Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
Загружено:
AlloiBialbaАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
Загружено:
AlloiBialbaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
ANATOMY
LECTURE: NOSE and PARANASAL SINUSES
8.2
LECTURER: Dr. Colmenar
OUTLINE A. Skeletal Part
I. External Nose • Nasal bones
a. PARTS
• Frontal process of maxillae
LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Nasal part of frontal bone
• IF THE LECTURER DID NOT PROVIDE B. Cartilaginous Part
OBJECTIVES PUT “NO OBJECTIVES GIVEN”
• 2 Lateral cartilage
REFERENCES (CITE ALL REFERENCES!!!)
• 2 Alar cartilage - Cartilage-U SHAPED- dilate and
• Marieb, E. & Hoehn, K. (2011). Essentials of Human constricts the nares when muscle acting on the nose
th
Anatomy and Physiology (9 ed.). Pearson Education contracts
Inc. (THIS IS A SAMPLE REFERENCE ONLY) • 1 septal
Legend:
Remember
Lecturer Book
(Exams)
G &
*Italicize are from audio – even without the megaphone
icon
Book-blue font
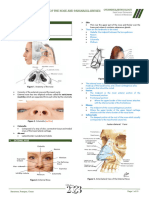
I. EXTERNAL NOSE
• Projects from the face
• Vary in size and shape (depending on ethnicity)
because of differences in nasal cartilages
PARTS
1. Root – Superior angle
2. Apex – nasal tip
3. Nares – 2 piriform openings
4. Alae – lateral boundaries U Kapain niyo nose niyo, yung malambot na part yung
5. Nasal septum – middle structure which separates 2 cartilaginous part
nares U EENT is a nice stepping stone for cosmeticsurgery
6. Vestibule – with stiff nasal hairs U Most common fractured bone of the head is the Nasal
U Vibrissae – medical term for nasal hair (remember bone (contact sports - kapag nasisiko)
th
this until 4 year) U When you undergo nose job, Alar and Lateral
U Vibrisectomy – if mag-pull kayo ng hair sa nose Cartilages yung tini-trim para lumiit. That’s what you
call Alarplasty.
NASAL SEPTUM
• Divides the chamber of the nose into 2 nasal cavities:
A. Components
1. Perpendicular plate of ethmoid – forms bony
superior part of the nasal septum
2. Vomer – thin flat bone
3. Septal cartilage – articulates with bony septum;
movable part
U Kiesselbach’s area or Little’s area – where nose
bleeding(epistaxis) usually occurs
U Kapag nag-nosebleed kayo, dyan usually
nanggagaling
Lecture Title: Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
Transcribed by: wow magic Checked and Edited by: Ursua 1
NASAL CONCHA
U In clinics, we call this “turbinates”
• 3 scroll-shaped elevations
• Superior,middle,inferior
• Divide the nasal cavity into 4 passages
Sphenoethmoidal recess
U Located in the middle aspect near the sphenoid
sinus
U Eskinita sa loob ng ilong yung mga spaces
U Bounded by bones which are the sinuses
NASAL CAVITIES U Leads to sphenoidal sinus
U Sinues are bone cavities that contain air lined by
U Starts from the front, from the external nares, then all mucosa and they have outflow tracts that leads
the way to the back, your nasopharynx to your
to nasal cavity
posterior choanae
U Important structures clinically please
remember
Superior meatus
U Posterior ethmoidal sinusis beimg drained by
superior meatus
Middle meatus
U Drains the following sinuses: Frontal, Anterior
and Middle Ethmoidal and Maxillary
Inferior meatus
U Exception no drainage
• Open posteriorly into the nasopharynx through the
U Pero the nasolacrimal duct kapag nagbara
conchae
magkakaroon ng tearing, luha kayo ng luha more
• Mucosa lines Nasal Cavity except for vestibule
(anterior part - which is lined by skin) of ophthalmologic disease entity
1. Olfactory area (mucosa part)
- Superior 1/3
- Contains organ of smell
2. Respiratory area
- Inferior 2/3
- Where air is warmed and
moistened before it goes to
respiratory tract
Lecture Title: Nose and Paranasal Sinuses 2
Transcribed by: eow Checked and Edited by: Ursua
NASAL PASSAGES o Olfactory nerve
o Olfactory bulb – forebrain
• Sphenoethmoidal recess – sphenoid sinus
• Superior meatus – posterior ethmoidal sinus U Not seen in cadaver kasi maliliit
• Middle meatus
- anterior/middle ethmoidal sinus
- frontal sinus
- maxillary sinus
• Inferior meatus – nasolacrimal duct
VASCULATURE
Arterial Supply:
Branches of:
• Sphenopalatine artery
• Anterior and posterior ethmoidal artery
• Greater palatine artery
• Superior labial artery
• Lateral nasal branches of facial artery
• Kiesselbach’s area – anterior, where all arteries PARANASAL SINUSES
anastomose, where nose bleeding occurs
U Septum made up of ridge, made of capillary
network kaya mabilis magdugo
Venous drainage:
• Sphenopalatine, facial and ophthalmic veins
• Air-filled extensions of the respiratory part of the nasal
cavity into the ff cranial bones:
• FRONTAL- behind the forehead
• ETHMOID- superior aspect of the nasal cavity
• SPHENOID - behind the ethmoid
• MAXILLARY
A. FRONTAL SINUS
• Between outer and inner tables of frontal bone
• Detectable by 7 y/o
• Drains thru frontonasal duct into infundibulum w/c
opens into semilunar hiatus of middle meatus
• NS: br of supraorbital n
NERVE SUPPLY Frontal Sinuses
• Nasal septum - The right and left frontal sinuses are rarely of equal size
o Nasopalatine nerve and the septum between them is not usually situated
entirely in the median plane.
o Greater palatine nerve
o Anterior ethmoidal nerve - Very in size approx. 5 mm
o Posterior ethmoidal nerve - Often has 2 parts:
Vertical part – in the squamous part of frontal bone
• Smell Horizontal part – in the orbital part of the frontal bone
Lecture Title: Nose and Paranasal Sinuses 3
Transcribed by: eow Checked and Edited by: Ursua
B. ETHMOIDAL SINUS TRANSERS NOTE
• Comprise several cavities-ethmoidal cells
• At ethmoid bone
I GOT UR THORACIC
• Parts: SPINE doctors
o Anterior- drain into middle meatus
o Middle- form ethmoidal bulla,drain into middle
meatus
o Posterior- drain into superior meatus
• NS: Nasociliary nerve [CN V1]
U Ethmoidal bulla – swelling on the superior border of
the semilunar hiatus
C. SPHENOIDAL SINUS
• Unevenly divided
• Body of sphenoid
• Separated by thin plates of bone from optic nerve and
chiasma, ICA, pituitary gland
• Opens into Sphenoethmoidal recess
• NS: posterior ethmoidal nerve
D. MAXILLARY SINUS
• Largest
• Pyramidal shaped Eow! It has been an honor serving you gross anatomy transes
future bedan doctor(2021). See you next school year!
• Parts:
o Apex- into zygomatic bone -Morte, Montes, Pascua, Robinion for SK members haha
o Base- part of nasal cavity
o Roof- formed by floor of orbit
o Floor- formed by alveolar part of maxilla
• Drains via maxillary ostium into middle meatus
• NS: Superior alveolar nerves
Lecture Title: Nose and Paranasal Sinuses 4
Transcribed by: eow Checked and Edited by: Ursua
Вам также может понравиться
- Pediatric Surg TransДокумент4 страницыPediatric Surg TransSven OrdanzaОценок пока нет
- ILA - Hirschsprungs DiseaseДокумент48 страницILA - Hirschsprungs DiseaseSoleh Ramly100% (1)
- Super Parasitology TableДокумент11 страницSuper Parasitology Tablesleepyhead archerОценок пока нет
- Microbiology Mock Board RationalizationДокумент228 страницMicrobiology Mock Board RationalizationCla NuvalОценок пока нет
- (GYNE) 3.05 Gestational Trophoblastic Disease - Co-HidalgoДокумент7 страниц(GYNE) 3.05 Gestational Trophoblastic Disease - Co-HidalgoMeg MisaОценок пока нет
- UROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasДокумент33 страницыUROLOGY 2020 (Doc BarcenasJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoОценок пока нет
- Obgyn Revalida Review 2013 For PrintingДокумент96 страницObgyn Revalida Review 2013 For PrintingMon Ordona De Guzman100% (2)
- Gynecology HXДокумент4 страницыGynecology HXlovelots1234Оценок пока нет
- Pedia - Reviewer-AuditДокумент9 страницPedia - Reviewer-AuditJoanna Mae CarolinoОценок пока нет
- Infertility: Dr. Carolina Paula C. MartinДокумент6 страницInfertility: Dr. Carolina Paula C. MartinMaikka IlaganОценок пока нет
- Nematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Документ4 страницыNematodes-Reviewer (Revised)Primo GeorgeОценок пока нет
- S4 L5 SchistosomaДокумент5 страницS4 L5 Schistosoma2013SecBОценок пока нет
- GYNE 4.04 Pelvic Organ DisordersДокумент7 страницGYNE 4.04 Pelvic Organ DisordersGray SnellОценок пока нет
- Osce Cranial Nerves PDFДокумент42 страницыOsce Cranial Nerves PDFriczen vilaОценок пока нет
- Junior Intern Review - Oral Revalida 2016Документ170 страницJunior Intern Review - Oral Revalida 2016Cyrus ZalameaОценок пока нет
- Internal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoДокумент3 страницыInternal Medicine - Nephrology: Topic: Cystic Kidney Diseases Lecturer: Dra. Myrna NgoVon HippoОценок пока нет
- Pediatric History & Physical ExamДокумент7 страницPediatric History & Physical ExamMelodia Turqueza GandezaОценок пока нет
- Our Lady of Fatima University Peptic UlcerДокумент37 страницOur Lady of Fatima University Peptic UlcerLord Pozak MillerОценок пока нет
- Procedural ReportДокумент14 страницProcedural ReportiamcharraeОценок пока нет
- Ectopic PregnancyДокумент6 страницEctopic PregnancyChristine Evan HoОценок пока нет
- Cellular AdaptationsДокумент19 страницCellular AdaptationssnehagptОценок пока нет
- TRIVIA: Dr. Tan Is The Father/Pioneer of Laparoscopic Surgery in The PhilippinesДокумент48 страницTRIVIA: Dr. Tan Is The Father/Pioneer of Laparoscopic Surgery in The PhilippinesJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoОценок пока нет
- Ob - Dystocia 2Документ88 страницOb - Dystocia 2api-3856051100% (1)
- Breast and AxillaeДокумент13 страницBreast and AxillaeJemma NocalanОценок пока нет
- 15 Physio OB - Normal LaborДокумент8 страниц15 Physio OB - Normal LabormaqmmОценок пока нет
- Moral Principles and Medical PracticeThe Basis of Medical Jurisprudence by Coppens, Charles, 1835-1920Документ71 страницаMoral Principles and Medical PracticeThe Basis of Medical Jurisprudence by Coppens, Charles, 1835-1920Gutenberg.org100% (2)
- Taenia Saginata Taenia Solium: "Beef Tapeworm"Документ6 страницTaenia Saginata Taenia Solium: "Beef Tapeworm"Gela ReyesОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics Physical ExaminationДокумент1 страницаPediatrics Physical ExaminationdzaddОценок пока нет
- TRANS - Pediatric Patient ProblemsДокумент4 страницыTRANS - Pediatric Patient ProblemsRencel Hope Bañez100% (1)
- Pyloric StenosisДокумент11 страницPyloric StenosisJustin CharlesОценок пока нет
- HerniaДокумент5 страницHerniasarguss14100% (5)
- Calcium, Magnesium, and Potassium Homeostasis: OutlineДокумент10 страницCalcium, Magnesium, and Potassium Homeostasis: OutlineMigs MedinaОценок пока нет
- Ogexamination 110401040414 Phpapp02 PDFДокумент26 страницOgexamination 110401040414 Phpapp02 PDFDika RizkiardiОценок пока нет
- MC NelsonsДокумент31 страницаMC NelsonsNiñoTanОценок пока нет
- Case 1 History & PEДокумент3 страницыCase 1 History & PEcbac1990Оценок пока нет
- Pedia Review Final Growth and DevelopementДокумент553 страницыPedia Review Final Growth and Developementervin_agena394Оценок пока нет
- OBGYNE Must-KnowsДокумент10 страницOBGYNE Must-KnowsPigwet KwisОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics PerpetualДокумент20 страницPediatrics PerpetualHazel Fernandez VillarОценок пока нет
- Pedia Finals ReviewerДокумент9 страницPedia Finals ReviewerMarron Jane GanoticeОценок пока нет
- 3.1 Applied Lecture - Pediatric History - BahaghariДокумент5 страниц3.1 Applied Lecture - Pediatric History - BahaghariAsylum AllegoryОценок пока нет
- Legal Medicine Review PDFДокумент10 страницLegal Medicine Review PDFGhie TangonanОценок пока нет
- Os 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Документ4 страницыOs 206: Pe of The Abdomen - ©spcabellera, Upcm Class 2021Ronneil BilbaoОценок пока нет
- PEDIA Review TransesДокумент12 страницPEDIA Review TransesanonymousОценок пока нет
- Legal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerДокумент17 страницLegal Medicine and Medical Jurisprudence Comprehensive Exam ReviewerYeshua Tura100% (1)
- Pedia Drugs and Dosages SlidesДокумент25 страницPedia Drugs and Dosages SlidesWipaporn ChaengsriОценок пока нет
- Obstetric FormДокумент4 страницыObstetric FormKhylamarie VillalunaОценок пока нет
- Surgery I Block 4 Super Reviewer PDFДокумент14 страницSurgery I Block 4 Super Reviewer PDFlems9Оценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology TransesДокумент10 страницAnatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology Transeshezekiah minОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics: 2 Case ReportДокумент50 страницPediatrics: 2 Case ReportSam Raven AndresОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.3 Urology Part 2 - Dr. YusiДокумент19 страниц(Surg2) 5.3 Urology Part 2 - Dr. YusiAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Revalida Reviewer AsmphДокумент237 страницRevalida Reviewer AsmphShey ShocОценок пока нет
- DISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneДокумент5 страницDISC, Drugs, Infection, Thick Basal MembraneHOPEОценок пока нет
- Strongyloides StercoralisДокумент17 страницStrongyloides StercoralisHadeer Mahmoud AbuslimaОценок пока нет
- Pedia HistoryДокумент4 страницыPedia HistorydoktoraronaОценок пока нет
- OPHTHALMOLOGY Revalida Review 2019Документ110 страницOPHTHALMOLOGY Revalida Review 2019anonymousОценок пока нет
- Ust Pharma Mock-2015 PDFДокумент8 страницUst Pharma Mock-2015 PDFJanna Janoras ŰОценок пока нет
- Trans Savi Oto Lec 05 Applied Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose 1st SemesterДокумент7 страницTrans Savi Oto Lec 05 Applied Anatomy and Physiology of The Nose 1st SemesterJoherОценок пока нет
- Nose and Parasinuses: I. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. II. A. B. C. D. IiiДокумент3 страницыNose and Parasinuses: I. A. B. C. D. E. F. G. II. A. B. C. D. IiiKenneth TorresОценок пока нет
- (Unit 6) M.01 Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal SinusesДокумент10 страниц(Unit 6) M.01 Anatomy of The Nose and Paranasal Sinusesjustme12345mОценок пока нет
- Simply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESДокумент38 страницSimply Put - ENT NOSE LECTURESCedric KyekyeОценок пока нет
- Health Care For PublishДокумент99 страницHealth Care For PublishAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- OB Journal AppraisalДокумент2 страницыOB Journal AppraisalAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Template) PediaДокумент7 страниц(Template) PediaAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.2 Urology Part 1 - Dr. YusiДокумент18 страниц(Surg2) 5.2 Urology Part 1 - Dr. YusiAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.1a Introduction To Anesthesia Part 1Документ21 страница(Surg2) 5.1a Introduction To Anesthesia Part 1AlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacotherapeutic (Medpharma30) AY 2020-2021 Treatment Drug SelectionДокумент2 страницыPharmacotherapeutic (Medpharma30) AY 2020-2021 Treatment Drug SelectionAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.4 Urology Part 3Документ23 страницы(Surg2) 5.4 Urology Part 3AlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Surger YII Clinic AL Case: Group 4B Bernabe, Bernardo, Bialba, BigorniaДокумент39 страницSurger YII Clinic AL Case: Group 4B Bernabe, Bernardo, Bialba, BigorniaAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.3 Urology Part 2 - Dr. YusiДокумент19 страниц(Surg2) 5.3 Urology Part 2 - Dr. YusiAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Medical Students Experiences of Moral Distress .33Документ7 страницMedical Students Experiences of Moral Distress .33AlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.1b Introduction To Anesthesia-Part 2Документ16 страниц(Surg2) 5.1b Introduction To Anesthesia-Part 2AlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- (Surg2) 5.1d Anesthesia PointersДокумент12 страниц(Surg2) 5.1d Anesthesia PointersAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Pharmacology: Outline PharmacodynamicsДокумент11 страницPharmacology: Outline PharmacodynamicsAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Over-the-Counter Medications in PregnancyДокумент8 страницOver-the-Counter Medications in PregnancyAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Cobalamin DeficiencyДокумент19 страницCobalamin DeficiencyAlloiBialba100% (1)
- Neuropreceptorial ChecklistДокумент33 страницыNeuropreceptorial ChecklistAlloiBialba0% (1)
- Drugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemДокумент13 страницDrugs Acting On The Respiratory SystemAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Paediatric Pharmacokinetics: Key Considerations: Hannah Katharine Batchelor & John Francis MarriottДокумент10 страницPaediatric Pharmacokinetics: Key Considerations: Hannah Katharine Batchelor & John Francis MarriottAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Acute Gastroenterit ISДокумент23 страницыAcute Gastroenterit ISAlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Allison Mei R. Bialba 4nur1 RLE 4Документ3 страницыAllison Mei R. Bialba 4nur1 RLE 4AlloiBialbaОценок пока нет
- Axial Skeleton LabelingДокумент4 страницыAxial Skeleton LabelingSeshanth KarthikОценок пока нет
- Cat Skeletal SystemДокумент30 страницCat Skeletal SystemBridgette JuarezОценок пока нет
- Scalp - 1 PDFДокумент50 страницScalp - 1 PDFTarek TharwatОценок пока нет
- Lumbar SpineДокумент43 страницыLumbar SpineVidhushi Vedhara100% (1)
- Bio 230 Axial Skeleton Lecture NotesДокумент4 страницыBio 230 Axial Skeleton Lecture NotesDenise MathreОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The Head and The Neck FinalДокумент156 страницAnatomy of The Head and The Neck FinalYudhi Aulia100% (1)
- Bone ChartsДокумент40 страницBone ChartsDhanushОценок пока нет
- OsteologiДокумент37 страницOsteologiNasrul NasehatiОценок пока нет
- Maglaqui - Skeletal SystemДокумент5 страницMaglaqui - Skeletal SystemNICOLE MAGLAQUIОценок пока нет
- Presented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyДокумент20 страницPresented By:-Dr. Sushma Tomar Associate Professor Department of AnatomyCristine EchaveОценок пока нет
- Identify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaДокумент7 страницIdentify The Boundaries of The Infratemporal FossaHARSHDESAI56929640Оценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Anatomy Physiology An Integrative Approach 4th Edition Michael Mckinley Valerie Oloughlin Theresa BidleДокумент110 страницTest Bank For Anatomy Physiology An Integrative Approach 4th Edition Michael Mckinley Valerie Oloughlin Theresa Bidlejavierdoyleafkqexcgzj100% (31)
- Neck InjuresДокумент12 страницNeck InjuresPepe Toño Bau OsoОценок пока нет
- Skull BonesДокумент25 страницSkull Bonesjohn mwambuОценок пока нет
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedДокумент88 страницLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoОценок пока нет
- Norma BasalisДокумент21 страницаNorma BasalisIndirackshi SundararajanОценок пока нет
- The Skeleton: Chapter 7 - Part AДокумент7 страницThe Skeleton: Chapter 7 - Part AJonathan HigginbothamОценок пока нет
- II - 4.anterior Cranial FossaДокумент2 страницыII - 4.anterior Cranial FossaalllexissssОценок пока нет
- Skeletal SystemДокумент17 страницSkeletal SystemRachell AvecillaОценок пока нет
- Paranasal Sinus (Repaired) EntДокумент48 страницParanasal Sinus (Repaired) EntDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaОценок пока нет
- Cephalometric Evaluation of GrowthДокумент79 страницCephalometric Evaluation of GrowthAhmedsy Ahmedsy AhmedsyОценок пока нет
- DR Emily Craig Osteology HandbookДокумент34 страницыDR Emily Craig Osteology HandbookSemrin DemirelОценок пока нет
- VISCEROCRANIUMДокумент157 страницVISCEROCRANIUMTrần NamОценок пока нет
- Anatomy and Surgical Appraches of The Temporal Bone PDFДокумент251 страницаAnatomy and Surgical Appraches of The Temporal Bone PDFThamescracker28809100% (2)
- Microsoft Word - The Skeletal SystemДокумент24 страницыMicrosoft Word - The Skeletal SystemNino Alania0% (2)
- Anatomy of Maxilla and Its Development - ORIGINALДокумент68 страницAnatomy of Maxilla and Its Development - ORIGINALHoang NhanОценок пока нет
- Snake SkeletonДокумент6 страницSnake SkeletonJacobo Alvarez SalasОценок пока нет
- Maxillary - Fractures - PPT Filename Utf-8''Maxillary FracturesДокумент23 страницыMaxillary - Fractures - PPT Filename Utf-8''Maxillary FracturesayeshaОценок пока нет
- GONSTEAD IFEC CervicalsДокумент6 страницGONSTEAD IFEC CervicalsAurelien BoschatОценок пока нет
- Anato TestДокумент69 страницAnato Testeyash.6Оценок пока нет