Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Role of Local Govt in Development
Загружено:
Joy CabalhinАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Role of Local Govt in Development
Загружено:
Joy CabalhinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Republic of the Philippines
Commission on Higher Education
Samar State University
COLLEGE OF GRADUATE STUDIES
Catbalogan City, Samar
Tel. Nos. (055) 543-8394 / (055) 251-2139
Website: www.ssu.edu.ph
Course : Masters in Public Management
Course Code : PM 505
Subject : Local Government Management
Reporters : Tuazon, Michael Ian
Borinaga, Angelo
Rebato, Jebith
Romero, Ranier
Gabitanan, Oscar
Semester : 1st semester of S.Y. 2017-2018
Professor : Prof. A. Poblete
Topic : Role of Local Government in Development /
(The Management of Local Services)
______________________________________________________________________________
LOCAL GOVERNMENT OF LOCAL SERVICES
MANAGEMENT OF LOCAL SERVICES
It is improving quality of life in the LGU.
Its purpose is to attain a certain level of standards of efficiency,
congruency and sustainability in Local Management of Local
Services, a methodical tool must be applied where the following
Baseline or Urban Karte Indicators must be fully captured, assessed
and addressed.
Major Components of Local Services in LGU
1. Social Service
2. Economic Services
3. Political/Administrative(Governance)
4. Local Management of Local Services
- It means capturing, assessing and addressing the above
components.
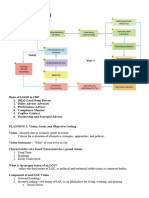
LOCAL DEVELOPMENT STRATEGY (LDS)
It is a Hybrid Process (Planning and Management Process)
It is when local people work together to achieve sustainable
economic growth that brings economic benefits and quality of life
improvements for the communities in the LGU.
Five (5) stages of Management in Local Services
1. Assessment (Where are we now?)
2. Develop Vision (Where do we want to be?)
3. Formulate Strategy (How do we get there?)
4. Prioritize Programs and Project (What actions need to be taken?)
5. Package-Implement-Review-Deepen
Local Government of Local Services
Page 1 of 4
Management of Context of LGU Local Services
Baseline Indicators:
SOCIAL SERVICES (LOCAL LIVABILITY) fit or suitable live in.
1. Basic Urban Services (Household Profile)
2. Healthful Environment
3. Safe Environment
4. Poverty
5. Amenity, Culture and Services
ECONOMIC SERVICES (LOCAL COMPETITIVENESS) Ability & Performance
1. Structure of Economic Activity
2. Human Resources
3. Availability of Technology
4. Market Accessibility
5. Support Services
6. Cost of Doing Business
POLITICAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE FUNCTIONS (GOVERNANCE)
1. Efficiency of Service Delivery
2. Transparency of LGU
3. Administrative Function
4. Bankability
PLANNING
LDS Process
- Is a tool for participatory planning
Participation
- It involves stakeholder in decision-making for the project and
allows them to partake in the opportunities it creates, they
should have also access to its immediate benefits and those it
produces.
Levels of Participation
- Information Sharing
- Consultation/Seeking Feedback (options/risks)
- Collaboration Joint decision making
- Empowerment/shared control- having the sense of ownership
or shared responsibility. (Legal power/authority)
FINANCING
The Capital Budget
- Is largely concerned with the creation of long term assets
(roads, pipes, schools and other services)
- It details the LGU long term capital improvements needs
Local Government of Local Services
Page 2 of 4
Components of Capital Budget
- Inventory of Capital Assets
- Developing of CIP
- Developing of Multi-year CIP
- Developing the Financial Plan (Sustainability)
- Process (Determine Financial Situation, Develop Financial
Goals, Identify alternative course of action, Evaluate
alternatives, Create & Implement Financial Action Plan,
reevaluate / revise the plan.
- Implementing the Capital Budget (Deals with big cost that
paid once to develop) e.g. construction of roads, buildings
etc.
Implementing the Capital Budget
The Multi-Year should include the following components (updated
annually)
1. All the relevant project/ investment cost details including
construction and financing cost.
2. The annual capital cost disbursement schedule including
direct construction payment but all principal/ interest
payments for debt financing; and
3. All the current account transfers including a separate
identification of costs to be transferred to the current
operating budget including; project design costs; future
operations and maintenance spending; and all feed and
interest charges required for successful project development.
Financial Analysis
- Central element of the capital budget and multi-year CIP
- Aimed at minimizing the financial effect of investment projects
on local budget, while maximizing the impact of the project
addressing the community’s needs(services)
Capital Budget Process
- Is a management tool for guiding the expenditures of public
resources over an extended period of time
- It represents commitment by the LGU to provide its community
with the desired and require level of service
- Sources and Utilization: 20% Development Plan (infra) and
Project Sector
IMPLEMENTATON
Capital Investment Plan (CIP) (detailed understanding of anticipated
investments into tangible capital assets, infrastructure, facilities, services,
installation needed.)
Decision used to undertake capital investment are motivated by several
criteria including:
- Degree of urgency of the project
- Benefits derived from the project
- Cost and financial impact of the project
- Acceptability to the local constituency
Local Government of Local Services
Page 3 of 4
- In developing the CIP, it is important to establish goals for the
level and quantity of service term of measurable indicators.
- The use of service goals as motivational instrument
underpinning/strengthening the investment plan enables
jurisdiction to determine whether infrastructure should be
replaced, upgraded, or extended.
- The development of multi-year investment plan usually begins
with inventory of existing assets and compares this inventory
and level of service provided to the jurisdiction desired service
goals.
- Benefits of Multi-year Horizon CIP.
1. Assisting the jurisdiction in programming scarce financial
resources
2. Allowing the jurisdiction the opportunity to select
alternative (cost effective) solutions.
3. Allowing the jurisdiction to engage in prudent borrowing
and other public debt policies.
Detailed Financial Analysis
- Is the most critical stage of CIP of the LGUs capacity and ability
to undertake the investment program.
EVALUATION
Methodology
- The Assessment System being used here in the LGPMS (Local
Government Performance Management System), this is Web
Based System (Customized Software)
LGPMS- the LGPMS is a self-assessment, management and development
tool that enables provincial, city and municipal governments to
determine their capabilities and limitations in the delivery of essential
public services.
Citizens Satisfaction Index System - the pipeline for integration into the
LGPMS and will enable local authorities to gauge customer views in
reach and quality of basic services. This will render the system citizens
centric
5 PERFORMANCE AREAS AND SERVICE AREAS OF LGMPS
1. GOVERNANCE – Local Legislations, Transparency and Participation.
2. ADMINISTRATION – Development Planning, Revenue Generation,
Resource Allocation and Utilities, Financial Accountability, Customer
Service and Human Resource.
3. SOCIAL SERVICES- Health and Nutrition, Education, Housing and Basic
Utilities, Peace, Security and Disaster Preparedness.
4. ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT – Agriculture, Fishing Development,
Business and Industry Promotion.
5. ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT – Natural Resources Management,
Solid Waste and Industry Pollution.
Local Government of Local Services
Page 4 of 4
Вам также может понравиться
- Tool Kit for Tax Administration Management Information SystemОт EverandTool Kit for Tax Administration Management Information SystemРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- LGU Competency Assessment Faci GuideДокумент11 страницLGU Competency Assessment Faci GuideFelicitas RelatoОценок пока нет
- Community Development Plan: (Summarize of CDP Chapter 1 - 2)Документ6 страницCommunity Development Plan: (Summarize of CDP Chapter 1 - 2)Dash AssxEzioОценок пока нет
- Approaches and Techniques in BudgetingДокумент8 страницApproaches and Techniques in Budgetinghijkayelmnop89% (9)
- State of Local Governance Report 2011Документ103 страницыState of Local Governance Report 2011Vincent Bautista100% (1)
- CDP Toolkit Book Second Revised 2012 As PrintingДокумент100 страницCDP Toolkit Book Second Revised 2012 As PrintingLiju MathewОценок пока нет
- Housing UrbanДокумент8 страницHousing UrbanHazel May Agagas EstrellaОценок пока нет
- Technical Proposal NUSP2 PROJECT: NEIGHBORHOOD UPGRADING AND SHELTER PROJECT - (PHASE 2)Документ13 страницTechnical Proposal NUSP2 PROJECT: NEIGHBORHOOD UPGRADING AND SHELTER PROJECT - (PHASE 2)Tiar Pandapotan PurbaОценок пока нет
- Planning For Asset Management in Urban Local Bodies - Hyderabad As A CaseДокумент13 страницPlanning For Asset Management in Urban Local Bodies - Hyderabad As A CaseRanjith ParvathapuramОценок пока нет
- Cip Update Fy 19 24 Final Copy - Wf.ffdfghtyuhj1234Документ145 страницCip Update Fy 19 24 Final Copy - Wf.ffdfghtyuhj1234someone elseОценок пока нет
- Terms of ReferenceДокумент8 страницTerms of ReferenceABUAMMAR60100% (1)
- IDAM Training MC Final - EmailДокумент56 страницIDAM Training MC Final - EmailMushtaq HussainОценок пока нет
- Government Expenditure Part 2Документ6 страницGovernment Expenditure Part 2Jeffrey RiveraОценок пока нет
- Newcastle Social Marketing Project Final Project ReportДокумент49 страницNewcastle Social Marketing Project Final Project Reportsadafkhan21Оценок пока нет
- Dilg Programs Per Sectoral OutcomeДокумент26 страницDilg Programs Per Sectoral OutcomeFender BoyangОценок пока нет
- Paper On Infrastructure Mangement A World Bank Perspective WДокумент16 страницPaper On Infrastructure Mangement A World Bank Perspective WCarl KirsteinОценок пока нет
- Sro I Guidance FinalДокумент16 страницSro I Guidance FinalSari ChimiОценок пока нет
- Effectiveness of The Public Financial Management Assessment Tool or (PFMAT) in Strengthening The Financial Capability of Local Government Unit in Talavera, Nueva EcijaДокумент10 страницEffectiveness of The Public Financial Management Assessment Tool or (PFMAT) in Strengthening The Financial Capability of Local Government Unit in Talavera, Nueva EcijaKomal sharmaОценок пока нет
- Capital Planning 2Документ87 страницCapital Planning 2kudasanyahОценок пока нет
- Local Development Investment Program, CY 2012 To 2014Документ61 страницаLocal Development Investment Program, CY 2012 To 2014Lgu Leganes100% (21)
- DL MGT 241Документ12 страницDL MGT 241Joshua AbogaОценок пока нет
- Key Technical Areas For: Developing Infrastructure ServicesДокумент56 страницKey Technical Areas For: Developing Infrastructure Servicesrajesh0005Оценок пока нет
- PUBLIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Intro To Public Sector Budgeting and Accounting 1 1Документ72 страницыPUBLIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Intro To Public Sector Budgeting and Accounting 1 1JS ManaguelodОценок пока нет
- Gingee PDFДокумент163 страницыGingee PDFvenkat_060Оценок пока нет
- Municipal Guide To Community Action Planning 2011Документ24 страницыMunicipal Guide To Community Action Planning 2011Adrian ManlangitОценок пока нет
- SatturДокумент180 страницSatturjoearunrajaОценок пока нет
- Public Finance Reviewer 1&2Документ5 страницPublic Finance Reviewer 1&2Rona Faith TanduyanОценок пока нет
- Rural Development Projects ReviewДокумент5 страницRural Development Projects Reviewmuhammad-arslan-3245Оценок пока нет
- e-CAT OrientationДокумент24 страницыe-CAT OrientationGreggy Roy Marquez100% (1)
- MPV's PaperДокумент12 страницMPV's PaperTHIMMAIAH BAYAVANDA CHINNAPPAОценок пока нет
- DILG Technical Assistance Project For Local Resource Institutes On The Utilization of CSIS Results For CY 2022Документ16 страницDILG Technical Assistance Project For Local Resource Institutes On The Utilization of CSIS Results For CY 2022Marie Holgado CarununganОценок пока нет
- MRD 103 emДокумент9 страницMRD 103 emRajni KumariОценок пока нет
- 8 JARIOL - REACTION PAPER - Budgeting and Management of FinancesДокумент3 страницы8 JARIOL - REACTION PAPER - Budgeting and Management of FinancesLorraine JariolОценок пока нет
- Local Development Systems Team Leader-ToR - 0Документ4 страницыLocal Development Systems Team Leader-ToR - 0waleedОценок пока нет
- 92438-Municipal - Growth - Readiness - Checklist - Final - July - 2015 2Документ13 страниц92438-Municipal - Growth - Readiness - Checklist - Final - July - 2015 2MerdzОценок пока нет
- ESSA Vol1 Analysis May 25Документ38 страницESSA Vol1 Analysis May 25amyfaustОценок пока нет
- Synthesis of Comprehensive Land Use Plan Guidelines 1Документ5 страницSynthesis of Comprehensive Land Use Plan Guidelines 1Jho Harry ForcadasОценок пока нет
- Moduel 2 ReviewerДокумент18 страницModuel 2 ReviewerKarl Anne DomingoОценок пока нет
- Legal Instruments & Guiding Frameworks For Planners: A ReportДокумент7 страницLegal Instruments & Guiding Frameworks For Planners: A ReportbarkhabaharОценок пока нет
- Infra MGMTДокумент12 страницInfra MGMTTHIMMAIAH BAYAVANDA CHINNAPPAОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 Government Agencies NewДокумент22 страницыChapter 5 Government Agencies NewCt Nurfatimah Hussen100% (1)
- Program Development ProcessДокумент37 страницProgram Development ProcessLeah NarneОценок пока нет
- LECTURE 07 Comprehensive Development PlanДокумент30 страницLECTURE 07 Comprehensive Development PlanTJ BungayОценок пока нет
- SAMF OverviewДокумент16 страницSAMF OverviewDedi Pramono100% (1)
- Practitioners GuideДокумент385 страницPractitioners GuideAlex GabrielОценок пока нет
- Katpadi Smart CityДокумент164 страницыKatpadi Smart CityushaОценок пока нет
- Victoria - CDP - Final Draft - Dec.22.21Документ122 страницыVictoria - CDP - Final Draft - Dec.22.21Jeffrey LoraОценок пока нет
- BM 404 Project Management ModuleДокумент52 страницыBM 404 Project Management ModuleLinos TichazorwaОценок пока нет
- Unit 5 Development Programs For MSMEs by NEDAДокумент11 страницUnit 5 Development Programs For MSMEs by NEDARena Mae BalmesОценок пока нет
- Tenkasi City PlanДокумент191 страницаTenkasi City PlanChenthur GardenОценок пока нет
- Project Life CycleДокумент11 страницProject Life CycleWahab Ahmad KhanОценок пока нет
- Financial Management 1Документ18 страницFinancial Management 1Richard mugashoОценок пока нет
- Boditi NDP2 Pate SiteДокумент43 страницыBoditi NDP2 Pate Sitetemesgen100% (1)
- Term PaperДокумент11 страницTerm PaperAiresh TungalОценок пока нет
- Road Asset Management - DILGSession1Intro - DavaoДокумент78 страницRoad Asset Management - DILGSession1Intro - DavaoJeaneth Dela Pena CarnicerОценок пока нет
- SengottaiДокумент189 страницSengottaisennirajeshОценок пока нет
- DEVOLUTION-The Transfer of Power and Authority From The National Government To LocalДокумент2 страницыDEVOLUTION-The Transfer of Power and Authority From The National Government To LocalillaОценок пока нет
- Capacity Building Programs For Philippine Local Special BodiesДокумент33 страницыCapacity Building Programs For Philippine Local Special BodiesChe AquinoОценок пока нет
- Change Management Plan: Toronto Police ServiceДокумент16 страницChange Management Plan: Toronto Police ServicecastillojayОценок пока нет
- Asset Management 2001: Australian Procurement & Construction Council IncДокумент29 страницAsset Management 2001: Australian Procurement & Construction Council IncShahab HosseinianОценок пока нет
- Logistics Project ReportДокумент67 страницLogistics Project ReportJadeja Hiralba0% (1)
- Slides - MGMT90032 Week 04-2Документ19 страницSlides - MGMT90032 Week 04-2Sam ChawlaОценок пока нет
- Perpetual Inventory System Journal EntriesДокумент1 страницаPerpetual Inventory System Journal EntriesJasmeen KhanОценок пока нет
- OML6 - Supply Chain ManagementДокумент34 страницыOML6 - Supply Chain ManagementBENZINОценок пока нет
- Rizwan Ul Hassan O and A Level Accounting 0322-7222240Документ28 страницRizwan Ul Hassan O and A Level Accounting 0322-7222240rizwan ul hassanОценок пока нет
- Performance Measures in Supply Chain Management: Zikrul Mcips PMPДокумент45 страницPerformance Measures in Supply Chain Management: Zikrul Mcips PMPMd Zikrul IslamОценок пока нет
- Bos 54380 CP 6Документ198 страницBos 54380 CP 6Sourabh YadavОценок пока нет
- Degree Thesis of Zobayer Hosen - A Business Plan For Establishing A Bangladeshi Restaurant in FinlandДокумент59 страницDegree Thesis of Zobayer Hosen - A Business Plan For Establishing A Bangladeshi Restaurant in FinlandAhmed Al MasudОценок пока нет
- SCM Summaries Karthik Sai DhanduДокумент9 страницSCM Summaries Karthik Sai DhanduKarthik SaiОценок пока нет
- Quiz No. 1 Part 3 Multiple Choice Problems Attempt ReviewДокумент1 страницаQuiz No. 1 Part 3 Multiple Choice Problems Attempt ReviewEly RiveraОценок пока нет
- Case - BarillaДокумент3 страницыCase - BarillaPrabhjot SinghОценок пока нет
- BCom Third Year AssignmentsДокумент2 страницыBCom Third Year AssignmentsRamesh0% (4)
- Working Capital ManagementДокумент71 страницаWorking Capital ManagementNaveen Kumar Rudrangi100% (1)
- Answer: Problem 10-4: Requirement AДокумент17 страницAnswer: Problem 10-4: Requirement APatricia Nicole BarriosОценок пока нет
- Mrk202 Final Test Spring 2021 RevisedДокумент16 страницMrk202 Final Test Spring 2021 RevisedHancox MwendaОценок пока нет
- Akif AliДокумент2 страницыAkif AliAkif AliОценок пока нет
- Retail Hardware Store Business PlanДокумент13 страницRetail Hardware Store Business PlanIsaac Hassan50% (2)
- DaimlerChrysler and GM Organization Technology and Business.Документ6 страницDaimlerChrysler and GM Organization Technology and Business.arbhian rizqqoОценок пока нет
- Chopra Scm5 Ch01 GeДокумент33 страницыChopra Scm5 Ch01 GeJAVIER ENRIQUE MU„OZ QUIROZОценок пока нет
- BuggetДокумент45 страницBuggetTrexie De Vera JaymeОценок пока нет
- Asian Paints Chain Reaction CaseДокумент8 страницAsian Paints Chain Reaction CaseHardik KshatriyaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 HRMДокумент28 страницChapter 4 HRMJatin MandhyanОценок пока нет
- Week8 MG320 Supply Chain ManagementДокумент55 страницWeek8 MG320 Supply Chain ManagementAbdul Hanan NasirОценок пока нет
- Channels of DistributionДокумент31 страницаChannels of DistributionBavly MakramОценок пока нет
- TB Ch03Документ67 страницTB Ch03CG100% (1)
- Cost Accounting Problems 7 & 8 de LeonДокумент26 страницCost Accounting Problems 7 & 8 de LeonPrinceОценок пока нет
- Managerial AccountingДокумент11 страницManagerial AccountingKalyan MukkamulaОценок пока нет
- Solution On Estimation of Working CapitalДокумент5 страницSolution On Estimation of Working Capitaljeta_prakash100% (2)
- Test Bank 3 - Ia 1Документ25 страницTest Bank 3 - Ia 1JEFFERSON CUTE100% (1)
- Case Study On Dell's Supply ChainДокумент6 страницCase Study On Dell's Supply ChainVaibhav SinghОценок пока нет
- The Black Girl's Guide to Financial Freedom: Build Wealth, Retire Early, and Live the Life of Your DreamsОт EverandThe Black Girl's Guide to Financial Freedom: Build Wealth, Retire Early, and Live the Life of Your DreamsОценок пока нет
- You Need a Budget: The Proven System for Breaking the Paycheck-to-Paycheck Cycle, Getting Out of Debt, and Living the Life You WantОт EverandYou Need a Budget: The Proven System for Breaking the Paycheck-to-Paycheck Cycle, Getting Out of Debt, and Living the Life You WantРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (104)
- Budget Management for Beginners: Proven Strategies to Revamp Business & Personal Finance Habits. Stop Living Paycheck to Paycheck, Get Out of Debt, and Save Money for Financial Freedom.От EverandBudget Management for Beginners: Proven Strategies to Revamp Business & Personal Finance Habits. Stop Living Paycheck to Paycheck, Get Out of Debt, and Save Money for Financial Freedom.Рейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (89)
- Financial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassОт EverandFinancial Literacy for All: Disrupting Struggle, Advancing Financial Freedom, and Building a New American Middle ClassОценок пока нет
- CDL Study Guide 2022-2023: Everything You Need to Pass Your Exam with Flying Colors on the First Try. Theory, Q&A, Explanations + 13 Interactive TestsОт EverandCDL Study Guide 2022-2023: Everything You Need to Pass Your Exam with Flying Colors on the First Try. Theory, Q&A, Explanations + 13 Interactive TestsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- How To Budget And Manage Your Money In 7 Simple StepsОт EverandHow To Budget And Manage Your Money In 7 Simple StepsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (4)
- Personal Finance for Beginners - A Simple Guide to Take Control of Your Financial SituationОт EverandPersonal Finance for Beginners - A Simple Guide to Take Control of Your Financial SituationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- How to Pay Zero Taxes, 2020-2021: Your Guide to Every Tax Break the IRS AllowsОт EverandHow to Pay Zero Taxes, 2020-2021: Your Guide to Every Tax Break the IRS AllowsОценок пока нет
- CAPITAL: Vol. 1-3: Complete Edition - Including The Communist Manifesto, Wage-Labour and Capital, & Wages, Price and ProfitОт EverandCAPITAL: Vol. 1-3: Complete Edition - Including The Communist Manifesto, Wage-Labour and Capital, & Wages, Price and ProfitРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Swot analysis in 4 steps: How to use the SWOT matrix to make a difference in career and businessОт EverandSwot analysis in 4 steps: How to use the SWOT matrix to make a difference in career and businessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (4)
- The Best Team Wins: The New Science of High PerformanceОт EverandThe Best Team Wins: The New Science of High PerformanceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (31)
- The Financial Planning Puzzle: Fitting Your Pieces Together to Create Financial FreedomОт EverandThe Financial Planning Puzzle: Fitting Your Pieces Together to Create Financial FreedomРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (2)
- The 30-Day Money Cleanse: Take Control of Your Finances, Manage Your Spending, and De-Stress Your Money for Good (Personal Finance and Budgeting Self-Help Book)От EverandThe 30-Day Money Cleanse: Take Control of Your Finances, Manage Your Spending, and De-Stress Your Money for Good (Personal Finance and Budgeting Self-Help Book)Рейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (9)
- Basic Python in Finance: How to Implement Financial Trading Strategies and Analysis using PythonОт EverandBasic Python in Finance: How to Implement Financial Trading Strategies and Analysis using PythonРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (9)
- The Money Mentor: How to Pay Off Your Mortgage in as Little as 7 Years Without Becoming a HermitОт EverandThe Money Mentor: How to Pay Off Your Mortgage in as Little as 7 Years Without Becoming a HermitОценок пока нет
- Budgeting: The Ultimate Guide for Getting Your Finances TogetherОт EverandBudgeting: The Ultimate Guide for Getting Your Finances TogetherРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (14)
- Rich Nurse Poor Nurses: The Critical Stuff Nursing School Forgot To Teach YouОт EverandRich Nurse Poor Nurses: The Critical Stuff Nursing School Forgot To Teach YouРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Debt Freedom: A Realistic Guide On How To Eliminate Debt, Including Credit Card Debt ForeverОт EverandDebt Freedom: A Realistic Guide On How To Eliminate Debt, Including Credit Card Debt ForeverРейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (2)
- Money Made Easy: How to Budget, Pay Off Debt, and Save MoneyОт EverandMoney Made Easy: How to Budget, Pay Off Debt, and Save MoneyРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Radically Simple Accounting: A Way Out of the Dark and Into the ProfitОт EverandRadically Simple Accounting: A Way Out of the Dark and Into the ProfitРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (9)
- Inflation Hacking: Inflation Investing Techniques to Benefit from High InflationОт EverandInflation Hacking: Inflation Investing Techniques to Benefit from High InflationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)