Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Necrotizing Otitis Externa in Paediatric Patient With Primary Immunodeficiency: A Rare Case Report
Загружено:
AyuAnatrieraОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Necrotizing Otitis Externa in Paediatric Patient With Primary Immunodeficiency: A Rare Case Report
Загружено:
AyuAnatrieraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NECROTIZING OTITIS EXTERNA IN PAEDIATRIC PATIENT WITH PRIMARY
IMMUNODEFICIENCY: A RARE CASE REPORT
R. Ayu Anatriera1, Harim Priyono2, Trimartani3, Zakiudin Munasir4, Hindra Irawan Satari5
1
Otorhynolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery Department RSUPN Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo
2
Otology Division Otorhynolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery Department RSUPN Dr. Cipto
Mangunkusumo
3
Plastic Recosntruction Division Otorhynolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery Department RSUPN Dr. Cipto
Mangunkusumo
4
Allergy Immunology Division Pediatrics Department RSUPN Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo
5
Tropical Infection Division Pediatrics Department RSUPN Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo
Abstract
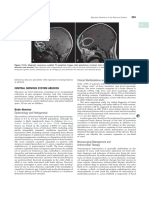
Necrotizing otitis externa (NOE) is a rare infection of external auditory canal and adjacent anatomic
structures, including bone. NOE commonly affecting immunocompromomised patient and had mortality
rates of nearly 50% if treatment is not sufficient. The sequence of NOE in children has more insidious
symptoms of fever, malaise, leukocytosis, and higher incidence of facial nerve paralysis in some studies.
About 90% necrotizing otitis externa in children is caused by Pseudomonas, though some cases due to other
microorganism. Patients with primary immunodeficiency (PID) considered by errors in immune response.
The incidence of PID is still undoubtedly underdiagnosed. Most pediatric PID cases of necrotizing otitis
externa resolve within several weeks of intravenous antibiotics administration, although longer sequences
can be required. This paper reported a case of primary immunodeficiency in paediatric patients along with
necrotizing otitis externa as its severe infection and complications. The aim of this paper explained
about proper diagnosis and management of the disease hence could prevent serious complications and
mortality.
Keywords: Necrotizing otitis externa, paediatric, primary immunodeficiency
Abstrak
Otitis eksterna nekrotik (OEN) merupakan salah satu kasus infeksi unik melibatkan kanalis auditorius
eksternus dan struktur anatomis sekitarnya termasuk tulang. Kasus otitis eksterna nekrotik dapat ditemukan
pada pasien-pasien imunokompromais dan mempunyai angka mortalitas mendekati 50% jika tatalaksana
tidak efektif. Otitis eksterna nekrotik pada anak mempunyai inisiasi gejala lebih parah berupa demam,
malaise, dan leukositosis, serta insiden tinggi terjadinya paralisis nervus fasialis pada beberapa studi.
Pseudomonas adalah salah satu penyebab terbanyak pada lebih dari 90% kasus otitis eksterna nekrotik
pada anak, walau sebagian kasus dapat disebabkan oleh mikrooragnisme lainnya. Pasien dengan
imunodefisiensi primer ditandai dengan adanya defek pada sistem imun yang seringkali tidak terdiagnosis
dengan tepat. Kasus otitis eksterna nekrotik pada pediatrik mengalami perbaikan setelah pemberian
antibiotik intravena, walaupun terkadang penggunaan jangka panjang diperlukan. Tulisan ini melaporkan
sebuah kasus pasien anak dengan imunodefisiensi primer yang mengalami otitis eksterna nekrotik sebagai
bagian dari infeksi dan komplikasi kronik. Tujuan dari makalah ini untuk menjelaskan diagnosis dan
tatalaksana optimal sehingga dapat mencegah komplikasi serius dan kematian.
Kata Kunci: otitis eksterna nekrotik, pediatrik, imunodefisiensi primer
Вам также может понравиться
- Necrotizing Otitis Externa in Paediatric Patient With Primary Immunodeficiency: A Rare Case ReportДокумент1 страницаNecrotizing Otitis Externa in Paediatric Patient With Primary Immunodeficiency: A Rare Case ReportAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Malignant Otitis Externa: An Emerging Complication: Original ArticleДокумент3 страницыMalignant Otitis Externa: An Emerging Complication: Original ArticleWa Ode Meutya ZawawiОценок пока нет
- Selulitis PDFДокумент5 страницSelulitis PDFDhisa Zainita HabsariОценок пока нет
- Infections of The EarДокумент9 страницInfections of The Earrumaisyah alkatiriОценок пока нет
- Otitis ExternaДокумент4 страницыOtitis ExternaCesar Mauricio Daza CajasОценок пока нет
- Jurnal Otitis EksternaДокумент4 страницыJurnal Otitis EksternaZóélkårnåín PhåntómhívéОценок пока нет
- Malignant Otitis Externa in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Case ReportДокумент0 страницMalignant Otitis Externa in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Case ReportSuci PramadianiОценок пока нет
- Ayu Jurnal Inggris OEДокумент22 страницыAyu Jurnal Inggris OEAyu Putri HaryantiОценок пока нет
- BMJ Case ReportДокумент4 страницыBMJ Case ReportGisda AzzahraОценок пока нет
- A Clinical Study of Otomycosis: H.S. Satish, Viswanatha.B, Manjuladevi.MДокумент6 страницA Clinical Study of Otomycosis: H.S. Satish, Viswanatha.B, Manjuladevi.MKepompong KupukupuОценок пока нет
- Malignant Otitis ExternaДокумент5 страницMalignant Otitis Externasergeantchai068Оценок пока нет
- Jurnal Otitis Eksterna WordДокумент14 страницJurnal Otitis Eksterna WordmedyaanaОценок пока нет
- Aom PDFДокумент8 страницAom PDFMei Risanti SiraitОценок пока нет
- Malignant Otitis External-Our Experience: R. B. Sardesai, T. KrishnakumarДокумент4 страницыMalignant Otitis External-Our Experience: R. B. Sardesai, T. KrishnakumarSuci PramadianiОценок пока нет
- Ref 1Документ5 страницRef 1Nanda SapitriОценок пока нет
- Fatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sДокумент6 страницFatal Airway Obstruction Due To Ludwig'sRegina MugopalОценок пока нет
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010Документ11 страницPenyebab Otalgia 2010siska tiaraОценок пока нет
- Penyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFДокумент11 страницPenyebab Otalgia 2010 PDFnotpentingОценок пока нет
- Descriptive Study On Malignant Otitis Externa in Diabetic Patients at A Tertiary Care Hospital at MadurandhagamДокумент5 страницDescriptive Study On Malignant Otitis Externa in Diabetic Patients at A Tertiary Care Hospital at MadurandhagamAditya HendraОценок пока нет
- Case Report Acute Coalescent MastoiditisДокумент6 страницCase Report Acute Coalescent MastoiditisWidi Yuli HariantoОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S0165587617302975 Main PDFДокумент4 страницы1 s2.0 S0165587617302975 Main PDFAchmad YunusОценок пока нет
- Acute Otitis MediaДокумент26 страницAcute Otitis Mediaimran qaziОценок пока нет
- Clinical Manifestations of Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: A Clinical Review of 173 CasesДокумент7 страницClinical Manifestations of Ocular Toxoplasmosis in Yogyakarta, Indonesia: A Clinical Review of 173 CasesRiza Haida WardhaniОценок пока нет
- Meningitis IN PDF PEDIATRICДокумент14 страницMeningitis IN PDF PEDIATRICCruz Roelia Ruiz SanchezОценок пока нет
- 55 61 Brain AbscessДокумент7 страниц55 61 Brain AbscessNadia OktarinaОценок пока нет
- Case Report... ChamindiДокумент5 страницCase Report... Chamindisajanagamage95Оценок пока нет
- Optic Neuritis: More Than A Loss of VisionДокумент5 страницOptic Neuritis: More Than A Loss of VisionRahmat AajhaОценок пока нет
- Orbital CellulitisДокумент20 страницOrbital CellulitissarahОценок пока нет
- Putt's Puffy TumorДокумент6 страницPutt's Puffy Tumorkeith isamelОценок пока нет
- Management of Malignant (Necrotising) Otitis Externa: S Hollis, K EvansДокумент6 страницManagement of Malignant (Necrotising) Otitis Externa: S Hollis, K EvansNur LaelaОценок пока нет
- Jurnal OtitisДокумент22 страницыJurnal OtitisLavfy NjlaaОценок пока нет
- Crao PosterДокумент1 страницаCrao PosterNataShini RajaRatnamОценок пока нет
- Otitis Media3Документ6 страницOtitis Media3Anthony LopezОценок пока нет
- To Determine The Symptoms, Predisposing Factors and Causative Organisms of OtomycosisДокумент3 страницыTo Determine The Symptoms, Predisposing Factors and Causative Organisms of OtomycosisAnonymous lAfk9gNPОценок пока нет
- Gradenigo's Syndrome - A Rare Case Report: Medical SciencesДокумент2 страницыGradenigo's Syndrome - A Rare Case Report: Medical SciencesSODAZZZAОценок пока нет
- Clinical Study of Primary Ocular TuberculosisДокумент4 страницыClinical Study of Primary Ocular TuberculosisIntan Kumalasari RambeОценок пока нет
- Acute Otitis Media: by DR - Imran Qazi T.M.O Ent A Ward KTH MTI PeshawarДокумент26 страницAcute Otitis Media: by DR - Imran Qazi T.M.O Ent A Ward KTH MTI Peshawarimran qaziОценок пока нет
- AbcesoДокумент2 страницыAbcesoRocio LedesmaОценок пока нет
- Discitis and Spinal Infection: Classi Fication and EpidemiologyДокумент5 страницDiscitis and Spinal Infection: Classi Fication and Epidemiologyraul ramboyongОценок пока нет
- Empijem SinusaДокумент4 страницыEmpijem SinusaIvan GalicОценок пока нет
- Malignant Otitis Externa 20070821Документ0 страницMalignant Otitis Externa 20070821Suci PramadianiОценок пока нет
- Orbital Cellulitis ManagemenДокумент5 страницOrbital Cellulitis ManagemenErina ImronikhaОценок пока нет
- 04 179englishsummaryДокумент1 страница04 179englishsummarymedisproОценок пока нет
- Tubercular Otitis Media: Demystifying Its Nuances and An Update On The Tenets of Emerging PerspectivesДокумент9 страницTubercular Otitis Media: Demystifying Its Nuances and An Update On The Tenets of Emerging PerspectivesAditya HendraОценок пока нет
- Perichondritis - Not Just Simple Cellulitis - REBEL EM - Emergency Medicine BlogДокумент8 страницPerichondritis - Not Just Simple Cellulitis - REBEL EM - Emergency Medicine BlogMarica SibulovОценок пока нет
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, KarnatakaДокумент13 страницRajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, Karnatakasyed imdadОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S2255482312702126 MainДокумент9 страниц1 s2.0 S2255482312702126 MainsarinovitapratiwiОценок пока нет
- Kronmed: Congresul Național Pentru Studenți Și Tineri MediciДокумент87 страницKronmed: Congresul Național Pentru Studenți Și Tineri MediciIubiОценок пока нет
- Management of Odontogenic Infection of Primary Teeth in Child That Extends To The Submandibular and Submental Space Case ReportДокумент5 страницManagement of Odontogenic Infection of Primary Teeth in Child That Extends To The Submandibular and Submental Space Case ReportMel FAОценок пока нет
- Manual of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery: Ballenger'sДокумент9 страницManual of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery: Ballenger'sYuniParaditaDjunaidiОценок пока нет
- Invasive Cryptococcal Meningitis Presenting As A Skull Base Mass in An Immunocompetent Host: A Case ReportДокумент5 страницInvasive Cryptococcal Meningitis Presenting As A Skull Base Mass in An Immunocompetent Host: A Case ReportAsep RiswandiОценок пока нет
- Acute Otitis Media - StatPearls (Internet) - Treasure Island (FL) StatPearls Publishing (2023)Документ12 страницAcute Otitis Media - StatPearls (Internet) - Treasure Island (FL) StatPearls Publishing (2023)Kezia KurniaОценок пока нет
- Brain Abscess in Immunocompetent Adult PatientsДокумент6 страницBrain Abscess in Immunocompetent Adult PatientsshofwaОценок пока нет
- Brain Abscesses: An Overview in Children: Andrzej Krzyszto Fiak Paola Zangari Maia de Luca Alberto VillaniДокумент4 страницыBrain Abscesses: An Overview in Children: Andrzej Krzyszto Fiak Paola Zangari Maia de Luca Alberto VillaniSannita Mayusda BadiriОценок пока нет
- Gradenigo SyndromeДокумент7 страницGradenigo SyndromeYayan AkhyarОценок пока нет
- Clinical Examination Techniques in Otology Edition IIДокумент43 страницыClinical Examination Techniques in Otology Edition IIDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (2)
- ADJ-odontogenic InfectionДокумент9 страницADJ-odontogenic Infectiondr.chidambra.kapoorОценок пока нет
- Selulitis Orbita Pada Laki-Laki Usia 64 Tahun: Laporan KasusДокумент8 страницSelulitis Orbita Pada Laki-Laki Usia 64 Tahun: Laporan KasusLuh Dita YuliandinaОценок пока нет
- Orbital Cellulitis 2018Документ20 страницOrbital Cellulitis 2018María Alejandra Rojas MontenegroОценок пока нет
- 03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19Документ2 страницы03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 6th UKM PAEDIATRIC AIRWAY WEBINAR - EXAM TIPS AND TRICKS FOR TRAINEES E17Документ3 страницы6th UKM PAEDIATRIC AIRWAY WEBINAR - EXAM TIPS AND TRICKS FOR TRAINEES E17AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 11 - 1st SARC Sleep Workshop Programme - 30jan19Документ4 страницы11 - 1st SARC Sleep Workshop Programme - 30jan19AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- APOST 2018 Singapore Couse ProgrammeДокумент2 страницыAPOST 2018 Singapore Couse ProgrammeAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 10th ORLIAC Scientific Program As of 26 Jan 2018Документ6 страниц10th ORLIAC Scientific Program As of 26 Jan 2018AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Reologi Nanokomposit Polipropilen/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/OrganoclayДокумент9 страницReologi Nanokomposit Polipropilen/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube/OrganoclayAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Cell Proliferation Kit I (MTT) : Cat. No. 11 465 007 001Документ4 страницыCell Proliferation Kit I (MTT) : Cat. No. 11 465 007 001AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Patient Reported Outcome Measures in Microtia Surgery: Farhana Akter, Joanna C. Mennie, Ken Stewart, Neil BulstrodeДокумент9 страницPatient Reported Outcome Measures in Microtia Surgery: Farhana Akter, Joanna C. Mennie, Ken Stewart, Neil BulstrodeAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Clinical and Radiologic Behaviour of Ameloblastoma in 4 CasesДокумент4 страницыClinical and Radiologic Behaviour of Ameloblastoma in 4 CasesNovieta PratiwieОценок пока нет
- Asean Orl-Hns 2019 Detailed Programme 04mar19 Website HeaderДокумент7 страницAsean Orl-Hns 2019 Detailed Programme 04mar19 Website HeaderAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 31Документ16 страниц31AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 21Документ15 страниц21AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 52Документ7 страниц52AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19Документ2 страницы03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Kojima Et Al-2014-The Anatomical RecordДокумент7 страницKojima Et Al-2014-The Anatomical RecordAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19Документ2 страницы03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Preoperative Computer Simulation For Asian Rhinoplasty Patients: Analysis of Accuracy and Patient PreferenceДокумент10 страницPreoperative Computer Simulation For Asian Rhinoplasty Patients: Analysis of Accuracy and Patient PreferenceAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19Документ2 страницы03 6th Sarc Fess Programme 03jan19AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Jmbaena BHC Regemat June18Документ58 страницJmbaena BHC Regemat June18AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Temporal Bone Resection: Brian Ho, MD, C. Arturo Solares, MD, FACS, Benedict Panizza, MBBS, MBA, FRACSДокумент5 страницTemporal Bone Resection: Brian Ho, MD, C. Arturo Solares, MD, FACS, Benedict Panizza, MBBS, MBA, FRACSAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 07 RJR 08 Particularities of Anesthesia in ENT Endoscopic SurgeryДокумент8 страниц07 RJR 08 Particularities of Anesthesia in ENT Endoscopic SurgeryAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Cell Proliferation Kit I (MTT) : Cat. No. 11 465 007 001Документ4 страницыCell Proliferation Kit I (MTT) : Cat. No. 11 465 007 001AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- 10 1002@lary 27865-1Документ10 страниц10 1002@lary 27865-1AyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Abstract SARC 2018 Mucocele FINALДокумент1 страницаAbstract SARC 2018 Mucocele FINALAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Necrotizing Otitis Externa in Paediatric Patient With Primary Immunodeficiency: A Rare Case ReportДокумент1 страницаNecrotizing Otitis Externa in Paediatric Patient With Primary Immunodeficiency: A Rare Case ReportAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: SeminarДокумент13 страницNasopharyngeal Carcinoma: SeminarAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: SeminarДокумент13 страницNasopharyngeal Carcinoma: SeminarAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- MR Skin Prick TestingДокумент9 страницMR Skin Prick TestingAyuAnatrieraОценок пока нет
- The Art of Case Taking and Practical Repertorisation in Homoeopathy Ramanlal P Patel.03259 2analysis and Evaluation of SymptomsДокумент6 страницThe Art of Case Taking and Practical Repertorisation in Homoeopathy Ramanlal P Patel.03259 2analysis and Evaluation of Symptomsnadeemtyagi0% (1)
- Gingivita Din Ciclul MenstrualДокумент10 страницGingivita Din Ciclul MenstrualRamonaОценок пока нет
- Habitation Household Data Capture Template Ver21.7Документ21 страницаHabitation Household Data Capture Template Ver21.7Nishkarsh MishraОценок пока нет
- Treatment of Giant Cell Arteritis - UpToDateДокумент26 страницTreatment of Giant Cell Arteritis - UpToDateBeatriz SilvaОценок пока нет
- Immediate Newborn Care Definition 23Документ6 страницImmediate Newborn Care Definition 23Courtney Dela FierraОценок пока нет
- Seminar OverdentureДокумент73 страницыSeminar OverdentureNisha GargОценок пока нет
- Diabetes (6. Metas Glucémicas - Estándares de Atención Médica en Diabetes-2022)Документ14 страницDiabetes (6. Metas Glucémicas - Estándares de Atención Médica en Diabetes-2022)Antony Yamid Bolaños VillarrealОценок пока нет
- Transfer Briggs FormДокумент4 страницыTransfer Briggs FormMikkaОценок пока нет
- Project Proposal 5 28 19Документ5 страницProject Proposal 5 28 19api-461464117Оценок пока нет
- Data Collection Tool-For Newly Recruited Nurse Joining On 30 October 2018 - DGNM PDFДокумент2 страницыData Collection Tool-For Newly Recruited Nurse Joining On 30 October 2018 - DGNM PDFMd Imran33% (3)
- CARE ScriptДокумент3 страницыCARE ScriptJay SteeleОценок пока нет
- Sepsis, Septic Shock, MODSДокумент19 страницSepsis, Septic Shock, MODSPaul Zantua80% (5)
- Sun MediMax TableДокумент1 страницаSun MediMax TableKhairul RafiziОценок пока нет
- DR - Prateek ResumeДокумент1 страницаDR - Prateek ResumePrateek KumarОценок пока нет
- Che 225 Control of Communicable DiseasesДокумент19 страницChe 225 Control of Communicable DiseasesAbdullahi Bashir SalisuОценок пока нет
- English DialogueДокумент3 страницыEnglish DialogueAnonymous ZL7WvYОценок пока нет
- 5.2spatial Translations Administrative Office Matrix DiagramДокумент3 страницы5.2spatial Translations Administrative Office Matrix DiagramAthena AciboОценок пока нет
- A Case of Aspartate Aminotransferase MacroenzymeДокумент3 страницыA Case of Aspartate Aminotransferase MacroenzymeOlfiany Laurenzia PongohОценок пока нет
- 7 Doh Approved Herbal Medicine: Pictures Indicataion Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityДокумент5 страниц7 Doh Approved Herbal Medicine: Pictures Indicataion Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilityShaira Ann CalambaОценок пока нет
- Ruq Abdominal PainДокумент55 страницRuq Abdominal PainriphqaОценок пока нет
- Comments Fritz Jama EBM2016Документ1 страницаComments Fritz Jama EBM2016Ju ChangОценок пока нет
- Psychological Complications, Post Partum Blues, Depression, PsychosisДокумент42 страницыPsychological Complications, Post Partum Blues, Depression, Psychosisbasamma kumbarОценок пока нет
- Fhap Family Summary: Group MembersДокумент5 страницFhap Family Summary: Group MembersJacob JrОценок пока нет
- Delaying Cancer Cases in Urology During COVID-19 - Review of The LiteratureДокумент8 страницDelaying Cancer Cases in Urology During COVID-19 - Review of The Literaturekartini ciatawiОценок пока нет
- Kizilarslanoglu 2016Документ7 страницKizilarslanoglu 2016EviОценок пока нет
- Effect of Low Level Laser Therapy On Wound Healing AfterДокумент6 страницEffect of Low Level Laser Therapy On Wound Healing AfterYou're Just As Sane As DivaОценок пока нет
- American Urological Association (AUA) GuidelineДокумент23 страницыAmerican Urological Association (AUA) GuidelineGiovani BragaОценок пока нет
- References: Healthcare Management: Cases, Concepts, and Skills. 2nd EdДокумент1 страницаReferences: Healthcare Management: Cases, Concepts, and Skills. 2nd Edamin rossОценок пока нет
- COVID-19 Vaccine Acceptability and Its Determinants in Mozambique: An Online SurveyДокумент10 страницCOVID-19 Vaccine Acceptability and Its Determinants in Mozambique: An Online Surveyh3493061Оценок пока нет
- Skin CancerДокумент27 страницSkin CancerHealth Education Library for People100% (1)