl C 2s atomic orbital
ANS: B
32. What type of orbital contains the unpaired electron of the tert-butyl radical?
a. s
b. p
c. sp3
d.
ANS: B
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 7
33. Which of the following is an accurate statement of Hammond's postulate?
a. the transition state of an exothermic reaction will resemble the starting materials
(reactants) more than the product
b. the transition state of an exothermic reaction will resemble the products more than the
starting materials (reactants)
c. the transition state of an endothermic reaction will resemble the starting materials
(reactants) more than the product
d. the difference in energy between the starting materials (reactants) and transition state
controls the rate of a reaction
ANS: A
34. Which of the following statements is not true regarding the halogenation of alkanes upon treatment
with halogen and light?
a. bromination is more selective for 3 positions than chlorination
b. the reaction proceeds via a radical intermediate
c. the reaction proceeds via a chain reaction
d. this is a useful process for the formation of fluorides, chlorides, bromides and iodides
ANS: D
35. What type of reactive intermediate is formed in the reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide in the
presence of peroxides to give 1-bromopropane?
a. 1 radical
b. 1 carbocation
c. 1 radical
d. 2 radical
ANS: D
36. What is the major product obtained from the reaction of 2-methyl-2-butene with hydrogen bromide in
the presence of peroxides?
a. 2,3-dibromo-2-methylbutane
b. 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
c. 2-bromo-2-methylbutane
d. (E)-1-bromo-2-methyl-2-butene
ANS: B
37. Which of the following statements is not true?
a. Bromine radicals add to the least substituted end of a carbon-carbon double bond of an
alkene.
b. The major anti-Markovnikov product obtained upon addition of HBr to alkenes in the
presence of a peroxide is formed in a radical termination step.
c. Two radicals combine in radical termination steps.
d. Alkoxy radicals remove a hydrogen atom from HBr to give an alcohol and a bromine
atom.
ANS: B
38. Which of the following compounds is most susceptible to autooxidation?
a. propene
b. 1,3-butadiene
c. 1,4-pentadiene
d. 1,5-hexadiene
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 8
ANS: C
39. What is the reactive intermediate in the autooxidation of cyclohexene?
a. an allylic radical
b. a 2 carbocation
c. a carbocation
d. a diene
ANS: A
40. What is the major product of autooxidation of cyclohexene?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: C
41. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: C
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 9
42. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: C
43. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
ANS: A
44. What are the major products formed upon treatment of (E) 3-methyl-2-hexene with HBr in the
presence of peroxides?
1. (S,S) 2-bromo-3-methylhexane
2. (S,R) 2-bromo-2-methylhexane
3. (R,S) 2-bromo-2-methylhexane
4. (R,R) 2-bromo-2-methylhexane
a. only 1 and 2
b. only 1 and 4
c. only 2 and 3
d. a mixture of 1, 2, 3, and 4
ANS: D
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 10
45. What are the major products formed upon treatment of (E) 3-methyl-2-hexene with HBr in the absence
of peroxides?
1. (S) 3-bromo-3-methylhexane
2. (R) 3-bromo-2-methylhexane
3. 2-bromo-3-methylhexane
a. only 1
b. only 2
c. a mixture of 1 and 2
d. only 3
ANS: D
46. Which of the following accounts for the anti-Markovnikov regiochemistry of the reaction of an alkene
with HBr in the presence of peroxides?
a. the alkene reacts with HBr to give a carbocation
b. the alkene reacts with a bromine atom to give a radical
c. the alkene reacts with a hydrogen atom to give a radical
d. the alkene reacts with peroxide to five an allylic radical
ANS: B
PROBLEM
1. Provide the IUPAC name of the following compound.
ANS:
(S)-4-bromo-2-methylhexane
2. Provide the IUPAC name of the following compound.
ANS:
(S)-2-chloro-4-methylpentane
3. Provide the IUPAC name of the following compound (shown as a Fischer projection).
ANS:
(S)-2-fluorobutane
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 11
4. Provide the IUPAC name of the following compound (shown as a Fischer projection).
ANS:
(S)-2-iodopentane
5. What is the structure of all of the monobrominated products, including regioismers and stereoisomers,
obtained from the following reaction?
ANS:
6. What is the structure of all of the monobrominated products, including regioismers and stereoisomers,
obtained from the following reaction?
ANS:
7. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
ANS:
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 12
8. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
ANS:
9. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
ANS:
10. What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
ANS:
11. Provide neatly drawn resonance structures of the key intermediate in the following reaction.
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 13
ANS:
12. What is the structure of the key intermediate in the following reaction?
ANS:
Brown Organic Chemistry 6e Test Bank 14
Вам также может понравиться
- Kia Picanto II Gen. (TA) EWD - Engine Control System (General Head Lamp Type)Документ9 страницKia Picanto II Gen. (TA) EWD - Engine Control System (General Head Lamp Type)mutaz ahmed100% (4)
- ACS Review 9 AlkynesДокумент9 страницACS Review 9 AlkynesMohamad HabbabaОценок пока нет
- Rover V8 Fuel Injection SystemsДокумент16 страницRover V8 Fuel Injection SystemsClint Cooper100% (1)
- Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Crossed Aldol Reaction Product Prediction DocumentДокумент27 страницConcise SEO-Optimized Title for Crossed Aldol Reaction Product Prediction DocumentJosh Wishman50% (2)
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesДокумент10 страницAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesPanda Boy100% (2)
- Controls InstrumentationДокумент245 страницControls InstrumentationFreddy Yánez100% (1)
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsОт EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsОценок пока нет
- VFDДокумент23 страницыVFDibnrafeeqОценок пока нет
- ch13 ProblemsДокумент84 страницыch13 Problemsbrownhazel67% (6)
- Sample PapersДокумент65 страницSample PapersKatara BittuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11: Radical Reactions: Multiple ChoiceДокумент24 страницыChapter 11: Radical Reactions: Multiple Choicelp_blackout50% (2)
- Chapter 7Документ71 страницаChapter 7cjn999980% (10)
- Chapter 08 MergedДокумент38 страницChapter 08 MergedreemОценок пока нет
- MERCEDES MEDIC ACROYNMS GUIDEДокумент6 страницMERCEDES MEDIC ACROYNMS GUIDEDProkhorov100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundsДокумент34 страницыOrganic Chemistry Carbonyl CompoundsLovely Joysweet100% (2)
- FEED Deliverables ListДокумент3 страницыFEED Deliverables ListS.KAMBANОценок пока нет
- Chapter 16Документ33 страницыChapter 16Vinod Agrawal100% (7)
- Chapter 21 - Test Bank Chem 200Документ64 страницыChapter 21 - Test Bank Chem 200Jan Chester Chan67% (3)
- Mechanisms and Intermediates Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент117 страницMechanisms and Intermediates Multiple Choice Questionsbrownhazel50% (4)
- Sebp4195 76 01 Allcd - 003 PDFДокумент965 страницSebp4195 76 01 Allcd - 003 PDFFacturas hidrodieselОценок пока нет
- MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Part 5: Stereochemistry: Topic: Identifications and ComparisonsДокумент13 страницMULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS Part 5: Stereochemistry: Topic: Identifications and ComparisonsErica Chang100% (2)
- Organic Chemistry 11th Edition Solomons Test BankДокумент64 страницыOrganic Chemistry 11th Edition Solomons Test Bank박훈희100% (1)
- TBA Chapter9Документ23 страницыTBA Chapter9Ha Vi100% (1)
- Chapter 15 Test Bank Chem 200Документ123 страницыChapter 15 Test Bank Chem 200Lika GonashviliОценок пока нет
- ch12 Ques 2013Документ47 страницch12 Ques 2013VictoriaMcKaba90% (10)
- ch11 PDFДокумент96 страницch11 PDFMau BaraquelОценок пока нет
- Method of Statement-RTДокумент7 страницMethod of Statement-RTbuddhikasat50% (2)
- Chapter 7Документ56 страницChapter 7itsjc0% (1)
- ch16 TEST BANK SOLOMONSДокумент110 страницch16 TEST BANK SOLOMONSPatrick Malcolm Santos0% (1)
- ch18 Ques 2013Документ39 страницch18 Ques 2013av90% (21)
- CH 4 AlkanesДокумент16 страницCH 4 AlkanesBrittnay Marie100% (4)
- wph11 01 Que 20230111Документ28 страницwph11 01 Que 20230111Sanjeev NОценок пока нет
- CH 6 Test Bank PDFДокумент23 страницыCH 6 Test Bank PDFVanessa James100% (5)
- Astm G154Документ11 страницAstm G154jesoneliteОценок пока нет
- Benzene Derivatives Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент33 страницыBenzene Derivatives Multiple Choice QuestionsDante Ramoth75% (4)
- CH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersДокумент10 страницCH203 Fall 2014 Exam Two Practice Test With AnswersBUCH203Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Test BankДокумент80 страницChapter 6 Test BankPam Garcia90% (10)
- Laundry Engineering and Planning HandbookДокумент343 страницыLaundry Engineering and Planning HandbookKhanh mai quocОценок пока нет
- ALKYNEДокумент22 страницыALKYNENatasha Nadya Hussin80% (5)
- ALKYNEДокумент22 страницыALKYNENatasha Nadya Hussin80% (5)
- Carboxylic Acid Multiple Choice QuestionsДокумент18 страницCarboxylic Acid Multiple Choice QuestionsVinod Agrawal100% (9)
- Instructions: MOTOMAN-EA1400Документ62 страницыInstructions: MOTOMAN-EA1400Mrutunjay RaipureОценок пока нет
- Paper 3 Acid Dew Point Corrosion in HRSGsДокумент83 страницыPaper 3 Acid Dew Point Corrosion in HRSGsKarna2504100% (1)
- Compressor Station MallnowДокумент8 страницCompressor Station MallnowMANIU RADU-GEORGIANОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition by BrownДокумент23 страницыTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 7th Edition by BrownandielanaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsДокумент13 страницChapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsRahma AshrafОценок пока нет
- Enolate Aldol ReactionsДокумент28 страницEnolate Aldol ReactionsRosalina CabaОценок пока нет
- Stereochem Test BankДокумент19 страницStereochem Test BankCarmela Liria100% (15)
- Solomons Test Bank 1H NMR MCQsДокумент84 страницыSolomons Test Bank 1H NMR MCQsPatrick Malcolm Santos80% (5)
- BA L M EPA Carb4 PDFДокумент83 страницыBA L M EPA Carb4 PDFCristiTancuОценок пока нет
- Nonequilibrium Statistical MechanicsДокумент299 страницNonequilibrium Statistical MechanicsKshitij LauriaОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry Reactions of Benzene and Substituted BenzenesДокумент69 страницOrganic Chemistry Reactions of Benzene and Substituted BenzenesRebecca Campbell71% (7)
- Organic Chemistry by Janice Smith Test BankДокумент15 страницOrganic Chemistry by Janice Smith Test Bankalikaastrid87% (15)
- Organic Chemistry-Chapter 1 TestbankДокумент57 страницOrganic Chemistry-Chapter 1 TestbankAllison Allen100% (2)
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesДокумент27 страницAlkanes and CycloalkanesGia HoàngОценок пока нет
- Solomons Test Bank Chapter 12 MCQsДокумент99 страницSolomons Test Bank Chapter 12 MCQsKathy Yella100% (2)
- DSM Carbon Footprint StudyДокумент12 страницDSM Carbon Footprint StudyAbdul Rahman100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Alkenes - SmithДокумент14 страницChapter 10 Alkenes - SmithRen Liew Jia Qing75% (4)
- Chapter 16 - Test Bank Chem 200Документ110 страницChapter 16 - Test Bank Chem 200Jan Chester Chan80% (5)
- Chapter 3Документ41 страницаChapter 3francisco88% (8)
- Chapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonДокумент6 страницChapter 9 Organic Chemistry SolomonSukhi Sohal0% (1)
- Chapter 17Документ47 страницChapter 17Luke Dhillon100% (1)
- ch16 ProblemsДокумент104 страницыch16 Problemsbrownhazel92% (12)
- Chapter 9 Alkynes SolutionsДокумент11 страницChapter 9 Alkynes SolutionsRahma AshrafОценок пока нет
- Chem PreboardДокумент13 страницChem Preboardvirender.pinghalОценок пока нет
- Question PAPERДокумент6 страницQuestion PAPERharsh.mahori09Оценок пока нет
- XII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - FinalДокумент65 страницXII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - Finalkrishnapradhani091Оценок пока нет
- Half Yearly Exam Chemistry Theory QuestionsДокумент11 страницHalf Yearly Exam Chemistry Theory QuestionsNorish SamdaniОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper, XII, 2023-24, PDFДокумент8 страницSample Paper, XII, 2023-24, PDFfareehafatima18Оценок пока нет
- CLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Документ16 страницCLASS XII Chemistry-SQP 22-23Yug GandhiОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper Chemistry Theory SectionДокумент11 страницSample Paper Chemistry Theory SectionSariska MehraОценок пока нет
- Chemistry SQP 2Документ11 страницChemistry SQP 2ACHAL PATILОценок пока нет
- Chemistry SQPДокумент11 страницChemistry SQPMohd Zaid KhanОценок пока нет
- 12TH ChemistryДокумент11 страниц12TH ChemistryAkshatОценок пока нет
- QP Chemistry Pb2 Xii Set2Документ13 страницQP Chemistry Pb2 Xii Set2Yug GandhiОценок пока нет
- 11 Chemistry Sample Paper 01Документ16 страниц11 Chemistry Sample Paper 01loduuОценок пока нет
- Exam Three Practice Test Answers PDFДокумент19 страницExam Three Practice Test Answers PDFBUCH203100% (1)
- All Girls Are Barbies - A Feminist Critique of Nicki Minaj - S BarДокумент27 страницAll Girls Are Barbies - A Feminist Critique of Nicki Minaj - S BarVanessa JamesОценок пока нет
- Liver Problems-21Документ18 страницLiver Problems-21Vanessa JamesОценок пока нет
- Kidney Problems-20Документ19 страницKidney Problems-20Vanessa JamesОценок пока нет
- Tanya CogNeuro Final Courses Only BSДокумент3 страницыTanya CogNeuro Final Courses Only BSVanessa JamesОценок пока нет
- MCAT Science Workbook Biology OnlyДокумент220 страницMCAT Science Workbook Biology OnlyVanessa JamesОценок пока нет
- Greece WasteДокумент64 страницыGreece WasteYiannis AntonopoulosОценок пока нет
- CHEN 4460 - Process Synthesis, Simulation and OptimizationДокумент40 страницCHEN 4460 - Process Synthesis, Simulation and Optimizationmppatilmayur1679Оценок пока нет
- TCA7Документ1 страницаTCA7choirul dwiОценок пока нет
- Bel Ray BrochureДокумент20 страницBel Ray BrochureaditОценок пока нет
- Wave-Particle Duality FundamentalsДокумент7 страницWave-Particle Duality FundamentalsRahmatullahОценок пока нет
- Fly Ash Soil Blocks PDFДокумент42 страницыFly Ash Soil Blocks PDFTahir KhalidОценок пока нет
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOДокумент7 страницExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOChesta MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Installation: Residential/Light Commercial Generator SetsДокумент64 страницыInstallation: Residential/Light Commercial Generator SetsJackОценок пока нет
- Ship EducationДокумент34 страницыShip EducationBabu MuruganОценок пока нет
- Pump QuotationsДокумент3 страницыPump Quotationsdibyendu65Оценок пока нет
- Hyundai XG350 3.5L V6 Specs & TolerancesДокумент185 страницHyundai XG350 3.5L V6 Specs & TolerancesAngie Bravo CangasОценок пока нет
- Project Report - TarunДокумент5 страницProject Report - TarunrajuОценок пока нет
- Turbo CompressorДокумент6 страницTurbo Compressorrajanrane420Оценок пока нет