Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary
Загружено:
zin15080 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
89 просмотров7 страницStorage Technology Foundations - Glossary Item Access Control Actuator AES Also Known As Definition Security techniques used so only authorized users can access a computer or network. The act of copying files and databases to protect them in the event of a system failure and retrieving them at a later date.
Исходное описание:
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документStorage Technology Foundations - Glossary Item Access Control Actuator AES Also Known As Definition Security techniques used so only authorized users can access a computer or network. The act of copying files and databases to protect them in the event of a system failure and retrieving them at a later date.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
89 просмотров7 страницStorage Technology Foundations Glossary
Загружено:
zin1508Storage Technology Foundations - Glossary Item Access Control Actuator AES Also Known As Definition Security techniques used so only authorized users can access a computer or network. The act of copying files and databases to protect them in the event of a system failure and retrieving them at a later date.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 7
Storage Technology Foundations – Glossary
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
Access Control Security techniques used so only authorized users can access a computer or Security
network.
Actuator The part of the hard drive which positions the read/write heads on the platter. Storage
AES Advanced A cryptographic algorithm designated by NIST. Security
Encryption
Standard
Application AOI A set of function calls that enables communication between applications or between CAS
Programming an application and an operating system.
Interface
Arbitrated Loop FC-AL Fibre Channel topology analogous to a token ring. SAN
Archival Backup A common requirement used to preserve transaction records, email, and other Backup - Restore
business work products for regulatory compliance.
Array A group of disks that work together as a unit, typically, in a RAID implementation. Storage
Availability The accessibility of a computer system or network resource. Systems
Backup A copy of the online data that resides on primary storage. The backup copy is created Backup - Restore
and retained for the sole purpose of recovering deleted, broken, or corrupted data on
the primary disk.
Backup Catalog A database used by the backup environment, to keep track of everything that has Backup - Restore
been backed up.
Backup Client The software that retrieves data (such as a file, a directory or a filesystem) from a Backup - Restore
machine (such as a database production server), sending it, to a Storage Node
Backup Information about the backup data: File names, time of backup, size, permissions, Backup - Restore
Metadata ownership, and most important, tracking information to allow locating the data to be
restored.
Backup Server The piece of the backup software package controlling the backup environment tasks Backup - Restore
and policies. This includes jobs, policies and catalogs. A Backup Server receives
metadata from Backup Clients to perform its activities.
Backup/Restore The act of copying files and databases to protect them in the event of a system failure Backup - Restore
or similar catastrophe and retrieving them at a later date.
BBU Battery A battery-operated power supply used as an auxiliary source of electricity in the event Systems
Backup Unit of power failure. The battery guarantees no lost writes and orderly transitions or
shutdowns during power outages.
BCV Business Copies of active production volumes that can be used to run simultaneous tasks in Systems
Continuance parallel with one another. This gives the ability to do concurrent operations without
Volumes affecting production systems.
BIOS Basic The base functions of the computer. Systems
Input/Output
System
Block A unit of contiguous data. Storage
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 1
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
Block Size The size of the unit of contiguous data. Storage
Business The ability to ensure that a business is able to weather a natural or man-made Systems
Continuity catastrophe through the deployment of fault-tolerant and redundant hardware and
software systems.
Bus A data and control path which acts as a bridge between the computer and Systems
peripherals.
Cache Acts as a buffer between a relatively fast process (requests from the host) and a Storage
relatively slow one
Capacity The amount of data that a drive can store. Storage
CAS Content Storage arranged by content type. Storage
Addressable
Storage
CD-ROM Compact Storage media that, once written (“burned”), can then only be read. Storage
Disk Read-
Only Media
Channel A high bandwidth connection between a processor and other processors or devices. Systems
Checksum A number of bits that is transmitted with data so that the receiving device can verify Systems
the accuracy of the data that it received. If the number of bits that arrives is the same
that is sent, the transmission is believed to be complete.
Cluster A collection of high-performance, interconnected computer servers working together Systems
as a single processing resource in an application environment to provide scalable,
high availability to both users and applications.
Cold Backup The application will be shut down for the backup to take place.
Concatenation When two logical block address ranges are combined as a single virtual unit with a Storage
contiguous address range.
Connectivity The ability of hardware devices or software to communicate with other hardware or Systems
software.
Content Address CA An identifier that uniquely address the content of a file and not its location. CAS
Content CAS An object-orients, location independent approach to data storage.
Addressed
Storage
Content CDF The content address and metadata about a CAS objects that are save in an XML file. CAS
Descriptor File
Controller Communicates with the host to facilitate read/write requests. Systems
Content ID Content Content address of a CDF that contains the Content Address of the actual data on a CAS
Handle or CAS environment.
Content
Reference
Cumulative Differential A type of incremental backup that contains changes made to a file since the last full Backup - Restore
Backup backup backup.
Cylinder A set of identical tracks on each of the platters in a disk drive—all of which are the Storage
same distance from the central spindle.
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 2
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
Data Transfer The number of megabytes per second that a drive can deliver data to the CPU. Storage
Rate
DAS Direct Storage devices are attached directly to a single host computer, and use block-level Storage
Attached access protocols such as ATA and SCSI. Physical sharing of the storage devices is
Storage; and not practical, and data sharing must be coordinated through the host computer.
SAS (Server
Attached
Storage)
Dense Wave DWDM A technology that puts data from different sources together on an optical fiber with Network
Division each signal carried on its own separate light wavelength (commonly referred to as a
Multiplexing lambda or λ).
Disaster To be able to restore all, or a large part of, an IT infrastructure in the event of a major Storage
Recovery disaster.
Disk Geometry Characteristics of a disk. Storage
ECC Error An encoding method that detects and corrects errors at the receiving end of data Storage
Correction transmission. ECC is used by most modems.
Coding
Fabric A Fibre Channel topology with one or more switching devices. SAN
Fault Tolerance Hardware and software set up in such a way so errors in one area will be Network
compensated for by another area.
FCIP Fibre Channel over IP protocol. TCP/IP Based tunneling protocol for connecting IP SAN
Fibre Channel SANs.
Fibre Channel FC Set of standards for a serial I/O bus. Network
Firmware Software that is part of a device. Systems
Full Backup A backup of all data on the target volumes, regardless of any changes made to the
data itself.
Granularity Determines how often and what type of data is backed up. Backup - Restore
Hard Drive A storage device which consists of a series of rotating platters within a sealed case. Storage
HBA Host Bus Hardware that connects a host computer to a network Server/Host
Adapter
Host A computer server, typically networked, that runs applications used by or from other Server/Host
computers (e.g., web servers, file servers, and application servers).
Hot Backup The application is still up and running, with users accessing it, while backup is taking Backup - Restore
place.
Hot Spare An idle disk drive which replaces a failed drive in any protected RAID Group Storage
Hot Swap An additional idle piece of hardware which replaces a defective piece of hardware in Systems
the event of a failure.
Hub A device joining communications lines at a central location, providing a common Network
connection to all devices on the network.
iFCP Gateway-to-gateway protocol for sending FCP over IP. IP SAN
iSCSI Internet SCSI protocol. Native TCP/IP protocol for establishing and managing IP SAN
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 3
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
connections between IP-based storage devices, hosts and clients.
ILM Information Acronym for data management. Systems
Lifecycle
Management
Incremental Contains the changes since the last backup, of any type, whichever was most recent. Backup - Restore
Backup
Initiators Devices that start a data request. Storage
I/O Channel Input/Output Provides the communication between the I/O Bus and the CPU so that the actual Network
Channel or information can be recorded on a platter in a hard drive.
Read/Write
Channel
Intelligent A device that is controlled by one or more processors integral to the device.
Interoperability The ability of hardware and software made by a variety of different manufacturers to Systems
work seamlessly together.
JBOD Just a Bunch Acronym for disk-based storage. Storage
of Disks
Latency The time from when the head is over the correct track until the data rotates around Storage
and is under the head and can be read.
LBA Logical Block A sequential address for accessing blocks on storage media. Storage
Address
Link A connection between two Fibre Channel ports.
LU Logical Unit Devices with SCSI IDs. Systems
LUN Logical Unit An encoded 3-bit identifier used on an SCSI bus to distinguish among up to eight Storage
Number devices (logical units) with the same SCSI ID. An LUN is an indivisible unit presented
by a storage device to its host. LUNs are assigned to each disk drive in an array so
the host can address and access the data on those devices.
LUN Masking An array security feature that lets a server access only its own (and no other) LUNs Network
on a Fibre Channel. Each LUN can specify what host or combination of hosts to have
access to that LUN.
LVM Logical Management of a virtual disk made up of multiple logical disks. Storage
Volume
Management
Metadata Data about data. Describes the content, quality, condition, and other characteristics
of data. Also used to identify file characteristics in some file systems.
MTBF Mean Time A statistical calculation that measures average failure rates of devices. Storage
Between
Failure
MTTF Mean Time A statistical calculation that measures the average time until data loss occurs. Storage
to Data Loss
Mirroring A data redundancy technique where all data is written simultaneously to two disk Storage
drives to provide protection against disk failure.
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 4
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
Modularity An approach to developing hardware or software that breaks projects into smaller
units (or modules) that are deliberately designed as standalone units that can work
with other sections of the program. The same module can perform the same task in
another or several other programs or components so modifying the way that module
works will have no adverse affects on the other components of a program.
Monolithic Array Integrated A storage subsystem Storage
array,
enterprise
array, or
cache centric
array
Multi-pathing Allows for two or more data paths to be simultaneously used for read/write Network
operations, enhancing performance by automatically and equally dispersing data
access across all the available paths.
Name Services Worldwide-exclusive names that allow a device to log into the switch. Network
Login
NAS Network Amounts of storage accessible from your network. Storage
Attached
Storage
Node A device that is directly connected to the network, such as file servers and shared Network
peripherals. Alternatively it can describe one of the links in the network, such as Host
Node or Intercept Node.
Non-volatile Data in memory, cache and other electronic repositories are protected by a battery Storage
backup system to prevent their loss in the event of a power failure.
OLTP Online A system that processes transactions the instant the computer receives them and Network
Transaction updates master files immediately. OLTP is essential for good financial record keeping
Processing and inventory tracking.
Operational The collection of data for the eventual purpose of restoring, at some point in the Backup - Restore
Backup future, data that has become lost or corrupted.
Optical Disk Disk storage using optical storage technology. Storage
Parity A data-error-checking procedure where the number of 1s must always be the same— Storage
either even or odd— for each group of bits submitted without error. Parity information
is saved and compared with each subsequent calculations of whether the number is
odd or even.
Parity Bit An extra bit used in checking for errors in transferred groups of data bits. In modem Network
communications, it is used to check the accuracy of each transmitted character. In
RAM, a parity bit is used to check the accuracy with which each byte is stored.
Partition A logical division of a hard drive. Storage
Platter A component of a hard drive which is the media for storing the data. Storage
Port On a computer, it is a physical connecting point to which a device is attached. Network
Protocol A set of rules or standards intended to enable computers to communicate. Network
RAID Redundant The combining of multiple small, inexpensive disk drives into an array of disk drives, Storage
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 5
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
Array of which yields performance exceeding that of a Single Large Expensive Drive (SLED).
Independent RAIDs appear to the computer as a single logical storage unit or drive.
Disks
Read-Only Data can be retrieved (read) but not altered (written).
Read/Write The components of the hard drive which record the data onto the tracks of the platter. Storage
Heads
Redundancy The storing of duplicate data on multiple drives to ensure data availability. Storage
Remote Backup A copy from the primary storage is done directly to the backup media that is sitting on Backup - Restore
another site. The backup media can be a real library, a virtual library or even a remote
filesystem.
Retention Period The length of time that a particular version of a dataset is available to be restored. Backup - Restore
Rotation Speed The speed at which a hard drive platter rotates. Storage
RPO Recovery The point in time to which data must be restored in order to resume processing Backup - Restore
Point transactions. RPO is the basis on which a data projection strategy is developed.
Objective
RTO Recovery The maximum allowable time to fully recover application data. Backup - Restore
Time
Objective
SAN Storage Area A dedicated network that carries data between computer systems and storage Storage
Networks devices that can include tape and disk resources.
Scalability The ability of hardware, software and networks to change size according to the Systems
number of users that they accommodate. Most often, scalability refers to the capacity
to expand rather than shrink.
SCSI Small The standard set of protocols for host computers communicating with attached Network
Computer peripherals. SCSI allows connection to as many as six peripherals including printers,
Systems scanners, hard drives, zip drives, and CD-ROM drives.
Interface
Sector A portion of a track on a hard disk platter. Storage
Seek Time The time required for the read/write heads in a disk drive to move between tracks of Storage
the disk.
SLED Single Large A single, generally more expensive drive, attached to a computer. Storage
Expensive
Drive
Snapshot A pioint-in-time copy of data. Backup - Restore
Spindle The part of the hard drive that connects the platters. Storage
Striping A method of storing data that improves system performance. Storage
Storage Node A part of the backup package that controls one or more backup devices (a tape drive, Backup - Restore
tape library, or a backup to disk device), and receives backup data from Backup
Clients.
Structured Data Data that is formal, well organized, and usually stored in a database or spreadsheet.
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 6
Item Also Known Definition Related
As Technology
Switch A network device that selects a path or circuit for sending a data between Network
destinations.
Switched Fabric FC-SW Fibre Channel topology where each device has a unique, dedicated I/O path to the SAN
device it is communicating with.
Synchronous SONET A standard for optical telecommunications transport where traffic from multiple Network
Optical Network subscribers is multiplexed together and sent out onto a ring as an optical signal.
Target A SCSI device that carries out a request from an initiator.
Terabyte TB A thousand billion bytes or one thousand gigabytes. Storage
Throughput In networking, it is a measurement of the amount of data that can be successfully Storage
transferred with a set time period.
Tracks The concentric rings around disk drive platters where data is written. Storage
Unstructured Data that is informal, possibly text (such as XML tagged content), disorganized or Storage
Data stored in files as whole documents or in content management systems.
Volume A virtual disk into which a file system, database management system or other Storage
application places data. A volume can be a single disk partition or multiple partitions
on one or more physical drives.
Wide Area WAN A high-speed network used to connect computers over long distances. Network
Network
Warm Site An alternate processing site which is only partially equipped. Business Continuity
Write-Cache A temporary storage area in memory, where data can be stored before being written Storage
out to disk for permanent storage. This improves system performance.
Write Once WORM Data written to a storage device (such as an optical disk) that is unchanging but can
Read Many be accessed and read many times.
Zoned-bit A method of recording data that takes advantage of the disk’s geometry. Storage
recording
Zoning A method of securing data, where hosts are given access to specific storage devices. Storage
Hosts can only “see” and access storage devices within a specified zone.
Storage Technology Foundations Glossary 7
Вам также может понравиться
- 1 Prof Chauvins Instructions For Bingham CH 4Документ35 страниц1 Prof Chauvins Instructions For Bingham CH 4Danielle Baldwin100% (2)
- P1 Chp12 DifferentiationДокумент56 страницP1 Chp12 DifferentiationbobОценок пока нет
- Integrator Windup and How To Avoid ItДокумент6 страницIntegrator Windup and How To Avoid ItHermogensОценок пока нет
- DS - EE Hash Stage Disk CachingДокумент26 страницDS - EE Hash Stage Disk Cachingcms_gcolesОценок пока нет
- Storage Terms Glossary A: Asynchronous ReplicationДокумент4 страницыStorage Terms Glossary A: Asynchronous Replicationvaibhao1428Оценок пока нет
- Ceph: A Scalable, High-Performance Distributed File SystemДокумент14 страницCeph: A Scalable, High-Performance Distributed File SystemManuel PobreОценок пока нет
- Oda x10 Ha DatasheetДокумент8 страницOda x10 Ha DatasheetSinh DangОценок пока нет
- Object-Based Storage: IEEE Communications Magazine September 2003Документ8 страницObject-Based Storage: IEEE Communications Magazine September 2003Sachi N NerkarОценок пока нет
- Architecting and Managing Apps Matt Tavis July 2010Документ30 страницArchitecting and Managing Apps Matt Tavis July 2010Xinyu DaiОценок пока нет
- h18241 Dell Powerstore Best Practices GuideДокумент17 страницh18241 Dell Powerstore Best Practices Guideeduardo.rosales.islasОценок пока нет
- EXPT NO.: 07: Case Study On Content Addressable StorageДокумент4 страницыEXPT NO.: 07: Case Study On Content Addressable StorageShrinivasa RaoОценок пока нет
- 02-17 Object Storage OverviewДокумент26 страниц02-17 Object Storage OverviewNatalia PardoОценок пока нет
- h18155 Dell Emc Powerstore File CapabilitiesДокумент46 страницh18155 Dell Emc Powerstore File CapabilitiesdanycuppariОценок пока нет
- Problem Definition: Application Aware Backup SystemДокумент38 страницProblem Definition: Application Aware Backup Systemswapy_04Оценок пока нет
- UE20CS351 Unit3 Slides PDFДокумент177 страницUE20CS351 Unit3 Slides PDFGaurav MahajanОценок пока нет
- 01 MR-1CP-SANMGMT - SAN Management Overview - v4.0.1Документ42 страницы01 MR-1CP-SANMGMT - SAN Management Overview - v4.0.1Takieddine ahmed DekkarОценок пока нет
- Object StorageДокумент45 страницObject StorageSaravanaRaajaa100% (1)
- A New Revolution in Enterprise Storage ArchitecturДокумент4 страницыA New Revolution in Enterprise Storage ArchitecturMihaiОценок пока нет
- Data Domain, Deduplication and MoreДокумент6 страницData Domain, Deduplication and MorebinhОценок пока нет
- Blancco 5 ManualДокумент64 страницыBlancco 5 ManualDaniel Martinez CollazoОценок пока нет
- Cryptographic Security For A High-Performance Distributed File SystemДокумент6 страницCryptographic Security For A High-Performance Distributed File SystemvikasbhowateОценок пока нет
- h6811 Datadomain DsДокумент5 страницh6811 Datadomain DsChristian EstebanОценок пока нет
- Dell PowerFlex Specification DatasheetДокумент14 страницDell PowerFlex Specification DatasheetLucas Rodrigues de MouraОценок пока нет
- INFRASTRUCTURE AS A SERVICE-IaaS - BG0Документ15 страницINFRASTRUCTURE AS A SERVICE-IaaS - BG0Trung NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Huawei FusionStorage Data SheetДокумент6 страницHuawei FusionStorage Data SheetLakshmi KiranОценок пока нет
- Standby Technical FeaturesДокумент3 страницыStandby Technical FeaturesTimОценок пока нет
- Ms Winxp - Symbols GlossaryДокумент104 страницыMs Winxp - Symbols GlossaryesshorОценок пока нет
- Red Hat Glossary: /etc/samba/smb - ConfДокумент46 страницRed Hat Glossary: /etc/samba/smb - Confash1758Оценок пока нет
- Oracle Database Appliance X9-2-HA: Fully Redundant Integrated SystemДокумент8 страницOracle Database Appliance X9-2-HA: Fully Redundant Integrated SystemTwins LeongОценок пока нет
- Of File Systems and Storage ModelsДокумент52 страницыOf File Systems and Storage ModelsTrancyОценок пока нет
- Quiz 1 To Finals AdbmsДокумент4 страницыQuiz 1 To Finals AdbmsJayson LucenaОценок пока нет
- Complete Glossary of Terms For Windows XP Operating SystemДокумент38 страницComplete Glossary of Terms For Windows XP Operating SystemKhim AlcoyОценок пока нет
- ManualДокумент79 страницManualRam KumarОценок пока нет
- h18151 Dell Powerstore Data EfficienciesДокумент19 страницh18151 Dell Powerstore Data EfficienciesPabloОценок пока нет
- Glossary XPДокумент54 страницыGlossary XPFatih Mehmet CetinОценок пока нет
- Oracle Database Appliance X8-2-HA: Fully Redundant Integrated SystemДокумент6 страницOracle Database Appliance X8-2-HA: Fully Redundant Integrated SystemOliveira RubensОценок пока нет
- Windowsserver2019 220810014852 7d48539bДокумент37 страницWindowsserver2019 220810014852 7d48539bAditia HamidОценок пока нет
- Distributed Computing EnvironmentДокумент21 страницаDistributed Computing EnvironmentSweta KamatОценок пока нет
- Basic Introduction Availability, Security, and Scalability. RAID Technology Made AnДокумент17 страницBasic Introduction Availability, Security, and Scalability. RAID Technology Made AnvishnuОценок пока нет
- Web Hosting Re Lasted GlossaryДокумент4 страницыWeb Hosting Re Lasted GlossaryKobe ThuyОценок пока нет
- Data Domain Arch InternalsДокумент5 страницData Domain Arch InternalscoolmeenalОценок пока нет
- Sa301 (Midterm Coverage)Документ12 страницSa301 (Midterm Coverage)EFREN LAZARTEОценок пока нет
- Storage Area Network Module-1Документ77 страницStorage Area Network Module-1student MITM CSEОценок пока нет
- Secure Backup 12.2 - DatasheetДокумент4 страницыSecure Backup 12.2 - DatasheetHot MaleОценок пока нет
- Database TerminologiesДокумент13 страницDatabase TerminologiesUnais_Оценок пока нет
- Redp4426 - Apr08 - IBM SAN Volume Controller 4.2.1 Cache PartitioningДокумент12 страницRedp4426 - Apr08 - IBM SAN Volume Controller 4.2.1 Cache PartitioningStefan VelicaОценок пока нет
- Information Storage Management ExcerptДокумент3 страницыInformation Storage Management ExcerptRaghvendra Pratap SinghОценок пока нет
- Commcell Logical Architecture: Logical Management of Production DataДокумент6 страницCommcell Logical Architecture: Logical Management of Production DataRishabh KumarОценок пока нет
- OS Micro 2022 Final Exam WorksheetДокумент78 страницOS Micro 2022 Final Exam Worksheetjan luОценок пока нет
- Final Unit II CC 2022Документ56 страницFinal Unit II CC 2022sairabanu pansareОценок пока нет
- Ilovepdf MergedДокумент79 страницIlovepdf MergedMarceloОценок пока нет
- MSCIT 4th COMP2115 1,2,3Документ23 страницыMSCIT 4th COMP2115 1,2,3countsohaib.asОценок пока нет
- CoudPlus Glossary PDFДокумент17 страницCoudPlus Glossary PDFMeОценок пока нет
- Cloud Migration of Oracle Analytical DB (On-Premise) To AWS RedshiftДокумент10 страницCloud Migration of Oracle Analytical DB (On-Premise) To AWS Redshiftjagadeesh jagadeОценок пока нет
- Distributed File SystemДокумент49 страницDistributed File SystemRicha SinghОценок пока нет
- Operating System (3439) 2Документ14 страницOperating System (3439) 2Tooba Hassan 364-FSS/BSIAA/F19Оценок пока нет
- Windows Server Administrator GlossaryДокумент9 страницWindows Server Administrator Glossarypriya_psalmsОценок пока нет
- Cloud Storage InfrastructuresДокумент40 страницCloud Storage InfrastructuresNikhil Kumar100% (1)
- Storage TermsДокумент10 страницStorage TermsOscar MezaОценок пока нет
- Teknologi Pusat DataДокумент9 страницTeknologi Pusat Datahendroni2210Оценок пока нет
- Types of Storage Virtualization: Block vs. FileДокумент5 страницTypes of Storage Virtualization: Block vs. FilejonahОценок пока нет
- SB Netbackup Flex Scale For Eda WorkloadsДокумент3 страницыSB Netbackup Flex Scale For Eda WorkloadsMuhammad Windiarto HermawanОценок пока нет
- “Information Systems Unraveled: Exploring the Core Concepts”: GoodMan, #1От Everand“Information Systems Unraveled: Exploring the Core Concepts”: GoodMan, #1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 4Документ76 страницChapter 1 4Sean Suing100% (1)
- 7 ElevenДокумент80 страниц7 ElevenakashОценок пока нет
- D. Das and S. Doniach - Existence of A Bose Metal at T 0Документ15 страницD. Das and S. Doniach - Existence of A Bose Metal at T 0ImaxSWОценок пока нет
- Switching Lab-05b Configuring InterVLAN RoutingДокумент2 страницыSwitching Lab-05b Configuring InterVLAN RoutingHernan E. SalvatoriОценок пока нет
- Datos Adjuntos Sin Título 00013Документ3 страницыDatos Adjuntos Sin Título 00013coyana9652Оценок пока нет
- Arithmetic-Progressions - MDДокумент8 страницArithmetic-Progressions - MDJay Jay GwizaОценок пока нет
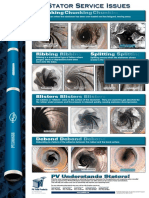
- Chunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesДокумент1 страницаChunking Chunking Chunking: Stator Service IssuesGina Vanessa Quintero CruzОценок пока нет
- Research Methods in Developmental PsychologyДокумент9 страницResearch Methods in Developmental PsychologyHugoОценок пока нет
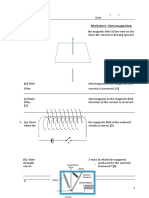
- Electromagnetism WorksheetДокумент3 страницыElectromagnetism WorksheetGuan Jie KhooОценок пока нет
- Managemant PrincipleДокумент11 страницManagemant PrincipleEthan ChorОценок пока нет
- Nikasil e AlusilДокумент5 страницNikasil e AlusilIo AncoraioОценок пока нет
- Revised Corporation Code - Non Stock Close and Special CorporationsДокумент19 страницRevised Corporation Code - Non Stock Close and Special CorporationsVenziel PedrosaОценок пока нет
- What Is A Fired Heater in A RefineryДокумент53 страницыWhat Is A Fired Heater in A RefineryCelestine OzokechiОценок пока нет
- User ManualДокумент96 страницUser ManualSherifОценок пока нет
- English For General SciencesДокумент47 страницEnglish For General Sciencesfauzan ramadhanОценок пока нет
- Anviz T5 RFID ManualДокумент52 страницыAnviz T5 RFID ManualLuis Felipe Olaya SandovalОценок пока нет
- Lecture 12 Health Management Information SystemДокумент14 страницLecture 12 Health Management Information SystemKamran SheikhОценок пока нет
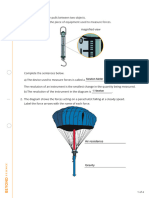
- Forces L2 Measuring Forces WSДокумент4 страницыForces L2 Measuring Forces WSAarav KapoorОценок пока нет
- The Serious Student of HistoryДокумент5 страницThe Serious Student of HistoryCrisanto King CortezОценок пока нет
- Report-Smaw Group 12,13,14Документ115 страницReport-Smaw Group 12,13,14Yingying MimayОценок пока нет
- PNGRB - Electrical Safety Audit ChecklistДокумент4 страницыPNGRB - Electrical Safety Audit ChecklistKritarth SrivastavОценок пока нет
- Catalog Tu ZG3.2 Gian 35kV H'MunДокумент40 страницCatalog Tu ZG3.2 Gian 35kV H'MunHà Văn TiếnОценок пока нет
- UBMM1011 Unit Plan 201501Документ12 страницUBMM1011 Unit Plan 201501摩羯座Оценок пока нет
- Mangement of Shipping CompaniesДокумент20 страницMangement of Shipping CompaniesSatyam MishraОценок пока нет
- Reproduction in PlantsДокумент12 страницReproduction in PlantsAnand Philip PrasadОценок пока нет
- RevlonДокумент13 страницRevlonSarosh AtaОценок пока нет
- Risha Hannah I. NazarethДокумент4 страницыRisha Hannah I. NazarethAlpaccino IslesОценок пока нет