Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
The Water We Drink 2 Ano
Загружено:
americobrazilИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
The Water We Drink 2 Ano
Загружено:
americobrazilАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
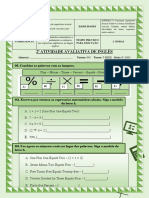
Atividade Avaliativa de Língua Estrangeira Moderna
a) ( ONE – Inglês.
) obtain nitrates from wells. TURMA:__________
b) ( ) have purified well water.
NOME:____________________________________________________________ Nº: water.
c) ( ) also have problems with their _______________
d) ( ) obtain agricultural fertilizers from nitrates.
B. Write T for True and F for False:
THE WATER WE DRINK
1. Nitrates pollute the water. ( V )
The water we drink usually comes from reservoirs, lakes,
2. People dump purified water into the river. ( F )
or rivers. A large number of cities uses river water and dumps it
3. We drink water from reservoirs. ( V )
back into the river. Sometimes another city downstream uses the
4. Fertilizers purify the water. ( F )
same water. This water may be badly polluted with chemicals and
5. Chemical reactions carry bacteria into a settling basing. ( V )
pathogenic bacteria. Many different chemical treatments are
6. Fluoride doesn't reduce tooth decay. ( F )
necessary to make it safe and palatable.
7. The smaller communities obtain water from lakes. ( F )
Chemical engineers usually place the water into a settling
8. Many cities use river water. ( V )
basin to purify it. Then, they treat it with slaked lime and
9. Chemical treatments are necessary to make water palatable.
aluminum sulfate. The chemical reaction of these elements forms
(V )
a gelatinous mass. This mass carries down dirt particles and
10. The maximum safe level of nitrate in water is 1.0 ppm. ( V )
bacteria.
Many communities add some form of fluoride to their
C. Answer the questions in portuguese.
water. Fluoride in concentrations of 0.7 to 1.0 ppm (parts per
1. Where does the water we drink come from?
million) can significantly reduce tooth decay in children.
A água que bebemos geralmente vem de reservatórios, lagos ou
Some communities, usually the smaller ones, obtain water
rios.
from wells. Even they have problems because sometimes the
2. Where do many cities dump their water?
ground water is contaminated. In some parts of the country the
Elas despejam de volta no rio.
contamination of nitrates in well water is above the maximum safe
3. What do chemicals and pathogenic bacteria cause to water?
level of 1.0 ppm. These nitrates come from agricultural fertilizers
Esta água pode ficar muito poluída.
and from the decomposition of organic wastes.
4. What is necessary to make water safe and palatable?
What can we do? We can fight for clear water and
Muitos tratamentos químicos diferentes são necessários para
convince our neighbors to do the same. We can demand an end to
torná-la segura e saborosa.
water pollution by industries and cities. And finally, we must
5. Why do chemical engineers use a settling basing?
know how to use the water of the earth because that is all we have.
Para purificá-la
VOCABULARY
6. What chemical elements do they use to purify the water?
dumps: despeja dowstream: rio abaixo , corrente abaixo
Cal apagada (Hidróxido de cálcio) e sulfato de alumínio
badly: mal; muito (sentido negativo, de coisa ruim) fluorine: flúor
7. What does the gelatinous mass do?
nitrate; nitrato
Essa massa carrega partículas de sujeira e bactérias.
smaller: menores wells; poços
8. How do many communities reduce tooth decay in children?
demand: exigência tooth decay; carie nos dentes
Muitas comunidades adicionam alguma forma de flúor à sua
place the water into a settling basin: colocar a água em uma
água.
bacia de decantação
9. What's the problem with well water?
Mesmo eles têm problemas porque às vezes a água do solo está
COMPREHENSION
contaminada.
A. Choose the correct alternative. 10. What do nitrates cause?
1. Aluminum sulfate reacts with: A contaminação em água de poço.
a) ( ) a gelatinous mass.
b) ( ) bacteria.
c) ( ) slaked lime.
d) ( ) nitrates. D. Find the synonyms
(1) add ( 7) clean
2. A gelatinous mass: (2) polluted (5 ) consume
a) ( ) reduces tooth decay. (3) usually (9 ) secure
b) ( ) purifies the settling basing. (4) dump ( 2) contaminated
c) ( ) contaminates ground water. (5) use ( 1) put
d) ( ) carries down dirt particles and bacteria. (6) earth ( 10 ) get
(7) purified ( 4 ) throw
3. We obtain safe and palatable water: (8) dump back ( 3 ) generally
a) ( ) from wells. (9) safe ( 6 ) ground
b) ( ) after chemical treatments. (10) obtain ( 8 ) return
c) ( ) from lakes.
d) ( ) from agricultural fertilizers.
4. We can:
a) ( ) demand an end to water pollution.
b) ( ) stop the decomposition of organic wasters.
c) ( ) use river water.
d) ( ) convince our neighbors to use fluoride.
5. Some small communities:
GABARITO OFICIAL DA ATIVIDADE AVALIATIVA DE LÍNGUA ESTRANGEIRA MODERNA.
COMPREHENSION
A. Choose the correct alternative.
1. C
2. D
3. B
4. A
5. C
B. Write T for True and F for False:
1.(V)
2.(F)
3.(V)
4.(F)
5.(V)
6.(F)
7.(F)
8.(V)
9.(V)
10.(V)
C. Answer the questions in portuguese.
1. A água que bebemos geralmente vem de reservatórios, lagos ou rios.
2. Elas despejam de volta no rio.
3. Esta água pode ficar muito poluída.
4. Muitos tratamentos químicos diferentes são necessários para torná-la segura e saborosa.
5. Para purificá-la.
6. Cal apagada (Hidróxido de cálcio) e sulfato de alumínio
7. Essa massa carrega partículas de sujeira e bactérias.
8. Muitas comunidades adicionam alguma forma de flúor à sua água.
9. Mesmo eles têm problemas porque às vezes a água do solo está contaminada.
10. A contaminação em água de poço.
D. Find the synonyms
(1) add ( 7) clean
(2) polluted (5 ) consume
(3) usually (9 ) secure
(4) dump ( 2) contaminated
(5) use ( 1) put
(6) earth ( 10 ) get
(7) purified ( 4 ) throw
(8) dump back ( 3 ) generally
(9) safe ( 6 ) ground
(10) obtain ( 8 ) return
Вам также может понравиться
- Língua Inglesa PDFДокумент25 страницLíngua Inglesa PDFKarine Tiepo33% (3)
- Atividade Ingles Simple PresentДокумент2 страницыAtividade Ingles Simple PresentClesiane Lima100% (1)
- Exercícios Sobre Adjetivos em Inglês 9ºano Com Gabarito - Texto Sobre AdolescênciaДокумент8 страницExercícios Sobre Adjetivos em Inglês 9ºano Com Gabarito - Texto Sobre AdolescênciaAntonio Marco CastilhoОценок пока нет
- 2 Série Ensino Médio Inglês Atividade 1 1 Quinzena Atividade DiagnósticaДокумент5 страниц2 Série Ensino Médio Inglês Atividade 1 1 Quinzena Atividade DiagnósticaFrancisco MárcioОценок пока нет
- Atividade Sobre Cognatos 9º AnoДокумент3 страницыAtividade Sobre Cognatos 9º AnoDenis75% (4)
- Avaliação Intermediária 7º AnoДокумент3 страницыAvaliação Intermediária 7º AnoMarilande GuimarãesОценок пока нет
- Atividade 5 de Inglês - 6 AnoДокумент1 страницаAtividade 5 de Inglês - 6 AnoAdineia Mendonça100% (1)
- Atividade de InglêsДокумент2 страницыAtividade de InglêsRegiane Souzas0% (1)
- Simulado Ingles 1º Ano Ensino MedioДокумент6 страницSimulado Ingles 1º Ano Ensino MedioElaine Belo50% (2)
- Inglês - Descritores e Intervenção.2 MaterialДокумент28 страницInglês - Descritores e Intervenção.2 MaterialDanielle Souza80% (5)
- Atividades Texto Com Simple Present 7 AnoДокумент1 страницаAtividades Texto Com Simple Present 7 AnoFlavia SoaresОценок пока нет
- Gabarito Ensino Medio 1Документ5 страницGabarito Ensino Medio 1Denis100% (1)
- ATIVIDADE de INGLÊS 1º AnoДокумент2 страницыATIVIDADE de INGLÊS 1º AnoJusciléia PradoОценок пока нет
- Plano Curricular Etapa III Inglês-EjaДокумент3 страницыPlano Curricular Etapa III Inglês-Ejaeliteles1 123100% (1)
- Atividade 3 Inglês - 6 AnoДокумент1 страницаAtividade 3 Inglês - 6 AnoAdineia Mendonça75% (4)
- Atividade Ingles Simple PresentДокумент2 страницыAtividade Ingles Simple PresentMarrone Dias100% (1)
- Simulado InglêsДокумент4 страницыSimulado InglêsLorena Nascimento Amaro100% (1)
- Atividade de Inglês 900 Comic StripsДокумент2 страницыAtividade de Inglês 900 Comic StripsElga Amarante Campos100% (2)
- Avaliação Diag. de Ingles 6 Ano RisiДокумент5 страницAvaliação Diag. de Ingles 6 Ano RisifabioОценок пока нет
- Avaliação 6 Ano Da I UnidДокумент3 страницыAvaliação 6 Ano Da I UnidEvani Souza100% (1)
- 6 Ano HorasДокумент2 страницы6 Ano HorasNayrarodrigues100% (2)
- Gincana 7º AnoДокумент3 страницыGincana 7º AnoGGeovanОценок пока нет
- Atividade. Substantivos Contáveis e IncontaveisДокумент1 страницаAtividade. Substantivos Contáveis e IncontaveisThays Nadijanara dos Santos Lima100% (3)
- ATIVIDADE AVALIATIVA 9° ANO - OkДокумент2 страницыATIVIDADE AVALIATIVA 9° ANO - OkDenisОценок пока нет
- Plano de Aula 6 Ao 9 AnoДокумент5 страницPlano de Aula 6 Ao 9 AnoBebete Yo100% (1)
- Atividade 3 InglesДокумент7 страницAtividade 3 InglesRaphael Augusto100% (1)
- Exercícios Sobre Phrasal VerbsДокумент1 страницаExercícios Sobre Phrasal Verbspmalencar100% (1)
- 9º Ano Simple PresentДокумент2 страницы9º Ano Simple PresentJuliana Marcos Ropelli Arantes100% (1)
- Prova Bimestral - Inglês - 9° Ano - TâniaДокумент4 страницыProva Bimestral - Inglês - 9° Ano - TâniaSara Martins100% (1)
- Atividade - ESTRANGEIRISMO - ENSINO MÉDIO - FEVEREIROДокумент2 страницыAtividade - ESTRANGEIRISMO - ENSINO MÉDIO - FEVEREIROAmanda Oliveira100% (1)
- Simulado Do Segundo Bimestre Inglês 7 Ano SantanaДокумент4 страницыSimulado Do Segundo Bimestre Inglês 7 Ano SantanaHeron DantasОценок пока нет
- AVALIACAO 9 Ano Ingles 3 BimestreДокумент3 страницыAVALIACAO 9 Ano Ingles 3 BimestreMelissa Vieira100% (1)
- 7 Ano - Inglês - Roteiro de EstudoДокумент2 страницы7 Ano - Inglês - Roteiro de EstudoJC Campos100% (1)
- Simulado de Ingles 6º Ano PDFДокумент2 страницыSimulado de Ingles 6º Ano PDFnunesdeboraОценок пока нет
- Artigo de Opinião Gabarito - Simulado 9º Ano - Cemaly PDFДокумент17 страницArtigo de Opinião Gabarito - Simulado 9º Ano - Cemaly PDFGustavo PazОценок пока нет
- 2 Ano - Inglês 4 UnidadeДокумент2 страницы2 Ano - Inglês 4 UnidadeCaio SenaОценок пока нет
- Apostila - ImperativeДокумент5 страницApostila - ImperativeIvoneide FrançaОценок пока нет
- Arte 6ano Slides Aula9Документ39 страницArte 6ano Slides Aula9EMANUELLY DE SOUZA JANICKI MACIEL100% (1)
- Atv Compl - 6º - Ano Pet 2Документ7 страницAtv Compl - 6º - Ano Pet 2Carla Pereira100% (1)
- Mult II7 Ano 1 Chamada 1 Bimestrede 2018Документ15 страницMult II7 Ano 1 Chamada 1 Bimestrede 2018americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Atividade Avaliativa. Textos 2anoДокумент2 страницыAtividade Avaliativa. Textos 2anoJusciléia PradoОценок пока нет
- Tag Questions - Explicação e ExercíciosДокумент4 страницыTag Questions - Explicação e ExercíciosAna Beatriz EliasОценок пока нет
- 6 Ano Inglês PDFДокумент5 страниц6 Ano Inglês PDFlucilabackОценок пока нет
- Prova de Ingles 6 Ao 9 AnoДокумент2 страницыProva de Ingles 6 Ao 9 AnoSan Carvalho50% (6)
- Avaliação de Língua Estrangeira Moderna 6Документ2 страницыAvaliação de Língua Estrangeira Moderna 6Bento MarianoОценок пока нет
- 9º ING 1 SemanaДокумент2 страницы9º ING 1 SemanaJanaina Ferreira100% (1)
- Estrangeirismo - Samba Do Approach 2 E3 AnoДокумент2 страницыEstrangeirismo - Samba Do Approach 2 E3 AnoKarlMarx Santos100% (1)
- LP ING CIE 6 ProfДокумент41 страницаLP ING CIE 6 ProfCirlene Carla SilvaОценок пока нет
- 8 Ano - Roteiro de Estudo - INGLÊSДокумент2 страницы8 Ano - Roteiro de Estudo - INGLÊSJC Campos100% (2)
- Demonstrative PronounsДокумент22 страницыDemonstrative PronounsStrannik RuskiОценок пока нет
- Ava Bim - Inglês (7º Ano)Документ2 страницыAva Bim - Inglês (7º Ano)Cleide LaurindoОценок пока нет
- Exercício Genitive CaseДокумент10 страницExercício Genitive CaseFrancisvaldo Cândido de BritoОценок пока нет
- Trabalho Pesquisado de Língua Portuguesa 1º Ano Do Ensino MédioДокумент3 страницыTrabalho Pesquisado de Língua Portuguesa 1º Ano Do Ensino MédioEliane MikasОценок пока нет
- BARROCOДокумент1 страницаBARROCOViviane Barbosa RasgaОценок пока нет
- Lesson 7 Adjectives (Lição 7 Adjetivos)Документ5 страницLesson 7 Adjectives (Lição 7 Adjetivos)Jana Rodrigues100% (1)
- 7º Ano InglesДокумент2 страницы7º Ano InglesHélida Bedin Nunes75% (8)
- Prova de Inglês 6º Ano 2 Etapa2021Документ2 страницыProva de Inglês 6º Ano 2 Etapa2021Stanlley Leandro100% (2)
- Revisão de Português Do 8º AnoДокумент4 страницыRevisão de Português Do 8º Anoilza MariaОценок пока нет
- Atividade Triste BahiaДокумент2 страницыAtividade Triste BahiaInternautaОценок пока нет
- ProvaДокумент3 страницыProvaPatricia CordeiroОценок пока нет
- Gabarito Texto The Water We DrinkДокумент1 страницаGabarito Texto The Water We DrinkChrisОценок пока нет
- LEM - Inglês InstrumentalДокумент26 страницLEM - Inglês InstrumentalamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 2 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - Verso NewДокумент1 страница2 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - Verso NewamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 1 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - FrenteДокумент1 страница1 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - FrenteamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 1 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - VersoДокумент1 страница1 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - VersoamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- Questoes de Ingles para 2020Документ1 страницаQuestoes de Ingles para 2020americobrazilОценок пока нет
- 1 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - Verso AdptadaДокумент1 страница1 ATIVIDADE - 6 ANO - Verso AdptadaamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 2 Simulado 6 Ano ATGДокумент2 страницы2 Simulado 6 Ano ATGamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- Atividade Avaliativa 3º ANO DC 2018Документ1 страницаAtividade Avaliativa 3º ANO DC 2018americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Apresentação 1Документ6 страницApresentação 1americobrazilОценок пока нет
- 2 Simulado 9 Ano ATGДокумент2 страницы2 Simulado 9 Ano ATGamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- Verdade e Vida 1Документ1 страницаVerdade e Vida 1americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Resolução Alternativo - #06-07-05 - 2018.Pdf - 2Документ32 страницыResolução Alternativo - #06-07-05 - 2018.Pdf - 2americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Atividade Avaliativa 6º ANO GUIMA 2018 PDFДокумент1 страницаAtividade Avaliativa 6º ANO GUIMA 2018 PDFamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 2 Simulado 8 Ano ATGДокумент2 страницы2 Simulado 8 Ano ATGamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- Gabpb Inglês 7 AnoДокумент1 страницаGabpb Inglês 7 AnoamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 2º Simulado de Ingles - JEQ - 2018Документ1 страница2º Simulado de Ingles - JEQ - 2018americobrazilОценок пока нет
- 1st English Valuation - 3 - ANO MANHA 2017Документ2 страницы1st English Valuation - 3 - ANO MANHA 2017americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Edital Arcon PaДокумент9 страницEdital Arcon PaamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- Resumo Direito AdministrativoДокумент72 страницыResumo Direito AdministrativoAline *Materiais de estudo para concursos*100% (1)
- GRAMÁTICAДокумент4 страницыGRAMÁTICARosinéa SantiagoОценок пока нет
- Resolução ARCON No. 01 - 2018 - Complementar - 2Документ3 страницыResolução ARCON No. 01 - 2018 - Complementar - 2americobrazilОценок пока нет
- 1.resolução ARCON Nº 03 - 2001-Registro e Atualização Cadastral - AtualizadaДокумент3 страницы1.resolução ARCON Nº 03 - 2001-Registro e Atualização Cadastral - AtualizadaamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- p5 Tipo M 5 1º Ano emДокумент11 страницp5 Tipo M 5 1º Ano emamericobrazilОценок пока нет
- 20180516181052641Документ22 страницы20180516181052641americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Res 01 00Документ19 страницRes 01 00americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Resolução Alternativo - #06-07-05 - 2018.Pdf - 2Документ32 страницыResolução Alternativo - #06-07-05 - 2018.Pdf - 2americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Res 03 01Документ3 страницыRes 03 01americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Res 09 00Документ13 страницRes 09 00americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Res 02 01Документ8 страницRes 02 01americobrazilОценок пока нет
- Hidrografia BrasileiraДокумент1 страницаHidrografia BrasileiraLiberОценок пока нет
- Poluiçao AquáticaДокумент30 страницPoluiçao AquáticataniacatarinaОценок пока нет
- Publicação Outorga Diario Oficial SPДокумент1 страницаPublicação Outorga Diario Oficial SPCarlos Henrique TosiОценок пока нет
- PARH PirangaДокумент127 страницPARH PirangaMatheus SalesОценок пока нет
- 8 EclusasДокумент49 страниц8 EclusasBruno VitorinoОценок пока нет
- 1° Lista de Exercícios - Drenagem 2 Semestre - 2018 - Resolvida - 9 e 10Документ4 страницы1° Lista de Exercícios - Drenagem 2 Semestre - 2018 - Resolvida - 9 e 10Mario MachadoОценок пока нет
- Ambientes EstuarinosДокумент35 страницAmbientes EstuarinosHerstein MatematicaОценок пока нет
- Importância Da Gestão Da ÁguaДокумент7 страницImportância Da Gestão Da ÁguaAristidesОценок пока нет
- BACIAS HIDROGRÁFICAS e RIOS FLUMINENSESДокумент74 страницыBACIAS HIDROGRÁFICAS e RIOS FLUMINENSESlukasmetal100% (1)
- 25-05-2023 Boletim de Barragens CerbДокумент12 страниц25-05-2023 Boletim de Barragens CerbMarthaОценок пока нет
- BPL - Panfleto Jul - 2014Документ2 страницыBPL - Panfleto Jul - 2014Luís C. MestiçoОценок пока нет
- Exercício - Qualidade Da Água - Total PDFДокумент4 страницыExercício - Qualidade Da Água - Total PDFgalindo2105Оценок пока нет
- Aula 10 - Tratamento Secundário de Esgotos - Filtro BiológicoДокумент53 страницыAula 10 - Tratamento Secundário de Esgotos - Filtro BiológicoFrederico SchröderОценок пока нет
- Exercício de Hidrologia para p1Документ5 страницExercício de Hidrologia para p1CalouroBurroTiagoCettoPietralongaОценок пока нет
- Bacia Hidrografica Do Rio Magdalena (Colombia)Документ9 страницBacia Hidrografica Do Rio Magdalena (Colombia)Angenor Geovani AulerОценок пока нет
- Hidrogeologia e MineraçãoДокумент59 страницHidrogeologia e Mineraçãoplinio.enggeologoОценок пока нет
- Novo Memorial Fossa SumidoroДокумент1 страницаNovo Memorial Fossa SumidoroPedroAugustoSilveiraОценок пока нет