Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Standard Operating PServicing Exhaust Systems in Research Facilities
Загружено:
henreng0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров6 страницStandard Operating PServicing Exhaust Systems in Research Facilities
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документStandard Operating PServicing Exhaust Systems in Research Facilities
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
8 просмотров6 страницStandard Operating PServicing Exhaust Systems in Research Facilities
Загружено:
henrengStandard Operating PServicing Exhaust Systems in Research Facilities
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 6
Standard Operating Practice for Servicing
Exhaust Systems in Research Facilities
Objective
The following procedure was developed to protect maintenance
personnel and laboratory workers from potential exposure to hazardous
materials while servicing exhaust systems.
Scope
This policy applies to all Facilities Management maintenance
employees who perform work that requires entering or removing duct
work, entering the fan housing, changing filters, shutting off fans or any
other maintenance that requires entering the inside of the exhaust
system. Special precautions are not required when servicing equipment
which is outside of the hood cabinet and/or outside of the potentially
contaminated air stream. For example, belts and pulleys may be
serviced, vibration isolators may be caulked and lamps may be replaced
on many fume hoods without entering the interior of the hood or
exhaust duct.
Program Components
1. Responsibilities
2. Pre-maintenance Activities
3. Maintenance Procedures
General Practices for Working Inside of Exhaust Systems
Special procedures
4. Routine Leak Inspection
5. Appendices
1. Responsibilities
Operations Supervisors:
1. Assure that employees assigned to work in potentially
contaminated systems are adequately trained and utilize the appropriate
personal protective equipment.
2. Assure that maintenance work requiring the shut-down of the
system is coordinated with the customer.
3. Assure that inspection checklists are submitted to the
Occupational Health and Safety Administrator upon completion.
Maintenance Employees:
1. Perform work in a manner consistent with this policy utilizing
the appropriate personal protective equipment.
2. Pre-maintenance Activities
A. Whenever service requires that a fumehood, biological safety
cabinet or other local exhaust system be shut down, the
designated laboratory supervisor must be informed of the time
and duration of the shut down.
B. Whenever work must be done inside of the exhaust system,
laboratory staff must confirm that hazardous materials have been
secured. Laboratory staff are also responsible to assure that a
work area in laboratory space is cleared of laboratory
equipment; maintenance staff need room to place their tools and
may occasionally need room to place a ladder. NOTE: Facilities
Management maintenance employees shall not remove alter or
move laboratory equipment or chemicals. Laboratory staff are
responsible these items.
C. Immediately before an exhaust system will be shut down, the
sign shown in Appendix A must be placed on the sash of the
fumehood. If the exhaust system being serviced, provides
ventilation for an entire room, this sign must also be placed on
the door to the room.
D. Some work inside an exhaust system may be accomplished
without shutting it down. However, hazardous chemicals must
be secured and the fumehood cleared so that work can be safely
performed. Some examples of work inside the exhaust system
which can be done while the fumehood is running include:
replacing lamps, cleaning behind fumehood baffles or replacing
airflow sensors.
3. Maintenance Procedures
A. General Practices for Working Inside of Exhaust Systems
1. Wear the following personal protective equipment: minimum
respiratory protection of a 3M 9913 dust mask, plastic or rubber gloves,
chemical goggles or face shield and coveralls.
2. Perform necessary maintenance
3. Dispose of coveralls and wash the outside of gloves or
dispose of gloves.
4. Remove mask and gloves; then wash hands and face.
B. Special Operating Procedures
Radioisotope Hoods
1. Whenever working on the inside of a fumehood cabinet
posted with a "Caution Radioactive Materials" sign,
contact the Department of Environmental Health and
Safety, Radiation Protection Division (RPD) and request
a survey to certify that hood contamination is below
applicable standards. Use the flowchart (Appendix B) to
determine if RPD should be contacted to perform a
survey. Following the survey, RPD staff will post the
hood with the notice shown in Appendix B.
2. When working inside of duct work or fan systems that
serves a radioisotope hood, the RPD need not be
contacted except in the following locations: W-41
Boynton, 338 An Sci/Vet Med, V73 VFW Bldg., 1-274 U
Hospital, and 2nd Floor Hosp Nuc Med Hood. A survey
is necessary for these hoodsbecause they are the only
locations where volatile radioisotopes are used which
might contaminate an air stream.
3. If contamination is below applicable standards the
general practices outlined above shall be used.
4. If contamination is above applicable standards, special
procedures will be specified by the RPD representative.
Perchloric Acid Hoods
1. Contact the Department of Environmental Health and
Safety (DEHS). The hood will be tested for the presence
for perchlorates.
2. If perchlorates are not present, proceed under general
practices as outlined above in 3.A.
3. If perchlorates are present, the hood must be washed
down with water until the levels are acceptable. After
safe levels are reached, proceed under general practices
as outlined above.
Biological Safety Cabinets
1. Follow the general practices discussed in 3.A. when
servicing building HVAC equipment serving a biological
safety cabinet. Particulate contaminants originating
inside the cabinet are filtered out by the biological safety
cabinet filters system before reaching the building HVAC
system.
2. Contact the Department of Environmental Health and
Safety before working inside contaminated spaces of the
biological safety cabinet such as the plenum, blower or
HEPA filter compartment.
Replacement/Repair of HEPA or Charcoal Filters
1. Follow the general practices as outlined above.
2. For removal of these filters, follow the precautions and
procedures listed below:
a. At least the following equipment will be required:
ladder, duct tape, large U of MN #21058 poly
bag, + and - screwdrivers, pliers and adjustable
wrench.
b. Notify lab of required maintenance, tag out hood
then turn off the fumehood fan.
c. Put on protective equipment.
d. Remove the filter access panel and place in a bag.
Verify that filter locking devices are loosened.
e. Attach the large #21058 bag around the filter
access panel opening in a manner that seals the
filter access opening using duct tape or elastic
cord.
f. Remove the prefilter by grasping the filter from
outside the bag (with the bottom of the bag) and
pull it into the bag.
g. Pull the HEPA filter into the bag in the same
manner. NOTES: a) Charcoal filters are heavy
when compared to a HEPA filter. Because a used
charcoal filter can weigh 100 pounds, you may
require assistance to remove it. b) In some cases,
it may be necessary to remove the bag with the
prefilter and tape a second bag to the access panel
for removal of the HEPA filter.
h. Remove the bag from the duct work, then seal the
bag shut with tape, leave the bag on the lab floor
near the fumehood.
i. Replace the access panel(s).
j. Restart the fumehood fan.
k. Reassemble the fumehood.
l. Any tools that have had contact with the interior
of the filter enclosure should be placed in a bag
by filter and RPD will survey them.
m. Clean up any dust or debris outside of the
fumehood with wet paper towels and place them
in a bag. Then remove coverall, respirator, glove
and place them in a bag. Wash hands when job
completed.
n. Contact the RPD of the Department of
Environmental Health and Safety to clearance
check the filters which were removed from the
fumehood.
o. RPD will contact FM to have them remove the
filters to a dumpster if the item was cleared for
disposal. If not cleared for general disposal, RPD
staff will remove the filters for special disposal.
p. The fumehood system must be rebalanced to
assure that face velocities are between 90 and 110
feet per minute. When completed, the mechanic
will advise an operations supervisor. The
Operations Supervisor will notify DEHS that the
system has been balanced. Also, notify lab staff
and remove tag out posting upon completion of
the job.
2. Do not replace filters in fumehood ducts unless directed
to do so by DEHS staff.
Repair of Heat Recovery Coils
1. Follow the general practices as outlined in above.
2. Prefilters must be carefully removed and placed into
heavy polyethylene bags. The bags must be taped shut
and placed in the general waste stream.
4. Routine Leak Inspection
1. Inspect the fan housing, vibration isolator and the positive
pressure duct work for leaks.
2. Seal minor leaks that have been identified NOTE: If you are not
able to seal the leaks, notify your operations supervisor and note
the duct work condition.
5. Appendices
1. Appendix A:
o Health and Safety Notice for Fume Hoods (PDF)
o Fume Hood Out-of-Service Notice (PDF)
2. Appendix B:
o Fume Hood Flow Chart
Вам также может понравиться
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Read MeДокумент1 страницаRead MehenrengОценок пока нет
- SpreadsheetДокумент9 страницSpreadsheethenrengОценок пока нет
- Testing of Ventilation SystemsДокумент24 страницыTesting of Ventilation SystemshenrengОценок пока нет
- TD Outside Air White PaperДокумент7 страницTD Outside Air White PaperhenrengОценок пока нет
- File 1365802787 PDFДокумент2 страницыFile 1365802787 PDFhenrengОценок пока нет
- Femap Tips and Tricks: Solid Mesh Internal BeamsДокумент4 страницыFemap Tips and Tricks: Solid Mesh Internal BeamshenrengОценок пока нет
- Simulation of Acoustic and Vibroacoustic Problems in LS-DYNA® Using Boundary Element MethodДокумент10 страницSimulation of Acoustic and Vibroacoustic Problems in LS-DYNA® Using Boundary Element MethodhenrengОценок пока нет
- Global Directory 2016Документ2 страницыGlobal Directory 2016henreng100% (1)
- Single Analysis - Static Structural: © 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ANSYS, Inc. ProprietaryДокумент3 страницыSingle Analysis - Static Structural: © 2009 ANSYS, Inc. All Rights Reserved. ANSYS, Inc. ProprietaryhenrengОценок пока нет
- On An Automated Headland Turn of Wide Width Air Seeders: Conference PaperДокумент9 страницOn An Automated Headland Turn of Wide Width Air Seeders: Conference PaperhenrengОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
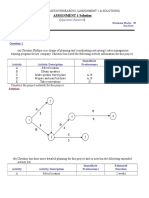
- Assignment 01 SolutionДокумент5 страницAssignment 01 SolutionNeven Ahmed HassanОценок пока нет
- Vulnerability Assessment Best PracticesДокумент25 страницVulnerability Assessment Best Practicesdehnhaide100% (1)
- Cigarette Smoking Teens Published JNSRДокумент10 страницCigarette Smoking Teens Published JNSRJusil RayoОценок пока нет
- CV Dr. HB - Croxatto - English March 2008Документ9 страницCV Dr. HB - Croxatto - English March 2008Camillita BelénОценок пока нет
- The Legend of The Seven WhalesДокумент1 страницаThe Legend of The Seven WhalesSue WestОценок пока нет
- Experimental Psychology and The Scientific Method: Instructor: Mr. Omar T. BualanДокумент22 страницыExperimental Psychology and The Scientific Method: Instructor: Mr. Omar T. BualanAndrea JonОценок пока нет
- Screen Time ChildДокумент11 страницScreen Time ChildTere NavaОценок пока нет
- Dynamind StudyДокумент17 страницDynamind StudyCarlos VizcarraОценок пока нет
- CompaniesДокумент2 страницыCompaniesPrachi AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Informed Consent Evaluation Form: University of Cebu AcademeДокумент3 страницыInformed Consent Evaluation Form: University of Cebu AcademeMary Sam QuindaoОценок пока нет
- Functionalist Theories of ReligionДокумент19 страницFunctionalist Theories of ReligionHimanshu KapkotiОценок пока нет
- Pengendalian Mutu Pada Produksi Keripik SukunДокумент10 страницPengendalian Mutu Pada Produksi Keripik SukunSatrio FebriansyahОценок пока нет
- A Project On A Statistical Analysis of The OTT Platform Business in Bangladesh-ReportДокумент24 страницыA Project On A Statistical Analysis of The OTT Platform Business in Bangladesh-ReportNayeem Ahamed AdorОценок пока нет
- Baldwin Multiplying Fractions 5e Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницBaldwin Multiplying Fractions 5e Lesson Planapi-468871101Оценок пока нет
- XRF-2020 Series: Coating Thickness Gauge Elemental Analysis ROHS AnalyzerДокумент3 страницыXRF-2020 Series: Coating Thickness Gauge Elemental Analysis ROHS AnalyzerPhạm DươngОценок пока нет
- LDR 475 SyllabusДокумент18 страницLDR 475 Syllabusapi-272923884Оценок пока нет
- OR II Lecture NotesДокумент15 страницOR II Lecture NotesGiramia Moniquea OmodingОценок пока нет
- Homework and Practice Workbook Holt Middle School Math Course 2 AnswersДокумент4 страницыHomework and Practice Workbook Holt Middle School Math Course 2 Answersd0t1f1wujap3100% (1)
- Article-8066-Coressponding author-AdiFRДокумент7 страницArticle-8066-Coressponding author-AdiFRafran ramadhanОценок пока нет
- Summer Internship Report On HR Recruitment and SelectionДокумент65 страницSummer Internship Report On HR Recruitment and SelectionNarvada Shankar Singh94% (35)
- Target Markets, Segmentation and EvaluationДокумент42 страницыTarget Markets, Segmentation and EvaluationoneОценок пока нет
- Audit Fee Premium and Auditor Change - The Effect of Sarbanes-Oxley Act (Review)Документ3 страницыAudit Fee Premium and Auditor Change - The Effect of Sarbanes-Oxley Act (Review)Kharisma BaptiswanОценок пока нет
- B.Ed. First Year - Sem. 1 Course - 104 Understanding Disciplines and School SubjectsДокумент4 страницыB.Ed. First Year - Sem. 1 Course - 104 Understanding Disciplines and School SubjectsMukesh KumarОценок пока нет
- ENISA Cyber-Exercises Analysis Report-V1.0 PDFДокумент32 страницыENISA Cyber-Exercises Analysis Report-V1.0 PDFPaulo FelixОценок пока нет
- Physics Revision Booklet 2015 v4Документ38 страницPhysics Revision Booklet 2015 v4kautiОценок пока нет
- Effects of Online Learning Mode in Psychological Aspect of College StudentsДокумент4 страницыEffects of Online Learning Mode in Psychological Aspect of College StudentsChrizel DiamanteОценок пока нет
- Research Paper Scaffold WorksheetДокумент6 страницResearch Paper Scaffold Worksheetfvgxy2ha100% (3)
- Mbti ResultsДокумент2 страницыMbti Resultsapi-534096580Оценок пока нет
- Nonparametric Statistics and Model Selection: 5.1 Estimating Distributions and Distribution-Free TestsДокумент10 страницNonparametric Statistics and Model Selection: 5.1 Estimating Distributions and Distribution-Free TestshalijahОценок пока нет
- Thesis About Mother Tongue Based EducationДокумент8 страницThesis About Mother Tongue Based Educationkimstephenswashington100% (2)