Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
HW 1
Загружено:
AlexSeniukИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
HW 1
Загружено:
AlexSeniukАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Due Jan 23, 2018
CIVE 321 Homework #1
(1) List five basic hydrologic processes
(2) What is the hydrologic cycle? Atmospheric water is one of the 3 basic components of the
hydrologic cycle. Name the other two components. What is the primary driving force behind
the hydrologic cycle? Why is it challenging to predict the future water supply and resources of
any place in the world accurately? Name one primary factor. How is the hydrology of a river
basin related to its climate?
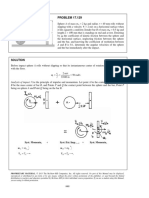
(3) A given storage reservoir has a normal pool area of 4000 acres (1 acre=43,560 ft2) and serves a
river basin of area of 200 miles2 (1 mile = 5280 ft). During an average year the annual rainfall
(P) is 37 inches, rainfall excess (R) is 10 inches, and the reservoir annual evaporation (E) is 30
inches (no transpiration since there is no vegetation). Determine the net change in the reservoir’s
storage in ft3 during the year if a local municipality is allowed to take 100 mgd (million gallon
per day, and 7.48 gallon = 1 ft3) from the reservoir. Neglect infiltration loss from the reservoir.
Apply R + Ia (depression storage) = O + ΔS (Change in river basin’s water storage) to get O,
outflow of the river basin. In this problem, the reservoir is the control volume. See Figure 1
(4) Suppose ground temperature is 5oC, and cooling takes place at a dry adiabatic lapse rate. What
is the air temperature at 7 km from the mean sea level? Why the actual lapse rate of rising air
masses usually is smaller than the dry adiabatic lapse?
(5) Assuming dry and wet-bulb temperatures of 20oC and 14oC respectively, at a pressure of 1013.2
mb, using the Table on dew point temperature & saturation vapor pressure provided, determine
(a) dew point temperature (TD), (b) saturation vapor pressure (es), (c) relative humidity (f), and
(d) actual vapor pressure ea.
(6) Given the dry adiabatic lapse rate of air is dT/dZ =-g/Cp, where T = air temperature, Z =
elevation, Cp=specific heat at constant pressure, g = gravity, compute dT/dZ in oC/km if Cp = 1004
J oC-1 kg-1. If air temperature is 20oC and vapor pressure of air is 12.2 mb, estimate the elevation
the air parcel must rise before the vapor pressure of air becomes saturated, assuming the lapse rate
is 7oC/km. Note 1 Joule = 1 Nm, 1 Newton = 1 kg.m/sec2.
200 Sq. Miles
P = 37”
E = 30”
Figure 1
Control
4000 acres Volume
Municipal Withdrawal
at 100mgd
Вам также может понравиться
- Outline: Hydrologic Cycle: Processes Hydrologic EquationДокумент11 страницOutline: Hydrologic Cycle: Processes Hydrologic EquationChaudryMuhammadHasnatОценок пока нет
- FE Exam Formatted ProblemsДокумент12 страницFE Exam Formatted ProblemsCarlo Galicia100% (1)
- Hydrology-Lecture Notes PDFДокумент83 страницыHydrology-Lecture Notes PDFalialjazaeryОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Hydrologic CycleДокумент20 страницIntroduction To Hydrologic Cycleklien ningascaОценок пока нет
- Homework 1 SolutionДокумент9 страницHomework 1 SolutionNaveen100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Answer Key Concept Check: © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All Rights ReservedДокумент46 страницChapter 1-Answer Key Concept Check: © 2019 Pearson Education, Inc., Hoboken, NJ. All Rights ReservedDenise CastilloОценок пока нет
- Evaporacion y EvapotranspiracionДокумент50 страницEvaporacion y EvapotranspiracionRaul Cordova Alvarado100% (1)
- Laboratory or Field - Lysimeters: Different Methods To Measure ETДокумент24 страницыLaboratory or Field - Lysimeters: Different Methods To Measure ETlance carterОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Hydrology: ReferencesДокумент5 страницCivil Engineering Hydrology: ReferencesYM HMОценок пока нет
- CE 334 - Module 1.0Документ42 страницыCE 334 - Module 1.0Samson EbengaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Examples of Water Budget Eqtn - Student'sДокумент3 страницыChapter 3 Examples of Water Budget Eqtn - Student'sJeana Lew SCОценок пока нет
- ECW331-Topic 1Документ9 страницECW331-Topic 1MUHAMMAD DZAKIRIN HANNAN NORASHIDОценок пока нет
- Abe Quiz Bee Season IIДокумент4 страницыAbe Quiz Bee Season IISita HousОценок пока нет
- CE570 Final Exam Fall 2023Документ4 страницыCE570 Final Exam Fall 2023farajelmabroukОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Main Hydro Logical ConceptsДокумент15 страницChapter 1 - Main Hydro Logical ConceptshafeezaminОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2Документ29 страницLecture 2Muhammad Hammad KhanОценок пока нет
- 1A - Hydrologic Cycle - READY - FINAL - 2019-2020 - FINALДокумент40 страниц1A - Hydrologic Cycle - READY - FINAL - 2019-2020 - FINALDanОценок пока нет
- Climate Change: Soil Water PlantДокумент50 страницClimate Change: Soil Water PlantMelkamu Ateka DerebeОценок пока нет
- 05 Hydrologic LossesДокумент39 страниц05 Hydrologic LossesMaan HinolanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12011Документ13 страницLecture 12011KubaОценок пока нет
- CE467 First Fall 09Документ3 страницыCE467 First Fall 09farajelmabroukОценок пока нет
- CE 374K Hydrology - Lecture 1Документ13 страницCE 374K Hydrology - Lecture 1jamilthaljiОценок пока нет
- Hydrology CycleДокумент25 страницHydrology CycleSaeed FatahОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three EvaporationДокумент41 страницаChapter Three EvaporationAbdizalaam ElmiОценок пока нет
- Hydrology - Lecture 1Документ13 страницHydrology - Lecture 1xyzt5000Оценок пока нет
- F. Huang - Engineering ThermodynamicsДокумент52 страницыF. Huang - Engineering ThermodynamicsHectorCabz100% (1)
- Tutorial 1Документ1 страницаTutorial 1Agilen MagalingamОценок пока нет
- HYDROLOGY AND WATER QUALITY CONTROL FirstДокумент7 страницHYDROLOGY AND WATER QUALITY CONTROL FirstAljon LanguingОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Water Budget Equation Catchment Area: Solution: GivenДокумент4 страницы1.1 Water Budget Equation Catchment Area: Solution: GivenShiela GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Water Losses EvaporationДокумент8 страницWater Losses EvaporationYM HMОценок пока нет
- Calculations: 1. Air Flow Calculations, According To Natural Draft Pressure CalculatorДокумент4 страницыCalculations: 1. Air Flow Calculations, According To Natural Draft Pressure CalculatorchunkyОценок пока нет
- Chapter Three Water Losses: Evaporation From Water Surfaces (Lake Evaporation)Документ14 страницChapter Three Water Losses: Evaporation From Water Surfaces (Lake Evaporation)به شدار ازاد عبدالرحمن عليОценок пока нет
- PracticeExamSolutions PDFДокумент9 страницPracticeExamSolutions PDFMohmmed HusseinОценок пока нет
- CE 394K.2 Hydrology - Lecture 1: Some Slides in This Presentation Were Prepared by Venkatesh MerwadeДокумент16 страницCE 394K.2 Hydrology - Lecture 1: Some Slides in This Presentation Were Prepared by Venkatesh MerwadeJayson PagalОценок пока нет
- EvaporationДокумент41 страницаEvaporationGoodluck NyagybОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 1Документ72 страницыThermodynamics 1Victor CapistranoОценок пока нет
- Essay Journal4Документ33 страницыEssay Journal4Thrinley OngchuckОценок пока нет
- Water EconomicsДокумент15 страницWater EconomicskellygiraudОценок пока нет
- CH 1 IrrigationДокумент28 страницCH 1 Irrigationatef01020805106Оценок пока нет
- 3-Evaporation - READY - FINAL - 2019-20 - ModifiedДокумент28 страниц3-Evaporation - READY - FINAL - 2019-20 - ModifiedDanОценок пока нет
- Hydro Ass 1Документ5 страницHydro Ass 1CHRISTIAN VERGEL DATINGALINGОценок пока нет
- Hydrology (1 - 51)Документ51 страницаHydrology (1 - 51)Ayat AlhilawyОценок пока нет
- CE 334 - Module 3.1Документ44 страницыCE 334 - Module 3.1Samson EbengaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 4 Questions - Major Ions, Conservative Elements and Dissolved GasesДокумент5 страницLecture 4 Questions - Major Ions, Conservative Elements and Dissolved GasesAndrew SetiadiОценок пока нет
- 2015 CVL300 Tutorial 4 SolutionДокумент7 страниц2015 CVL300 Tutorial 4 SolutionAhmed Abuzour100% (2)
- Hydrology 5: Evaporation & TranspirationДокумент20 страницHydrology 5: Evaporation & TranspirationAve de GuzmanОценок пока нет
- Water and Its Properties: An Unusual MoleculeДокумент41 страницаWater and Its Properties: An Unusual MoleculejoseluistaveОценок пока нет
- F. Huang - Chapter 1Документ3 страницыF. Huang - Chapter 1HectorCabzОценок пока нет
- Tutorial Problems On Air Conditioning - 2018Документ6 страницTutorial Problems On Air Conditioning - 2018Ar Vaishnavi VennuОценок пока нет
- 3rd BTech 2022-23civil EE Ses-K2Документ7 страниц3rd BTech 2022-23civil EE Ses-K2Telugu films and technical IОценок пока нет
- 4.3 To 4.7 Palihog Kog Rephrase Sa Paragraph Answers Kay Gkan Nis Laing Group HeheДокумент9 страниц4.3 To 4.7 Palihog Kog Rephrase Sa Paragraph Answers Kay Gkan Nis Laing Group HeheJaphetBalasabasNovabosОценок пока нет
- Incomplete Exam: Answer All QuestionsДокумент4 страницыIncomplete Exam: Answer All Questionsfarag alhassiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - EVAPORATION, TRANSPIRATION & INFILTRATIONДокумент111 страницChapter 3 - EVAPORATION, TRANSPIRATION & INFILTRATIONintern kncesbОценок пока нет
- Environmental Engineering Lecture NotesДокумент116 страницEnvironmental Engineering Lecture NotesDebrah Debbie100% (1)
- H. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)Документ20 страницH. Sta. Maria - Thermodynamics (Selected and Modified Problems)HectorCabzОценок пока нет
- chp1 AtdДокумент3 страницыchp1 AtdNivesh JalanОценок пока нет
- Groundwater Basics: (Calculation)Документ16 страницGroundwater Basics: (Calculation)Rahat fahimОценок пока нет
- Lecture3&4 Mass Transfer STDДокумент27 страницLecture3&4 Mass Transfer STDNuria Armenteros MenaОценок пока нет
- 2018 Year 9 Science ProgramДокумент16 страниц2018 Year 9 Science Programapi-364379734Оценок пока нет
- Anti-Dandruff Shampoo With Zinc Pyrithione: INCI Name, Trade Name Weight % FunctionДокумент2 страницыAnti-Dandruff Shampoo With Zinc Pyrithione: INCI Name, Trade Name Weight % FunctionandreeaОценок пока нет
- NSTSE Class 7 SolutionДокумент5 страницNSTSE Class 7 SolutionMota ChashmaОценок пока нет
- Ball Valve SeatДокумент2 страницыBall Valve Seatmrkadu_61Оценок пока нет
- WEDECO LBXSeriesДокумент8 страницWEDECO LBXSeriesÁrpád VassОценок пока нет
- Safety Data Sheet: 3M Brand Fire Barrier CP-25WB+Документ12 страницSafety Data Sheet: 3M Brand Fire Barrier CP-25WB+ErickoОценок пока нет
- A Sustainable Bioplastic Obtained From Rice StrawДокумент12 страницA Sustainable Bioplastic Obtained From Rice StrawNovrynda Eko SatriawanОценок пока нет
- Planck's Law - WikipediaДокумент88 страницPlanck's Law - Wikipedia朱岳宸Оценок пока нет
- Limnologica: Wojciech Ejankowski, Tomasz LenardДокумент8 страницLimnologica: Wojciech Ejankowski, Tomasz LenardMoltimer Folchart CrawОценок пока нет
- Shear Wall Modelling Techniques: A ReviewДокумент9 страницShear Wall Modelling Techniques: A ReviewAmanulla MullaОценок пока нет
- Spectrophotometric Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate Using Phosphomolybdenum Blue ComplexДокумент8 страницSpectrophotometric Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate Using Phosphomolybdenum Blue ComplexkhekhyОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 Study Guide Solutions - Kinetics & ThermoДокумент3 страницыUnit 4 Study Guide Solutions - Kinetics & ThermoPenguin/CatОценок пока нет
- 3-Cstr Models f12Документ6 страниц3-Cstr Models f12Jon Bisu DebnathОценок пока нет
- TurbidityДокумент4 страницыTurbiditylaxminarayanОценок пока нет
- Assignment For BCH3356Документ2 страницыAssignment For BCH3356farehaОценок пока нет
- Maharashtra HSC Chemistry Paper 2-Target PublicationДокумент45 страницMaharashtra HSC Chemistry Paper 2-Target PublicationKhanAbdullah100% (1)
- Adsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuДокумент7 страницAdsorption From Solutions, Acetic Acid On Charcoal: Lorenz John T. ChuZhu Chen ChuanОценок пока нет
- ChemEngineering - Flash EvaporationДокумент3 страницыChemEngineering - Flash EvaporationmegakiranОценок пока нет
- Asahi KaseiДокумент24 страницыAsahi KaseiRitam GhoshОценок пока нет
- Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (Compulsory)Документ19 страницSection A: Multiple Choice Questions (Compulsory)ivyОценок пока нет
- Nsejs2014 Js 505Документ13 страницNsejs2014 Js 505ChiruhaasОценок пока нет
- Elastic Modulas of Gravel Mix Sand PDFДокумент1 страницаElastic Modulas of Gravel Mix Sand PDFPrakash Singh RawalОценок пока нет
- Practice Exam 2.4Документ6 страницPractice Exam 2.4jamalОценок пока нет
- Voe Main2Документ4 страницыVoe Main2prevrtljivacОценок пока нет
- FaienceДокумент15 страницFaienceRenata TatomirОценок пока нет
- Elvis 4Документ9 страницElvis 4Azhar Ali Zafar0% (1)
- 9701 w05 QP 4Документ12 страниц9701 w05 QP 4Hubbak KhanОценок пока нет
- Coatings Word August 2010Документ52 страницыCoatings Word August 2010sami_sakrОценок пока нет
- PROBLEM 17.129: SolutionДокумент14 страницPROBLEM 17.129: SolutiontaОценок пока нет
- 19 Heat of Combustion MGДокумент5 страниц19 Heat of Combustion MGmanuelscribdgonzalesОценок пока нет
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОт EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessОценок пока нет
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldОт EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (597)
- Fire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutОт EverandFire Season: Field Notes from a Wilderness LookoutРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (142)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogОт EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincОт EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (137)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionОт EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (812)
- Water to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesОт EverandWater to the Angels: William Mulholland, His Monumental Aqueduct, and the Rise of Los AngelesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (21)
- When You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsОт EverandWhen You Find Out the World Is Against You: And Other Funny Memories About Awful MomentsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (13)
- Smokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersОт EverandSmokejumper: A Memoir by One of America's Most Select Airborne FirefightersОценок пока нет
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorОт EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (137)
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsОт EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (223)
- The Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterОт EverandThe Storm of the Century: Tragedy, Heroism, Survival, and the Epic True Story of America's Deadliest Natural DisasterОценок пока нет
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsОт EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (65)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildОт EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (44)
- A Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeОт EverandA Brief History of the Earth's Climate: Everyone's Guide to the Science of Climate ChangeРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- The Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessОт EverandThe Soul of an Octopus: A Surprising Exploration into the Wonder of ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (254)