Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
5 Scalp
Загружено:
drpnnreddyОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
5 Scalp
Загружено:
drpnnreddyАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
HUMAN ANATOMY 93
Gross Anatomy
SCALP
Soft tissues covering cranial vault
EXTENT
Lateral: temporal lines
Anterior: eyebrows-superior orbital margins
Posterior: superior nuchal line
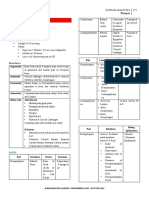
Layers Contents Applied anatomy
S: Thin skin with sweat and sebaceous glands Sebaceous cysts
Skin
C: Thin layer of fat and fibrous tissue in form of Injury blood vessels walls non-
(dense) Connective locules with blood vessels and nerves (with its collapsible severe bleeding,
tissue walls attached to its fibrous walls) inflammation very painful
A: Aponeurosis is membranous, tendon of fleshly Injury (horizontal) leads to gapping of
Aponeurosis/ bellies of epicranial muscle (formed by wound by contraction of fronto-occipitalis
Gálea aponeurótica occipitalis and frontalis muscles, each with
two bellies)
L: Layer provides an easy plane of separation "Danger Zone" because of the ease by
Loose areolar between the upper three layers and the which infectious agents can spread
connective tissue Pericranium through it to emissary veins which then
drain into the cranium.
It contains the major blood vessels of the
scalp.
Safety-valve hematoma-fracture of the
skull with tear of dura, signs of cerebral
compression do not develop until this
space is filled with blood.
P: Pericranium Periosteum of the skull bones Cephalohaematoma / traumatic
(continuous with endocranium at sutural cephalohydrocele - takes shape of related
lines) bone
BLOOD SUPPLY
Location Arteries Branches of
Supratrochlear Artery
INTERNAL CAROTID
Anterior to auricle Supraorbital Artery
Superficial Temporal Artery
Posterior Auricular Artery EXTERNAL CAROTID
Posterior to auricle
Occipital Artery
© BRIHASPATHI ACADEMY ׀SUBSCRIBER’S COPY ׀NOT FOR SALE
HUMAN ANATOMY 94
Gross Anatomy
VENOUS DRAINAGE
Location Veins Drain into
Supratrochlear vein Join to form Angular vein, continue as Facial vein; join
with anterior division of Retromandibular vein
Supraorbital common facial vein Internal jugular vein
Anterior to auricle
Superficial Temporal Join with maxillary vein, forms Retromandibular vein
Join with posterior division of Retromandibular vein
Posterior Auricular
External jugular vein Sub clavian vein
Posterior to auricle
Occipital Joins Sub-occipital venous plexus
NERVE SUPPLY - "Z-GLASS"
Location Nature Nerves Branches of
Supratrochlear
Ophthalmic division of the Trigeminal nerve
Supraorbital
Anterior to Sensory
auricle Zygomatico temporal Maxillary division of the Trigeminal nerve
Auriculo temporal Mandibular division of the Trigeminal nerve
Motor Temporal Facial nerve
Greater Auricular C2, C3-Cervical Plexus
Lesser occipital C2 -Cervical Plexus
Posterior to Sensory
auricle Greater occipital C2-Cervical Plexus
Third occipital C3-Cervical Plexus
Motor Posterior auricular Facial
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE
Anterior to Auricle: Pre-auricular/Superficial parotid node
Posterior to Auricle: Post auricular/Mastoid and Occipital nodes
*****
© BRIHASPATHI ACADEMY ׀SUBSCRIBER’S COPY ׀NOT FOR SALE
HUMAN ANATOMY 93
Gross Anatomy
1. Most of the movement of scalp occurs D. Deep cervical
between
A. Skin and subcutaneous tissue Ref: Gray’s Anatomy 39/e, p. 512
B. Subcutaneous tissue and galea
1. Following are the sensory nerve for scalp
aponeurotica
except;
C. Galea aponeurotica and periosteum
A. Supratrochlear
D. Periosteum and bone.
B. Supraorbital
C. Greater occipital
D. Suboccipital
2. The wounds of the scalp bleed
continuously because
Ref: Gray’s Anatomy 39/e, p.513
A. Scalp is highly vascular
B. Blood vessels lie just beneath the skin 1. Which layer of the scalp is known as the
C. Wounds gape dangerous layer of the scalp
D. Vessesls wall falls to retract A. Skin
B. Aponeurosis
C. Loose areolar tissue
3. Collection of fluid deep to the sponeurotic D. Pericranium
layer of th scalp can extend into the
A. Back of the neck Ref: Essentials of Human Anatomy, A.K
B. Check below the nygomatic arch. Datta vol 2, Head and Neck, p.67
C. eyelids
D. lower part of the nose. 2. Which out of the following nerve does not
supply the scalp
1. The superficial fasica in the scalp is; A. Auriculotemporal
A. More loose and irregular in the center B. Zygmaticotemporal
B. More fibrous and dense in the center C. Infratrochlear
C. More fibrous and dense in the periphery D. Greater occipital
D. None of the above
Ref: Gray’s Anatomy 39/e, p .512-513
Ref: Gray’s Anatomy 39/e, p. 578
2. The frontal belly of occipito-frontalis is
supplied by;
A. Temporal branch of facial nerve
B. Zygomatic branch of facial nerve
C. Posterior auricular branch of facial nerve
D. Frontal nerve
Ref: Gray’s Anatomy 39/e, p. 500
3. The anterior part of the scalp drains into the
following;
A. Jugulo-digastric
B. Jugulo-omohyoid
C. Parotid
© BRIHASPATHI ACADEMY ׀SUBSCRIBER’S COPY ׀NOT FOR SALE
Вам также может понравиться
- Channel List 20210427Документ13 страницChannel List 20210427drpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- ChikatikiVeyikallu by KommuriДокумент69 страницChikatikiVeyikallu by Kommurikannan_govinda160% (5)
- 1MBBS 2019-SchemeДокумент1 страница1MBBS 2019-SchemedrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Te-Econom Line: The Economical Solution For Direct RestorativeДокумент4 страницыTe-Econom Line: The Economical Solution For Direct RestorativedrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITДокумент5 страницPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Picture Based MCQ Case 1Документ1 страницаPicture Based MCQ Case 1drpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Restorative Materials, or Auxiliary Materials.: 1. Preventive Dental Materials Include Pit and FissureДокумент5 страницRestorative Materials, or Auxiliary Materials.: 1. Preventive Dental Materials Include Pit and Fissurecdfg ghjyОценок пока нет
- 9.allergic and Immunologic DiseasesДокумент20 страниц9.allergic and Immunologic DiseasesdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Restorative Materials, or Auxiliary Materials.: 1. Preventive Dental Materials Include Pit and FissureДокумент5 страницRestorative Materials, or Auxiliary Materials.: 1. Preventive Dental Materials Include Pit and Fissurecdfg ghjyОценок пока нет
- Case BasedДокумент3 страницыCase BaseddrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Cons & Endo 1: Operative DentistryДокумент1 страницаCons & Endo 1: Operative DentistrydrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Clinical Denture SessionsДокумент2 страницыClinical Denture SessionsdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- 1.principles of Oral SurgeryДокумент13 страниц1.principles of Oral SurgerydrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Indices: Ideal Requisites of IndexДокумент9 страницIndices: Ideal Requisites of IndexdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- 1 Forensoc Dentistry History Advance DevelopmentsДокумент5 страниц1 Forensoc Dentistry History Advance DevelopmentsdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Osteology Corrected 08 July 2019Документ50 страницOsteology Corrected 08 July 2019drpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Oral Histology - NEET MDSДокумент6 страницOral Histology - NEET MDSdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Endomax-F: Multi-Directional, Reciprocating & Continuous Rotation Cordless EndomotorДокумент2 страницыEndomax-F: Multi-Directional, Reciprocating & Continuous Rotation Cordless EndomotordrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Oral Pathology - NEET MDSДокумент8 страницOral Pathology - NEET MDSdrpnnreddy100% (2)
- General Pathology: Case Based McqsДокумент7 страницGeneral Pathology: Case Based McqsdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Brihaspathi ProspectusДокумент12 страницBrihaspathi ProspectusdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- General Oral HealthДокумент44 страницыGeneral Oral HealthdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- General Pathology: Case Based McqsДокумент7 страницGeneral Pathology: Case Based McqsdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Sec. 1 Chapter 1Документ10 страницSec. 1 Chapter 1drpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of CarbohydratesДокумент57 страницChemistry of Carbohydratesdrpnnreddy100% (1)
- Armamentariumforbasicoralsurgery 130729131703 Phpapp01Документ140 страницArmamentariumforbasicoralsurgery 130729131703 Phpapp01drpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Comedk DentalallotmentdetailsДокумент79 страницComedk DentalallotmentdetailsdrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Business Model TemplateДокумент5 страницBusiness Model TemplatedrpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Aiims Nov 2015Документ9 страницAiims Nov 2015drpnnreddyОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Decriptive Anatomical Terminology Body PlanesДокумент2 страницыDecriptive Anatomical Terminology Body Planesskyler andrada100% (1)
- BSДокумент6 страницBSBeda MalecdanОценок пока нет
- Range of Motion Procedure Checklist-1Документ2 страницыRange of Motion Procedure Checklist-1api-288919673100% (2)
- Transhumeral Amputation Levels and Prosthetic ComponentsДокумент8 страницTranshumeral Amputation Levels and Prosthetic Componentsمحمد عدلي عدلانОценок пока нет
- Warm-Up & Stretch Ex For SwimmersДокумент18 страницWarm-Up & Stretch Ex For SwimmerskirancshetОценок пока нет
- Tendon Transfers: Doug Humphreys Division of Plastic Surgery Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova ScotiaДокумент48 страницTendon Transfers: Doug Humphreys Division of Plastic Surgery Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova ScotiatomasurizarОценок пока нет
- Atlas of Approaches in Neurosurgery - J.FischerДокумент7 страницAtlas of Approaches in Neurosurgery - J.FischerZdravko HeinrichОценок пока нет
- Cat MusclesДокумент8 страницCat MusclesPattyОценок пока нет
- Pilates For KyphosisДокумент13 страницPilates For KyphosisAnonymous NKGMQv9Оценок пока нет
- Deep Neck InfectionДокумент46 страницDeep Neck InfectionVicky SankaranОценок пока нет
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory System.Документ3 страницыParts and Functions of Respiratory System.Alvin Patrick Colobong AsisОценок пока нет
- Nervous SystemДокумент2 страницыNervous SystemShanel Aubrey AglibutОценок пока нет
- Area Inspection Palpation Auscultation Percussion: Physical AssessmentДокумент6 страницArea Inspection Palpation Auscultation Percussion: Physical AssessmentKris TejereroОценок пока нет
- Dental Terminology GuideДокумент4 страницыDental Terminology GuideBrbr LndsyОценок пока нет
- Syllabus SCSIДокумент92 страницыSyllabus SCSIDcStrokerehab100% (1)
- Anatomy Revision Slides PDFДокумент133 страницыAnatomy Revision Slides PDFAbhijit0% (1)
- CHOKE! With PicturesДокумент28 страницCHOKE! With PictureslojixОценок пока нет
- MCQs For Netters Head and Neck Anatomy For DentistryДокумент211 страницMCQs For Netters Head and Neck Anatomy For DentistryDR. ISHITA SINGHAL88% (8)
- Muscles and MovementДокумент4 страницыMuscles and MovementmcgarrigleОценок пока нет
- Esthetics and Smile Characteristics From The Layperson's PerspectiveДокумент10 страницEsthetics and Smile Characteristics From The Layperson's PerspectivegeraldineОценок пока нет
- Example: Computed Radiology Exposure Guide: Anatomical Exam KVP SID Grid Small Medium Large Region Medium MASДокумент1 страницаExample: Computed Radiology Exposure Guide: Anatomical Exam KVP SID Grid Small Medium Large Region Medium MASevaОценок пока нет
- Musculos ParaproteticosДокумент63 страницыMusculos Paraproteticosestefania100% (2)
- Breathing ExercisesДокумент3 страницыBreathing ExercisesCelia Steiman100% (3)
- Yogaasana Yic 2Документ154 страницыYogaasana Yic 2denim2servОценок пока нет
- Somatic Anatomy - Muscles and The Postural FluteДокумент6 страницSomatic Anatomy - Muscles and The Postural Fluteshivnair100% (6)
- Radiographic Anatomy of VertebraeДокумент32 страницыRadiographic Anatomy of VertebraeRienaAbrahamsОценок пока нет
- Facelift Anatomy GuideДокумент22 страницыFacelift Anatomy Guidehansmaloo100% (1)
- Joints Movement Powerpoint PDFДокумент21 страницаJoints Movement Powerpoint PDFDean Albert Arnejo100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Spine: Cervical (Neck) - The Main Function of The CervicalДокумент5 страницAnatomy of The Spine: Cervical (Neck) - The Main Function of The Cervicalid_pandianОценок пока нет
- ALBERTA INFANT MOTOR SCALE RECORDДокумент6 страницALBERTA INFANT MOTOR SCALE RECORDGUSTAVOОценок пока нет