Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Protein Plasma Cells Immune System Pathogens Pathogenic Bacteria Viruses Antigen Fab's Variable Region Paratope Epitope Microbe
Загружено:
Judy Ann BoseОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Protein Plasma Cells Immune System Pathogens Pathogenic Bacteria Viruses Antigen Fab's Variable Region Paratope Epitope Microbe
Загружено:
Judy Ann BoseАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
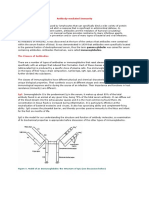
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-
shaped protein produced mainly by plasma cells that is used by the immune system to
neutralize pathogens such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a
unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen, via the Fab's variable region. Each tip of
the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope(analogous to a lock) that is specific for one
particular epitope (similarly analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to
bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an
infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize its target directly
(for example, by blocking a part of a microbe that is essential for its invasion and survival).
Вам также может понравиться
- The notes of antibody: Understanding antibody structure and functionДокумент3 страницыThe notes of antibody: Understanding antibody structure and functionpunithОценок пока нет
- Antibody: Lecture Five Dr. Mouruj Alaubydi and Dr. Jenan AlsaffarДокумент8 страницAntibody: Lecture Five Dr. Mouruj Alaubydi and Dr. Jenan Alsaffarهند نهاد سلمان حسينОценок пока нет
- Antigen: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchДокумент9 страницAntigen: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchKnight StingrayОценок пока нет
- Types of Antibodies Explained in 40 CharactersДокумент17 страницTypes of Antibodies Explained in 40 CharactersSadia NadeemОценок пока нет
- Structure and Functions of Antibody ClassesДокумент15 страницStructure and Functions of Antibody ClassesFaiza RashidОценок пока нет
- Chapter III. Alterations Problems and Its Pathophysiologic Basis in Immunologic Responses, Acute and ChronicДокумент29 страницChapter III. Alterations Problems and Its Pathophysiologic Basis in Immunologic Responses, Acute and ChronicJR Rolf NeuqeletОценок пока нет
- Antigen From Wikipedia and OthersДокумент10 страницAntigen From Wikipedia and OthersGC Biswas RinkuОценок пока нет
- Antibody Iggandiga: Presented by Syed - Khaja.Ali Uddin M.S.D (Endodontics)Документ39 страницAntibody Iggandiga: Presented by Syed - Khaja.Ali Uddin M.S.D (Endodontics)Ali SyedОценок пока нет
- AntibodyДокумент29 страницAntibodyMoneeshОценок пока нет
- BTG 402 - Biotechnology - 2022Документ37 страницBTG 402 - Biotechnology - 2022Emmanuella OffiongОценок пока нет
- About AntigenДокумент7 страницAbout AntigensumantonoОценок пока нет
- Enzyme Hormone AntibodyДокумент1 страницаEnzyme Hormone AntibodyPRINTDESK by DanОценок пока нет
- What Are AntibodiesДокумент11 страницWhat Are Antibodiesishaanjha.21.2007Оценок пока нет
- Antibody StructureДокумент7 страницAntibody StructureMayowa OgunmolaОценок пока нет
- pdf 20230419 071706 ٠٠٠٠Документ24 страницыpdf 20230419 071706 ٠٠٠٠manarsaad978Оценок пока нет
- Learn About Acquired Immunity and LymphocytesДокумент8 страницLearn About Acquired Immunity and LymphocytesVenkatesan VidhyaОценок пока нет
- Bio Project ImmunityДокумент16 страницBio Project Immunityapushpendra400Оценок пока нет
- Bahan Materi DR SaidahДокумент11 страницBahan Materi DR SaidahIrmadaniОценок пока нет
- Immunoglobulin SДокумент22 страницыImmunoglobulin Scessy.manusig9Оценок пока нет
- AntigensДокумент13 страницAntigenshumaira chandaОценок пока нет
- Immune SystemДокумент12 страницImmune SystemIzazОценок пока нет
- AntibodyДокумент10 страницAntibodyRokhmat Bintang DjaisОценок пока нет
- MB 504 Basic ImmunologyДокумент63 страницыMB 504 Basic ImmunologyDr. Jadhav arjit singhОценок пока нет
- 12th Biology Project on ImmunityДокумент16 страниц12th Biology Project on ImmunityShorya Bhaskar89% (9)
- Antibodies: Antibody, Also Called Immunoglobulin, A Protective Protein Produced by The ImmuneДокумент4 страницыAntibodies: Antibody, Also Called Immunoglobulin, A Protective Protein Produced by The ImmuneMansi SingalОценок пока нет
- Bio Project ImmunityДокумент16 страницBio Project Immunityapushpendra981Оценок пока нет
- Immunoglobulins/Antibody: Presented By: Shashi Regd. No. 11006142 Roll No. B15 Section RP8003Документ17 страницImmunoglobulins/Antibody: Presented By: Shashi Regd. No. 11006142 Roll No. B15 Section RP8003Shashi SharmaОценок пока нет
- Body's Third Line of Defence Mechanism: Nonspecific Resistance (Innate Immunity)Документ8 страницBody's Third Line of Defence Mechanism: Nonspecific Resistance (Innate Immunity)taysi tafriОценок пока нет
- Structure and Function of Different Class of Immunoglobulins Antigen Antibody InteractionДокумент36 страницStructure and Function of Different Class of Immunoglobulins Antigen Antibody InteractionNikita Singh RaghavОценок пока нет
- Topic: AntibodyДокумент31 страницаTopic: AntibodyVINDHYA SHANKERОценок пока нет
- Avian Immune System - 1Документ12 страницAvian Immune System - 1Amer AdasОценок пока нет
- Monoclonal Antibodies As Drug Delivery System: by Dr. Sunit Kumar SahooДокумент70 страницMonoclonal Antibodies As Drug Delivery System: by Dr. Sunit Kumar SahooDRx Sonali TareiОценок пока нет
- Interaksi Antigen Dan AntibodiДокумент5 страницInteraksi Antigen Dan AntibodiYusvina QrОценок пока нет
- Lymphatic System and Immunity 2Документ2 страницыLymphatic System and Immunity 2Joven GloriaОценок пока нет
- Immunology: Antigens, Antibodies, and Immune CellsДокумент18 страницImmunology: Antigens, Antibodies, and Immune CellsZulfaidaОценок пока нет
- ANTIBODIES CLASSIFICATIONДокумент25 страницANTIBODIES CLASSIFICATIONmydadyОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Topic - 9Документ22 страницыBiochemistry Topic - 9nonu nouОценок пока нет
- Key Elements of Immunity: SpecificityДокумент9 страницKey Elements of Immunity: SpecificityParth KulkarniОценок пока нет
- Immunology NotesДокумент8 страницImmunology NotesSumit Mukherjee100% (1)
- Immune System 2018Документ3 страницыImmune System 2018Luna SartoriОценок пока нет
- 486 - VPM 403 Introductory Veterinary ImmunologyДокумент52 страницы486 - VPM 403 Introductory Veterinary ImmunologyMachira MuturiОценок пока нет
- Antibody and AntigenДокумент22 страницыAntibody and Antigenwildan pratamaОценок пока нет
- Defence Mechanism of BodyДокумент26 страницDefence Mechanism of BodyTika GurungОценок пока нет
- AntigensДокумент11 страницAntigenssaloОценок пока нет
- Antibody - WikipediaДокумент190 страницAntibody - WikipediatammamalkdatiОценок пока нет
- Understanding the Immune SystemДокумент16 страницUnderstanding the Immune SystemadfggОценок пока нет
- ImmunityДокумент27 страницImmunityMuhammad Fawad100% (1)
- CHAPTER 13 Effector Mechanisms of Humoral ImmunityДокумент21 страницаCHAPTER 13 Effector Mechanisms of Humoral ImmunitySri Sulistyawati AntonОценок пока нет
- Immune System GlossaryДокумент70 страницImmune System GlossaryRaven DoradoОценок пока нет
- Immunity Biology ProjectДокумент17 страницImmunity Biology ProjectSalman Ashraf100% (1)
- Chap 16 Part 2 Major Arms of The Immune System Humoral Immunity (Antibodies)Документ5 страницChap 16 Part 2 Major Arms of The Immune System Humoral Immunity (Antibodies)clrssОценок пока нет
- LymphaticSystem BodyDefensesДокумент2 страницыLymphaticSystem BodyDefensesKhylene Zhen MARQUEZОценок пока нет
- Specific Host Defenses: The Immune ResponseДокумент54 страницыSpecific Host Defenses: The Immune Responseadyaly44Оценок пока нет
- Lect 5 Adaptive ImmДокумент4 страницыLect 5 Adaptive ImmСоња БакраческаОценок пока нет
- Engineered Antibodies for Disease TreatmentДокумент14 страницEngineered Antibodies for Disease TreatmentJholina Aure ReyesОценок пока нет
- Bookshelf: Chapter 8specific Acquired ImmunityДокумент12 страницBookshelf: Chapter 8specific Acquired ImmunityBlake KamminОценок пока нет
- Lahore College For Women University: Biochemistry AssignmentДокумент9 страницLahore College For Women University: Biochemistry AssignmentAzka AsimОценок пока нет
- The Immune System Explained: Innate vs Adaptive DefensesДокумент21 страницаThe Immune System Explained: Innate vs Adaptive DefensesRachelle GuitoriaОценок пока нет
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityОт EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityОценок пока нет
- Immunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988От EverandImmunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988J. F. BachОценок пока нет
- Activity 01 - Bose, Judy AnnДокумент10 страницActivity 01 - Bose, Judy AnnJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Sponsorship Letter To Rizal MayorДокумент2 страницыSponsorship Letter To Rizal MayorJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Work Experience Sheet: Instructions: 1. Include Only The Work Experiences Relevant To The Position Being Applied ToДокумент1 страницаWork Experience Sheet: Instructions: 1. Include Only The Work Experiences Relevant To The Position Being Applied ToJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Protein Plasma Cells Immune System Pathogens Pathogenic Bacteria Viruses Antigen Fab's Variable Region Paratope Epitope MicrobeДокумент1 страницаProtein Plasma Cells Immune System Pathogens Pathogenic Bacteria Viruses Antigen Fab's Variable Region Paratope Epitope MicrobeJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- On-the-job training in agricultural laboratoriesДокумент2 страницыOn-the-job training in agricultural laboratoriesJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Car Rental Agreement Template: Prepared For (Client - Firstname) (Client - Lastname) by (Sender - Firstname) (Sender - Lastname)Документ8 страницCar Rental Agreement Template: Prepared For (Client - Firstname) (Client - Lastname) by (Sender - Firstname) (Sender - Lastname)Judy Ann Bose100% (1)
- Judy Experiment Chelab1Документ2 страницыJudy Experiment Chelab1Judy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of FuelsДокумент2 страницыCharacteristics of FuelsJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Life Cycle Analysis of Cement IndustryДокумент26 страницLife Cycle Analysis of Cement IndustryJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Distillation ConceptsДокумент3 страницыDistillation ConceptsJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Nonisothermal CSTR TutorialДокумент7 страницNonisothermal CSTR TutorialStefanie Guzman AznaranОценок пока нет
- Flowsheet Symbols and PenI DiagramsДокумент30 страницFlowsheet Symbols and PenI DiagramsJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Ps PDДокумент1 страницаPs PDJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- 7Документ5 страниц7tarhuniОценок пока нет
- Lapse Rate and StabilityДокумент4 страницыLapse Rate and StabilityJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Conclusion and RecommendationДокумент1 страницаConclusion and RecommendationJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Batch Distillation Unfin 1Документ13 страницBatch Distillation Unfin 1Judy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Batch Distillation Unfin 1Документ20 страницBatch Distillation Unfin 1Judy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Density vs concentration and w/w% of dye solutionsДокумент16 страницDensity vs concentration and w/w% of dye solutionsJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Day 1 Exam 1Документ3 страницыDay 1 Exam 1Cheng PasionОценок пока нет
- Commercial Applications of EnzymesДокумент3 страницыCommercial Applications of EnzymesJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Gases.: By: Junelyn P. ArquilloДокумент11 страницGases.: By: Junelyn P. ArquilloJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Blowdown Drums: From Technical InvestigationДокумент1 страницаBlowdown Drums: From Technical InvestigationJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Conclusion and RecommendationДокумент3 страницыConclusion and RecommendationJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Drying Is An Energy Intensive Process Involving Simultaneous Heat and Mass TransferДокумент1 страницаDrying Is An Energy Intensive Process Involving Simultaneous Heat and Mass TransferJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Conclusion and RecommendationДокумент1 страницаConclusion and RecommendationJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Result and Discussion1Документ8 страницResult and Discussion1Judy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- A. Calculations: ML M ML C V C V CДокумент5 страницA. Calculations: ML M ML C V C V CJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Adsorption Isotherm and Fixed Bed Adsorption of Dye onto Activated CarbonДокумент4 страницыAdsorption Isotherm and Fixed Bed Adsorption of Dye onto Activated CarbonJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- Ps PDДокумент8 страницPs PDJudy Ann BoseОценок пока нет
- SM pc300350 lc6 PDFДокумент788 страницSM pc300350 lc6 PDFGanda Praja100% (2)
- HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of DrugsДокумент7 страницHPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of DrugsWidya Dwi Arini100% (1)
- 08.kecakapan Bahari (Indo)Документ150 страниц08.kecakapan Bahari (Indo)ariОценок пока нет
- Animal BitesДокумент48 страницAnimal BitesJalouis GabalfinОценок пока нет
- Anger Child of Fear: How Vulnerability Leads to AngerДокумент2 страницыAnger Child of Fear: How Vulnerability Leads to AngerYeferson PalacioОценок пока нет
- Summary of Verb TensesДокумент4 страницыSummary of Verb TensesRamir Y. LiamusОценок пока нет
- Akhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihДокумент44 страницыAkhila-Rasamrta-Murtih Prasrmara-Ruci-Ruddha-Taraka-PalihSauri ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- ESL S9 W3 P14-15 Project Challenge Part 2Документ27 страницESL S9 W3 P14-15 Project Challenge Part 2Emma Catherine BurkeОценок пока нет
- Method in Dogmatic Theology: Protology (First Revelatory Mystery at Creation) To Eschatology (Last RedemptiveДокумент62 страницыMethod in Dogmatic Theology: Protology (First Revelatory Mystery at Creation) To Eschatology (Last RedemptiveefrataОценок пока нет
- Terese LiteДокумент211 страницTerese Liteoguruma100% (1)
- Magic Writ: Textual Amulets Worn On The Body For Protection: Don C. SkemerДокумент24 страницыMagic Writ: Textual Amulets Worn On The Body For Protection: Don C. SkemerAsim HaseljicОценок пока нет
- 2021 GSFR General ChecklistДокумент12 страниц2021 GSFR General Checklistapi-584007256Оценок пока нет
- Adeptia BPM Suite DatasheetДокумент2 страницыAdeptia BPM Suite DatasheetadeptiaОценок пока нет
- Maghrib Time Nairobi - Google SearchДокумент1 страницаMaghrib Time Nairobi - Google SearchHanan AliОценок пока нет
- The Fundamentals of Lighting PDFДокумент20 страницThe Fundamentals of Lighting PDFVasilis Karageorgiou100% (1)
- Let's Meet Peter Conozcamos A PeterДокумент4 страницыLet's Meet Peter Conozcamos A PeterJuan Felipe Restrepo MayaОценок пока нет
- Extension Worksheet For Week 5Документ4 страницыExtension Worksheet For Week 5PRAVITHA SHINEОценок пока нет
- As Work: Self Perceptions and Perceptions of Group Climate Predictors of Individual Innovation atДокумент17 страницAs Work: Self Perceptions and Perceptions of Group Climate Predictors of Individual Innovation atMuqadas KhanОценок пока нет
- Central Venous Access Devices (Cvads) andДокумент68 страницCentral Venous Access Devices (Cvads) andFitri ShabrinaОценок пока нет
- 7 Day Diet AnalysisДокумент5 страниц7 Day Diet AnalysislipakevinОценок пока нет
- English Language (1122)Документ26 страницEnglish Language (1122)TD X Mzinda100% (1)
- Person On The StreetДокумент12 страницPerson On The StreetalyssajdorazioОценок пока нет
- Act 1 Scene 1 Script 1Документ3 страницыAct 1 Scene 1 Script 1api-551719156Оценок пока нет
- HPC - 2022-JIAF - Guide-1.1Документ60 страницHPC - 2022-JIAF - Guide-1.1Emmanuel LompoОценок пока нет
- DMBS Asgnmt 3Документ2 страницыDMBS Asgnmt 3abhi404171Оценок пока нет
- Figures of Speech AND 21 Literary GenresДокумент33 страницыFigures of Speech AND 21 Literary GenresMike AsuncionОценок пока нет
- UPSC PSIR Test 11 Model Answers ExplainedДокумент16 страницUPSC PSIR Test 11 Model Answers ExplainedSahil TomarОценок пока нет
- RMXPRT Manual PDFДокумент481 страницаRMXPRT Manual PDFsch12332163% (16)
- History E XДокумент13 страницHistory E XTamboli Shaikh Muaavvir AkbarОценок пока нет