Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Basic Life Support (BLS) : Abad, Angelica Joy N. BSN Iv-B1
Загружено:
Angelica Joy Abad0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
46 просмотров14 страницbzzz
Оригинальное название
er
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документbzzz
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
46 просмотров14 страницBasic Life Support (BLS) : Abad, Angelica Joy N. BSN Iv-B1
Загружено:
Angelica Joy Abadbzzz
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 14
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (BLS)
Definition: A level of medical care used for victims of life-threatening illnesses or injuries until they
can be given full medical care at a hospital. It can be provided by trained medical personnel,
including emergency medical technicians, paramedics, and by qualified bystanders.
Purpose: Promotes adequate blood circulation in addition to breathing through a clear airway.
ADVANCED CARDIAC LIFE SUPPORT (ACLS)
Definition: refers to a set of clinical interventions for the urgent treatment of cardiac arrest, stroke and
other life-threatening medical emergencies, as well as the knowledge and skills to deploy those
interventions.
Purpose: Achieve the best possible outcome for individuals experiencing a life-threatening event
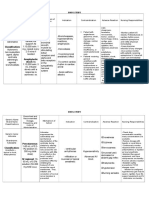
Code Team
NURSE ACTIVITIES
NURSE 1 (Bedside Nurse) Identifies the situation
Calls for code
Initiates BLS and continues until reliever
arrives (Nurse 5)
Monitor VS
NURSE 2 (Airway Nurse) Inserts cardiac board
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
Assists with BLS (airway) until physician
arrives
Prepares intubation set and assists in
intubation
Laryngoscope
ET with stylet
KY Jelly
10 cc syringe
Bite block/OPA
Gloves
Swaps position with N1 or N5
NURSE 3 (Medication Nurse) Prepares venoclysis equipment and starts IB
line
Prepares medication IV drips
Prepares bolus medications and administers it
Passes equipment from the crash cart
Does other procedures (ABG, SpO2)
NURSE 4 (Documentation Nurse) Gather initial information
Document vital information (Time code
stated, medications given, procedures done,
ECG checks, defib energy levels, VS, time
code ended)
Coordinates activities of all personnel and
recaps events
Interprets ECG q 2mins.
Reminds rhythm checks and medications due
NURSE 5 (Reliever Nurse) Connects electrodes
Prepares equipment and performs
defibrillation
Swaps position with N1 or N2 (Team
members should switch q 2 mins.)
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
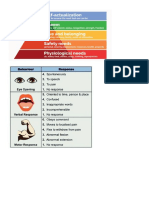
ALGORITHMS
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
EMERGENCY ROOM CRASH CART MEDICATIONS
DRUG CLASS. DRUG INDICATION ACTION S/E
Analgesics Codeine -Mild to moderate -Binds with opiate -Dizziness
(Narcotics) pain reeptors in CNS, -N/V
altering pereption -Respiratory
of and emotional depression
response to pain
Tramadol -Moderate to severe -Binds to opioid -Headache
pain receptor sites -N/V
inhibiting reuptake -Respiratory
of norepinephrine depression
and serotonin
Morphine -Severe pain -Binds with opioid -Sedation
receptors in CNS, -Hypotension
altering perception -bradycardia
of and emotional -N/V
response to pain -respiratory
depression
Fentanyl -Chronic pain -Binds with opioid -Sedation
-Postop pain receptors in CNS, -dry mouth
altering pain -N/V
perception and -respiratory
response depression
(Non-narcotics) Paracetamol -Mild pain -Produces analgesia -rash
-Fever by inhibiting -urticaria
prostaglandin
synthesis
-Relieves fever by
action in
hypothalamic heat-
regulating center
Ibuprofen -Mild to moderate -Inhibits -headache
pain prostaglandin -drowsiness
-Fever synthesis -dizziness
-epigastric pain
Anesthetics Lidocaine -Anesthetic -Alters signal -confusion
-Arrythmias conduction in -lethargy
neurons blocks -bradycardia
fast voltage gated N -restlessness
channels in
neuronal cell
membrane
membrane of
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
postsynaptic neuron
will not depolarize
-Decrease
depolarization,
automaticity and
excitability in
ventricles during
diastolic phase by
direct action on
tissues
(Infiltrative) Bupivacaine -local anesthetic -Inhibits initiation -decrease BP
and conduction of -bradycardia
sensory nerve -dizziness
impulses by -anxiety
altering influx of
sodium, and
potassium in
neurons, slowing or
stopping pain
transmission.
Lidocaine with -regional anesthesia Stabilizes neuronal -confusion
Epinephrine (peripheral nerve membrane by -lethargy
block) inhibiting the ionic -bradycardia
fluxes required for -restlessness
the initiation and -light headedness
conduction of
impulses, effecting
local anesthetic
action
Anti-bleeding Vit K -Prevent -Promotes hepatic -flushing
hemorrhage formation of active -dizziness
prothrombin
controls abnormal
bleeding
Tranexamic Acid -Prevent -Inhibits activation -hypotension
hemorrhage of plasminogen, -dizziness
preventing -N/V
conversion of
plasminogen to
plasmin
Anti-convulsants Midazolam -Sedation -Depresses CNS at -headache
limbic and -N/V
subcortical levels of -decrease RR
brain by
potentiating effects
of GABA
promoting calmness
and sleep
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
Phenytoin -Control of tonic- -Stabilizes neuronal -confusion
clonic and complex membranes in the -nervousness
partial seizures motor cortex by -headache
altering sodium ion
movement across
them stopping
seizures
Lorazepam -Anxiety -Stimulates gamma- -drowsiness
-Status epilepticus aminobutyric -lethargy
receptors in the
ascending reticular
activating system,
promoting calmness
Diazepam -Anxiety -Depresses CNS at -drowsiness
-Muscle spasm limbic and -hypotension
-Status epilepticus subcortical levels
of the brain
relieving seizures
Phenobarbitol -Epilepsy -Depresses CNS -drowsiness
-Status epilepticus synaptic -resp depression
transmission and -apnea
increase seizure
activity threshold
in motor cortex
Anti-diabetics Insulin R -DM -Increases glucose -hypoglycemia
-DKA transport across -Lipohypertrophy
muscle and fat cell
membranes
reducing blood
glucose level.
converts glucose to
its storage form
glycogen
triggers AA uptake
converts protein
in muscle cells
inhibits protein
degradation ->
stimulates
triglyceride
formation
inhibits release of
free fatty acids
from fats lowers
glucose levels
CVS Agents Captopril -Hypertension -Inhibits ACE, -hypotension
(ACE Inhibitors) -Heart failure preventing -dizziness
onversion of
angiotensin I to
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
angiotensin II
decreasing
peripheral aterial
resistance and
aldosterone
secretion
Adrenergic Norepinephrine -restore BP during -Stimulates alpha -headache
Stimulants hypotension, shock and beta adrenergic -weakness
and cardiac arrest receptors in the -bradycardia
SNS
Dobutamine -Inreases cardiac -Directly stimulates -increased heart
output, cardiac beta 1 receptors to rate
contractility increase myocardial -hypertension
contractility and -angina
stroke volume thus
increasing cardiac
output
Dopamine -Improves -Stimulates -hypotension
perfusion dopaminergic beta- -bradycardia
-Increase cardiac adrenergic and
output alpha-adrenergic
receptors of
sympathetic
nervous system
Beta-blockers Metoprolol -Hypetension -Reduces -hypotension
Propanolol -Angina pectoris myocardial oxygen -bradycardia
consumption, -dizziness
myocardial
contractility and
heart rate by
inhibiting the beta
adrenergic site
Calcium channel Diltiazem -Angina -Inhibits calcium -headeache
blockers -Hypertension ion influx across -bradycardia
-Afib/Aflutter cardiac and smooth N/V
muscle cells -hypotension
decreasing
myocardial
contractility
demand; dilating
coronary arteries
Vasodilators Nitroglycerin -Angina -Reduces cardiac -h/a
oxygen demand -orthostatic
decreasing preload hypotension
and afterload -tachycardia
increasing blood
flow through
coronary vessels
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
ABAD, ANGELICA JOY N.
BSN IV-B1
PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION MANAGEMENT
Definition: PIH is defined as hypertension (blood pressure ≥ 140/90 mmHg) with or without proteinuria
( ≥ 300 mg/24 hours) emerging after 20 weeks gestation, but resolving up to 12 weeks postpartum.1–10)
PIH is also defined as new onset proteinuria ( ≥ 300 mg/24 hours) in hypertensive women who exhibit
no proteinuria before 20 weeks gestation
Signs and symptoms
Hypertension - An increase in the usual blood pressure of the woman is the first indicator of this
disease.
Proteinuria - Protein leaks out during this condition and can be detected in the urine.
Edema - Since protein has already leaked out and it is responsible for containing water inside the
vessels, edema starts to occur.
Classifications:
1. Gestational Hypertension
BP reaches ≥ 140/90 mmHg for the first time during pregnancy (after 20 weeks gestation), but
without proteinuria. Blood pressure normalizes by 12 weeks postpartum
Perinatal mortality is not increased with simple gestational hypertension, so no drug therapy is
necessary.
BP returns to normal after birth.
2. Mild Preeclampsia
Hypertension (blood pressure ≥ 140 / 90 mmHg) accompanied with proteinuria of 1+ or 2+
on a reagent test strip on a random sample but both symptoms normalize by 12 weeks
postpartum.
A weight gain of more than 2 lbs/week in the second trimester or 1 lb/week in the third
trimester usually indicates abnormal tissue fluid retention.
3. Severe Preeclampsia
BP is 160 mmHg systolic and 110 mmHg diastolic or above on at least two occasions 6 hours
apart at bed rest.
Proteinuria. 3+ or 4+ on a random urine sample or more than 5 g in a 24-hour sample and
extensive edema are also present.
Extreme edema will be noticeable as puffiness in a woman’s face and hands.
May manifest oliguria (altered renal function), elevated serum creatinine (more than 1.2
mg/dL); cerebral or visual disturbances (blurred vision); thrombocytopenia and epigastric
pain.
4. Eclampsia
Onset of convulsions in a woman with PIH that cannot be attributed to other causes. The
seizures are generalized and may appear before, during, or after labor
Management
Activity restriction
Quiet environment
Anticonvulsive therapy
Antihypertensive therapy
Delivery of fetus
Вам также может понравиться
- Manajemen Nyeri Motik RS BhinaДокумент36 страницManajemen Nyeri Motik RS Bhinayn_faisalОценок пока нет
- NCP PainДокумент2 страницыNCP PainChristineAlaОценок пока нет
- Nalbuphine NubainДокумент1 страницаNalbuphine NubainB PОценок пока нет
- Essentials On Acute Pain ManagementДокумент57 страницEssentials On Acute Pain ManagementSri Ariantini AriantiniОценок пока нет
- Pain Daily PracticeДокумент30 страницPain Daily Practicesukasuka azaОценок пока нет
- Acute Pain: Dr. I Putu Pramana Suarjaya, Span. Mkes. KMNДокумент35 страницAcute Pain: Dr. I Putu Pramana Suarjaya, Span. Mkes. KMNAdhi WiratmaОценок пока нет
- 0026 - Jan DobrogowskiДокумент39 страниц0026 - Jan Dobrogowskized Trending HitsОценок пока нет
- NCP Acute PainДокумент3 страницыNCP Acute PainBasema HashhashОценок пока нет
- 21F MEDICINE 2 Rehab Patient With Low Back and Neck Pains (Dr. Capistrano)Документ7 страниц21F MEDICINE 2 Rehab Patient With Low Back and Neck Pains (Dr. Capistrano)herrerachaimОценок пока нет
- Management NyeriДокумент49 страницManagement NyeriYuke ArmikaОценок пока нет
- E PaediatricsfordoctorsДокумент53 страницыE PaediatricsfordoctorsJimmy RahuОценок пока нет
- Nyeri Nosiseptif Sup - XIДокумент82 страницыNyeri Nosiseptif Sup - XIDiana SariОценок пока нет
- Chest InjuryДокумент17 страницChest InjuryAira Dy PinedaОценок пока нет
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyДокумент10 страницNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Pain: MakassarДокумент67 страницIntroduction To Pain: MakassarPutrirzqiОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент6 страницDrug StudyBrix John PortellanoОценок пока нет
- Tuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainДокумент2 страницыTuano, Salma M. Bsn4-1 Acute PainSALMA M. TUANOОценок пока нет
- Pain Dr. HenryДокумент36 страницPain Dr. Henryreagan setiawanОценок пока нет
- AAA Mixed Pain SMGДокумент37 страницAAA Mixed Pain SMGandhita96Оценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Nursing Midterm ReviewДокумент15 страницPsychiatric Nursing Midterm Reviewleo ramoresОценок пока нет
- Pain MedДокумент2 страницыPain MedmsathenaОценок пока нет
- Drug Tab - For VedadДокумент5 страницDrug Tab - For VedadJM Mizraime Gallo Dela-peñaОценок пока нет
- Neuropathic Pain English ClassДокумент38 страницNeuropathic Pain English Classmulyaok285Оценок пока нет
- NCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyДокумент7 страницNCP Draft - Ectopic PregnancyD CОценок пока нет
- Drugs 1Документ5 страницDrugs 1Charme Jean RaygonОценок пока нет
- Generic Name: Adult: IVДокумент3 страницыGeneric Name: Adult: IVBasema HashhashОценок пока нет
- Managing Pain in HospitalsДокумент45 страницManaging Pain in HospitalsRadit NasillaОценок пока нет
- Understanding types and classifications of painДокумент28 страницUnderstanding types and classifications of painHAFIZH CAHYA ARYANSYAHОценок пока нет
- Nurses' role in assessing and alleviating painДокумент7 страницNurses' role in assessing and alleviating painCalaena SardothienОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Non-Pharmacological InterventionsДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan: Non-Pharmacological InterventionsVivian PhamОценок пока нет
- Pain ManagementДокумент21 страницаPain ManagementTedi SunandarОценок пока нет
- DR Yuneldi Anwar Sps (K) Bagian Neurologi Fk-Usu/ Rsup H. Adam Malik MedanДокумент59 страницDR Yuneldi Anwar Sps (K) Bagian Neurologi Fk-Usu/ Rsup H. Adam Malik MedanZikri Putra Lan LubisОценок пока нет
- Independent:: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент6 страницIndependent:: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationBryanRachelle__403Оценок пока нет
- Kuliah Neurologi NyeriДокумент88 страницKuliah Neurologi NyeriLaksita dinnyaputeriОценок пока нет
- Fentanyl Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыFentanyl Drug StudyAngelica shane Navarro100% (3)
- Lower Limb Trauma in A Young Man CASE STUDY1Документ8 страницLower Limb Trauma in A Young Man CASE STUDY1Renee RoSeОценок пока нет
- CH12AnalgesiaLabor (9 AgustuДокумент27 страницCH12AnalgesiaLabor (9 AgustuAnonymous FX2NVrd4c2Оценок пока нет
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP)Документ11 страницDiabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP)gjgibson2784Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Case ScenarioДокумент14 страницNursing Care Plan: Case ScenarioShelvin Jules LayvaОценок пока нет
- N220 W8 Nursing Care Plan RevisedДокумент3 страницыN220 W8 Nursing Care Plan RevisedVivian PhamОценок пока нет
- Dr. Ken Wirastuti, Mkes, SP.S Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fakultas Kedokteran-Universitas Islam Sultan AgungДокумент20 страницDr. Ken Wirastuti, Mkes, SP.S Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Saraf Fakultas Kedokteran-Universitas Islam Sultan AgungmarkoyenОценок пока нет
- Acute PainДокумент3 страницыAcute PainHu DawiОценок пока нет
- Drug Mechanism Nursing ResponsibilitiesДокумент8 страницDrug Mechanism Nursing ResponsibilitiesSalwa ZeinОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Evaluation Objective of Care Intervention Rationale Subjective CuesДокумент16 страницAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Evaluation Objective of Care Intervention Rationale Subjective CuesRoshin TejeroОценок пока нет
- 2. Morphine SulfateДокумент1 страница2. Morphine SulfateyeshaellatapucayОценок пока нет
- Acute Periopertive Pain Management (Sby)Документ87 страницAcute Periopertive Pain Management (Sby)Adam KurniaОценок пока нет
- Haloperidol: College of Health SciencesДокумент2 страницыHaloperidol: College of Health SciencesKervy JuntillaОценок пока нет
- SNG 1Документ4 страницыSNG 1HoloОценок пока нет
- Yanga - NCP, Drug Study, FdarДокумент7 страницYanga - NCP, Drug Study, Fdar3amabelle arevaloОценок пока нет
- DemerolДокумент1 страницаDemerolCassie100% (1)
- Proper Hygiene Prevents Spread of PathogensДокумент4 страницыProper Hygiene Prevents Spread of PathogensSheda BondОценок пока нет
- Drug StudyДокумент1 страницаDrug StudyRudelyn BarcelonaОценок пока нет
- Neuropathic PainДокумент40 страницNeuropathic PainHasmirahОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of PainДокумент31 страницаPathophysiology of PainJonniwal Sanusi100% (4)
- 1 Introduction To ANSДокумент43 страницы1 Introduction To ANSAlex HaileyesusОценок пока нет
- By Frederick C. Loyola, M.D.: S4 Lec 1: AnesthesiaДокумент7 страницBy Frederick C. Loyola, M.D.: S4 Lec 1: Anesthesia2013SecBОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Distraction (TVДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan: Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Distraction (TVVivian PhamОценок пока нет
- Pain Free 1-2-3: A Proven Program for Eliminating Chronic Pain NowОт EverandPain Free 1-2-3: A Proven Program for Eliminating Chronic Pain NowРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- Mental Health and Pain: Somatic and Psychiatric Components of Pain in Mental HealthОт EverandMental Health and Pain: Somatic and Psychiatric Components of Pain in Mental HealthОценок пока нет
- The Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentОт EverandThe Basics: A Comprehensive Outline of Nursing School ContentРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- LEVELS OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES (Memorial Sloan Kettering Lymph Node Levels)Документ6 страницLEVELS OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES (Memorial Sloan Kettering Lymph Node Levels)Angelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Create and Update Table of Contents in WordДокумент7 страницCreate and Update Table of Contents in WordAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- LEVELS OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES (Memorial Sloan Kettering Lymph Node Levels)Документ6 страницLEVELS OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES (Memorial Sloan Kettering Lymph Node Levels)Angelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- GI stimulant, anticholelithic, anti-infectives, Ca-channel blocker, analgesics, GI regulators drug guideДокумент1 страницаGI stimulant, anticholelithic, anti-infectives, Ca-channel blocker, analgesics, GI regulators drug guideAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Create and Update Table of Contents in WordДокумент7 страницCreate and Update Table of Contents in WordAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- EfsfgghДокумент2 страницыEfsfgghAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Biology ReviewerДокумент22 страницыIntroduction To Biology ReviewerAnton Miguel Jordan83% (6)
- SFGFSGBDFGДокумент2 страницыSFGFSGBDFGAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- GI stimulant, anticholelithic, anti-infectives, Ca-channel blocker, analgesics, GI regulators drug guideДокумент1 страницаGI stimulant, anticholelithic, anti-infectives, Ca-channel blocker, analgesics, GI regulators drug guideAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- WsadsДокумент2 страницыWsadsAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Create and Update Table of Contents in WordДокумент7 страницCreate and Update Table of Contents in WordAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- RwteДокумент2 страницыRwteAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Handwashing and Dietary Guidelines for Disease PreventionДокумент2 страницыHandwashing and Dietary Guidelines for Disease PreventionAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- AsdsasДокумент1 страницаAsdsasAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- WsДокумент2 страницыWsAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Prinzmetal Question 1Документ1 страницаPrinzmetal Question 1Angelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- EfedДокумент2 страницыEfedAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Basic Life Support (BLS) : Abad, Angelica Joy N. BSN Iv-B1Документ14 страницBasic Life Support (BLS) : Abad, Angelica Joy N. BSN Iv-B1Angelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- WsДокумент2 страницыWsAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Prinzmetal Question 1Документ1 страницаPrinzmetal Question 1Angelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Endoscopy JournalДокумент4 страницыEndoscopy JournalAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Endoscopy JournalДокумент4 страницыEndoscopy JournalAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- QwertyuiopДокумент10 страницQwertyuiopAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- HighlightsДокумент1 страницаHighlightsAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- 441 PDFДокумент7 страниц441 PDFAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Disaster Preparedness and Perceived Barriers Among Student Nurses. IДокумент3 страницыEvaluation of Disaster Preparedness and Perceived Barriers Among Student Nurses. IAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- DotДокумент5 страницDotAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Rh Incompatibility: A Mother's Immune Response to an Rh+ BabyДокумент1 страницаRh Incompatibility: A Mother's Immune Response to an Rh+ BabyAngelica Joy AbadОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology: AppendicitisДокумент3 страницыPathophysiology: AppendicitisEqah TajuddinОценок пока нет
- Breakthroughs That Change Patients' Lives: Annual ReviewДокумент56 страницBreakthroughs That Change Patients' Lives: Annual ReviewAnindita SahaОценок пока нет
- Community Health Nursing Board Exam 2Документ12 страницCommunity Health Nursing Board Exam 2rhenier_ilado100% (5)
- JCQWORKHEET No.2Документ3 страницыJCQWORKHEET No.2Jan Cleo Cerdiña QuijanoОценок пока нет
- Covid Injections For Dummkopfs - A Summary For Us in Flyover CountryДокумент74 страницыCovid Injections For Dummkopfs - A Summary For Us in Flyover CountryBerk ShireОценок пока нет
- Technique of Blood CollectionДокумент8 страницTechnique of Blood CollectionVivek TiwariОценок пока нет
- Surgical Intern Manual (For Pre-Intern) QEHДокумент10 страницSurgical Intern Manual (For Pre-Intern) QEHChris Jardine LiОценок пока нет
- Enteral Tube Administration of Oral Chemotherapy DrugsДокумент15 страницEnteral Tube Administration of Oral Chemotherapy DrugsCoté HuertaОценок пока нет
- Dosages and Flow Rates and Pediatric Drug Administration AssignmentДокумент6 страницDosages and Flow Rates and Pediatric Drug Administration AssignmentNavin Barnwal0% (1)
- BrochureДокумент3 страницыBrochureapi-400730798Оценок пока нет
- List of Drugs: DRUGS Acting On ANS Respiratory DrugsДокумент2 страницыList of Drugs: DRUGS Acting On ANS Respiratory DrugsShambhu AshokОценок пока нет
- Typhoid FeverДокумент16 страницTyphoid FeverJolyn Ivy CatalanОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric Comprehensive Case StudyДокумент12 страницPsychiatric Comprehensive Case Studyapi-544878035Оценок пока нет
- Tratamiento para UPP en FisioterapiaДокумент44 страницыTratamiento para UPP en FisioterapiaKimberly GomezОценок пока нет
- Obsessive Compulsive DisorderДокумент13 страницObsessive Compulsive Disorderapi-296998780Оценок пока нет
- Unit 5Документ44 страницыUnit 5bereket gashuОценок пока нет
- Patho Immune System PathologyДокумент7 страницPatho Immune System PathologyCoy Nuñez100% (1)
- Basic Life Support Protocol MatrixДокумент1 страницаBasic Life Support Protocol MatrixAleksandar PetrovicОценок пока нет
- Psychosurgery: Year 11 GCSE Psychology Key Topic 8: AggressionДокумент2 страницыPsychosurgery: Year 11 GCSE Psychology Key Topic 8: AggressionFaisal AhmedОценок пока нет
- ADA Ortho CodesДокумент1 страницаADA Ortho CodesAmerican Aesthetic MCОценок пока нет
- Data Alat Kalibrasi Rs TNGДокумент10 страницData Alat Kalibrasi Rs TNGHelena LowaОценок пока нет
- Staying Healthy Book in PDF FormatДокумент110 страницStaying Healthy Book in PDF FormatBОценок пока нет
- A Persuasive Speech About Why Smoking Should Be Illegal SmokingДокумент3 страницыA Persuasive Speech About Why Smoking Should Be Illegal SmokingQ. ad1622Оценок пока нет
- Hyperthyroidism Vs HypothyroidismДокумент12 страницHyperthyroidism Vs Hypothyroidismazizan hannyОценок пока нет
- Ma. Cricel T. Dela Cruz, RMTДокумент4 страницыMa. Cricel T. Dela Cruz, RMTMa. Cricel T. Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Position Paper Group 2 - Physician-Assisted SuicideДокумент13 страницPosition Paper Group 2 - Physician-Assisted SuicideRYAN VARGAS BURCEОценок пока нет
- Liver Function TestsДокумент3 страницыLiver Function Testssamdaman001Оценок пока нет
- CV AustraliaДокумент10 страницCV Australiaralfh1992Оценок пока нет
- PericarditisДокумент19 страницPericarditisxmitchxОценок пока нет
- February Compliance Report On Parkland Memorial HospitalДокумент79 страницFebruary Compliance Report On Parkland Memorial HospitalmilesmoffeitОценок пока нет