Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Signalling Analysis of LTE PDF
Загружено:
ShaXaib AkhtarОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Signalling Analysis of LTE PDF
Загружено:
ShaXaib AkhtarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
2013/1/16 Security Level: INTERNAL
LTE TDD
Signaling Procedure and
Analysis
www.huawei.com
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Objective
Upon the completion of this course,
you will be able to:
Recognize the LTE signaling
procedures.
Understand the typical signaling
procedures of network access,
paging, and handover.
Analyze basic problems.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 2
Contents
Chapter 1 Network Access Signaling Procedure
Chapter 2 Handover Signaling Procedure
Chapter 3 Paging Signaling Procedure
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 3
Contents
Chapter 1 Network Access Signaling Procedure
1 Cell Searching
2 PLMN and Cell Selection
3 Attach
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 4
Cell Searching
Cell searching, known as downlink (DL) synchronization, is a process to
resolve primary synchronization signals (PSS) and secondary synchronization
signals (SSS) on DL.
Power on
PSS Timeslot
monitoring layer-1 timer
ID
Frame timer, cell ID,
SSS CP monitoring,
monitoring TDD/FDD
Neighboring-cell Initial
monitoring synchronization
PBCH
RS monitoring RSRP/RSRQ MIB/ SIB
decoding
PLMN and
cell selection PLMN/cell
Idle
state
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 5
Cell Searching
In FDD mode, PSSs are on the last OFDM symbol of slot 0 and slot 10, and
SSSs on the second OFDM symbol from the end of slot 0 and slot 10.
In TDD mode, PSSs are on the second OFDM symbol from the end of slot
2 and slot 12, and SSSs on the last OFDM symbol of slot 1 and slot 11.
PSSs are the same for transmission from the two slots. Whereas, SSSs are
different for transmission from the two slots. PSS resolution triggers a timer
of 5 ms, and SSS resolution triggers a timer of 10 ms.
The cell ID on the physical layer can be obtained by using PSS resolution,
the cell group ID (504 cells are divided into 168 groups) can be obtained by
using the SSS resolution, and the physical cell identifiers (PCIs) of the
current cell (each cell group has three cell PCIs) can be obtained by using
both PSS resolution and SSS resolution. PCIs of the current cell = Cell
group ID x 3 + Cell ID.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 6
Contents
Chapter 1 Network Access Signaling Procedure
1 Cell Searching
2 PLMN and Cell Selection
3 Attachment
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 7
PLMN and Cell Selection
After cell searching is complete, the UE obtains the PCIs of the current cell to resolve
the master information blocks (MIBs) and system information blocks (SIBs) in the
current cell. By performing MIB resolution, the UE obtains key information, including
DL synchronization and system bandwidth of the cell, detects physical dedicated
control channel (PDCCH) in the SIB time domain, and then obtains the System
Information Block Type1 (SIB1) information based on the PDCCH before resolving
other SIB information.
UE E-UTRAN
MasterInformationBlock
SystemInformationBlockType1
SystemInformation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 8
PLMN and Cell Selection: MIB
The transmission period for MIBs is 40 ms. In a period, the physical broadcast channel
(PBCH) is located in subframe 0 of each radio frame and occupies the first four
symbols of slot 2 within each subframe 0. PSSs and SSSs are the same in the
frequency domain, occupying 1.08 MHz in the center, that is, the 6 RBs in the middle
of the frequency domain.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 9
PLMN and Cell Selection: SIB1
The transmission period for
SIB1 is 80 ms. The first
transmission is performed in
the radio frame numbered a
multiple of 8 within a TTI, and
repeated transmission is
performed on other even-
numbered radio frames in the
TTI. Transmission is fixed on
subframe 5 in the
corresponding frame. The UE
detects the PDCCH on these
subframes. If there is a system
information radio network
temporary identity (SI-RNTI),
the UE receives SIB1 on the
physical dedicated sharing
channel (PDSCH).
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 10
PLMN and Cell Selection: SIBn
The transmission period for SIBn
is a multiple of 80 ms. SIB2
contains radio resource–related
configuration. SIBs 3 to 5 contain
the cell reselection configuration
of the LTE system. SIBs 6 to 8
contain the reselection
configuration of the UTRA,
GERAN, and CDMA2000
systems. SIB 9 contains the HNB
configuration. SIB 10 contains the
primary earthquake and tsunami
warning system (ETWS)
notification, and SIB 11 contains
the secondary ETWS notification.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 11
PLMN and Cell Selection
SIB1 contains the public land mobile network (PLMN) table. The
access stratum (AS) of the UE transmits the resolved PLMN
table to the non-access stratum (NAS) of the UE. Then, the NAS
selects an appropriate PLMN.
After selecting a PLMN, the UE selects an appropriate cell of
the PLMN to camp on a cell with the strongest signal.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 12
Contents
Chapter 1 Network Access Signaling Procedure
1 Cell Searching
2 PLMN and Cell Selection
3 Attach
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 13
Attach: Attach
UE RRC connection Setup
eNB MME
Request
RRC connection Setup NAS message: :Attach
RRC connection Setup Complete Request, PDN
Initial UE message Connectivity Request
DL NAS Transfer
DL Information Transfer Authentication
UL Information Transfer UL NAS Transfer
DL Information Transfer DL NAS Transfer
UL Information Transfer NAS Encryption
UL NAS Transfer
Initial Context Setup Request NAS message: Attach
Security Mode Command
Radio Interface Accept, Active Default EPS
Security Mode Complete
Encryption Bearer Context Request
UE Capability Enquiry
UE Capability Information UE Capability Information
Indication
UE capability reporting
RRC connection Reconfiguration
RRC connection Reconfiguration NAS message: Attach
Complete Initial Context Setup Response
Complete, Active Default
UL Information Transfer
EPS Bearer Context
UL NAS Transfer
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 14
Attach: RRC Connection Setup
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 15
Attach: RRC Connection Setup Request
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 16
Attach: RRC Connection Setup
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 17
Attach: RRC Connection Setup Complete
The UL dedicated control channel (DCCH) carries the UE registration
information and NAS messages (Initial Direct Transfer messages).
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 18
Attach: Initial UE Message (I)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 19
Attach: Initial UE Message (II)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 20
Attach: DL/UL NAS/Information Transfer
Uu tracing
S1 tracing
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 21
Attach: Initial Context Setup Request (I)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 22
Attach: Initial Context Setup Request (II)
Message resolution
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 23
Attach: Initial Context Setup Request (III)
Message resolution (continued)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 24
Attach: RRC Security Mode Command/Complete
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 25
Attach: UE Capability Enquiry/Information
UE eNB
UE Capability Enquiry
UE Capability Infomation
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 26
Attach: RRC Connection Reconfiguration
Used to establish signaling radio bearer (SRB) 2 and data radio bearer
(DRB) 1.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 27
Attach: Initial UE Context Setup Response
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 28
Attach: Signaling over the Uu and S1 Interfaces
Signaling over the Uu interface
Signaling over the S1 interface
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 29
Attach: IMSI-Based Entire-Network Signaling Tracing (I)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 30
Attach: IMSI-Based Entire-Network Signaling
Tracing (II)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 31
Attach: IMSI-Based Entire-Network Signaling
Tracing (III)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 32
Contents
Chapter 2 Handover Signaling Procedure
1 Introduction to a Handover
2 Intra-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
3 Inter-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 33
Introduction to Handovers
Definition
A handover is implemented when a UE in the connected state
moves to a different cell to perform the UE context update.
Objective
Coverage-based handover: to achieve continuity of services for
a moving UE
Load-based handover: load-triggered handover; to ensure the
optimal performance of the whole system
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 34
Introduction to Handovers
Three types of handovers in the LTE system
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 35
Introduction to Handovers: LTE System
Handover is implemented in three phases: handover
measurement, handover decision, and handover execution.
In the handover measurement phase, the UE performs measurements
according to the measurement configuration delivered by the eNodeB
and reports measurement results to the eNodeB.
In the handover decision phase, the eNodeB checks the measurement
results reported by the UE and determines whether to initiate a handover.
In the handover execution phase, the eNodeB controls the procedure of
UE handover to the target cell based on the decision, to complete the
handover.
The whole handover procedure is performed based on UE-assisted
network control. The eNodeB delivers measurement configuration to
the UE, the UE reports the measurement results, and then the
eNodeB performs handover decision, resource preparation, handover
execution, and release of original resources.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 36
Introduction to Handovers: Measurement Control
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 37
Introduction to Handovers: Measurement Report
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 38
Introduction to Handovers: Handover Command
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 39
Contents
Chapter 2 Handover Signaling Procedure
1 Introduction to a Handover
2 Intra-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
3 Inter-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 40
Intra-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
Intra-eNodeB handover between cells is divided into
intra-frequency handover and inter-frequency handover.
In the handover, only resources on the Uu interface are updated.
The eNodeBs use internal messages to apply for and release
resources of the source cell and the target cell.
Inter-eNodeB data transfer is unnecessary, so are the random
access procedure of the UE and the signaling interaction with
the evolved packet core (EPC).
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 41
Intra-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
UE Source Cell Target Cell eNB MME/MMEs Serving Gateway
Area Restriction Provided
1. Measurement Control
packet data packet data packet data
UL allocation The UE reports the Legend
2. Measurement Reports Measurement Report L3 signalling
message in the source cell.
Handover Pre paration
Measurement Reports L1/L2 signalling
User Data
3. HO decision
Handover Command
DL allocation
4. Handover Command Buffer packets from The eNodeB delivers a Handover Command
MME
message after completing cell admission control
and radio resource allocation in the target cell.
Handover Execution
Detach from old cell and packet data
synchronize to new cell
5. Synchronization
The UE accesses the target cell.
6. UL allocation + TA for UE
7. Handover Confirm
After the handover is complete,
Handover Confirm
resources of the source cell are
released.
Handover Completion
Flush DL buffer, continue
delivering in transit packets
packet data packet data
packet data packet data
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 42
Intra-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
Uu tracing on the UE side
Uu tracing on the eNodeB side
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 43
Contents
Chapter 2 Handover Signaling Procedure
1 Introduction to a Handover
2 Intra-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
3 Inter-eNodeB Handover Between Cells
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 44
Inter-eNodeB Handover over the X2 Interface
If the target cell and source cell belong to two different eNodeBs
over two different X2 links, an inter-eNodeB handover needs to be
triggered over the X2 interface, and event A3 or A4 is reported.
The prerequisite is that the X2 relationship has been configured
between the two eNodeBs.
After receiving the measurement report from the UE and deciding a
UE handover to the target eNodeB, the source eNodeB applies to the
target eNodeB over the X2 interface for resources for the purpose of
resource preparation in the target cell, and then informs the UE to
trigger a handover to the target cell through the reconfiguration
message over the radio interface. After the handover is successful,
the target eNodeB informs the source eNodeB to release radio
resources of the source cell. In addition, the source eNodeB transfers
non-transmitted data to the target eNodeB and updates the node
relationship on the user plane and control plane.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 45
Inter-eNodeB Handover over the X2 Interface (I)
Handover preparation: The source eNodeB sends a
The UE has accessed to the cell and Handover Request message to the target eNodeB.
performs services. The Handover Request message contains the service
information and other access layer information
The source eNodeB delivers (encryption, integrity, and measurement information)
UE Source eNB Target eNB MME Serving Gateway
measurement control information of the current UE.
and notifies the UE of
neighboring-cell measurement. 0. Area Restriction Provided
1. Measurement Control
packet data packet data
The UE returns the
measurement report after The source eNodeB decides a Legend
UL allocation
detecting a cell that meets handover based on the handover L3 signalling
handover conditions. 2. Measurement Reports algorithm and current state.
L1/L2 signalling
3. HO decision
User Data
The source eNodeB sends the container delivered by 4. Handover Request
Handover Preparation
the target eNodeB to the UE through the radio
5. Admission Control
message to inform the UE to trigger a handover.
6. Handover Request Ack
DL allocation
Sequence number (SN) information is used to transfer the SN
7. Handover Command status and hyper frame number (HFN) information of the UE
from the source eNodeB to the target eNodeB for the purpose of
Detach from old cell
synchronize
and to new
Deliver buffered and in transit data retransmission and encryption integrity protection.
packets to target eNB
cell
Handover Execution
8. SN Status Transfer
The target eNodeB returns the admission Data forwarding. For details, see
result and radio resource configuration
Data Forwarding subsequent description in this
information to the source eNodeB, document.
Buffer packets from
completing the handover preparation. Source eNB
9. Synchronisation
10. UL allocation + TA for UE
After receiving the Handover Request message from
the source eNodeB, the target eNodeB performs
admission control based on the contained service
information and radio resource configuration.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 46
Inter-eNodeB Handover over the X2
Interface (II)
UE Source eNB Target eNB MME Serving Gateway
11. Handover Confirm
12. Path Switch Request 13.User Plane update
After the UE complete the random request
access procedure to access the target
eNodeB, the UE sends a Handover
Confirm message to the target eNodeB. End Marker
14.Switch DL path
Handover Completion
After receiving the Handover Confirm message 15.User Plane update
from the UE, the target eNodeB initiates a path
switch to the MME to complete the user data response
transmission. 16. Path Switch Request Ack
17.Release Resource After completing the user data transmission,
the MME sends a Path Switch Request Ack
Flush DL buffer,Contiue message.
delivering transmited
packets Data Forwarding
End Marker
After the path switch procedure, the target
18.Release eNodeB informs the source eNodeB to release
Resources
related resources, completing the whole
packet data handover procedure.
packet data
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 47
Signaling Procedure for the Inter-eNodeB Handover
over the X2 Interface (I)
Uu tracing on the UE side
Uu tracing on the source eNodeB side
X2 tracing on the source eNodeB side (same as X2 tracing on the target
eNodeB side)
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 48
Signaling Procedure for the Inter-eNodeB
Handover over the X2 Interface (II)
Uu tracing on the target eNodeB side
S1 tracing on the target eNodeB side
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 49
Inter-eNodeB Handover over the S1 Interface
Inter-eNodeB handover over the S1 interface is similar to that over
the X2 interface. The only difference lies in the fact that there is no
X2 link between two eNodeBs. If no X2 link is configured, an inter-
eNodeB handover is performed over the S1 interface. If X2 and S1
links are configured simultaneously, an inter-eNodeB handover is
preferentially performed over the X2 interface.
If a handover uses the S1 interface, the Handover Request and
Handover Acknowledge messages and data are transmitted over the
S1 interface.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 50
Inter-eNodeB Handover over the S1 Interface (I)
UE Source eNB Target eNB MME/MMEs Serving Gateway
Area Restriction Provided
1. Measurement Control The source eNodeB sends a Handover
Request message to the MME.
packet data The MME transfers the Handover packet data
UL allocation Request message to the corresponding Legend
2. Measurement Reports target eNodeB for handover preparation. L3 signalling
L1/L2 signalling
3. HO decision
User Data
4. Handover Reauired
5. Handover Request
After completing admission control and radio
Handover Preparation
resource configuration, the target eNodeB
returns a Handover Ack message to the MME. 7. Admission Control
7. Handover Request Acknologe
8. Handover Command
DL allocation Similar to the handover over the X2
9. Handover Command interface, the source target send the SN
information to the MME, which then
transfers the SN information to the
Detach from old cell and Deliver buffered and in
synchronize to new cell transit packets to target eNB target eNodeB.
Handover Execution
10. eNB SN Status Transfer
The MME transfers the Handover ACK 11. MME SN Status Transfer
message to the source eNodeB. Data Forwarding
Data Forwarding
Buffer packets from
MME
12. Synchronization
13. UL allocation + TA for UE
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 51
Inter-eNodeB Handover over the S1 Interface (II)
UE Source eNB Target eNB MME/MMEs Serving Gateway
14. Handover Confirm
The target eNodeB notifies the
MME of the handover completion.
The UE accesses the
Completion
target eNodeB.
15. Handover Notify
The MME notifies the source
eNodeB of resource release. packet data
Handover
16. UE Context Release Command
The source eNodeB returns a resource
release completion message.
16. UE Context Release Completed
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 52
Signaling Procedure for the Inter-eNodeB
Handover over the S1 Interface (I)
Uu tracing on the UE side
Uu tracing on the source eNodeB side
S1 tracing on the source eNodeB side
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 53
Signaling Procedure for the Inter-eNodeB
Handover over the S1 Interface (II)
Uu tracing on the target eNodeB side
S1 tracing on the target eNodeB side
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential
Page 54
Contents
Chapter 3 Paging Signaling Procedure
1 Introduction to Paging
2 Paging Signaling analysis
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 55
Introduction to Paging
Paging is triggered in the following three situations:
The UE is in the idle state and the network needs
to send data to the UE.
The network notifies the UE of an SIB update.
The network notifies the UE of an available ETWS
notification.
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 56
Introduction to the Paging Procedure (1)
The UE is in the idle state and the network needs to send data to
the UE.
UE eNB SAE
S1_Paging
RRC_Paging
RRC_CONN_REQ
RRC_CONN_SETUP
RRC_CONN_SETUP_CMP
S1AP_INITIAL_UE_MSG
RRC_SECUR_MODE_CMD S1AP_INITIAL_CONTEXT_SETUP_REQ
RRC_CONN_RECFG
RRC_SECUR_MODE_CMP
RRC_CONN_RECFG_CMP
S1AP_INITIAL_CONTEXT_SETUP_RSP
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 57
Introduction to the Paging Procedure (2)
The network notifies the UE of an SIB update or an ETWS
notification.
If a UE receives a paging message of SIB update, the UE must
resolve the SIB again and use the network configuration parameters
contained in newly received SIBs.
If the UE receives a paging message containing an ETWS notification,
the UE must resolve the SIB1 immediately. If the SIB1 contains the
SIB10 or SIB11 scheduling, the UE must resolve SIB10 or SIB11.
UE eNB SAE
S1_Paging
RRC_Paging
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 58
Summary
Processes of cell searching, PLMN selection, and cell selection
for a UE just powered on
UE attach procedure and different types of attach procedures
LTE handover procedure and several common handover types in
the LTE system
LTE paging procedure
3 to 5 key points upon the completion of this course
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD. Huawei Confidential Page 59
Thank you
www.huawei.com
Вам также может понравиться
- XCAL-M Operation Handbook (Smart) v1.1Документ12 страницXCAL-M Operation Handbook (Smart) v1.1ShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Accuver VoLTE Solutions Performance AnalysisДокумент34 страницыAccuver VoLTE Solutions Performance AnalysisShaXaib Akhtar100% (1)
- 2.1 GBA User Security Setting (USS) : 3GPP TSG SA WG3 Security - SA3#35 S3-040741 October 5-8, 2004 ST Paul's Bay, MaltaДокумент14 страниц2.1 GBA User Security Setting (USS) : 3GPP TSG SA WG3 Security - SA3#35 S3-040741 October 5-8, 2004 ST Paul's Bay, MaltaShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- ETSI TS 103 289-3: Technical SpecificationДокумент23 страницыETSI TS 103 289-3: Technical SpecificationShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Volte CallsetupДокумент121 страницаVolte CallsetupMenard Cruz80% (5)
- The Mobile Broad Band Stand Ard: Unifo RM Reso Urce Ident Ifier (URI) ListДокумент29 страницThe Mobile Broad Band Stand Ard: Unifo RM Reso Urce Ident Ifier (URI) ListShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Sector C RET ReportДокумент5 страницSector C RET ReportShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- LMPTДокумент2 страницыLMPTShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- 2600 Project - License Retrieval From Old CardДокумент5 страниц2600 Project - License Retrieval From Old CardShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Cell State CheckДокумент1 145 страницCell State CheckShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- FE SupportДокумент3 страницыFE SupportShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
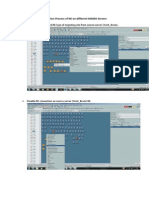
- Migration Process of NE On Different M2000 ServersДокумент2 страницыMigration Process of NE On Different M2000 ServersShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Maaz Idrees C.VДокумент2 страницыMaaz Idrees C.VShaXaib AkhtarОценок пока нет
- Flexi WCDMA BTS Quick GuideДокумент12 страницFlexi WCDMA BTS Quick GuideShaXaib Akhtar100% (5)
- RNW Overview PresentationДокумент35 страницRNW Overview PresentationMat RicsonОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- SV150 Doubletruck 042416Документ1 страницаSV150 Doubletruck 042416BayAreaNewsGroup100% (4)
- Sadia's RésuméДокумент1 страницаSadia's RésuméSadia TabassumОценок пока нет
- Synology Cloud Station White Paper-Based On DSM 6.0Документ28 страницSynology Cloud Station White Paper-Based On DSM 6.0marian_costache_2Оценок пока нет
- CRUISER User Manual V117Документ24 страницыCRUISER User Manual V117Arnold KleinhansОценок пока нет
- AA - Bot Creator AssessmentДокумент5 страницAA - Bot Creator Assessmentpraveen80% (5)
- Iot: Challenges and Issues in Indian Perspective: February 2018Документ6 страницIot: Challenges and Issues in Indian Perspective: February 2018fisa kiahsОценок пока нет
- 8th Sem Syllabus (CSIT) TUДокумент25 страниц8th Sem Syllabus (CSIT) TUkurtkesuОценок пока нет
- Trimble R4 Gnss System: Key FeaturesДокумент2 страницыTrimble R4 Gnss System: Key FeaturesAnonymous r8jDxNqMl0% (1)
- SIM7500 - SIM7600 Series - Jamming Detection - Application Note - V3.00Документ8 страницSIM7500 - SIM7600 Series - Jamming Detection - Application Note - V3.00AlbertoGonzálezОценок пока нет
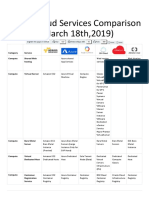
- AWS Vs Azure Vs Google Vs IBM Vs Oracle Vs Alibaba A Detailed ComparisonДокумент12 страницAWS Vs Azure Vs Google Vs IBM Vs Oracle Vs Alibaba A Detailed ComparisonRamboОценок пока нет
- Sever MonitoringДокумент355 страницSever Monitoringkvinoth22100% (2)
- Optical Technologies: An Important Enabler For Smart Systems and InfrastructuresДокумент8 страницOptical Technologies: An Important Enabler For Smart Systems and InfrastructuresFakhry Hario PОценок пока нет
- S5612 Switch: Product OverviewДокумент5 страницS5612 Switch: Product OverviewitОценок пока нет
- A Brief Discussion On Network DevicesДокумент24 страницыA Brief Discussion On Network Devicesarifeee2002Оценок пока нет
- DS-License Server RLM ManualДокумент61 страницаDS-License Server RLM Manualpedir_discoОценок пока нет
- How To - Synchronous Analog, Digital, and Encoder Measurements in LabVIEWДокумент5 страницHow To - Synchronous Analog, Digital, and Encoder Measurements in LabVIEWandi suntoroОценок пока нет
- Mechatrolink II Interface System:: Yaskawa's MECHATROLINK II For A High-End Digital Servo and I/O NetworkДокумент2 страницыMechatrolink II Interface System:: Yaskawa's MECHATROLINK II For A High-End Digital Servo and I/O NetworkshahОценок пока нет
- 9C. GSM - Roaming and SwitchingДокумент35 страниц9C. GSM - Roaming and SwitchingHồ ThôngОценок пока нет
- How To Configure The VPLS Multicast ServiceДокумент6 страницHow To Configure The VPLS Multicast ServiceElizabeth RichОценок пока нет
- GigaSPEED XL Solution BrochureДокумент20 страницGigaSPEED XL Solution BrochureAde SetiawanОценок пока нет
- Nat Practice LabДокумент1 страницаNat Practice LabaennekОценок пока нет
- NST Assignment 2010 NewДокумент8 страницNST Assignment 2010 NewsekharlОценок пока нет
- Configuring Satellite Transmission Over Abis InterfaceДокумент2 страницыConfiguring Satellite Transmission Over Abis InterfaceFlorentine AmattabriОценок пока нет
- Automatic Frequency CorrectionДокумент17 страницAutomatic Frequency CorrectionMuhammad Ahsan ChaudhryОценок пока нет
- Internet ArchitectureДокумент17 страницInternet ArchitectureNithilan AОценок пока нет
- RADWIN System DescriptionДокумент28 страницRADWIN System Descriptiontho2007100% (1)
- 12.00 Dang The Ngoc Free Space Optical Communication SystemsДокумент19 страниц12.00 Dang The Ngoc Free Space Optical Communication SystemsFrederick MccartyОценок пока нет
- Admin Free - Active Directory and Windows, Part 1 - Understanding Privileged Groups in AD - An Infrastructure Geek Floating in A Sea of UberCoders - Site Home - TechNet BlogsДокумент7 страницAdmin Free - Active Directory and Windows, Part 1 - Understanding Privileged Groups in AD - An Infrastructure Geek Floating in A Sea of UberCoders - Site Home - TechNet Blogsferro4uОценок пока нет
- 24-Substation Control and AutomationДокумент20 страниц24-Substation Control and AutomationSristick90% (10)
- Debug 1214Документ4 страницыDebug 1214Anne SiaОценок пока нет