Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Concept Map - F and E
Загружено:
Abigail Lonogan0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
88 просмотров1 страницаConcept Map on fluid and electrolyte
Оригинальное название
Concept map | F and E
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документConcept Map on fluid and electrolyte
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
88 просмотров1 страницаConcept Map - F and E
Загружено:
Abigail LonoganConcept Map on fluid and electrolyte
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
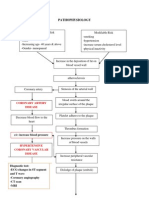
FLUID AND
ELECTROLYTES
Osmolality of intracellular fluid and
extracellular fluid tends to equalize
because of the constant shifting of water.
1. Intracellular
Fluid with in cell DIAGNOSTIC TESTS AND PROCEDURES
2. Extracellular
Found in blood vessels Hematocrit
3. Interstitial fluid 25%
Creatnine
(the third space)
Surrounding cells, BUN
including lymph Albumin
4. Transcellular fluids Serum electrolytes
Lymph, digestive tract,
sweat, cerebrospinal
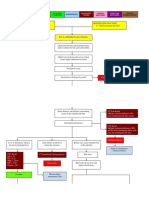
ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCES ACID - BASE IMBALANCES
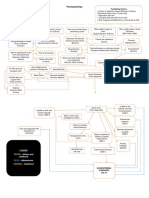
1. Sodium (Na) Major cation of
1. Respiratory Acidosis
extracellular fluid
a. Hyponatremia a. pH<7.35
orthostatic hypotension b. PaCO2>45
b. Hypernatremia c. Hypoventilation →
flushed skin, dry mucous Hypoxia
membranes
2. Potassium (K) d. Shallow breathing, ↑K+
a. Hypokalemia
Muscle cramps ↓BP oliguria 2. Respiratory Alkalosis
b. Hyperkalemia a. pH>7.45
Patients at risk:
decreased renal function,
b. PaCO2<32
in metabolic acidosis, c. Deep breathing,
taking potassium hyperventilation,
supplements
3. Chloride (Cl) tachycardia, lethargy
a. Hyperchloremia & confusion.
Usually associated with
metabolic acidosis 3. Metabolic Acidosis
b. Hypochloremia
a. pH<7.35
Usually occurs when sodium
is lost because chloride b. HCO3<20
most frequently bound with c. Kussmaul respiration,
sodium
severe diarreah,
4. Calcium (Ca)
a. Hypocalcemia N,V,D, muscle
↓intake of vit D twitching
b. Hypercalcemia
↑ intake of vitamin D 4. Metabolic Alkalosis
5. Magnesium (Mg2+)
a. pH>7.45
a. Hypomagnesemia
b. HCO3>26
usually from vomiting and
diarrhea
c. Severe vomiting,
b. Hypermagnesemia tremors, muscle cramps
excessive use of magnesium
Вам также может понравиться
- Metabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandMetabolic Alkalosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideОт EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideОценок пока нет
- Chapter041 DIABETESДокумент8 страницChapter041 DIABETESJelly BeanОценок пока нет
- Grand Coaching: Medical Surgical NursingДокумент22 страницыGrand Coaching: Medical Surgical NursingEsarpy (Nana)Оценок пока нет
- NCC-SickleCellAnemiaManagement ConceptMap InteractivePDFДокумент2 страницыNCC-SickleCellAnemiaManagement ConceptMap InteractivePDFLoggerz Arck100% (1)
- AtireviewДокумент163 страницыAtireviewGlory Mimi0% (1)
- Management of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersДокумент47 страницManagement of Patients With Gastric and Duodenal DisordersJor GarciaОценок пока нет
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationДокумент1 страницаNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyОценок пока нет
- Cushing's SyndromeДокумент5 страницCushing's SyndromesummerduskОценок пока нет
- Rheumatic Joint Disease Study GuideДокумент18 страницRheumatic Joint Disease Study Guidechalinsammy1Оценок пока нет
- Tetanus Toxoid Immunization Schedule For WomenДокумент4 страницыTetanus Toxoid Immunization Schedule For WomenEdwin Delos Reyes AbuОценок пока нет
- Community Acquired PneumoniaДокумент28 страницCommunity Acquired Pneumoniadionisiusvrm100% (1)
- Renal and Urinary SystemДокумент5 страницRenal and Urinary SystemStaceyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract DisordersДокумент17 страницChapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract DisordersMary SingletonОценок пока нет
- PANCREATITISДокумент38 страницPANCREATITISVEDHIKAVIJAYANОценок пока нет
- De Sagun, Leila Camille, A. NCMB312-RLE BSN3Y1-1B Course Task #1Документ1 страницаDe Sagun, Leila Camille, A. NCMB312-RLE BSN3Y1-1B Course Task #1Carl SantosОценок пока нет
- Congestive Heart Failure OutlineДокумент4 страницыCongestive Heart Failure OutlineDominique PorterОценок пока нет
- G3 IAH and ACSДокумент29 страницG3 IAH and ACSRoshin Mae E. TejeroОценок пока нет
- 51 100Документ18 страниц51 100Jaessa Feliciano100% (1)
- Chapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (PrepUDONE)Документ7 страницChapter 23 - Management of Patients With Chest and Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders (PrepUDONE)Mary SingletonОценок пока нет
- Nusing CareplanДокумент3 страницыNusing Careplanardec_143Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The Client Questions RationaleДокумент19 страницNursing Interview Guide To Collect Subjective Data From The Client Questions RationaleKent Rebong100% (1)
- C C C M MMMM MM M MMM 3mm MMMMM MM M MMMMMДокумент4 страницыC C C M MMMM MM M MMM 3mm MMMMM MM M MMMMMjohkieОценок пока нет
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal/Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationLorraine Punla PanganОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic CommunicationДокумент7 страницTherapeutic CommunicationJoseph Rommel Castro CortezОценок пока нет
- TCA Suppression and DM1Документ22 страницыTCA Suppression and DM1Rubyrose TagumОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisДокумент2 страницыPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaОценок пока нет
- NCPДокумент2 страницыNCPMelissa David100% (1)
- Case Analysis On Respiratory DisordersДокумент5 страницCase Analysis On Respiratory DisordersAaron ConstantinoОценок пока нет
- Status Epilepticus Case Study Kristopher Kirby.Документ4 страницыStatus Epilepticus Case Study Kristopher Kirby.KrisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 22 - Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract Disorders (INCOMPLETEon 13)Документ16 страницChapter 22 - Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract Disorders (INCOMPLETEon 13)Mary Singleton100% (1)
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in ChildrenДокумент10 страницCarbon Monoxide Poisoning in ChildrenSubash PaudealОценок пока нет
- Nursing Assessment S - O Pt. May ManifestДокумент4 страницыNursing Assessment S - O Pt. May Manifestk_a1990Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerДокумент2 страницыNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- MedSurg 2Документ69 страницMedSurg 2Claire Maurice JuaneroОценок пока нет
- MicrocephalyДокумент4 страницыMicrocephalykurei_bluflamedОценок пока нет
- Hepatocellula R CarcinomaДокумент45 страницHepatocellula R Carcinomamhean azneitaОценок пока нет
- 118 Skills Lab-Week 1-Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionsДокумент8 страниц118 Skills Lab-Week 1-Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionsKeisha BartolataОценок пока нет
- Communication With Older AdultsДокумент22 страницыCommunication With Older AdultsNathaniel Karl Enin PulidoОценок пока нет
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Документ6 страницConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloОценок пока нет
- Hypertension NCLEX Quiz Questions: A. I Will Make Sure I Consume Foods High in PotassiumДокумент5 страницHypertension NCLEX Quiz Questions: A. I Will Make Sure I Consume Foods High in PotassiumMelodia Turqueza GandezaОценок пока нет
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionДокумент2 страницыHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionPamela DomingoОценок пока нет
- Desires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.Документ19 страницDesires - How Are You Feeling Today Sir? If Huminto Po Si PT, Iallow Po Natin Siya & Bigyan Siya NG Time To Fully Undertand What He Is Feeling Right Now.melodia gandezaОценок пока нет
- Ordonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleДокумент4 страницыOrdonio, Alyn Kyla S. BSN-1C TFN-MW7:40-9:10: Name of Theorist Theory Description Florence NightingaleKyla OrdonioОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilОценок пока нет
- Oxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Документ16 страницOxytocin (Pitocin) : Slide 1Kalesha JonesОценок пока нет
- GRP 4 CLO 2 Concept Map PT 1 PDFДокумент14 страницGRP 4 CLO 2 Concept Map PT 1 PDFMaria Lyn Ocariza ArandiaОценок пока нет
- Concept Map FinalДокумент1 страницаConcept Map Finalapi-383763177Оценок пока нет
- Pathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionДокумент2 страницыPathognomonic Signs of Communicable Diseases: JJ8009 Health & NutritionMauliza Resky NisaОценок пока нет
- Asthma Impaired Gas ExchangeДокумент2 страницыAsthma Impaired Gas ExchangeAndrea Chua BuadoОценок пока нет
- Buerger's DiseaseДокумент4 страницыBuerger's DiseasesweetyjonasОценок пока нет
- Transcultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodДокумент5 страницTranscultural Perspective in The Nursing Care of Adults Physiologic Development During AdulthoodeuLa-mayzellОценок пока нет
- Aging Perspective and Demography Ncm114 Gerontology Aging PerspectivesДокумент19 страницAging Perspective and Demography Ncm114 Gerontology Aging PerspectivesLeslie CruzОценок пока нет
- Shock Concept MapДокумент2 страницыShock Concept MapElizabeth GarretsonОценок пока нет
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions Onco1Документ12 страницMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions Onco1dee_day_8100% (2)
- LCPDДокумент7 страницLCPDakoismeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13: Clients With Fluid ImbalancesДокумент6 страницChapter 13: Clients With Fluid ImbalancesTrixie AlvarezОценок пока нет
- Fluid and Electrolytes, Burns, G.UДокумент56 страницFluid and Electrolytes, Burns, G.Uapi-3735995100% (4)
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableДокумент2 страницыAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonОценок пока нет
- Week 10 - Ch. 38 - OxygenationДокумент36 страницWeek 10 - Ch. 38 - OxygenationMary SingletonОценок пока нет
- For Drug Recitation 1Документ33 страницыFor Drug Recitation 1Abigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент4 страницыDrug StudyAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Name: Age: Gender: Civil Status: Religion: Birthday: Birth Place: Nationality: Address: Occupation: Phic: Case: Date & Time Admitted: Chief Complaint: History of Present IllnessДокумент2 страницыName: Age: Gender: Civil Status: Religion: Birthday: Birth Place: Nationality: Address: Occupation: Phic: Case: Date & Time Admitted: Chief Complaint: History of Present IllnessAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Spaulding Classification of InstrumentsДокумент1 страницаSpaulding Classification of InstrumentsAbigail Lonogan100% (1)
- Prioritization of Nursing ProblemsДокумент1 страницаPrioritization of Nursing ProblemsAbigail Lonogan100% (2)
- Batch Jacket FormatДокумент2 страницыBatch Jacket FormatAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Palliative Care NursingДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To Palliative Care NursingAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Quantitative and Qualitative ResearchДокумент7 страницQuantitative and Qualitative ResearchAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Predisposing Factors Facilitating Factors: PsychopathologyДокумент2 страницыPredisposing Factors Facilitating Factors: PsychopathologyAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Chemotherapy Benefit PackageДокумент2 страницыChemotherapy Benefit PackageAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Careers in Nursing: Click Arrows To Move Ahead & BackДокумент27 страницCareers in Nursing: Click Arrows To Move Ahead & BackAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- HIV Journal - PhilippinesДокумент1 страницаHIV Journal - PhilippinesAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology - Obstructive JaundiceДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology - Obstructive JaundiceAbigail Lonogan0% (1)
- Mini Cog ToolДокумент2 страницыMini Cog ToolSegun Dele-davidsОценок пока нет
- The Battle of MactanДокумент4 страницыThe Battle of MactanAbigail Lonogan100% (3)
- Content - Surgical Consent FormДокумент4 страницыContent - Surgical Consent FormAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques - NursingДокумент3 страницыTherapeutic Communication Techniques - NursingAbigail Lonogan100% (1)
- Sigmund Freud: Psychoanalytic TheoryДокумент18 страницSigmund Freud: Psychoanalytic TheoryAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- History of Past IllnessДокумент1 страницаHistory of Past IllnessAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Fluid and Electrolyte JournalДокумент10 страницFluid and Electrolyte JournalAbigail LonoganОценок пока нет
- Sample Menu With JustificationДокумент1 страницаSample Menu With JustificationAbigail Lonogan100% (1)
- (PEDIA) 2.04 Pediatric Neurologic Exam - Dr. Rivera PDFДокумент15 страниц(PEDIA) 2.04 Pediatric Neurologic Exam - Dr. Rivera PDFJudith Dianne IgnacioОценок пока нет
- Sharon Denise Gross: 513 Grazing Field Drive, Tuscaloosa, AL 35405 (C) 205-242-3670 (W) 205-554-2000 Ext. 3617 (E) (E)Документ6 страницSharon Denise Gross: 513 Grazing Field Drive, Tuscaloosa, AL 35405 (C) 205-242-3670 (W) 205-554-2000 Ext. 3617 (E) (E)api-469030612Оценок пока нет
- Pediatrics MCQs - DR Ranjan Singh - Part 2Документ10 страницPediatrics MCQs - DR Ranjan Singh - Part 2k sagarОценок пока нет
- Disability HandbookДокумент231 страницаDisability HandbookRoberto Manuel Meléndez NegrónОценок пока нет
- Role of Pain Placebo Analgesia: Gordont, Fields FДокумент4 страницыRole of Pain Placebo Analgesia: Gordont, Fields Fmaurina rizkiОценок пока нет
- Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy HOACllДокумент9 страницPelvic Floor Physiotherapy HOACllEsteban CayuelasОценок пока нет
- ABO Blood Group System CAIДокумент34 страницыABO Blood Group System CAIrupertgrint2000Оценок пока нет
- BotoxMedical Patient BrochureДокумент21 страницаBotoxMedical Patient BrochurePatricia Avalos C.Оценок пока нет
- Blood PressureДокумент11 страницBlood PressureHilma NadzifaОценок пока нет
- 2021 Batangas Medical Center - Updated Citizens Charter HandbookДокумент447 страниц2021 Batangas Medical Center - Updated Citizens Charter HandbookHarlyn MagsinoОценок пока нет
- Group 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Документ7 страницGroup 6 Part 1 Review of The Aging of Physiological System Notes Part 1Crissan Jejomar AbanesОценок пока нет
- Oral Pathology Key PointsДокумент4 страницыOral Pathology Key PointsRohit Bansal100% (1)
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)Документ4 страницыDAFTAR PUSTAKA (Kasus Mendalam 2)mkpnurdinОценок пока нет
- Essentials of Microbiology 1st Edition PDFДокумент648 страницEssentials of Microbiology 1st Edition PDFJohn Khna100% (1)
- Sec 5 - Fa - Gas Exchange - T2 - QSДокумент3 страницыSec 5 - Fa - Gas Exchange - T2 - QSnoorlailyОценок пока нет
- Tabata Exercise Pe 1Документ1 страницаTabata Exercise Pe 1Joshua Jae AquinoОценок пока нет
- Auricular Causative Diagnosis-Finding The Roots of Diseases: A Study of Clinical CasesДокумент11 страницAuricular Causative Diagnosis-Finding The Roots of Diseases: A Study of Clinical Casesyan92120Оценок пока нет
- Https Learn - Cellsignal.com Hubfs Pdfs 21-Bpa-35731-Therapeutics-brochure-digitalДокумент12 страницHttps Learn - Cellsignal.com Hubfs Pdfs 21-Bpa-35731-Therapeutics-brochure-digitalashuwillusinfraОценок пока нет
- EPN Book 2Документ40 страницEPN Book 2Budhi Priyanto DitaraОценок пока нет
- Case No 37Документ5 страницCase No 37Aila GoliasОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract InfectionsДокумент44 страницыUrinary Tract Infectionstummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Nutrition PostoperativeДокумент47 страницNutrition PostoperativeAnonymous 86gki5Оценок пока нет
- CV For FellowshipДокумент3 страницыCV For Fellowshipapi-568710214Оценок пока нет
- Things To Read: A. Trauma: Fractures and DislocationsДокумент4 страницыThings To Read: A. Trauma: Fractures and DislocationsHanien YeeОценок пока нет
- Medical AbbreviationsДокумент31 страницаMedical AbbreviationsLailaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To NCM 118Документ16 страницIntroduction To NCM 118Frank Jomari MurilloОценок пока нет
- Bahasa Inggris - NurfadilahДокумент6 страницBahasa Inggris - NurfadilahHardianiОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Tinnitus and Evidence-Based Options For Tinnitus ManagementДокумент12 страницPathophysiology of Tinnitus and Evidence-Based Options For Tinnitus ManagementEli HuertaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacy Journals 100Документ7 страницPharmacy Journals 100alexpharmОценок пока нет
- INFLAMATORY AND STDsДокумент26 страницINFLAMATORY AND STDsNathaniel BudayОценок пока нет