Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
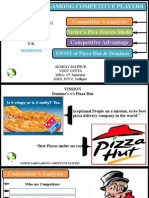
SWOT-Analysis
Загружено:
Poulami GhoshИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SWOT-Analysis
Загружено:
Poulami GhoshАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SWOT ANALYSIS
SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats analysis) is a
framework for identifying and analyzing the internal and external factors that can have an
impact on the viability of a project, product, place or person.
SWOT analysis is most commonly used by business entities, but it is also used
by nonprofit organizations and, to a lesser degree, individuals for personal assessment.
Additionally, it can be used to assess initiatives, products or projects.
The framework is credited to Albert Humphrey, who tested the approach in the 1960s and
1970s at the Stanford Research Institute. Developed for business and based on data from
Fortune 500 companies, the SWOT analysis has been adopted by organizations of all
types as an aid to making decisions.
When and why you should do a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis is often used at the start of or as part of a strategic planning exercise.
The framework is considered a powerful support for decision-making because it enables
an entity to uncover opportunities for success that were previously unarticulated or to
highlight threats before they become overly burdensome. For example, this exercise can
identify a market niche in which a business has a competitive advantage or help
individuals plot career success by pinpointing a path that maximizes their strengths while
alerting them to threats that can thwart achievement.
Elements of a SWOT analysis
As its name states, a SWOT analysis examines four elements:
Strengths: Internal attributes and resources that support a successful outcome.
Weaknesses: Internal attributes and resources that work against a successful outcome.
Opportunities: External factors that the entity can capitalize on or use to its advantage.
Threats: External factors that could jeopardize the entity's success.
A SWOT matrix is often used to organize items identified under each of these four
elements. A SWOT matrix is usually a square divided into four quadrants, with each
quadrant representing one of the specific elements. Decision-makers identify and list
specific strengths in the first quadrant, weaknesses in the next, then opportunities and,
lastly, threats.
Entities undertaking a SWOT analysis can opt to use any one of the various SWOT
analysis templates in existence; these templates are generally variations of the standard
four-quadrant SWOT matrix.
How to do a SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis generally requires decision-makers to first specify the objective they
hope to achieve for the business, organization, initiative or individual.
From there, the decision-makers list the strengths and weaknesses as well as
opportunities and threats.
Various tools exist to guide decision-makers through the process, often using a series of
questions under each of the four elements. For example, decision-makers may be guided
through questions such as "What do you do better than anyone else?" and "What
advantages do you have?" to identify strengths; they may be asked "Where do you need
improvement?” to identify weaknesses. Similarly, they'd run through questions such as
"What market trends could increase sales?" and "Where do your competitors have market
advantages?" to identify opportunities and threats.
Вам также может понравиться
- Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) AnalysisДокумент3 страницыStrengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) AnalysisAngelica BuenaventuraОценок пока нет
- Swot AnalysisДокумент5 страницSwot AnalysisghatgerutuОценок пока нет
- Principle of Marketing Explain What Is SWOT?Документ2 страницыPrinciple of Marketing Explain What Is SWOT?Liana DeanОценок пока нет
- SWOT-AnalysisДокумент4 страницыSWOT-AnalysisMaidhani OjhaОценок пока нет
- Components of SWOT AnalysisДокумент5 страницComponents of SWOT AnalysisstrtdelossantosОценок пока нет
- What Is SWOT AnalysisДокумент2 страницыWhat Is SWOT AnalysistdhdhdjОценок пока нет
- Swot AnalysisДокумент23 страницыSwot AnalysisDevendra SawantОценок пока нет
- Swot AnalysisДокумент16 страницSwot AnalysisRAVI GIRI GOSWAMIОценок пока нет
- Complete SWOT Analysis GuideДокумент12 страницComplete SWOT Analysis GuideBernard GonesoОценок пока нет
- De Leon - Dwight - Ce175-1c - E01 - CW2Документ3 страницыDe Leon - Dwight - Ce175-1c - E01 - CW2Suzuya JuuzouОценок пока нет
- Swot XyzДокумент3 страницыSwot Xyzmohsin_20008896Оценок пока нет
- GROUP-2-Applied-Econ-ReportДокумент57 страницGROUP-2-Applied-Econ-ReportJanrick Matiga NodaloОценок пока нет
- SM Notes (5 Strategy tools)Документ3 страницыSM Notes (5 Strategy tools)nur nashirahОценок пока нет
- EDE AssignmentДокумент13 страницEDE AssignmentPranay ZadeОценок пока нет
- Lecture SWOT Analysis 265Документ7 страницLecture SWOT Analysis 265Sh Mati Elahi100% (1)
- Strategic Planning Project Business: Opportunities, and Threats Involved in AДокумент3 страницыStrategic Planning Project Business: Opportunities, and Threats Involved in ABadder Danbad100% (1)
- Generate Strategies with TOWS MatrixДокумент8 страницGenerate Strategies with TOWS Matrixdhrruv kkОценок пока нет
- On TOWS AnalysisДокумент8 страницOn TOWS Analysisdhrruv kkОценок пока нет
- SWOT Vs TOWSДокумент8 страницSWOT Vs TOWSdhrruv kkОценок пока нет
- History of Swot AnalysisДокумент42 страницыHistory of Swot Analysiscreation toolsОценок пока нет
- What Is A SWOT Analysis?: STRENGTHS-make A List of Your Company's Internal Strengths. These Are Any CompetitiveДокумент5 страницWhat Is A SWOT Analysis?: STRENGTHS-make A List of Your Company's Internal Strengths. These Are Any CompetitiveJoice Ann Delos SantosОценок пока нет
- Mba SWOT Analysis Report PDFДокумент11 страницMba SWOT Analysis Report PDFPrinceОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент12 страницSWOT AnalysisCarmelaОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент49 страницSWOT AnalysisvikasОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент5 страницSWOT Analysisgyugam100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis - Docx 2Документ11 страницSWOT Analysis - Docx 2RD OseñaОценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis: SWOT Analysis (Or SWOT Matrix) Is A Strategic Planning Technique Used To Help A Person orДокумент6 страницSWOT Analysis: SWOT Analysis (Or SWOT Matrix) Is A Strategic Planning Technique Used To Help A Person orАлинаОсадчук-ФердохлебОценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis I-WPS OfficeДокумент11 страницSWOT Analysis I-WPS OfficebrightrexpondaniОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент10 страницSWOT AnalysisDipanjan DasОценок пока нет
- Hoe To Download From ScribdДокумент42 страницыHoe To Download From ScribdSurya ThakurОценок пока нет
- Analysis - SWOT, Porter, PESTELДокумент13 страницAnalysis - SWOT, Porter, PESTELBayram Cahan100% (1)
- SWOT Analysis: Strategic Planning Project BusinessДокумент3 страницыSWOT Analysis: Strategic Planning Project BusinessSruthy R NathОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент3 страницыSWOT AnalysisGeneTearBodgesОценок пока нет
- Swot Analysis TATA MotarДокумент20 страницSwot Analysis TATA Motarkalpesh1956Оценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis 1Документ8 страницSWOT Analysis 1Myint FrancoОценок пока нет
- EnterДокумент8 страницEnterAfomiya ZelalemОценок пока нет
- Internal and External Factors: The Art of War Sun TzuДокумент3 страницыInternal and External Factors: The Art of War Sun Tzumohsin_20008896Оценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis: Rani Durgavati University JabalpurДокумент5 страницSWOT Analysis: Rani Durgavati University JabalpurAnushree BhowareОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент12 страницSWOT AnalysisLalit ThakurОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент16 страницSWOT Analysisrizwansaeed73Оценок пока нет
- Write A Brief Note On SWOT AnalysisДокумент2 страницыWrite A Brief Note On SWOT AnalysisSibtul HassanОценок пока нет
- Swot Analysis ReportДокумент3 страницыSwot Analysis Reportleers mcthorn100% (1)
- Swot & TowsДокумент4 страницыSwot & TowsSumit GaudОценок пока нет
- HUL's Marketing Strategy and Business Plans AnalysisДокумент34 страницыHUL's Marketing Strategy and Business Plans AnalysisAhsan Abdul Rashid KhanОценок пока нет
- SWOT Analysis of Amul Dairy CooperativeДокумент35 страницSWOT Analysis of Amul Dairy CooperativeDilshaad ShaikhОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент13 страницSWOT AnalysisAkshat Kaul100% (2)
- How To Do A SWOT Analysis For Better Strategic PlanningДокумент4 страницыHow To Do A SWOT Analysis For Better Strategic PlanningDatuОценок пока нет
- Strategic Planning Project Business: SWOT Analysis Is AДокумент1 страницаStrategic Planning Project Business: SWOT Analysis Is ANitin GoriОценок пока нет
- Swot Analysis ABCДокумент3 страницыSwot Analysis ABCmohsin_20008896Оценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент53 страницыSWOT Analysisdivjn367% (6)
- Benefits and Limitations of SWOT AnalysisДокумент33 страницыBenefits and Limitations of SWOT AnalysisCoke Aidenry SaludoОценок пока нет
- SWOT AnalysisДокумент7 страницSWOT AnalysisNguyễn Tiến ĐứcОценок пока нет
- Project Strategic Analysis Report FinalДокумент16 страницProject Strategic Analysis Report FinalNimra KarimОценок пока нет
- Term Paper 515Документ8 страницTerm Paper 515toja_hОценок пока нет
- How to Write a SWOT Analysis Company ReportДокумент12 страницHow to Write a SWOT Analysis Company Reportmohammed yaseenОценок пока нет
- Internal and External Factors: Planning Project BusinessДокумент3 страницыInternal and External Factors: Planning Project Businessmohsin_20008896Оценок пока нет
- The SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyОт EverandThe SWOT Analysis: A key tool for developing your business strategyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (10)
- Swot analysis in 4 steps: How to use the SWOT matrix to make a difference in career and businessОт EverandSwot analysis in 4 steps: How to use the SWOT matrix to make a difference in career and businessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- Top Ten Strategic Decision-Making Tools for Operational Excellence: Leadership and Organizational Development Executive Guide SeriesОт EverandTop Ten Strategic Decision-Making Tools for Operational Excellence: Leadership and Organizational Development Executive Guide SeriesОценок пока нет
- Union Tax Saver Scheme Growth Option Direct Plan: H R T y UДокумент1 страницаUnion Tax Saver Scheme Growth Option Direct Plan: H R T y UPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Dissertation Proposal: Title: BackgroundДокумент3 страницыDissertation Proposal: Title: BackgroundPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- M&M's Core Business and Marketing StrategiesДокумент14 страницM&M's Core Business and Marketing StrategiesPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- TDCДокумент1 страницаTDCPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Mean Reversion Is A Strategy Practiced by Many Quantitative Hedge Funds and DayДокумент1 страницаMean Reversion Is A Strategy Practiced by Many Quantitative Hedge Funds and DayPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Dependent Details - PWC SDCДокумент1 страницаDependent Details - PWC SDCPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- ValueДокумент1 страницаValuePoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- ELSS Direct PlanДокумент1 страницаELSS Direct PlanPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Sales Analysis Report On Mahindra & Mahindra and Swaraj Private Ltd. in Nagpur District - 150102638Документ48 страницSales Analysis Report On Mahindra & Mahindra and Swaraj Private Ltd. in Nagpur District - 150102638Poulami Ghosh0% (1)
- IG Azar: Analyzing & Interpreting Brand Positioning ofДокумент12 страницIG Azar: Analyzing & Interpreting Brand Positioning ofPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Employment Application Form (V5)Документ6 страницEmployment Application Form (V5)Poulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Moving AvgДокумент3 страницыMoving AvgPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Sub: Application For Grade Improvement Examinations/Make-Up/ Re Examination (Term III) (Batch 2017-19) (Tick Whichever Is Applicable)Документ1 страницаSub: Application For Grade Improvement Examinations/Make-Up/ Re Examination (Term III) (Batch 2017-19) (Tick Whichever Is Applicable)Poulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Understanding the McKinsey 7s Model Strategic Planning ToolДокумент1 страницаUnderstanding the McKinsey 7s Model Strategic Planning ToolPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Case 3Документ1 страницаCase 3Poulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Country Name-Thailand: Land BoundariesДокумент6 страницCountry Name-Thailand: Land BoundariesPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Poulami GhoshДокумент3 страницыPoulami GhoshPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Air Asia - Case AnalysisДокумент8 страницAir Asia - Case AnalysisPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Macro ReportДокумент10 страницMacro ReportPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Pricing 1Документ2 страницыPricing 1Poulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Ball CROP performance management caseДокумент1 страницаBall CROP performance management casePoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Public Private Partnership in Infrastructure, Agriculture and Skillset Training Could Work Wonders For India's EconomyДокумент3 страницыPublic Private Partnership in Infrastructure, Agriculture and Skillset Training Could Work Wonders For India's EconomyPoulami GhoshОценок пока нет
- Retail ManagementДокумент40 страницRetail Managementij 1009Оценок пока нет
- Chapter (1) The Accounting EquationДокумент46 страницChapter (1) The Accounting Equationtunlinoo.067433100% (3)
- Salary Slip (70015409 February, 2023)Документ1 страницаSalary Slip (70015409 February, 2023)حامدولیОценок пока нет
- EtopДокумент11 страницEtopMohamed AadhilОценок пока нет
- Mexican Steel 2006 - Consolidation & Growth: AMM ConferencesДокумент4 страницыMexican Steel 2006 - Consolidation & Growth: AMM ConferencespdiconpОценок пока нет
- Presented To: Sir Safdar Hussain Tahir By: M. Fahad Ali G.C. Uni. FaisalabadДокумент18 страницPresented To: Sir Safdar Hussain Tahir By: M. Fahad Ali G.C. Uni. FaisalabadFahad AliОценок пока нет
- The Optimal Choice of Index-Linked Gics: Some Canadian EvidenceДокумент14 страницThe Optimal Choice of Index-Linked Gics: Some Canadian EvidenceKevin DiebaОценок пока нет
- Final Individual Proposal - GelatissimoДокумент12 страницFinal Individual Proposal - Gelatissimoapi-521941371Оценок пока нет
- Cash Cash Equivalents Reviewer2Документ9 страницCash Cash Equivalents Reviewer2anor.aquino.upОценок пока нет
- Valuation of BondsДокумент7 страницValuation of BondsHannah Louise Gutang PortilloОценок пока нет
- Report On Non Performing Assets of BankДокумент53 страницыReport On Non Performing Assets of Bankhemali chovatiya75% (4)
- Profits and Gains of Business or ProfessionДокумент13 страницProfits and Gains of Business or Professionajaykumar0011100% (2)
- A Globalization and Public AdministrationДокумент15 страницA Globalization and Public AdministrationsemarangОценок пока нет
- Organizational Culture in 40 CharactersДокумент18 страницOrganizational Culture in 40 CharactersParva ChandaranaОценок пока нет
- Bio Pharma Case StudyДокумент2 страницыBio Pharma Case StudyAshish Shadija100% (2)
- ABC PracticeДокумент5 страницABC PracticeAbhijit AshОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For International Economics 9tДокумент12 страницTest Bank For International Economics 9tGisha100% (2)
- Presentation 6Документ14 страницPresentation 6Akshay MathurОценок пока нет
- Road MapДокумент40 страницRoad MapAdhe IdhiОценок пока нет
- Capital Intensive Labor Intensive: Required: Determine The FollowingДокумент2 страницыCapital Intensive Labor Intensive: Required: Determine The FollowingMahediОценок пока нет
- of OlayДокумент14 страницof OlaySneha KhapardeОценок пока нет
- Global Family Offices SampleДокумент13 страницGlobal Family Offices Sampledsrkim100% (1)
- Emkay LEAD PMS - JULY 2019Документ17 страницEmkay LEAD PMS - JULY 2019speedenquiryОценок пока нет
- ECO 120 Principles of Economics: Chapter 2: Theory of DEMAND and SupplyДокумент30 страницECO 120 Principles of Economics: Chapter 2: Theory of DEMAND and Supplyizah893640Оценок пока нет
- Disputes in Islamic Banking: Case of Bai Bithaman Ajil (BBA) in MalaysiaДокумент18 страницDisputes in Islamic Banking: Case of Bai Bithaman Ajil (BBA) in MalaysiagivamathanОценок пока нет
- Organigrama Ypfb 20180208Документ1 страницаOrganigrama Ypfb 20180208Ana PGОценок пока нет
- Aguila, Paulo Timothy - Cis c10Документ5 страницAguila, Paulo Timothy - Cis c10Paulo Timothy AguilaОценок пока нет
- Rural Urban MigrationДокумент42 страницыRural Urban MigrationSabitha Ansif100% (1)
- Cost Estimation ProcurementДокумент21 страницаCost Estimation ProcurementEng-Ahmed BaasaayОценок пока нет
- An Evaluation of The Customers' Satisfaction of Social Islami Bank Limited: A Study On Savar Branch Submitted ToДокумент44 страницыAn Evaluation of The Customers' Satisfaction of Social Islami Bank Limited: A Study On Savar Branch Submitted ToHafiz Al AsadОценок пока нет