Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Earth Mat Designing of Substation
Загружено:
Dipak Bandyopadhyay0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
44 просмотров1 страницаEarth Mat design
Оригинальное название
51710556 Earth Mat Designing of Substation
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документEarth Mat design
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
44 просмотров1 страницаEarth Mat Designing of Substation
Загружено:
Dipak BandyopadhyayEarth Mat design
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
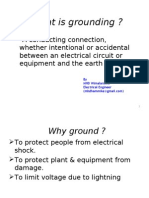
Earthing practices adopted at generating stations,
substations, distribution structures and lines are of great importance.
The earth is made up of materials that is electrically
conductive.
When a fault occurs , the current increases rapidly. This
unwanted fault current will flow to earth through the live conductor i.e. through
low resistance path
Classification
y System earthing : Connection between part of
substation in an operating system like LV neutral of a Transformer winding and
earth. y Equipment earthing : Connecting frames of equipment (Transformer tank,
Switch gear box, Bases of CTs & PTs, circuit breakers, Busbars etc.) to earth. y
Substation Fence earthing : Connecting fence (which is of steel) to earth.
Flow chart
Step-1: DESIGN DATA
y Let size of MAT is l × b y Area a = l × b y Average soil resistivity =
Step -2: Conductor size
y For line to ground fault calculationy If = 3I0 (if station resistance neglected)
y where y Calculate X/R ratio from z1,z2,z0 and Rf y The fault current If is used
to size the grounding
conductor y for maximum fault duration tc , we take decrement factor (Df) by the
given datasheet
y We have to consider melting temperature for fault
duration of tc
y Where I is in KA
y 1 Kcmil = 5.056 mm2 y Amm2 = r2 y Radius of conductor can be calculated by above
equation
Step-3: Touch and step potential
Вам также может понравиться
- Ptrak650 PDFДокумент318 страницPtrak650 PDFMf Lui83% (6)
- NeuroAmp ManualДокумент36 страницNeuroAmp ManualAlberto Barradas100% (1)
- The Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsОт EverandThe Technology of Instrument Transformers: Current and Voltage Measurement and Insulation SystemsОценок пока нет
- Detail Project Report (DPR) : 1MW Utility Scale Solar PV Power PlantДокумент28 страницDetail Project Report (DPR) : 1MW Utility Scale Solar PV Power Plantamritmandal019188% (51)
- Ear Thing and Lightning Protection ProjectДокумент26 страницEar Thing and Lightning Protection ProjectNishrachОценок пока нет
- Solar Generations Impact On Fault CurrentДокумент32 страницыSolar Generations Impact On Fault CurrentchintanpОценок пока нет
- NZECP 35 1993 New Zealand Electrical Code of Practice For Power System Earthing - Published 18 March 1993 PDFДокумент29 страницNZECP 35 1993 New Zealand Electrical Code of Practice For Power System Earthing - Published 18 March 1993 PDFTaylor Martinez100% (1)
- Design of A Bay Control Unit in A Substation Automation SystemДокумент63 страницыDesign of A Bay Control Unit in A Substation Automation Systemscottsaw100% (2)
- 4 Inch Pipe Threader: Owner'S ManualДокумент13 страниц4 Inch Pipe Threader: Owner'S ManualzzapiecheОценок пока нет
- Concepts of EarthingДокумент6 страницConcepts of EarthingKonda SrinivasОценок пока нет
- Grounding CalculationДокумент15 страницGrounding CalculationReza PahlepiОценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Fields of High-Speed Transportation Systems: The International Maglev BoardДокумент22 страницыElectromagnetic Fields of High-Speed Transportation Systems: The International Maglev BoardMayur PuriОценок пока нет
- Annexure 7 - 220V Speci MSETCL Trombay Nerul 260419 20190903173116Документ54 страницыAnnexure 7 - 220V Speci MSETCL Trombay Nerul 260419 20190903173116Anonymous cj7JdRbDbОценок пока нет
- PSCAD EMTDC, FuzzyControl, HVDC Transmission, VoltageDependentCurrentOrderLimit VDCOLДокумент9 страницPSCAD EMTDC, FuzzyControl, HVDC Transmission, VoltageDependentCurrentOrderLimit VDCOLKurniawan Indra LeksanaОценок пока нет
- Soil Thermal Resistivity FactsДокумент4 страницыSoil Thermal Resistivity FactspvpavanОценок пока нет
- DEBA-EL-CC-3143.B.1 Earthing Transformer Calculation NoteДокумент6 страницDEBA-EL-CC-3143.B.1 Earthing Transformer Calculation Notejie zhangОценок пока нет
- 9 Recommended Practices For GroundingДокумент6 страниц9 Recommended Practices For Groundingsikander843562Оценок пока нет
- Effect of High Resistive Barrier On Earthing System: Abstract: Substation Earthing Provides A LowДокумент4 страницыEffect of High Resistive Barrier On Earthing System: Abstract: Substation Earthing Provides A Lowalcie_scribdОценок пока нет
- Optimal Neutral Ground Resistor Rating of The Medium Voltage Systems in Power Generating StationsДокумент10 страницOptimal Neutral Ground Resistor Rating of The Medium Voltage Systems in Power Generating StationsGirish OniyilОценок пока нет
- SafeGrid Design ReportДокумент11 страницSafeGrid Design ReportkamilawehbeОценок пока нет
- S-TR-COM-LMS (Rev.0-2009)Документ7 страницS-TR-COM-LMS (Rev.0-2009)Ashutosh SharmaОценок пока нет
- EMF Study Report for Cricket Valley Energy ProjectДокумент127 страницEMF Study Report for Cricket Valley Energy ProjectNagendra SinghОценок пока нет
- RARP - Appendix C EMF Study - FinalДокумент40 страницRARP - Appendix C EMF Study - FinalkunhalparikhОценок пока нет
- EE-442 (Electric Energy Utilization)Документ2 страницыEE-442 (Electric Energy Utilization)dhineshkm10100% (1)
- Presentation EIL Project by JMV LPSДокумент59 страницPresentation EIL Project by JMV LPSMahesh Chandra ManavОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Large Grounding SystemsДокумент13 страницAnalysis of Large Grounding Systemsmirko.tОценок пока нет
- Grounding electrical systems safetyДокумент3 страницыGrounding electrical systems safetyMiko Quijano100% (1)
- APTRANSCO Spec - 11KV Polymer Insulators (C&T) RevisedДокумент13 страницAPTRANSCO Spec - 11KV Polymer Insulators (C&T) RevisedAshutosh SharmaОценок пока нет
- ECS 06-0024 Earthing Testing and Measurements PDFДокумент43 страницыECS 06-0024 Earthing Testing and Measurements PDFRajendra Prasad ShuklaОценок пока нет
- Large Scale Solar Power System DesignДокумент90 страницLarge Scale Solar Power System Design김동욱Оценок пока нет
- Understanding Ground Resistance TestingДокумент39 страницUnderstanding Ground Resistance Testingupt vadodaraОценок пока нет
- Solar PV Inverter Test ProceduresДокумент62 страницыSolar PV Inverter Test ProceduresskylarksОценок пока нет
- K-rated transformers handle harmonic loadsДокумент11 страницK-rated transformers handle harmonic loadsreddymdhОценок пока нет
- RHO Related PDFДокумент11 страницRHO Related PDFelectrical_1012000Оценок пока нет
- IEEE 1850 GroundGridCalcsДокумент11 страницIEEE 1850 GroundGridCalcsaabts1413Оценок пока нет
- EMI RFI Generation From LRT SystemsДокумент27 страницEMI RFI Generation From LRT SystemsShahidan StellarОценок пока нет
- 000 EE 153 CAD For EEE PDFДокумент35 страниц000 EE 153 CAD For EEE PDFStampinusStephanoОценок пока нет
- Cable Sizing for Non-Linear LoadsДокумент12 страницCable Sizing for Non-Linear Loadskhaldoun samiОценок пока нет
- Earthing PrimerДокумент20 страницEarthing PrimerSami DeorajОценок пока нет
- Quick Guide On CDEGS CRДокумент28 страницQuick Guide On CDEGS CRrian0201100% (1)
- Is Your Installation Safely EarthedДокумент13 страницIs Your Installation Safely EarthedmelcugОценок пока нет
- DATE: 10 January 2007 Weightage Breakdown: TotalДокумент43 страницыDATE: 10 January 2007 Weightage Breakdown: TotalMohamed MusaОценок пока нет
- Abstract of National Electrical Code For Transformer's ProtectionДокумент2 страницыAbstract of National Electrical Code For Transformer's ProtectionJignesh ParmarОценок пока нет
- Appendix A Technical Specification PhotovoltaicsДокумент4 страницыAppendix A Technical Specification Photovoltaics4gen_1Оценок пока нет
- EarthingДокумент3 страницыEarthingvinay nagvanshiОценок пока нет
- Earthing Guidance Notes Central NetworksДокумент12 страницEarthing Guidance Notes Central NetworksSethu RatnamОценок пока нет
- 1 11 FR 11 Substation Lightning ProtectionДокумент12 страниц1 11 FR 11 Substation Lightning Protectionkhaldoun sami100% (1)
- Substation Engineer CVДокумент8 страницSubstation Engineer CVSyed Zuber AhmedОценок пока нет
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent Relay Part 1Документ10 страницTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relay Part 1carlos vidalОценок пока нет
- Stadium Lightning Risk Assessments Annex AДокумент27 страницStadium Lightning Risk Assessments Annex AspartanОценок пока нет
- SafeGrid Reference ManualДокумент16 страницSafeGrid Reference Manualrajarao1234Оценок пока нет
- Technical SpecДокумент298 страницTechnical SpecMe100% (1)
- Experiment No: 1 19bee069 Date: 20/01/2022 Aim: To Determine Magnetization Characteristics of A Given Current TransformerДокумент11 страницExperiment No: 1 19bee069 Date: 20/01/2022 Aim: To Determine Magnetization Characteristics of A Given Current TransformerR.D Sutariya100% (1)
- Wind Turbine Generator System Safety and Function Test Report For The Ventera VT10 Wind TurbineДокумент37 страницWind Turbine Generator System Safety and Function Test Report For The Ventera VT10 Wind Turbineashish sahaОценок пока нет
- Grounding & Earth ResistanceДокумент11 страницGrounding & Earth ResistanceDhammike100% (1)
- Calculate Numbers of Plate - Pipe - Strip Earthings (Part-3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesДокумент11 страницCalculate Numbers of Plate - Pipe - Strip Earthings (Part-3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesMohamad HishamОценок пока нет
- Selecting Arrester MCOV-UcДокумент9 страницSelecting Arrester MCOV-Ucjose GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Fault Current CalculationДокумент3 страницыFault Current CalculationfarhanajnОценок пока нет
- Improved Design and Evaluation of Electrical Earthing Systems For Maryland 13233 KV Transmission StationДокумент9 страницImproved Design and Evaluation of Electrical Earthing Systems For Maryland 13233 KV Transmission StationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- New Approaches to the Design and Economics of EHV Transmission Plant: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringОт EverandNew Approaches to the Design and Economics of EHV Transmission Plant: International Series of Monographs in Electrical EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Earth Mat Designing of SubstationДокумент7 страницEarth Mat Designing of SubstationAbhi2716Оценок пока нет
- Earth Mat Designing of SubstationДокумент7 страницEarth Mat Designing of Substationraghu008Оценок пока нет
- SI All Divisions Jan 2018 RevisedДокумент13 страницSI All Divisions Jan 2018 RevisedDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- PD GisДокумент4 страницыPD Giserson1981Оценок пока нет
- Earth Mat Design Calculation For 33 KV S/STN For M/s Sukhbir Agro Energy LTD, Shahjahanpur, U.PДокумент7 страницEarth Mat Design Calculation For 33 KV S/STN For M/s Sukhbir Agro Energy LTD, Shahjahanpur, U.PDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- MPPT Charge ControllerДокумент6 страницMPPT Charge ControllerDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Generation ProtectionДокумент12 страницGeneration ProtectionDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- System WorksheetДокумент5 страницSystem WorksheetPablo MarilОценок пока нет
- Power Line Carrier Communication (PLCC)Документ17 страницPower Line Carrier Communication (PLCC)Dipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Transimission Line Cost Calculation PDFДокумент72 страницыTransimission Line Cost Calculation PDFjuanperezpintoОценок пока нет
- PLC Design and EngineeringДокумент8 страницPLC Design and Engineeringjazz217Оценок пока нет
- How to Design a Solar PV System in 40 StepsДокумент3 страницыHow to Design a Solar PV System in 40 StepsMeena DhillonОценок пока нет
- Calculate Sag in Overhead Transmission LinesДокумент6 страницCalculate Sag in Overhead Transmission LinesDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- DESIGN PROCEDURE BLOCK DIAGRAM FOR EARTH GRID CALCULATIONSДокумент10 страницDESIGN PROCEDURE BLOCK DIAGRAM FOR EARTH GRID CALCULATIONSThirunavukkarasu Varatharajan100% (1)
- Design of Earthing System For HV Ac SubstationДокумент9 страницDesign of Earthing System For HV Ac Substationwas00266Оценок пока нет
- Earth Mat Design 33-11KV SSДокумент5 страницEarth Mat Design 33-11KV SSDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Earth Mat Design 33-11KV SSДокумент5 страницEarth Mat Design 33-11KV SSDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Tower Ratios CalculatorДокумент8 страницTower Ratios CalculatorDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Enhance Grid Reliability With Hybrid HVDC BreakerДокумент6 страницEnhance Grid Reliability With Hybrid HVDC BreakerDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Manual de Autocad BasicoДокумент17 страницManual de Autocad Basicoinfected521Оценок пока нет
- IE Rules for DP Structure AbstractДокумент3 страницыIE Rules for DP Structure AbstractDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Design Challenges of 765kV Air Insulated SubstationsДокумент8 страницDesign Challenges of 765kV Air Insulated SubstationsDipak Bandyopadhyay100% (2)
- ReligiousДокумент7 страницReligiousDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Healy 2010Документ15 страницHealy 2010nelubogatu9364Оценок пока нет
- Measurements and Instrumentation Lecture NotesДокумент199 страницMeasurements and Instrumentation Lecture NotesGaurav Vaibhav100% (6)
- Deller EvidenceДокумент46 страницDeller EvidenceDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Moroner PoreДокумент21 страницаMoroner PoreDipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- मरणोत्तर जीवन - स्वामी विवेकानंदДокумент40 страницमरणोत्तर जीवन - स्वामी विवेकानंदInsearchof_Knowledge67% (6)
- Agile Methodologies Bar U A 734Документ6 страницAgile Methodologies Bar U A 734Dipak BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Yaskawa vs626m5Документ305 страницYaskawa vs626m5tmsxptoОценок пока нет
- 1910.255 Resistance WeldingДокумент2 страницы1910.255 Resistance WeldingAlfredo VSОценок пока нет
- GFДокумент146 страницGFMuhammadKhalidRehanChОценок пока нет
- VL-1000 Om Eng E08971004Документ20 страницVL-1000 Om Eng E08971004ANDRE GRUBYОценок пока нет
- BENSHAW 890034-03-00-MV-MX3-User-ManualДокумент222 страницыBENSHAW 890034-03-00-MV-MX3-User-ManualVictor Hugo Luna MenachoОценок пока нет
- Autonics E30s ManualДокумент1 страницаAutonics E30s ManualAndrez BermudezОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Power Supply QuestionsДокумент13 страницAircraft Power Supply Questionsotss100% (1)
- KDL-40BX450 Az3fk 9-883-873-01Документ37 страницKDL-40BX450 Az3fk 9-883-873-01Александр АндриановОценок пока нет
- Skanmobile User Manual Rev 9Документ88 страницSkanmobile User Manual Rev 9keshav Chauhan100% (1)
- Gas Insulated SwitchgearsДокумент24 страницыGas Insulated Switchgearscody100% (3)
- Manual Televisión Sharp 19rm100Документ27 страницManual Televisión Sharp 19rm100Eduardo Alanis VazquezОценок пока нет
- MDS maintenance manual for AC servo amplifiersДокумент242 страницыMDS maintenance manual for AC servo amplifiersMACKAY9999Оценок пока нет
- FS-C2026MFP FS-C2126MFP Service ManualДокумент304 страницыFS-C2026MFP FS-C2126MFP Service Manualconnectingeurope8479100% (2)
- Thermal Power Stations ExplainedДокумент16 страницThermal Power Stations ExplainedAbdul HaseebОценок пока нет
- Interactive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Документ34 страницыInteractive Schematic: This Document Is Best Viewed at A Screen Resolution of 1024 X 768Julio Gaston Castellanos DuranОценок пока нет
- Sa Ux100gsДокумент24 страницыSa Ux100gssaxsimОценок пока нет
- Hi-Focus M41 Mini-Shelf: Installation ManualДокумент60 страницHi-Focus M41 Mini-Shelf: Installation ManualGiang VuОценок пока нет
- Smiths Medical Technical Manual 3500Документ184 страницыSmiths Medical Technical Manual 3500Kamal100% (1)
- Earthing. Earthing and It's TypesДокумент5 страницEarthing. Earthing and It's TypesKishore DagiaОценок пока нет
- RC45 Fire Safety in The Electroplating IndustryДокумент16 страницRC45 Fire Safety in The Electroplating IndustryPiersicuta EscuОценок пока нет
- ABB VFD EN - ACS320 - SFUM - A - A4 User ManualДокумент44 страницыABB VFD EN - ACS320 - SFUM - A - A4 User ManualRahul GuptaОценок пока нет
- Anz14 Net-OptionДокумент49 страницAnz14 Net-OptionP Plaza MolinaОценок пока нет
- 725 Electrical SchematicДокумент11 страниц725 Electrical SchematicKhaled Naseem Abu-Sabha0% (1)
- Perkin Elmer Lambda 25-35-45 ManualДокумент116 страницPerkin Elmer Lambda 25-35-45 ManualAnonymous 6kEQXAUeОценок пока нет
- CH 2Документ42 страницыCH 2esraezreqatОценок пока нет
- 19c140 - 19 - CRT - TV SHARPДокумент24 страницы19c140 - 19 - CRT - TV SHARPluisОценок пока нет
- SE 325 Manual PDFДокумент26 страницSE 325 Manual PDFGabriel SanchezОценок пока нет