Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CSE209 Document2
Загружено:
saluesИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CSE209 Document2
Загружено:
saluesАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka- 1000, Bangladesh
Phone: +880-2-9665650/7104 Fax: +880-2-9665612 Web: www.buet.ac.bd/cse
CSE 209
Digital Electronics and Pulse Technique
Date: April 27, 2008
Microelectronics- Jacob Millman
Chapter 5
Syllabus:
o Section: 5-2, 5-3, 5-4, 5-8, 5-9 (up to pg. 143), 5-11, 5-12, (up to pg. 151), 5-13, 5-14
(up to pg. 160 excluding fan-out).
Short Questions:
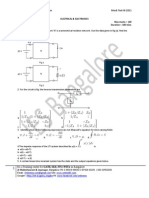
1. What do you mean by Negative logic and Positive logic?
2. Why R is chosen much larger than Rs in Fig. 5-3?
3. Explain how a negative logic OR gate is the same circuit as a positive AND gate?
4. What happens if the VR is larger than V(1) in Fig. 5-5(b)?
5. What happens in circuit of Fig. 5-5(b) if not all the inputs have the same upper
level V(1) ?
6. In designing transistor inverters like Fig. 5-7 what are the 3 transistor limitations?
(Learn specially the 3rd point in pg. 132).
7. Why the capacitor C1 is added in Fig. 5-14?
8. Define NM(0) and NM(1).
9. What is the significance of D2 in Fig. 5-18?
10. Why there is a limit in fan-out for the circuit in Fig. 5-18?
11. Why TTL has a low storage time (Fig. 5-21)?
12. What are the functions of input clamping diodes in Fig. 5-21?
13. Can TTL gate outputs be wire AND-ed? What is the problem when done so? What
is the solution? (Fig. 5-22)
14. Argument in favor of making Rc larger and smaller in Fig. 5-21?
15. What is the historical significance of totem-pole? How it is related to Fig. 5-23?
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka- 1000, Bangladesh
Phone: +880-2-9665650/7104 Fax: +880-2-9665612 Web: www.buet.ac.bd/cse
16. Which transistor is called ‘Phase Splitter’ and why in Fig. 5-23?
17. Explain the behavior of ‘Source transistor’ in Fig. 5-23 when the output changes
from V(0) to V(1). (Describe how it turns ON, saturates and then goes OFF after
making the CL charged).
18. Why can’t we completely eliminate 100 ohm resistor in Fig. 5-23?
19. Can Totem-pole outputs be wire AND-ed? (pg. 151)
20. What can be said about the V(1) of Fig. 5-25? Eliminating 450 ohm resistors from
the circuit can solve this problem, but what is the disadvantage of this new circuit?
21. Write down the advantages and disadvantages of DCTL.
22. Why Q5 and Q6 are added in Fig. 5-29 although Fig. 5-28 works as ECL OR/NOR
gate?
23. Write down the advantages and disadvantages of ECL.
Mathematical Problems:
o Example: 5-1, 5-3, 5-5, 5-7
o Exercise: 5-36, 5-38, 5-41, 5-42, 5-43, 5-56
Microelectronics- Jacob Millman
Chapter 8
Syllabus:
o Section: 8-8, 8-9 ( up to Fig. 8-27 of pg. 265)
Short Questions:
1. Remember the two characteristics equations of MOS. There could be very simple
mathematical problems based on it.
2. Why MOS is better than BJT? Advantage/disadvantage of MOS devises.
3. Why NMOS is better than PMOS?
4. Given truth table/function draw the circuit using only NMOS.
5. Given a circuit drawn with NMOS, write down the function it realizes.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka- 1000, Bangladesh
Phone: +880-2-9665650/7104 Fax: +880-2-9665612 Web: www.buet.ac.bd/cse
6. Explain the circuit diagram of bi-stable latch. (Fig. 8-24). [memorize this circuit
please]
7. Given truth table/function draw the circuit using CMOS.
8. Given a circuit drawn with CMOS, write down the function it realizes.
Microelectronics- Jacob Millman
Chapter 9
Syllabus:
o Section: 9.6, 9.7 (up to pg. 293 excluding Four MOSFET Dynamic RAM Cell)
Short Questions:
1. What is linear addressing scheme?
2. What is 2D addressing? Compare it with liner addressing.
3. Draw the basic RAM organization. (Fig. 9-18 + Table 9-2)
4. Expanding memory: practice all versions that were discussed in 13th week.
5. Explain read/write operations of static MOS RAM. (Fig. 9-20, memorize this circuit
please)
Digital Integrated Electronics- Taub/Schilling
Chapter 14
Syllabus:
o Section: 14.5, 14.6, 14.12 (up to pg. 518),
Short Questions:
1. Prove equation 14.5-4, 14.5-6
2. What is the advantage of using OPAMP in Fig. 14.5-3?
3. What are the disadvantages of weighted-resistor D/A converter?
4. Finding the contribution of some input in R-2R ladder circuit. (Say, in Fig. 14.6-1
or 14.6-2, S0 = S2=S3=0, S1=1 etc.)
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology, Dhaka- 1000, Bangladesh
Phone: +880-2-9665650/7104 Fax: +880-2-9665612 Web: www.buet.ac.bd/cse
5. Compute the value of r (in Fig. 14.6-3) for binary input format.
6. Compute the value of r (in Fig. 14.6-3) for BCD input format.
7. What do you mean by quantization error while A/D conversion?
8. Why the end registers in circuit 14.12-1 are R/2 whereas rests are R?
9. Explain a 2 bit parallel comparator type A/D converter.
Some tips/guidelines for final exam:
1. Do not write much in your answer script. Answer precisely.
2. Use sharp pencils for drawing.
3. Keep margins.
4. Answer all sub-questions of a question together. (If you have started question 1,
then answer 1(a), 1(b), 1(c) together, if possible serially.)
5. Start answering questions always at the start of a new page.
6. At the end of answering a mathematical problem, list the result(s) in a tabular
format.
7. Never take exams seriously.
S. M. Shahriar Nirjon
Lecturer,
Dept. of CSE, BUET.
email: nirjon@cse.buet.ac.bd
Вам также может понравиться
- Microsoft PowerPoint - ASEP - NSCP 2015 Chapter6 - WOODДокумент75 страницMicrosoft PowerPoint - ASEP - NSCP 2015 Chapter6 - WOODRay Ramilo67% (9)
- Mathematics for Electrical Engineering and ComputingОт EverandMathematics for Electrical Engineering and ComputingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (6)
- Part Submission ChecklistДокумент8 страницPart Submission ChecklistGeovanny HernándezОценок пока нет
- NSX Battle Card - FinalДокумент2 страницыNSX Battle Card - FinalElias Bezulle100% (1)
- Lesson Plan - Revit Intro Lesson OverviewДокумент56 страницLesson Plan - Revit Intro Lesson Overviewlingga123Оценок пока нет
- Fisher™ FIELDVUE™ DVC6200 SIS Digital Valve ControllerДокумент116 страницFisher™ FIELDVUE™ DVC6200 SIS Digital Valve ControllerMohsen HeidariОценок пока нет
- Example Pump CalcsДокумент4 страницыExample Pump CalcsSourav ChattopadhyayОценок пока нет
- L11-Leak Off Test, Kick Tolerance & Kick Circulation MethodsДокумент45 страницL11-Leak Off Test, Kick Tolerance & Kick Circulation MethodsLaxmi Kant PrasadОценок пока нет
- SRI FireFighting Equipments 2012 PDFДокумент46 страницSRI FireFighting Equipments 2012 PDFsullamsОценок пока нет
- Expt - 9 - R-2R Ladder DAC - 20-21Документ11 страницExpt - 9 - R-2R Ladder DAC - 20-21Noh NaimОценок пока нет
- Math 1030 Working in The YardДокумент4 страницыMath 1030 Working in The Yardapi-313345556Оценок пока нет
- ArChine-Food-Grade-Lubricants - eДокумент53 страницыArChine-Food-Grade-Lubricants - enghiaОценок пока нет
- Electrical Machines - IДокумент6 страницElectrical Machines - IRavichandran SekarОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsДокумент2 страницыGujarat Technological University: InstructionsPritesh SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 - B SecДокумент2 страницыAssignment 1 - B SecB17Manoj MRОценок пока нет
- Preliminary Q Paper BXEДокумент1 страницаPreliminary Q Paper BXEamit_k25Оценок пока нет
- Rr320405 Vlsi DesignДокумент6 страницRr320405 Vlsi DesignSrinivasa Rao GОценок пока нет
- Polytechnic of Namibia: M Ark Moderated M Ark Exam Ine RsДокумент3 страницыPolytechnic of Namibia: M Ark Moderated M Ark Exam Ine Rsmoses kakwenaОценок пока нет
- Eete 10073 Midterm Exam Deet 2 1Документ3 страницыEete 10073 Midterm Exam Deet 2 1Robert ApiladoОценок пока нет
- Mock Gate III (Eee 2012)Документ13 страницMock Gate III (Eee 2012)Sree EesavoinaОценок пока нет
- EEE 332 Summer 2021 Mid PoorДокумент9 страницEEE 332 Summer 2021 Mid PoorAli AshrafОценок пока нет
- Reg - No: S. Veerasamy Chettiar College of Engineering and TechnologyДокумент2 страницыReg - No: S. Veerasamy Chettiar College of Engineering and TechnologykrishnandrkОценок пока нет
- SODCДокумент1 страницаSODCpravin2275767Оценок пока нет
- Vlsi Internal Question Paper Mtech.Документ5 страницVlsi Internal Question Paper Mtech.Vinay ReddyОценок пока нет
- EE 431 Final Exam (15.09.21) - QuestionsДокумент3 страницыEE 431 Final Exam (15.09.21) - QuestionsKhaled alamssiОценок пока нет
- M.E Vlsi CY 1 QusДокумент6 страницM.E Vlsi CY 1 QusAkilandeswari SwaminathanОценок пока нет
- Expt9dicl1813086 PDFДокумент11 страницExpt9dicl1813086 PDFNoh NaimОценок пока нет
- Adic Assignment - 4 Without WMДокумент3 страницыAdic Assignment - 4 Without WMMATHANKUMAR.SОценок пока нет
- UEC750Документ1 страницаUEC750Shivam SharmaОценок пока нет
- Shweta DTE MicroДокумент15 страницShweta DTE MicroayushОценок пока нет
- PMMD Final Sem 2019-2020Документ2 страницыPMMD Final Sem 2019-20202019ht80591Оценок пока нет
- Assignment No. 6Документ3 страницыAssignment No. 6aditya nagrajanОценок пока нет
- Sheet 6-1Документ2 страницыSheet 6-1mostafa3aalyОценок пока нет
- MBI6024 Application NoteДокумент18 страницMBI6024 Application NoteBreNdaa OsorioОценок пока нет
- Advanced Power System ProtectionДокумент1 страницаAdvanced Power System ProtectionKranthi KumarОценок пока нет
- Instructions To Candidates:: C E DC B DCДокумент2 страницыInstructions To Candidates:: C E DC B DCAnmolОценок пока нет
- Scheme - e Fifth Semester (De, Ej, En, Et, Ex)Документ38 страницScheme - e Fifth Semester (De, Ej, En, Et, Ex)Harsh BhatiaОценок пока нет
- Project Report Ondigi FinalДокумент44 страницыProject Report Ondigi FinalDazzling SamОценок пока нет
- r05410207 Vlsi DesignДокумент7 страницr05410207 Vlsi Design9010469071Оценок пока нет
- Antenna Diode Vlsi Operation Positive ChargeДокумент21 страницаAntenna Diode Vlsi Operation Positive ChargeNegin HashemiОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Question Sem2!12!13Документ7 страницFinal Exam Question Sem2!12!13Christian Adkins100% (1)
- CMPS Lab ManualДокумент64 страницыCMPS Lab Manualomi ChavanОценок пока нет
- Reg - No: S. Veerasamy Chettiar College of Engineering and TechnologyДокумент4 страницыReg - No: S. Veerasamy Chettiar College of Engineering and TechnologykrishnandrkОценок пока нет
- Design of Folded Cascode OTA in Different Regions of Operation Through gmID Methodology PDFДокумент6 страницDesign of Folded Cascode OTA in Different Regions of Operation Through gmID Methodology PDFAyush MalhotraОценок пока нет
- Assignment - 5: ABES Engineering College, GhaziabadДокумент2 страницыAssignment - 5: ABES Engineering College, GhaziabadomenderОценок пока нет
- MechatronicsДокумент2 страницыMechatronicsSaravanan MathiОценок пока нет
- SRG Engineering College, Namakkal Unit Test-I Department of Eee Communication EngineeringДокумент2 страницыSRG Engineering College, Namakkal Unit Test-I Department of Eee Communication Engineeringkrr_apmОценок пока нет
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-2 2013-2014Документ9 страницFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-2 2013-2014Fatihah Aina100% (1)
- Analog Circuits - AssignmentДокумент1 страницаAnalog Circuits - AssignmentBindia HandaОценок пока нет
- MP Model QP Set1Документ26 страницMP Model QP Set1Jai MohanОценок пока нет
- Answer All QuestionsДокумент1 страницаAnswer All QuestionsBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANОценок пока нет
- Electrical & Electronic Engineering: Independent University, BangladeshДокумент2 страницыElectrical & Electronic Engineering: Independent University, BangladeshMd. Rakibol IslamОценок пока нет
- Aust Fall06 ReferredДокумент3 страницыAust Fall06 ReferredAbir LovesickОценок пока нет
- Screenshot 2021-04-28 at 1.40.14 PMДокумент26 страницScreenshot 2021-04-28 at 1.40.14 PMRazan AlyahyaОценок пока нет
- Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringДокумент1 страницаDepartment of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringVenkata SubramanianОценок пока нет
- FINAL EXAM - EED - Solar Cell Technology - FIRSTNAME - LASTNAME-REG - NumberДокумент2 страницыFINAL EXAM - EED - Solar Cell Technology - FIRSTNAME - LASTNAME-REG - NumberRiaz AhmadОценок пока нет
- ECL 202 Analog Circuits and Simulation Lab: Course Information & Course PlanДокумент10 страницECL 202 Analog Circuits and Simulation Lab: Course Information & Course PlanleevasusanОценок пока нет
- (BTL2 - Understanding) PO - (1, 2, 12), PSO - (1) (BTL2 - Understanding) PO - (1, 2, 12), PSOДокумент2 страницы(BTL2 - Understanding) PO - (1, 2, 12), PSO - (1) (BTL2 - Understanding) PO - (1, 2, 12), PSOVeera SwamyОценок пока нет
- Exp No 7Документ3 страницыExp No 7abheetpethe.scoe.entcОценок пока нет
- FINAL On PSPДокумент3 страницыFINAL On PSPdaveade100% (1)
- MODULE - Wise Question - 2022-ADE-COДокумент4 страницыMODULE - Wise Question - 2022-ADE-COvinayvinayakars313Оценок пока нет
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential EE/OCT 2008/KJE609/ECE590/KJE416Документ9 страницUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential EE/OCT 2008/KJE609/ECE590/KJE416nazhakimОценок пока нет
- Exp 11Документ6 страницExp 11Soham KhadkeОценок пока нет
- Switching Theory and Logic Design April 2019 PDFДокумент4 страницыSwitching Theory and Logic Design April 2019 PDFTulasi LassiОценок пока нет
- EEEДокумент290 страницEEEfaizu_ibmОценок пока нет
- Internal Test-II: Part-A (7x2 14 Marks)Документ1 страницаInternal Test-II: Part-A (7x2 14 Marks)krishnandrkОценок пока нет
- Analog and Digital Electronics B20EL0301 3D ReferДокумент12 страницAnalog and Digital Electronics B20EL0301 3D ReferBhargavi KmОценок пока нет
- CSE PUT Paper MicroprocessorДокумент3 страницыCSE PUT Paper Microprocessorrachit koundalОценок пока нет
- Advanced Chipless RFID: MIMO-Based Imaging at 60 GHz - ML DetectionОт EverandAdvanced Chipless RFID: MIMO-Based Imaging at 60 GHz - ML DetectionОценок пока нет
- VW-Audi Airbag Reset Tool User ManualДокумент14 страницVW-Audi Airbag Reset Tool User ManualgermantronikОценок пока нет
- ODAA Support LetterДокумент2 страницыODAA Support LetterStatesman JournalОценок пока нет
- Little Book of RubyДокумент104 страницыLittle Book of RubynoboОценок пока нет
- CTK230Документ15 страницCTK230barryhernsОценок пока нет
- User Manual For Soniclean Digital Benchtop Ultrasonic Cleaners 191013 PDFДокумент12 страницUser Manual For Soniclean Digital Benchtop Ultrasonic Cleaners 191013 PDFRafael GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Mayank Agrawal 2017UCH1725: Technical SkillsДокумент2 страницыMayank Agrawal 2017UCH1725: Technical SkillsMayank AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Single Phase Induction MotorДокумент5 страницSingle Phase Induction MotorSridhar SridharОценок пока нет
- IEEE Recommended Practice For Exc. Sys Models 2Документ4 страницыIEEE Recommended Practice For Exc. Sys Models 2Emmanuel ZamoranoОценок пока нет
- How To Make Acrylic Bending Machine DIY PVC Sheet Bender Mistry MakeToolДокумент8 страницHow To Make Acrylic Bending Machine DIY PVC Sheet Bender Mistry MakeToolnardusОценок пока нет
- Acoustic Simulation and Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Piping Systems IДокумент20 страницAcoustic Simulation and Analysis of Reciprocating Compressor Piping Systems IJose PradoОценок пока нет
- R05411101 ImageprocessingandpatternrecognitionДокумент4 страницыR05411101 ImageprocessingandpatternrecognitionSamiullah MohammedОценок пока нет
- Assessing The Feasibility of Using The Heat Demand-Outdoor Temperature Function For A Long-Term District Heat Demand ForecastДокумент5 страницAssessing The Feasibility of Using The Heat Demand-Outdoor Temperature Function For A Long-Term District Heat Demand ForecastmohammedelamenОценок пока нет
- 327101-BJ81-C-RCC-0007 Rev.00 - Client MarkupДокумент1 страница327101-BJ81-C-RCC-0007 Rev.00 - Client MarkupGokulprabhuОценок пока нет
- ADPlaylistEditor3 (Network Version)Документ42 страницыADPlaylistEditor3 (Network Version)Dramane BonkoungouОценок пока нет
- FB131Документ7 страницFB131Hoangvinh DuongОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual - DEДокумент41 страницаLab Manual - DEAnkur Giri100% (2)
- SHEET #1 Title Sheet Site Safety Logistic Plan ForДокумент5 страницSHEET #1 Title Sheet Site Safety Logistic Plan ForRadha BuildtechОценок пока нет
- Saep 1116Документ5 страницSaep 1116Anonymous 4IpmN7OnОценок пока нет
- Institute of Technology & Engineering, Malegaon BK.: Lesson Teaching Plan (LTP)Документ3 страницыInstitute of Technology & Engineering, Malegaon BK.: Lesson Teaching Plan (LTP)Pramod DhaigudeОценок пока нет
- Klauke - Bi-Metal Lugs & ConnectorsДокумент6 страницKlauke - Bi-Metal Lugs & ConnectorsBiplab PaulОценок пока нет