Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
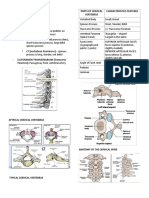
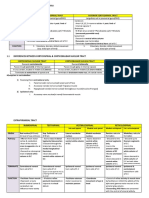
C1 Atlas C2 Axis C3 - C6 Typical Cervical Vertebra C7 Vertebra Prominens
Загружено:
miallyannaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
C1 Atlas C2 Axis C3 - C6 Typical Cervical Vertebra C7 Vertebra Prominens
Загружено:
miallyannaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
C1 C2 C3 – C6 C7
Atlas Axis Typical Cervical Vertebra Vertebra Prominens
Body No body Vertical projection ODONTOID Anterior part Wider than deep
PROCESS (DENS) represents the More massive, roughly cylindrical
body of C1 fused with body of C2 Small and broad from side to side
Vertebral Has an anterior and posterior arch PEDICLES: cylindrical; forms the sides of the
Arch ring-shaped bone arch
VERTEBRAL NOTCH
- Notch on the upper and lower border of
the pedicles
- Formed by the projection of the body
anteriorly and the articulating process
posteriorly
LAMINAE: flattened; completes the arch
posteriorly
Vertebral Large Large, triangular Walls: Vertebral Arch + Posterior Surface of Triangular
Foramen Vertebral Foramen
VERTEBRAL CANAL
- Formed by the succession of vertebral
foramina
- Contains the spinal cord, roots of the
spinal nerves, meninges, fat, and
associated vessels
Spinous No spinous process Largest of cervical region, bifid Small, bifid Longest; not bifid
Process
Transverse Short projection Form the ANTERIOR and FORAMEN TRANSVERSARIUM Large
Process POSTERIOR TUBERCLES transmits vertebral artery (C1-C6) and
vertebral vein (C7: only small accessory Foramen Transversarium is small
vertebral veins) transmits vertebral vein or small
accessory veins (could be empty)
ANTERIOR and POSTERIOR TUBERCLES
Bones of the Vertebral Column
By: FERNANDEZ MA
Articular Superior Articular Process: facets Superior Articular Process: facets flat to Superior Articular Process: facets face posteriorly and superiorly
Process concave, face generally superiorly slightly convex, face generally
superiorly Inferior Articular Process: facets face anteriorly and inferiorly (in C7: transitions to
Inferior Articular Process: facets flat typical thoracic vertebrae)
to slightly concave, face generally Inferior Articular Process: facets flat,
inferiorly face anteriorly and inferiorly
Articulations Upper (Superior Part): ATLANTO- Upper (Superior Part):
OCCIPITAL JOINT lateral mass ATLANTOAXIAL JOINT
on each side for articulation with the articulation with C1/Atlas
occipital condyles
Lower (Inferior Part):
ATLANTOAXIAL JOINT
articulation with C2/Axis
Other Atypical cervical vertebra Atypical cervical vertebra Atypical Cervical Vertebra
notable
characteristi Palpable at the back of the neck
cs (“prominens”)
Movements - Flexion: Longus cervicis, scalenus anterior, sternocleidomastoid
of the - Extension: Postovertebral muscles
Vertebral - Lateral Flexion: Scalenus anterior & medius, Trapezius, Sternocleidomastoid
Column - Rotation: Sternocleidomastoid, Splenius
Bones of the Vertebral Column
By: FERNANDEZ MA
T1-T12 L1-L5 S1-S5
Coccyx
Typical Thoracic Vertebra Typical Lumbar Vertebra Sacrum
Body Medium-sized Massive to support great amounts
of weight
Heart-shaped
Kidney-shaped (superior view)
COSTAL FACETS (1 or 2)
articulation with the head of the rib
Vertebral PEDICLES: strong, directed backward
Arch
LAMINAE: short in a vertical direction
Vertebral Circular, smaller than those of Triangular Forms the SACRAL CANAL contains the Vertebral Canal ends at the 1st
Foramen cervical and lumbar vertebrae anterior and posterior roots of the sacral and Coccyx
Larger than in thoracic vertebrae, coccygeal spinal nerves, filum terminale, and
smaller than in cervical vertebrae fibrofatty material; contains the lower part of
the subarachnoid space
Spinous Long, curves posteroinferiorly Short, flat, quadrangular (hatchet- Fused, rudimentary MEDIAN SACRAL
Process shaped), projected posteriorly CREST (1)
Tips extend to the level of vertebral
body below
Transverse Long, strong for muscle Long, slender Fused tips of transverse process
Process attachment LATERAL SACRAL CRESTS (2)
Accessory process on posterior surface
T1 – T10 facets for articulation of base of each process
with the tubercle of the rib
Articular Superior Articular Process: facets Superior Articular Process: facets face Fused INTERMEDIATE SACRAL Rudimentary (in Co1)
Process face posteriorly and laterally medially CRESTS (2) COCCYGEAL CORNUA articulate
with Sacral Cornua
Inferior Articular Process: facets face *Mamillary Process: on posterior Inferior articular process of S5 project
anteriorly and medially surface of each superior articular inferiorly on each side of the sacral hiatus
*T12: faces laterally process SACRAL CORNUA
Inferior Articular Process: facets face
laterally
Articulations Through the: Superior border: BASE articulates with L5
COSTAL FACETS
Found in the transverse process Inferior border: APEX articulates with
articulation with the tubercle of the rib coccyx
Bones of the Vertebral Column
By: FERNANDEZ MA
Found in the vertebral body Laterally: Sacroiliac Joints 2 iliac bones
articulation with the head of the rib
Other Largest: L5 (bears the weight of the Five rudimentary vertebrae fused together to Four vertebrae fused together to form
notable whole body form a wedge-shaped bone a single, small, triangular bone
characteristi
cs SURFACES Last 3 are completely fused together;
Four (4) Foramina on each sides 1st coccygeal bone is either fused or
passage of anterior and posterior rami of the incompletely fused with the 2nd bone
upper 4 sacral nerves
Exists until 8th week of fetal life;
Anterior/Pelvic Surface vestigial
- smooth and concave
- 4 transverse lines fusion of sacral
vertebrae
Posterior/Dorsal Surface
- rough and convex
- 5 longitudinal ridges:
Median Sacral Crest (1)
Intermediate Sacral Crest (2)
Lateral Sacral Crest (2)
- SACRAL HIATUS: results from the
absence of the laminae and spinous
process of S5 (and S4) does not meet
at the midline
- SACRAL CORNUA
Movements - Rotation: Unilateral contraction of - Flexion: Rectus abdominis, psoas
of the semispinalis & rotatores muscle, - Extension: Postvertebral muscles
Vertebral assisted by oblique muscles of - Lateral Flexion: Postvertebral
Column abdominal wall muscles, quadratus lumborum,
oblique muscles of anterolateral
No flexion & extension, no lateral abdominal wall, psoas
flexion - Rotation: Rotatores muscle,
oblique muscles of anterolateral
abdominal wall
Bones of the Vertebral Column
By: FERNANDEZ MA
Вам также может понравиться
- Nasm FlashcardsДокумент172 страницыNasm FlashcardsHilde Camp100% (3)
- Back Spine AnatomyДокумент3 страницыBack Spine AnatomyNinjaОценок пока нет
- Road Traffic SignsДокумент40 страницRoad Traffic SignsRonald McRonaldОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Judo Grappling TechniquesДокумент220 страницDynamic Judo Grappling TechniquesJuan Jose Opazo Carvajal100% (10)
- Carbohydrate MetabolismДокумент15 страницCarbohydrate Metabolismmiallyanna100% (2)
- Stew Smith's 3-5 Mile Run ProgramДокумент15 страницStew Smith's 3-5 Mile Run Programiiiu87y7Оценок пока нет
- Doh Noh 2017-2022Документ170 страницDoh Noh 2017-2022Alvin Cloyd Dakis, MHSS, RN, CGDP100% (3)
- Lower Leg Anatomy: Volume 0%Документ14 страницLower Leg Anatomy: Volume 0%zenik kusrini100% (1)
- Visual PathwayДокумент24 страницыVisual PathwayAkshara Eye FoundationОценок пока нет
- Lower Back PainsДокумент35 страницLower Back PainsMary Les RN100% (1)
- Cervical VertebraeДокумент70 страницCervical VertebraeMahnoor malikОценок пока нет
- Cervical Spine Proto GihДокумент8 страницCervical Spine Proto GihAndy Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- Two Mechanisms of Hypertensive NephrosclerosisДокумент2 страницыTwo Mechanisms of Hypertensive NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Anatomy of the Cervical SpineДокумент31 страницаAnatomy of the Cervical SpinehdthhhhОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Cervical SpineДокумент29 страницAnatomy of Cervical SpineManiОценок пока нет
- Spine Anatomy and Pathology GuideДокумент22 страницыSpine Anatomy and Pathology GuideCris Soliven DucosОценок пока нет
- Joints and Ligaments of The Skull and Neck-2Документ79 страницJoints and Ligaments of The Skull and Neck-2armanious64Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy of the Spine: Regions, Curves, and StructuresДокумент72 страницыAnatomy of the Spine: Regions, Curves, and StructuresMohammad Riedho Cahya AtazsuОценок пока нет
- Referat Carpal Tunnel SyndromeДокумент25 страницReferat Carpal Tunnel Syndromegede andreasОценок пока нет
- Axial Anatomy: AY 2019-2020 Dr. Paredes Aug. 27, 2019Документ11 страницAxial Anatomy: AY 2019-2020 Dr. Paredes Aug. 27, 2019Jose Emmanuel DolorОценок пока нет
- Vertebral Column: Nicole M. Reeves, Ph.D. Department of AnatomyДокумент58 страницVertebral Column: Nicole M. Reeves, Ph.D. Department of Anatomykrishna gОценок пока нет
- Back - Spine (Chapter 12)Документ9 страницBack - Spine (Chapter 12)Alenna BenitezОценок пока нет
- GA&E 5 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIIДокумент51 страницаGA&E 5 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIISu ZikaiОценок пока нет
- Vertebral Column and Contents of The Vertebral CanalДокумент6 страницVertebral Column and Contents of The Vertebral CanalCay KaiОценок пока нет
- 09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFДокумент24 страницы09:16 - Back & Spinal Cord PDFVidya BalaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2: The Boney Skeleton: Chapter 7 and 8Документ59 страницLecture 2: The Boney Skeleton: Chapter 7 and 8lemonОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of SpineДокумент33 страницыAnatomy of SpineMaria RobertaОценок пока нет
- Workshop 9 - Pre-Workshop and Workshop Slides - Student Version T2Документ21 страницаWorkshop 9 - Pre-Workshop and Workshop Slides - Student Version T2Thanh ThảoОценок пока нет
- The ThoraxДокумент16 страницThe ThoraxRosinah M KekanaОценок пока нет
- (849-853) Component PartsДокумент5 страниц(849-853) Component PartsMỉm CườiОценок пока нет
- Anaphy Skeletalsystem Backregion (Reviewer)Документ16 страницAnaphy Skeletalsystem Backregion (Reviewer)KaiОценок пока нет
- Vertebral Column and ContentsДокумент5 страницVertebral Column and ContentsJewelОценок пока нет
- Tema 04 - Columna VertebralДокумент18 страницTema 04 - Columna VertebralzulemaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy From The DoctorДокумент208 страницAnatomy From The DoctorSweet manОценок пока нет
- THORAXДокумент27 страницTHORAXOleashedОценок пока нет
- Anatomical Terminology GuideДокумент57 страницAnatomical Terminology GuideAlicina DaleОценок пока нет
- Bones and Joints of TrunkДокумент56 страницBones and Joints of Trunkapi-196413370% (1)
- VERTEBRAEДокумент3 страницыVERTEBRAEstaceytuando10Оценок пока нет
- SkeletonДокумент38 страницSkeletonLal PereraОценок пока нет
- Thorax 1Документ109 страницThorax 1Insyirah JohariОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Vertebral ColumnДокумент28 страницAnatomy of The Vertebral Columnsohailahmadinew786Оценок пока нет
- Deep Back Musculature ChartДокумент2 страницыDeep Back Musculature ChartTrisha HaОценок пока нет
- Lower Extremity Anatomy: Sari Tri Yulianti, S.FT., M.BiomedДокумент73 страницыLower Extremity Anatomy: Sari Tri Yulianti, S.FT., M.BiomedDindaОценок пока нет
- X Ray NormalДокумент19 страницX Ray NormalSean OoiОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Spinal Anatomy: Spine Made Up FromДокумент13 страницIntroduction To Spinal Anatomy: Spine Made Up Fromh_sadeghiОценок пока нет
- Anatomi Lagi Dikit JadiДокумент6 страницAnatomi Lagi Dikit JadiGodwin AnandaОценок пока нет
- Appendicular Skeleton 1-1Документ117 страницAppendicular Skeleton 1-1Anania EmmanuelОценок пока нет
- 2 System Musculo Sceletal 2014Документ41 страница2 System Musculo Sceletal 2014leni sharaОценок пока нет
- VertebraeДокумент32 страницыVertebraeThor ManlangitОценок пока нет
- Digital Anatomy LessonДокумент39 страницDigital Anatomy LessonkimОценок пока нет
- Lab 7 Pectoral Girdle 2Документ4 страницыLab 7 Pectoral Girdle 2Bechris BambiОценок пока нет
- Vertebral Column of DogДокумент3 страницыVertebral Column of DogEmit Rosary PenetranteОценок пока нет
- Lec.2 H&N Anatomy, BuraqДокумент55 страницLec.2 H&N Anatomy, BuraqAkramОценок пока нет
- Gen Anat 3Документ8 страницGen Anat 3ALIYAAHNICOLE SERNAОценок пока нет
- Notes - Part 3Документ8 страницNotes - Part 3ALIYAAHNICOLE SERNAОценок пока нет
- تشريح نظري م 4 غير مترجمةДокумент9 страницتشريح نظري م 4 غير مترجمةبايОценок пока нет
- Praktikum Anatomi VI: Axial SkeletonДокумент50 страницPraktikum Anatomi VI: Axial SkeletonAdhya TiaraОценок пока нет
- BIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Документ7 страницBIO 1133 Exercise 7 (Skeletal System of The Frog)Tonet LapeОценок пока нет
- Table 2.1 Cervical Vertebrae: LargeДокумент14 страницTable 2.1 Cervical Vertebrae: LargeReham QueОценок пока нет
- Table of Back Muscles RWДокумент3 страницыTable of Back Muscles RWFrank Zhang100% (1)
- Table - Comparative AnatДокумент13 страницTable - Comparative Anatthtu.sint.swuОценок пока нет
- Table Descending TractДокумент3 страницыTable Descending TractirfanzukriОценок пока нет
- Root of The Neck (Gross)Документ21 страницаRoot of The Neck (Gross)Kimsha ConcepcionОценок пока нет
- Types of VertebraДокумент2 страницыTypes of VertebramtangcaaОценок пока нет
- Bones of the Lower Limb: Hip, Thigh, Leg & FootДокумент9 страницBones of the Lower Limb: Hip, Thigh, Leg & FootffОценок пока нет
- The Human SkeletonДокумент71 страницаThe Human Skeletontszkin13527Оценок пока нет
- Orca Share Media1571800842460Документ27 страницOrca Share Media1571800842460Reniel De MesaОценок пока нет
- BAT Notes - 2017 For 2018Документ1 387 страницBAT Notes - 2017 For 2018Nadun MethwadaneОценок пока нет
- 01.pelvic Wall and FloorДокумент25 страниц01.pelvic Wall and FloorYara HaniОценок пока нет
- Guidelines TBC TerbaruДокумент160 страницGuidelines TBC TerbaruSutoto MoeljadiОценок пока нет
- ToxoplasmosisДокумент7 страницToxoplasmosisEgha Ratu EdoОценок пока нет
- Testicular TumorsДокумент8 страницTesticular TumorsmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Disruption of Nerves Coordinating Bowel Peristalsis Lab FindingsДокумент1 страницаDisruption of Nerves Coordinating Bowel Peristalsis Lab FindingsmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Second Long Exam Coverage of Descriptive and Analytical Study DesignsДокумент5 страницSecond Long Exam Coverage of Descriptive and Analytical Study DesignsmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Dot Grid PrintableДокумент1 страницаDot Grid PrintablemiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Lead Poisoning and Recurrent Abdominal Pain: Case ReportДокумент3 страницыLead Poisoning and Recurrent Abdominal Pain: Case ReportmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Inspiration Hut - 0.5Cm GridДокумент1 страницаInspiration Hut - 0.5Cm GridMilrosePaulinePascuaGudaОценок пока нет
- Metaanalysis Donation OrganДокумент10 страницMetaanalysis Donation OrganmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- 2017 Philippine NDHS Key Findings PDFДокумент49 страниц2017 Philippine NDHS Key Findings PDFHumanRights_PhОценок пока нет
- Care of The Hospitalized Patient With Acute Exacerbation of CopdДокумент25 страницCare of The Hospitalized Patient With Acute Exacerbation of CopdmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Using Wellbeing For Public Policy: Theory, Measurement, and RecommendationsДокумент35 страницUsing Wellbeing For Public Policy: Theory, Measurement, and RecommendationsmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Respi HarrisonДокумент10 страницRespi HarrisonmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Help-Seeking BehaviorДокумент6 страницHelp-Seeking BehaviormiallyannaОценок пока нет
- (Updated) PH.151 Trans Supplement AcronymsДокумент1 страница(Updated) PH.151 Trans Supplement AcronymsmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Game of Thrones (Literary Committee) : Specialized Committees - 2014EДокумент21 страницаGame of Thrones (Literary Committee) : Specialized Committees - 2014EmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Use of Colloids in MedicineДокумент150 страницUse of Colloids in MedicineThomas LeechОценок пока нет
- True vs False LaborДокумент2 страницыTrue vs False LabormiallyannaОценок пока нет
- WHO EINC PracticesДокумент2 страницыWHO EINC PracticesAllan NacinoОценок пока нет
- Group3 PH131 TheMusculoskeletalSystemandAging FWRДокумент15 страницGroup3 PH131 TheMusculoskeletalSystemandAging FWRmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Why Bears Have Short TailsДокумент1 страницаWhy Bears Have Short TailsmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- Musculoskeletal AgeingДокумент82 страницыMusculoskeletal Ageingmiallyanna100% (1)
- Gra-GO™: Rafaelo Paolo A. Fernandez Grade 7 - Valdocco General Technology Tr. MiggyДокумент2 страницыGra-GO™: Rafaelo Paolo A. Fernandez Grade 7 - Valdocco General Technology Tr. MiggymiallyannaОценок пока нет
- General Microbiology Fact SheetsДокумент5 страницGeneral Microbiology Fact Sheetswiranchana-na3014Оценок пока нет
- Group 2 LIPIDS Formal Written ReportДокумент7 страницGroup 2 LIPIDS Formal Written ReportmiallyannaОценок пока нет
- 151 Notes2ndExamДокумент5 страниц151 Notes2ndExammiallyannaОценок пока нет
- VUMC Facial Trauma Practice Management GuidelinesДокумент1 страницаVUMC Facial Trauma Practice Management GuidelinesIndra D KristionoОценок пока нет
- Osteology of The Lower ExtremityДокумент29 страницOsteology of The Lower ExtremityIELTSОценок пока нет
- 1advances in Occlusion Anterior GuidanceДокумент29 страниц1advances in Occlusion Anterior GuidanceSalem RawashdahОценок пока нет
- Gluteal and Thigh Muscle FunctionsДокумент5 страницGluteal and Thigh Muscle FunctionsrkdcelОценок пока нет
- Direct Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Adults - UpToDateДокумент74 страницыDirect Laryngoscopy and Endotracheal Intubation in Adults - UpToDateJorge Luis VanegasОценок пока нет
- PNF Techniques in The Upper ExtremityДокумент27 страницPNF Techniques in The Upper ExtremitysanalcrazyОценок пока нет
- Physical Fitness GuideДокумент9 страницPhysical Fitness GuidePaulyn Jhoy FajardoОценок пока нет
- Yoga and Breathing: Muscles Work TogetherДокумент2 страницыYoga and Breathing: Muscles Work Togethervksk1951Оценок пока нет
- Posterior Rhinoscopy by DR Meenesh JuvekarДокумент2 страницыPosterior Rhinoscopy by DR Meenesh JuvekarlguleОценок пока нет
- Histology DigestiveДокумент87 страницHistology DigestiveAnang Yanuar RamadhanОценок пока нет
- CH 15Документ26 страницCH 15Mohd Khairidzman BoeranОценок пока нет
- Muscular SystemДокумент41 страницаMuscular SystemGem Rose UretaОценок пока нет
- Chinese-Medical Terminology 33023 PDFДокумент1 страницаChinese-Medical Terminology 33023 PDFYS NateОценок пока нет
- 06a - Introduction To Spinal Cord - NeuroanatomyДокумент9 страниц06a - Introduction To Spinal Cord - Neuroanatomyhiba jasimОценок пока нет
- The Wrist ComplexДокумент35 страницThe Wrist ComplexKeshav Singhmaar AryaОценок пока нет
- NIKE-The Program DefenceДокумент20 страницNIKE-The Program DefenceCharlotteEngОценок пока нет
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsДокумент29 страницEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum Marie50% (2)
- Penegakan Diagnosis Dan Penanggulangan Cervicalys Herniated: Nucleus PulposusДокумент12 страницPenegakan Diagnosis Dan Penanggulangan Cervicalys Herniated: Nucleus PulposusMuhammad Rizki Mardiansyah MardiansyahОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and PhysiologyДокумент17 страницAnatomy and PhysiologychardiginОценок пока нет
- The Difficult or Failed Airway: Pat Melanson, MDДокумент28 страницThe Difficult or Failed Airway: Pat Melanson, MDMinorC3Оценок пока нет
- Passive Versus Active Theories of SleepДокумент5 страницPassive Versus Active Theories of Sleepغسن سمن المدنОценок пока нет
- Boundless Anatomy and Physiology: Overview of the Urinary SystemДокумент3 страницыBoundless Anatomy and Physiology: Overview of the Urinary Systemor1da2sa3Оценок пока нет