Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Power Electronics
Загружено:
kibrom atsbhaИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Power Electronics
Загружено:
kibrom atsbhaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
Problems
1. What will be the average power in the load for the circuit shown, when .
4
Assume SCR to be ideal. Supply voltage is 330 sin314t. Also calculate the RMS
power and the rectification efficiency.
T
+
330
Sin314t
~ R 100
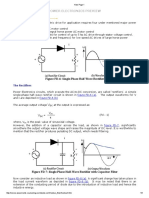
The circuit is that of a single phase half wave controlled rectifier with a resistive load
Vm
Vdc 1 cos ; radians
2 4
330
Vdc 1 cos
2 4
Vdc 89.66 Volts
Vdc2 89.662
Average Power 80.38 Watts
R 100
Vdc 89.66
I dc 0.8966 Amps
R 100
1
V 1 sin 2 2
VRMS m
2 2
1
2
330 1 sin 2 4
VRMS
2 4 2
VRMS 157.32 V
RMS Power (AC power)
2
VRMS 157.32 2
247.50 Watts
R 100
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 51
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
Average power
Rectification Efficiency
RMS power
80.38
0.3248
247.47
2. In the circuit shown find out the average voltage across the load assuming that the
conduction drop across the SCR is 1 volt. Take = 450.
VAK
+
330
Sin314t
~ R 100
The wave form of the load voltage is shown below (not to scale).
Vm
voltage
Load
Voltage across
resistance
VAK
0 t
It is observed that the SCR turns off when t , where because the
SCR turns-off for anode supply voltage below 1 Volt.
VAK Vm sin 1 volt (given)
V 1 1
Therefore sin 1 AK sin
0
0.17 0.003 radians
Vm 330
1800 ; By symmetry of the curve.
179.830 ; 3.138 radians.
1
Vdc
2 V
m sin t VAK d t
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 52
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
1
Vdc Vm sin t.d t VAK d t
2
1
Vdc Vm cos t VAK t
2
1
Vdc Vm cos cos VAK
2
1
Vdc 330 cos 450 cos179.830 1 3.138 0.003
2
Vdc 89.15 Volts
Note: and values should be in radians
3. In the figure find out the battery charging current when . Assume ideal
4
SCR.
R
10
+
200 V 24V
50 Hz ~ (VB)
Solution
It is obvious that the SCR cannot conduct when the instantaneous value of the
supply voltage is less than 24 V, the battery voltage. The load voltage waveform is as
shown (voltage across ion).
Vm
Voltage across
resistance
VB
0 t
VB Vm sin
24 200 2 sin
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 53
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
24
sin 1 0
4.8675 0.085 radians
200 2
3.056 radians
Average value of voltage across 10
1
Vm sin t VB .d t
2
(The integral gives the shaded area)
3.056
1
2
200 2 sin t 24 .d t
4
1
200 2 cos 4 cos 3.056 24 3.056 4
2
68 Vots
Therefore charging current
Average voltage across R
R
68
6.8 Amps
10
Note: If value of is more than , then the SCR will trigger only at t ,
(assuming that the gate signal persists till then), when it becomes forward biased.
1
Therefore Vdc Vm sin t VB .d t
2
4. In a single phase full wave rectifier supply is 200 V AC. The load resistance is
10 , 600 . Find the average voltage across the load and the power consumed
in the load.
Solution
In a single phase full wave rectifier
Vm
Vdc 1 cos
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 54
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
200 2
Vdc
1 cos 600
Vdc 135 Volts
Average Power
Vdc2 1352
1.823 kW
R 10
5. In the circuit shown find the charging current if the trigger angle 900 .
R = 10
+
200 V
50 Hz ~
+
10V
(VB)
Solution
With the usual notation
VB Vm sin
10 200 2 sin
10
Therefore sin 1 0.035 radians
200 2
900 radians ; 3.10659
2
2
Average voltage across 10 Vm sin t VB .d t
2
1
Vm cos t VB t
1
Vm cos cos VB
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 55
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
1
200 2 cos 2 cos 3.106 10 3.106 2
85 V
Note that the values of & are in radians.
dc voltage across resistance
Charging current
resistance
85
8.5 Amps
10
6. A single phase full wave controlled rectifier is used to supply a resistive load of
10 from a 230 V, 50 Hz, supply and firing angle of 900. What is its mean load
voltage? If a large inductance is added in series with the load resistance, what will
be the new output load voltage?
Solution
For a single phase full wave controlled rectifier with resistive load,
Vm
Vdc 1 cos
230 2
Vdc 1 cos
2
Vdc 103.5 Volts
When a large inductance is added in series with the load, the output voltage wave
form will be as shown below, for trigger angle 900 .
V0
0 t
2Vm
Vdc cos
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 56
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
Since ; cos cos 0
2 2
Therefore Vdc 0 and this is evident from the waveform also.
7. The figure shows a battery charging circuit using SCRs. The input voltage to the
circuit is 230 V RMS. Find the charging current for a firing angle of 450. If any
one of the SCR is open circuited, what is the charging current?
Solution
10 VL
+
Vs ~
+
100V
With the usual notations
VS Vm sin t
VS 2 230sin t
Vm sin VB , the battery voltage
2 230sin 100
100
Therefore sin 1
2 230
17.90 or 0.312 radians
0.312
2.829 radians
Average value of voltage across load resistance
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 57
LECTURE NOTES EE1351 POWER ELECTRONICS-UNIT 2
2
Vm sin t VB d t
2
1
Vm cos t VB t
1
Vm cos cos VB
1
230 2 cos 4 cos 2.829 100 2.829 4
1
230 2 0.707 0.9517 204.36
106.68 Volts
Voltage across resistance
Charging current
R
106.68
10.668 Amps
10
If one of the SCRs is open circuited, the circuit behaves like a half wave rectifier.
The average voltage across the resistance and the charging current will be half of that of a
full wave rectifier.
10.668
Therefore Charging Current 5.334 Amps
2
D.ELANGOVAN Department of EEE, SVCE Page 58
Вам также может понравиться
- Deep Excavation KLCCДокумент20 страницDeep Excavation KLCCamirriyyah100% (1)
- Labeling SOPДокумент22 страницыLabeling SOPEduard Moncunill MontesОценок пока нет
- Half Wave Rectifiers With Resistive and Inductive LoadДокумент5 страницHalf Wave Rectifiers With Resistive and Inductive Loadluqman059Оценок пока нет
- A High Performance Reference BGR Circuit With Improved Input Offset Voltage of Op-AmpДокумент7 страницA High Performance Reference BGR Circuit With Improved Input Offset Voltage of Op-AmpPriyanka SirohiОценок пока нет
- Analog CommunicationsДокумент98 страницAnalog CommunicationsP Kishore100% (1)
- Synopsis Proposal For 2021Документ4 страницыSynopsis Proposal For 20212k18-EE-243 Vethushan VinnayagamoorththiОценок пока нет
- Analog Circuit Design Notes-2Документ85 страницAnalog Circuit Design Notes-2itsnirosОценок пока нет
- PWM TechniquesДокумент27 страницPWM TechniquesDanny ChuОценок пока нет
- Design Calculations For Buck-Boost Converters: Michael Green Advanced Low Power SolutionsДокумент12 страницDesign Calculations For Buck-Boost Converters: Michael Green Advanced Low Power SolutionsnandhakumarmeОценок пока нет
- Power System Lab ManualДокумент17 страницPower System Lab ManualhavejsnjОценок пока нет
- Extra AC-DCДокумент34 страницыExtra AC-DCAhmed AbuNasserОценок пока нет
- DC - Ac Inv.Документ82 страницыDC - Ac Inv.Jegadeeswari GОценок пока нет
- 9086 CMOS Analog Design Chapter 6Документ24 страницы9086 CMOS Analog Design Chapter 6Yogindr SinghОценок пока нет
- EE 392 Measurement Lab Manual PDFДокумент29 страницEE 392 Measurement Lab Manual PDF002Pradeep002Оценок пока нет
- Generation of High Voltage DC Using Diodes & Capacitors in Ladder NetworkДокумент6 страницGeneration of High Voltage DC Using Diodes & Capacitors in Ladder NetworkEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- 3 Line ConverterДокумент10 страниц3 Line ConverterJay Romar PabianiaОценок пока нет
- Unit6 Resonance Circuit (VTU)Документ23 страницыUnit6 Resonance Circuit (VTU)fanah_13100% (1)
- DMA Controller - 8237Документ9 страницDMA Controller - 8237Umesh Harihara sudanОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics NotesДокумент80 страницPower Electronics NotesRishi Kant Sharma100% (2)
- Switched Reluctance MotorДокумент75 страницSwitched Reluctance Motor15BEE1120 ISHAV SHARDAОценок пока нет
- Brake Test On Three Phase Slip Ring Type Induction MotorДокумент3 страницыBrake Test On Three Phase Slip Ring Type Induction Motorramniwas123Оценок пока нет
- Power System Lab ManualДокумент39 страницPower System Lab ManualKvv Bapiraju100% (1)
- Questions & Answers On S-Domain AnalysisДокумент33 страницыQuestions & Answers On S-Domain Analysiskibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics NotesДокумент263 страницыPower Electronics NotesKalakata Manoj Reddy100% (1)
- Lab8 Log Antilog AmplifiersДокумент3 страницыLab8 Log Antilog AmplifiersLily SharmaОценок пока нет
- Ee 328 Lecture 4Документ33 страницыEe 328 Lecture 4Eric KerrОценок пока нет
- Effect of Source Inductance in 3Ø Full WaveДокумент12 страницEffect of Source Inductance in 3Ø Full WaveUmashankar Subramaniam100% (1)
- Wireless DC Motor Speed and Direction Control Using RFДокумент3 страницыWireless DC Motor Speed and Direction Control Using RFNidhin MnОценок пока нет
- Advanced Power ElectronicsДокумент4 страницыAdvanced Power ElectronicsLinkan PriyadarsiniОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Chapter#10Документ31 страницаPower Electronics Chapter#10Bilal HussainОценок пока нет
- Microcontroller Based Three Phase InverterДокумент4 страницыMicrocontroller Based Three Phase InverterEditor IJRITCCОценок пока нет
- Access Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsДокумент8 страницAccess Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsLEE KAR OON A17MJ00560% (1)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualДокумент47 страницPower Electronics Lab Manualshaan_patil100% (1)
- Power Electronics Kuestion PDFДокумент25 страницPower Electronics Kuestion PDFkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- The Development of Automatic Voltage Sabilizer For SmallДокумент17 страницThe Development of Automatic Voltage Sabilizer For SmallSarman TamilselvanОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Experiments ECE-P-672Документ9 страницPower Electronics Experiments ECE-P-672Sai SomayajulaОценок пока нет
- Power ElectronicsДокумент676 страницPower ElectronicsmesahooОценок пока нет
- Summer Training Embedded SystemДокумент18 страницSummer Training Embedded SystemmjcetpaОценок пока нет
- Buck Converter Using ArduinoДокумент12 страницBuck Converter Using ArduinoaaqibОценок пока нет
- 12V To 120V DC - DC Converter Using Power Electronics For Higher Efficiency and Reliable OperationДокумент23 страницы12V To 120V DC - DC Converter Using Power Electronics For Higher Efficiency and Reliable OperationRaghav ChawlaОценок пока нет
- Frequency Meter Lecture NotesДокумент4 страницыFrequency Meter Lecture NotesSam AndersonОценок пока нет
- AN1114 - Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipДокумент48 страницAN1114 - Switch Mode Power Supply (SMPS) Topologies (Part I) - MicrochipbmmostefaОценок пока нет
- PLCCДокумент89 страницPLCCBipandeep Gill100% (2)
- DCOM Lab ManualДокумент38 страницDCOM Lab ManualGaurav Kalra0% (1)
- Minimizing Penalty in Industrial Power Consumption by Engaging APFC UnitДокумент5 страницMinimizing Penalty in Industrial Power Consumption by Engaging APFC UnitZeeshan KhanОценок пока нет
- Power System Dynamics and ControlДокумент2 страницыPower System Dynamics and ControlSudip MondalОценок пока нет
- Eee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - SolutionДокумент73 страницыEee-V-dcmachines and Synchronous Machines (10ee54) - SolutionchaitanyaОценок пока нет
- #1 Generator Protection AДокумент12 страниц#1 Generator Protection ARodrigo Mendoza PerezОценок пока нет
- Superposition TheoremДокумент15 страницSuperposition Theoremsamarpit_anandОценок пока нет
- Dijkstra AlgorithmДокумент2 страницыDijkstra AlgorithmMegan VegaОценок пока нет
- Calculation PPT For EnergyДокумент12 страницCalculation PPT For EnergyMalyaj MishraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 Control of A C DrivesДокумент32 страницыChapter 15 Control of A C DrivesMuhammad AneesОценок пока нет
- Tutorial-2 LNA PDFДокумент19 страницTutorial-2 LNA PDFTeddy112100% (1)
- Power Electronics Chapter#11Документ25 страницPower Electronics Chapter#11Bilal HussainОценок пока нет
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsОт EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Converters and their Control for Renewable Energy ApplicationsОт EverandPower Electronics Converters and their Control for Renewable Energy ApplicationsArezki FekikОценок пока нет
- Topic 3.1 AnnotatedДокумент14 страницTopic 3.1 AnnotatedFurqan Bilal BhuttaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics ELECTENG 734Документ29 страницPower Electronics ELECTENG 734kibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Kuestion PDFДокумент25 страницPower Electronics Kuestion PDFkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Principles Power ElectДокумент67 страницPower Electronics Principles Power Electkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics2 PDFДокумент2 страницыPower Electronics2 PDFcp3y2000-scribdОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Laboratory 2BДокумент8 страницPower Electronics Laboratory 2Bkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- EE 452 Power ElectronicsДокумент4 страницыEE 452 Power Electronicskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- Lab No: 1: ExperimentДокумент4 страницыLab No: 1: Experimentkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Kuestion PDFДокумент25 страницPower Electronics Kuestion PDFkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsДокумент14 страницIntroduction To Power Electronicskibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Vibration Control of Mechanical SystemsДокумент6 страницVibration Control of Mechanical Systemskibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Signal Processsing ElementДокумент40 страницSignal Processsing Elementkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Signal Conditioning Elements Signal Conditioning Elements-2Документ22 страницыSignal Conditioning Elements Signal Conditioning Elements-2kibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Integration of Vessel Traffic Control SyДокумент14 страницIntegration of Vessel Traffic Control Sykibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- EE 351 Principles of Control Systems IntДокумент52 страницыEE 351 Principles of Control Systems Intkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Data or Output PresentationДокумент33 страницыData or Output Presentationkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- An Introduction To The Control of SwitchДокумент12 страницAn Introduction To The Control of Switchkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.1a Basics of Measur & InstruДокумент27 страницChapter 1.1a Basics of Measur & Instrukibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1.1bgeneral PrinciplesДокумент42 страницыChapter 1.1bgeneral Principleskibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Service Product Training - EWAD-EWYD-BZ - Chapter 1 - General Info - Presentations - EnglishДокумент23 страницыService Product Training - EWAD-EWYD-BZ - Chapter 1 - General Info - Presentations - Englishjmdc100% (1)
- 2015 Motorcycle Catalogue NGK 3Документ114 страниц2015 Motorcycle Catalogue NGK 3Ginger BrubakerОценок пока нет
- Accreditation Grading Metrics - Skills Ecosystem Guidelines10 - 04Документ8 страницAccreditation Grading Metrics - Skills Ecosystem Guidelines10 - 04Jagdish RajanОценок пока нет
- ANITS College ProfileДокумент5 страницANITS College ProfilemurthygvrОценок пока нет
- 40 Must Know Web 2.0 EdutoolsДокумент521 страница40 Must Know Web 2.0 EdutoolsDaniela BozganОценок пока нет
- Online Shopping Portal Project ReportДокумент33 страницыOnline Shopping Portal Project ReportSagar Chauhan50% (2)
- 206 PDFДокумент19 страниц206 PDFKim Terje Rudschinat GrønliОценок пока нет
- Lit1302e Termseries Datasheet v4Документ20 страницLit1302e Termseries Datasheet v4alltheloveintheworldОценок пока нет
- 113 14Документ8 страниц113 14rahul srivastavaОценок пока нет
- CPPДокумент22 страницыCPPShahmeer Ali MirzaОценок пока нет
- Solved Problems: Problem (7.1)Документ13 страницSolved Problems: Problem (7.1)Rafi SulaimanОценок пока нет
- THURBONДокумент2 страницыTHURBONNick NumlkОценок пока нет
- 1 1 1 43 PDFДокумент43 страницы1 1 1 43 PDFRameez AbbasiОценок пока нет
- .072" (1.8 MM) AWS D1.8:2016 March 01, 2022: Innershield® NR®-232Документ1 страница.072" (1.8 MM) AWS D1.8:2016 March 01, 2022: Innershield® NR®-232yousab creator2Оценок пока нет
- SR5 TOOL Equipment, Drones (Buyable), Compiled ListДокумент3 страницыSR5 TOOL Equipment, Drones (Buyable), Compiled ListBeki LokaОценок пока нет
- Woolridge - Reasnoning About Rational AgentsДокумент232 страницыWoolridge - Reasnoning About Rational AgentsAlejandro Vázquez del MercadoОценок пока нет
- FBR 1700TX (En)Документ86 страницFBR 1700TX (En)João FigueiredoОценок пока нет
- RG Cabble Losses ChartДокумент7 страницRG Cabble Losses Chartsyr_rif11Оценок пока нет
- Kathleen Steele ResumeДокумент2 страницыKathleen Steele Resumeapi-336824202Оценок пока нет
- Diamec U6 Spare PartДокумент3 страницыDiamec U6 Spare PartJairo Boechat JuniorОценок пока нет
- 5528 PDFДокумент33 страницы5528 PDFPham The TuОценок пока нет
- (No Subject) - Inbox - Yahoo! MailДокумент2 страницы(No Subject) - Inbox - Yahoo! Mailpradhap87Оценок пока нет
- 2010SeaDumpedChemicalWEapons Japan SatoДокумент16 страниц2010SeaDumpedChemicalWEapons Japan Satojiangwen1972Оценок пока нет
- Least Common MultipleДокумент4 страницыLeast Common MultipleWilliam BaileyОценок пока нет
- Genetic DiversityДокумент31 страницаGenetic DiversityAbegail AvilaОценок пока нет
- Nabl 600Документ350 страницNabl 600Gian Pierre CuevaОценок пока нет
- ALT Annual Conference 2019 (#Altc) Programme - ProgrammeДокумент12 страницALT Annual Conference 2019 (#Altc) Programme - ProgrammeAdfsОценок пока нет
- ECE Course DescriptionДокумент10 страницECE Course Descriptionengshimaa100% (1)