Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
TGA Analysis Techniques for Waste Management
Загружено:
nagendra_rd0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
37 просмотров3 страницыThermogravimetric analysis
Оригинальное название
Thermogravimetric Analysis
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThermogravimetric analysis
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
37 просмотров3 страницыTGA Analysis Techniques for Waste Management
Загружено:
nagendra_rdThermogravimetric analysis
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
Thermogravimetric analysis
Introduction:
Thermogravimetric analysis is an important tool in the environmental management particularly in
case of waste management. Waste management of organic based waste like polymer waste, biomass
are characterized by thermogravimetric analsyis. Apart from this, thermogravimetric analysis is quiet
important for the energy, polymers, mineral analysis etc.
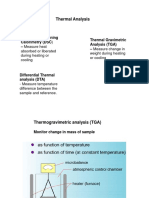
Thermogravimetric analysis can be classified as follow based on the property which is measured
a. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) : The change in weight as a function of temperature of the
sample is measured.
b. Derivative thermogravimetric analysis (DTG): The rate of change of weight as a function of
temrature of the sample is measured.
c. Differential Thermal analysis (DTA): The heat evolved or absorbed as a function of
temperature of the sample is measured. This analysis in particular provides the endothermic
or exothermic nature of the process.
Apart from this thermometric titrations are also involved which would be covered with calorimetry
i.e., differential calorimetry and isothermal calorimetry.
The most important part of the thermogravimetric analysis is the balance which is called
thermobalance. The first thermobalance is attributed to the work of P. Chevenard in 1944. However,
this balance was extensively used by Duval et al. (1953).
s. property technique notes
no.
1 heat Calorimetry
2 temperature Thermometry May also be described as heating or
cooling curves
3. Temperatur Differential Thermal Analysis Temperature difference between the
e difference (DTA) sample and reference material
4 Heat flow Differential Scanning Heat flow rate difference between a
Rate Calorimetry (DSC) sample and reference material
5 Mass Thermogravimetry (TG)
thermogravimetric analysis
(TGA)
6. Dimensiona Dynamic Mechanical Analysis Modulies are determined
l and (DMA) Deformation of the substance under
Mechnaical compression, tension, Flexure, Torsion or
elasticity
Thermomechanical Analysis
Dimensions are measured
(TMA)
Thermodialometry (TD)
Linear
Volumetric
7. Electrical Dielectric Thermal analysis Dielectric constant/ Dielectric loss
(DEA) measured
Thermally Stimulated Current Current
(TSC)
8. Magnetic Themomagnetometry (TM) Magnetic Susceptibility
Characterist
ics
9. Gas Flow The nature and/or amount of gas/vapour
Evolved gas analysis (EGA) is determined
Gasvolumetry Volume
Thermogastititrimetry Heat-conductivity
(TGT) Nature and amount by titration
Mass spectrometry Nature and amount by Mass spectrometry
(MS) Nature and amount by IR spectrometry
High temperature IR
Spectrometry (HTIR) Trapped Radioactive gas within the
Emanation Thermal Analysis sample released and measured
(ETA)
10. Pressure Thermomanometry (TM) Evolution of gas is detected by pressure
change
Thermobarometry Pressure exerted by a dense sample on the
walls of a constant volume cell is studied
11. Optical Thermooptometry (DRS) (Thermomicrosocpy)
Charcaterist
Thermophotometry
ics Measurement of total light
Thermorefractometry
Determination of refractive index
Dynamic reflection
spectrometry (DRS) Determination of relfection
Thermoluminescence (TL)
Emission of light
12. Acoustic Thermosonimetry Sound emitted by the substance
Imposed acoustic waves after passing
Thermoacoustometry through the substance
13. Structure Thermodiffractometry (IITRA) Compositional or chemical nature of the
Thermospectrometry sample is studied
High temorature X-Ray analysis
measured of light of specific
wavelength(s)
14. Reactions Thermometric titrimetry
in Solution
Вам также может понравиться
- Thermal Analysis V1: Instrumention,Organic Materials, and PolymersОт EverandThermal Analysis V1: Instrumention,Organic Materials, and PolymersRobert F. Jr. SchwenkerОценок пока нет
- ICTAC-IUPAC-TA Nomenclature 2014 PDFДокумент9 страницICTAC-IUPAC-TA Nomenclature 2014 PDFJulyanne RodriguesОценок пока нет
- Analysis Through Thermal EnergyДокумент27 страницAnalysis Through Thermal EnergySarah HosawiОценок пока нет
- Thermoanalytical Methods-1Документ19 страницThermoanalytical Methods-1Namish ManchandaОценок пока нет
- Thermal Methods of Analysis: CRI SONДокумент8 страницThermal Methods of Analysis: CRI SONhp pavilionОценок пока нет
- Thermal Methods PDFДокумент8 страницThermal Methods PDFqwljalkdjОценок пока нет
- Thermal PropertiesДокумент20 страницThermal PropertiesMONIRUZZAMAN MONIRОценок пока нет
- Abdoul Salam Issiaka IbrahimДокумент70 страницAbdoul Salam Issiaka IbrahimAbdoul Salam IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Unit 8Документ23 страницыUnit 8Anurag PandeyОценок пока нет
- Class 1 - New (4 Files Merged)Документ54 страницыClass 1 - New (4 Files Merged)alok nayak100% (1)
- Hermal Ethods of Nalysis: Mr. Ganesh B. Nigade, Assistant Professor, PDEA's S. G. R. S. College of Pharmacy, SaswadДокумент35 страницHermal Ethods of Nalysis: Mr. Ganesh B. Nigade, Assistant Professor, PDEA's S. G. R. S. College of Pharmacy, Saswadchemistchemist85Оценок пока нет
- Thermal AnalysisДокумент28 страницThermal AnalysisYuppie RajОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis 19 Feb 2023Документ29 страницThermal Analysis 19 Feb 2023eeman tariqОценок пока нет
- Thermal AnalysisДокумент21 страницаThermal AnalysisIndiraОценок пока нет
- Thermal Testing Methods for Material AnalysisДокумент16 страницThermal Testing Methods for Material AnalysisSAJITH NFОценок пока нет
- White Paper Characterization of Polymers Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSC M 012816 PDFДокумент5 страницWhite Paper Characterization of Polymers Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry DSC M 012816 PDFNurjanahОценок пока нет
- Lectrure Thermal AnalysisДокумент36 страницLectrure Thermal Analysisboniucira cantikОценок пока нет
- DSC Analysis of Pharmaceutical SamplesДокумент27 страницDSC Analysis of Pharmaceutical SamplesDivya Tripathy100% (1)
- Thermal Characterization of Textile MaterialsДокумент40 страницThermal Characterization of Textile Materialssubhaxyz9365Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Table 1 - 3Документ1 страницаLecture 1 Table 1 - 3ZUL KAMARUDDINОценок пока нет
- Principles of Thermal Analysis TechniquesДокумент10 страницPrinciples of Thermal Analysis TechniquesAlexis CarmonaОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis,: Ft-Ir SpectrometerДокумент41 страницаThermal Analysis,: Ft-Ir SpectrometerHarold MangaОценок пока нет
- Gathers 1986Документ57 страницGathers 1986Михаил ПарамоновОценок пока нет
- Thermal MethodsДокумент78 страницThermal Methodsshruti shahОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis of MaterialsДокумент45 страницThermal Analysis of MaterialsBHARTI GAURОценок пока нет
- 儀分 Ch31 ThermalДокумент57 страниц儀分 Ch31 ThermalSaurabh ShashankОценок пока нет
- Thermal Methods AnalysisДокумент31 страницаThermal Methods AnalysisMaliha aliОценок пока нет
- dokumen.tips_instrumental-methods-of-analysis-principle-and-application-of-thermal-methodsДокумент15 страницdokumen.tips_instrumental-methods-of-analysis-principle-and-application-of-thermal-methodsBRAHIMОценок пока нет
- DSC ShodgangaДокумент17 страницDSC ShodgangaPundaleek KalloliОценок пока нет
- Thermogravimetry (TGA) & Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)Документ29 страницThermogravimetry (TGA) & Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)SaurabhBhardwajОценок пока нет
- Thermo Mechanical AnalysisДокумент17 страницThermo Mechanical AnalysisHarold MangaОценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ17 страницUnit 2akashdhevaОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis of PolymersДокумент86 страницThermal Analysis of PolymersMarister OliveiraОценок пока нет
- MM358 - Thermal Analysis RevisedДокумент28 страницMM358 - Thermal Analysis Revisedvishal sharmaОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analysis Techniques ComparisonДокумент11 страницThermal Analysis Techniques ComparisonAhmadnurul muttaqinОценок пока нет
- Aaaaahhhhh I Don't Know If You Have AnyДокумент32 страницыAaaaahhhhh I Don't Know If You Have AnyTom VloggerОценок пока нет
- Process Instrumentation CH 403: Dr. Prince GeorgeДокумент39 страницProcess Instrumentation CH 403: Dr. Prince GeorgeibuddhaОценок пока нет
- Study of Mechanical AndcomparativeДокумент9 страницStudy of Mechanical Andcomparativenadir adelОценок пока нет
- Modulated-Temperature Thermomechanical Analysis: D. M. PriceДокумент8 страницModulated-Temperature Thermomechanical Analysis: D. M. PriceRizky EkoОценок пока нет
- Im SWP L 002fДокумент42 страницыIm SWP L 002fHotib PerwiraОценок пока нет
- Thermal AnalysisДокумент45 страницThermal AnalysisERIKO DARMAWANОценок пока нет
- Wang2009 PDFДокумент9 страницWang2009 PDFDaniela Forero RamírezОценок пока нет
- DSCДокумент56 страницDSCDildeep JayadevanОценок пока нет
- Analysis ChemistryДокумент19 страницAnalysis ChemistrySITI HUMAIRAH BINTI HAMZAHОценок пока нет
- Thernal AnalysisДокумент46 страницThernal AnalysisPulinda KasunОценок пока нет
- Definition and Principles of Thermal AnalysisДокумент7 страницDefinition and Principles of Thermal AnalysisMichał IkarОценок пока нет
- 636 2102 1 SM PDFДокумент6 страниц636 2102 1 SM PDFSávio MendesОценок пока нет
- Bab 7 5 Characterization 02 ThermoanalisisДокумент39 страницBab 7 5 Characterization 02 ThermoanalisisPutrik AgustinaОценок пока нет
- Differential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Differential Scanning CalorimetryДокумент27 страницDifferential Thermal Analysis (DTA) and Differential Scanning CalorimetryAgustynho MagimbaОценок пока нет
- Material Science Engineering: "Thermal Analytical Technique: DTA, TGA"Документ10 страницMaterial Science Engineering: "Thermal Analytical Technique: DTA, TGA"Upasana YОценок пока нет
- TMA (Thermomechanical Analysis) and Its ApplicationДокумент18 страницTMA (Thermomechanical Analysis) and Its Applicationbt19108055 Amarjeet KumarОценок пока нет
- Brown - Introduction To Thermal Analysis. Techniques and Applications PDFДокумент267 страницBrown - Introduction To Thermal Analysis. Techniques and Applications PDFSávio MendesОценок пока нет
- Instumental AnalysisДокумент16 страницInstumental AnalysisKhushbuChemical RautОценок пока нет
- Brown 2001 Introductionto Thermal AnalysisДокумент267 страницBrown 2001 Introductionto Thermal AnalysisFocuОценок пока нет
- Thermal Analys Course 2022Документ67 страницThermal Analys Course 2022lfvorster99Оценок пока нет
- T.Y.B.Sc. 4.1.3 DTA Analysis PPT TYДокумент32 страницыT.Y.B.Sc. 4.1.3 DTA Analysis PPT TYmohamed arifОценок пока нет
- Nanomaterials CharacterДокумент70 страницNanomaterials CharacterLogicAndFacts ChannelОценок пока нет
- Determination of The Adiabatic Time To Maximum Rate by DSC For Thermal Safety AssessmentДокумент4 страницыDetermination of The Adiabatic Time To Maximum Rate by DSC For Thermal Safety AssessmentklkumarОценок пока нет
- DTAДокумент14 страницDTABalaji NagisettyОценок пока нет
- 5 XpsДокумент17 страниц5 Xpsnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Adsorption PublicationsДокумент1 страницаAdsorption Publicationsnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Chemical ListДокумент1 страницаChemical Listnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Dr. Anant Kumar H.O.D. Department of Chemistry B.C.E. BakhtiyarpurДокумент69 страницDr. Anant Kumar H.O.D. Department of Chemistry B.C.E. Bakhtiyarpurnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Chemistry: Na NaДокумент4 страницыNuclear Chemistry: Na Nanagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Receipt DetailsДокумент1 страницаBharat Sanchar Nigam Limited: Receipt Detailsnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- CatalysisДокумент50 страницCatalysisnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Material ScienceДокумент2 страницыMaterial ScienceachalslОценок пока нет
- PHD Course Structure and SyllabusДокумент10 страницPHD Course Structure and Syllabusnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Mcqs - BiochemistryДокумент3 страницыMcqs - Biochemistrynagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- BSNL Payment Receipt Rs. 2272 SuccessfulДокумент1 страницаBSNL Payment Receipt Rs. 2272 Successfulnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Safety Laboratory SignsДокумент3 страницыSafety Laboratory Signsnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Understanding the Flexibility Mechanism of the Kyoto ProtocolДокумент38 страницUnderstanding the Flexibility Mechanism of the Kyoto Protocolnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- CatalysisДокумент50 страницCatalysisnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Nuclear ChemistryДокумент78 страницNuclear Chemistrynagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Complex Reaction MechanismДокумент36 страницComplex Reaction Mechanismnagendra_rd0% (1)
- Air Pollution ManagementДокумент138 страницAir Pollution Managementnagendra_rd100% (1)
- Thermochemistry SolutionsДокумент8 страницThermochemistry Solutionsnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Pottery Important PDFДокумент6 страницPottery Important PDFnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- EducationДокумент6 страницEducationnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Selenate Selenite SensorДокумент22 страницыSelenate Selenite Sensornagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- ABCDДокумент2 страницыABCDnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Air - Pollutants - Sources and PotencyДокумент57 страницAir - Pollutants - Sources and Potencynagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Environment and Health Share An Inseparable AssociationДокумент3 страницыEnvironment and Health Share An Inseparable Associationnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- Nepal Development of A Ceramic Water Filter For Nepal - University of British ColumbiaДокумент170 страницNepal Development of A Ceramic Water Filter For Nepal - University of British ColumbiaFree Rain Garden ManualsОценок пока нет
- Stack MonitoringДокумент35 страницStack Monitoringnagendra_rd100% (1)
- Request for Sample Testing and Analysis at CSMCRIДокумент3 страницыRequest for Sample Testing and Analysis at CSMCRInagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- ABCDДокумент2 страницыABCDnagendra_rdОценок пока нет
- ABCДокумент90 страницABCnagendra_rd100% (1)
- 301 Prome Series Laser Pointer ManualДокумент2 страницы301 Prome Series Laser Pointer Manualisabella matosОценок пока нет
- Information Sheet BulbДокумент9 страницInformation Sheet BulbRex Chambers LadaoОценок пока нет
- Michelson's InterferometerДокумент27 страницMichelson's InterferometerAyesha SarwarОценок пока нет
- Understanding Light:: Properties & ClassificationsДокумент35 страницUnderstanding Light:: Properties & ClassificationsColtonОценок пока нет
- Operation Heracles - Firefight SmolДокумент29 страницOperation Heracles - Firefight SmolIceStationLemonОценок пока нет
- Analogue Digital Signal - Electromagnetic SpectrumДокумент2 страницыAnalogue Digital Signal - Electromagnetic SpectrumruukiОценок пока нет
- How computers work and their types in 40 charactersДокумент30 страницHow computers work and their types in 40 charactersVidhya GОценок пока нет
- Sony Cdx-gt310 Ver-1.3 SMДокумент37 страницSony Cdx-gt310 Ver-1.3 SMMarco GalanОценок пока нет
- The Michelson InterferometerДокумент13 страницThe Michelson InterferometerVũ BìnhОценок пока нет
- Complete EDM Handbook - 3Документ16 страницComplete EDM Handbook - 3Neil BotesОценок пока нет
- Photo TransistorsДокумент15 страницPhoto TransistorsAditi JaОценок пока нет
- Avh-P7500dvd Avh-P5750 CRT3039Документ187 страницAvh-P7500dvd Avh-P5750 CRT3039Anonymous AsQcGUyCI100% (1)
- Ifm TW7000 Infrared Temperature Sensor GB 2014Документ5 страницIfm TW7000 Infrared Temperature Sensor GB 2014ifm electronicОценок пока нет
- An177 PDFДокумент34 страницыAn177 PDFSam PandezОценок пока нет
- JSS 5855-11-2016Документ28 страницJSS 5855-11-2016Pooja sharma100% (1)
- Ricoh B205 Service ManualДокумент883 страницыRicoh B205 Service Manualdwina rocheОценок пока нет
- Uniform Fiber Bragg Grating: PurposeДокумент39 страницUniform Fiber Bragg Grating: PurposeAnonymous gdutVXlUTОценок пока нет
- Guided vs unguided transmission mediaДокумент7 страницGuided vs unguided transmission mediaMehwish SabirОценок пока нет
- Automated Welding TechnologiesДокумент26 страницAutomated Welding TechnologiesAbie RexoMenОценок пока нет
- Image Sensor Kmpd0002eДокумент52 страницыImage Sensor Kmpd0002eLakmal GayanОценок пока нет
- Guidance For Field Segmentation and Welding of Induction Bends and ElbowsДокумент9 страницGuidance For Field Segmentation and Welding of Induction Bends and ElbowsMarcelo Varejão CasarinОценок пока нет
- Ch3000 At3552 Series Analog Externally Modulated Full Spectrum Transmitter Data SheetДокумент4 страницыCh3000 At3552 Series Analog Externally Modulated Full Spectrum Transmitter Data SheetGilmar Peterle PaganiniОценок пока нет
- L1 load circuit diagram for diesel generator controlДокумент1 страницаL1 load circuit diagram for diesel generator controlNabilBouabana100% (3)
- Hyperspectral Imaging and Forensic ScienceДокумент14 страницHyperspectral Imaging and Forensic ScienceJiyual MustiОценок пока нет
- Exercise Solution PDFДокумент3 страницыExercise Solution PDFAbdul Aziz100% (1)
- CHAIKA Cameras 1Документ14 страницCHAIKA Cameras 1Joe GreenОценок пока нет
- Andrew Db858dg65esyДокумент2 страницыAndrew Db858dg65esyEmmersonLisboaОценок пока нет
- Modal Analysis of On Chip Optical Waveguides Using BeamPROPДокумент7 страницModal Analysis of On Chip Optical Waveguides Using BeamPROPijaertОценок пока нет
- Leuze HRTR 2Документ4 страницыLeuze HRTR 2KDChowdaryPuvvadiОценок пока нет
- Case Study Two - DFM ChairsДокумент34 страницыCase Study Two - DFM Chairsapi-283594799Оценок пока нет