Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Pelvic Pain Case Discussion
Загружено:
aayceeАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Pelvic Pain Case Discussion
Загружено:
aayceeАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
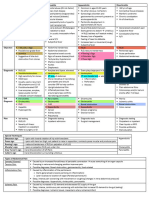
SUGGESTED FURTHER DIAGNOSTIC
HISTORY -FINDING DIAGNOSES CONSIDERATIONS
History of intrauterine Adenomyosis Magnetic resonance imaging
instrumentation, multiple (endometrial tissue
cesarean deliveries, or other grown into the
uterine surgeries uterine wall)
Pelvic adhesions Consider non-urgent referral to
gynecologist or general surgeon in
absence of other findings
Menstrual abnormalities
Amenorrhea Imperforate hymen Pelvic examination
Transverse vaginal Pelvic ultrasonography
septum
Dysmenorrhea Endometriosis, Pelvic ultrasonography (to assess for
ovarian cyst ovarian cyst)
Nausea and vomiting Appendicitis, ovarian If appendicitis is more likely: proceed with
torsion contrast CT
If ovarian torsion is more likely: proceed
with pelvic ultrasonography with Doppler
flow study
Early urgent referral for surgical evaluation
and treatment is recommended
Pain symptoms
Bilateral pain, Pelvic inflammatory Testing for sexually transmitted infections
particularly if associated disease
with mucopurulent
vaginal discharge
Complete blood count to test for
leukocytosis or left shift
SUGGESTED FURTHER DIAGNOSTIC
HISTORY -FINDING DIAGNOSES CONSIDERATIONS
Dull, unilateral adnexal Ovarian torsion Presence of risk factors (nausea, vomiting,
pain that is constant or pregnancy)
intermittent
Pelvic ultrasonography with Doppler flow
study
Consider urgent referral for surgical
evaluation and treatment
Right lower quadrant Acute appendicitis Complete blood count demonstrating
pain leukocytosis
Contrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis
Ectopic pregnancy Qualitative urine β-hCG can detect a
pregnancy at four weeks' gestation
Quantitative serum β-hCG can determine if
pregnancy is above the discriminatory level
such that an intrauterine pregnancy should
be visible on pelvic ultrasonography to rule
out ectopic gestation (Figure 2)
Blood type to determine Rh status; if
bleeding and pregnant, will need Rho(D)
immune globulin (RhoGam)
Pelvic ultrasonography
Ovarian torsion Pelvic ultrasonography with Doppler flow
study
Sexually active; pregnancy Ectopic pregnancy, Qualitative urine β-hCG can detect a
possible spontaneous pregnancy at four weeks' gestation
abortion
Quantitative serum β-hCG can determine if
pregnancy is above the discriminatory level
SUGGESTED FURTHER DIAGNOSTIC
HISTORY -FINDING DIAGNOSES CONSIDERATIONS
such that an intrauterine pregnancy should
be visible on pelvic ultrasonography to rule
out ectopic gestation (Figure 2)
Blood type to determine Rh status; if
bleeding and pregnant, will need Rho(D)
immune globulin
Pelvic ultrasonography
Urinary symptoms
Dysuria Urinary tract Urinalysis demonstrating white blood cells,
infection bacteria, leukocyte esterase, or nitrites
Gross hematuria Urolithiasis Abdominal ultrasonography
SUGGESTED FURTHER DIAGNOSTIC
P/E FINDING DIAGNOSES CONSIDERATIONS
Carnett sign (increased pain Musculoskeletal No further testing needed in the absence
to palpation when the (abdominal wall) of other historical or physical examination
abdominal wall musculature is pain findings that might suggest intrapelvic or
voluntarily contracted) intra-abdominal conditions
Cervical motion tenderness Pelvic inflammatory Consider testing for sexually transmitted
disease infections
Fever Appendicitis Ultrasonography or contrast CT of the
abdomen and pelvis
Complete blood count demonstrating
leukocytosis
Pelvic inflammatory Consider testing for sexually transmitted
disease infections
SUGGESTED FURTHER DIAGNOSTIC
P/E FINDING DIAGNOSES CONSIDERATIONS
Pyelonephritis Urinalysis demonstrating evidence of
urinary tract infection (white blood cells,
bacteria, leukocyte esterase, or nitrites)
Complete blood count demonstrating
leukocytosis, left shift
Tubo-ovarian Pelvic ultrasonography
abscess
Complete blood count demonstrating
leukocytosis, left shift
Pelvic mass Ectopic pregnancy See Table 2
Fibroid uterus Pelvic ultrasonography
Ovarian cancer Pelvic ultrasonography
Consider CT of the chest, abdomen, and
pelvis if metastatic disease is suspected
Ovarian cyst Pelvic ultrasonography
Tubo-ovarian Pelvic ultrasonography
abscess
Rovsing sign (palpation in the Appendicitis Contrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis
left lower quadrant causes
pain in the right lower
quadrant)
Complete blood count demonstrating
leukocytosis
Tachycardia, hypotension Ruptured ectopic Consider urgent referral to facility with
pregnancy immediate surgical
SUGGESTED FURTHER DIAGNOSTIC
P/E FINDING DIAGNOSES CONSIDERATIONS
Ruptured
hemorrhagic cyst
capability
Evaluation of Selected Common Causes of Acute Pelvic Pain After Ruling
Out Pregnancy
Ultrasonography and Laboratory Evaluation of a Patient in Early Pregnancy
with Acute Pelvic Pain
Вам также может понравиться
- Lower Genital Tract Precancer: Colposcopy, Pathology and TreatmentОт EverandLower Genital Tract Precancer: Colposcopy, Pathology and TreatmentОценок пока нет
- Appendix ModuleДокумент30 страницAppendix ModuleNagulan ChanemougameОценок пока нет
- Current and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 2: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryОт EverandCurrent and Future Developments in Surgery: Volume 2: Oesophago-gastric SurgeryОценок пока нет
- History Taking in A Gynae Patient For ECHSДокумент3 страницыHistory Taking in A Gynae Patient For ECHSBright KumwendaОценок пока нет
- Isolated Hematuria - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionДокумент3 страницыIsolated Hematuria - Genitourinary Disorders - MSD Manual Professional EditionleozdmОценок пока нет
- ABNORMALДокумент33 страницыABNORMALJc Mae CuadrilleroОценок пока нет
- Right Lower Quadrant PainДокумент19 страницRight Lower Quadrant PainSohaib Mohammad KhanОценок пока нет
- Vaginal Discharge Symptom Flow ChartДокумент2 страницыVaginal Discharge Symptom Flow ChartJeff ZhouОценок пока нет
- Aquifer Case 27Документ4 страницыAquifer Case 27Dina KristevaОценок пока нет
- Case-Presentation Final Nagd Ni ShetДокумент7 страницCase-Presentation Final Nagd Ni ShetMary Beth AbelidoОценок пока нет
- Spontaneous Perinephric Urinoma Presenting As Acute Abdomen in The Third Trimester: A Case ReportДокумент3 страницыSpontaneous Perinephric Urinoma Presenting As Acute Abdomen in The Third Trimester: A Case ReportSachin AjithОценок пока нет
- Peritonela TumorДокумент6 страницPeritonela TumorEuis Maya SaviraОценок пока нет
- Acute Appendicitis in a 15-Year-Old FemaleДокумент48 страницAcute Appendicitis in a 15-Year-Old FemaleSimon Peter MollanedaОценок пока нет
- EP C2 by EliДокумент40 страницEP C2 by EliElsai EsbОценок пока нет
- 1 Role of Ultrasound in The Evaluation of Acute Pelvic PainДокумент11 страниц1 Role of Ultrasound in The Evaluation of Acute Pelvic PainGhofran Ibrahim HassanОценок пока нет
- Abdomen Agudo en Enfermedades No QuirurgicasДокумент5 страницAbdomen Agudo en Enfermedades No QuirurgicasGonzalez ByronОценок пока нет
- Abdominal ChartsДокумент3 страницыAbdominal ChartsAmanda MuchaОценок пока нет
- Management of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinДокумент71 страницаManagement of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinRakaОценок пока нет
- Kel 39 - Ruptur ServiksДокумент7 страницKel 39 - Ruptur Servikswawan saifullah100% (1)
- Ectopic 2Документ48 страницEctopic 2Norsri WahyuОценок пока нет
- UTI Urinary Tract Infections: Causes, Symptoms, DiagnosisДокумент3 страницыUTI Urinary Tract Infections: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosisjishu baruaОценок пока нет
- History Taking in An Obstetric Patient For ECHSДокумент3 страницыHistory Taking in An Obstetric Patient For ECHSBright KumwendaОценок пока нет
- Long 1996Документ3 страницыLong 1996galihОценок пока нет
- The Acute AbdomenДокумент30 страницThe Acute Abdomenmary2001pkОценок пока нет
- JRCR 4 2 9Документ9 страницJRCR 4 2 9Berry BancinОценок пока нет
- Interstitial CystitisДокумент9 страницInterstitial CystitisKousik Amancharla100% (3)
- Appendicitis in Children: Common and Often UrgentДокумент6 страницAppendicitis in Children: Common and Often UrgentHasan MohammedОценок пока нет
- Appendicitis HasanДокумент6 страницAppendicitis HasanHasan MohammedОценок пока нет
- Usg ToaДокумент6 страницUsg ToaMuhammad Nugie ZifiОценок пока нет
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)Документ16 страницPelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)CHRISTIAN RAY ALPAS PASILIAOОценок пока нет
- Ectopic PregnancyДокумент18 страницEctopic PregnancyWondimu EliasОценок пока нет
- Gestational Trophic Disease & Placental DisordersДокумент4 страницыGestational Trophic Disease & Placental DisordersJannen CasasОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент40 страницUntitleddОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract Infection in PregnancyДокумент49 страницUrinary Tract Infection in PregnancyBALMERA, DANIELLA B.Оценок пока нет
- Acute Scrotum: DR - Ameer Alaraji College of Medicine, Fabms, FJMC, High Speciality in UrologyДокумент63 страницыAcute Scrotum: DR - Ameer Alaraji College of Medicine, Fabms, FJMC, High Speciality in UrologyHaider Nadhem AL-rubaiОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound Imaging of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10009-1276Документ8 страницUltrasound Imaging of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: 10.5005/jp-Journals-10009-1276ryan enotsОценок пока нет
- Abdominal PainДокумент1 страницаAbdominal PainironОценок пока нет
- Testicular Disorders Freeman 2013Документ56 страницTesticular Disorders Freeman 2013Evan PermanaОценок пока нет
- LITERATURE REVIEW ON ENDOSCOPY EXAMINATIONДокумент29 страницLITERATURE REVIEW ON ENDOSCOPY EXAMINATIONShenaquitaIvandraОценок пока нет
- Dr. Franklin - Acute Appendicitis - FDRДокумент31 страницаDr. Franklin - Acute Appendicitis - FDRAbel MncaОценок пока нет
- Acute AppendicitisДокумент18 страницAcute AppendicitisemailimelОценок пока нет
- Ectopic Pregnancy FINALДокумент32 страницыEctopic Pregnancy FINALZak KazОценок пока нет
- Acute Abdominal Pain: Associate Professor, Dept. of Surgery Mti, KMC, KTHДокумент45 страницAcute Abdominal Pain: Associate Professor, Dept. of Surgery Mti, KMC, KTHWaleed MaboodОценок пока нет
- Ket 5Документ4 страницыKet 5Handy SaputraОценок пока нет
- Urogenital Imaging Kuliah Coass - 210816 - 191356Документ77 страницUrogenital Imaging Kuliah Coass - 210816 - 191356ShashaОценок пока нет
- Torsion of Cystic Ovary: An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdomen in Midtrimester PregnancyДокумент4 страницыTorsion of Cystic Ovary: An Unusual Cause of Acute Abdomen in Midtrimester PregnancyFrank LavillaОценок пока нет
- Canine Prostatic Diseases: Reproduction and Periparturient CareДокумент13 страницCanine Prostatic Diseases: Reproduction and Periparturient CareSatria Adi MarhendraОценок пока нет
- Trauma GinjalДокумент26 страницTrauma GinjalMohamad ZulfikarОценок пока нет
- Trauma Abdomen in Critical Care Nursing-1Документ17 страницTrauma Abdomen in Critical Care Nursing-1doni januarindraОценок пока нет
- Angel Problem 4a GITДокумент48 страницAngel Problem 4a GITMaxend Arselino SilooyОценок пока нет
- Alterations in Genitourinary and Reproductive System - 3rd UEДокумент13 страницAlterations in Genitourinary and Reproductive System - 3rd UEBeyaaa GingoyonОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Testicular DisordersДокумент56 страницEvaluation of Testicular Disordersamal.fathullahОценок пока нет
- EctopicДокумент5 страницEctopicKramer ChangОценок пока нет
- Gynecology Notes Ebook PDFДокумент51 страницаGynecology Notes Ebook PDFThistell Thistle100% (1)
- Acute Abdomen Terri PresentationДокумент75 страницAcute Abdomen Terri PresentationterriОценок пока нет
- Placenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta GuideДокумент3 страницыPlacenta Previa and Abruptio Placenta GuideBryan MorteraОценок пока нет
- OSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSДокумент24 страницыOSCE Gynae-OSCE-MMSSMohammad Saifullah100% (1)
- Uwise HYДокумент3 страницыUwise HYJack GuccioneОценок пока нет
- Acute Scrotal PainДокумент46 страницAcute Scrotal PainAdi SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Urinary Tract Infection CMEДокумент43 страницыUrinary Tract Infection CMEDarwithaОценок пока нет
- CFPC 99 Topics Starter Study DocumentДокумент372 страницыCFPC 99 Topics Starter Study DocumentaayceeОценок пока нет
- Exercise Is MedicineДокумент1 страницаExercise Is MedicineaayceeОценок пока нет
- Motivational Interviews TipsДокумент1 страницаMotivational Interviews TipsaayceeОценок пока нет
- 2015 CHEPOnePageSummary EN PDFДокумент1 страница2015 CHEPOnePageSummary EN PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Gestational-Diabetes-Mellitus InfosheetДокумент1 страницаGestational-Diabetes-Mellitus InfosheetaayceeОценок пока нет
- Choosing Wisely Canada PDFДокумент152 страницыChoosing Wisely Canada PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Choosing Wisely Bullets To Primary CareДокумент10 страницChoosing Wisely Bullets To Primary CareaayceeОценок пока нет
- Infant-Nutrition GuideДокумент2 страницыInfant-Nutrition GuideaayceeОценок пока нет
- Calorie-Density SheetДокумент1 страницаCalorie-Density SheetaayceeОценок пока нет
- Beginners Guide to Getting Started with Indian CuisineДокумент34 страницыBeginners Guide to Getting Started with Indian CuisineaayceeОценок пока нет
- Clinical Reasoning SkillsДокумент2 страницыClinical Reasoning SkillsaayceeОценок пока нет
- My Safety PlanДокумент3 страницыMy Safety PlanaayceeОценок пока нет
- 2015 CHEPOnePageSummary EN PDFДокумент1 страница2015 CHEPOnePageSummary EN PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Choosing Wisely Canada PDFДокумент152 страницыChoosing Wisely Canada PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Medication - Chart ADHD PDFДокумент2 страницыMedication - Chart ADHD PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Most CommonДокумент9 страницMost CommonOsama AlhumisiОценок пока нет
- CPG Quick Reference Guide Web enДокумент10 страницCPG Quick Reference Guide Web enJianhua ShiОценок пока нет
- Abdominal X Rays Made Easy - Abnormal Intraluminal GasДокумент2 страницыAbdominal X Rays Made Easy - Abnormal Intraluminal GasRodry Mikhael Lumban TobingОценок пока нет
- Algoritma BradycardiaДокумент1 страницаAlgoritma BradycardiaFiya SahrulОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics Wisely Webinar PDFДокумент67 страницAntibiotics Wisely Webinar PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Gold 2018Документ142 страницыGold 2018histoginoОценок пока нет
- Medication - Chart ADHD PDFДокумент2 страницыMedication - Chart ADHD PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Geriatrics Medication-Management (With-Multi-Morbidity) PDFДокумент42 страницыGeriatrics Medication-Management (With-Multi-Morbidity) PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Geriatrics Medication-Management (With-Multi-Morbidity) PDFДокумент42 страницыGeriatrics Medication-Management (With-Multi-Morbidity) PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- Antibiotics Wisely Webinar PDFДокумент67 страницAntibiotics Wisely Webinar PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- 6 M's To Keep in Mind When You Next See A Patient With Anorexia NervosaДокумент2 страницы6 M's To Keep in Mind When You Next See A Patient With Anorexia Nervosaaaycee100% (1)
- AGS 2019 BEERS Pocket PRINTABLE PDFДокумент8 страницAGS 2019 BEERS Pocket PRINTABLE PDFWidya Mandala100% (1)
- Geriatrics Beers Criteria PDFДокумент13 страницGeriatrics Beers Criteria PDFaayceeОценок пока нет
- MENTAL EXAMINATION TemplateДокумент1 страницаMENTAL EXAMINATION TemplateaayceeОценок пока нет
- 5.3 User Interface Terason Application Integration Patient Information Array Microphone...Документ238 страниц5.3 User Interface Terason Application Integration Patient Information Array Microphone...Paulo FerreiraОценок пока нет
- PA Technical Guidelines Extract - enДокумент10 страницPA Technical Guidelines Extract - enRizwan Jamil0% (1)
- POCUS ProceduresДокумент123 страницыPOCUS Proceduresjaimin 666Оценок пока нет
- Semiology 998Документ121 страницаSemiology 998Popescu Nicusor100% (1)
- Medical Robotics For Ultrasound Imaging: Current Systems and Future TrendsДокумент17 страницMedical Robotics For Ultrasound Imaging: Current Systems and Future TrendsAshish Presanna ChandranОценок пока нет
- Utt NotesДокумент82 страницыUtt NotesDenzil D'SouzaОценок пока нет
- Product Data Aplio 500 Platinum SeriesДокумент16 страницProduct Data Aplio 500 Platinum SeriesdmseoaneОценок пока нет
- IUGR New Concepts - AJOG Review PDFДокумент13 страницIUGR New Concepts - AJOG Review PDFivanОценок пока нет
- ASTM E 2700-Phased ArraysДокумент9 страницASTM E 2700-Phased ArraysIvan ZafirovskiОценок пока нет
- TMCC Ecu Package 6.24.21Документ3 страницыTMCC Ecu Package 6.24.21Cinja ShidoujiОценок пока нет
- Shear Wave Measurement SectionДокумент22 страницыShear Wave Measurement SectionAndrei Dumitru100% (1)
- The Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques Act 2003 (Prohibition of Sex Selection in India - PNDT Act)Документ25 страницThe Pre-Conception and Pre-Natal Diagnostic Techniques Act 2003 (Prohibition of Sex Selection in India - PNDT Act)Laadli - A Population First InitiativeОценок пока нет
- Transducer Guide LOGIQДокумент32 страницыTransducer Guide LOGIQEmmanuel RamirezОценок пока нет
- Blood Flow Changes in RetinaДокумент10 страницBlood Flow Changes in Retinasyafa_mcqueenОценок пока нет
- Ultrasonography in Urology, Andrology, and Nephrology: Atlas ofДокумент11 страницUltrasonography in Urology, Andrology, and Nephrology: Atlas ofFatimah AssagafОценок пока нет
- Affiniti 30 Brochure PDFДокумент16 страницAffiniti 30 Brochure PDFRalucaОценок пока нет
- Management of Placenta Previa - UpToDateДокумент15 страницManagement of Placenta Previa - UpToDateJuanPulgarínОценок пока нет
- Prosound 4000: Specifications Diagnostic Ultrasound SystemДокумент12 страницProsound 4000: Specifications Diagnostic Ultrasound SystemPRUEОценок пока нет
- Physics of UltrasoundДокумент54 страницыPhysics of UltrasoundSharmila RudramambaОценок пока нет
- Ocular Foreign Bodies A Review 2155 9570 1000645 1Документ5 страницOcular Foreign Bodies A Review 2155 9570 1000645 1memey100% (1)
- Manual MX-3 PDFДокумент36 страницManual MX-3 PDFa_parrat100% (1)
- Sample Report Alpha DogДокумент130 страницSample Report Alpha DogUsman DastgirОценок пока нет
- Practical EXamДокумент5 страницPractical EXamNDTInstructor100% (6)
- Test Bank For Sonography Introduction To Normal Structure and Function 3rd Edition CurryДокумент34 страницыTest Bank For Sonography Introduction To Normal Structure and Function 3rd Edition Curryvoidedknuckle8txdk100% (36)
- GROUP 3. Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Diseases PAODДокумент73 страницыGROUP 3. Peripheral Arterial Occlusive Diseases PAODLeslie Anne Oayan DaulayanОценок пока нет
- ICD-9-CM TABULAR LIST OF PROCEDURESДокумент240 страницICD-9-CM TABULAR LIST OF PROCEDURESzulhirsan laluОценок пока нет
- HDI3000 FieldServiceManual 3639 2613 PDFДокумент752 страницыHDI3000 FieldServiceManual 3639 2613 PDFFrancisth ZeusОценок пока нет
- GEHC Vivid T8 TranducerGuide v7Документ4 страницыGEHC Vivid T8 TranducerGuide v7dinesh babuОценок пока нет
- P3 BrochureДокумент8 страницP3 BrochurebradchoiОценок пока нет
- Topik 4. Reading Intensive Care UnitДокумент18 страницTopik 4. Reading Intensive Care UnitioakasОценок пока нет
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (402)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (13)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОценок пока нет
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (3)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementОт EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (40)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsОт EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesОт EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (8)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingОт EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingОт EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsОт EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsОценок пока нет
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossОт EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)