Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Animal Tissue (Bio)
Загружено:
Cy VillafuerteАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Animal Tissue (Bio)
Загружено:
Cy VillafuerteАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
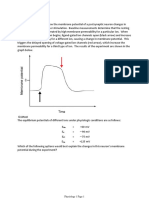
TYPES OF ANIMAL TISSUES
Epithelial Tissue— this type of tissue is commonly seen outside the body as coverings or as linings of organs and
cavities. Epithelial tissues are characterized by closely-joined cells with tight junctions (i.e., a type of cell modification).
Being tightly packed, tight junctions serve as barriers for pathogens, mechanical injuries, and fluid loss.
Cells that make up epithelial tissues can have distinct arrangements:
• Cuboidal—for secretion
• Simple columnar—brick-shaped cells; for secretion and active absorption
• Simple squamous—plate-like cells; for exchange of material through diffusion
• stratified squamous—multilayered and regenerates quickly; for protection
• pseudo-stratified columnar—single layer of cells; may just look stacked because of varying height; for lining of
respiratory tract; usually lined with cilia (i.e., a type of cell modification that sweeps the mucus).
Connective tissue- supports, connects or separates other tissues or organs of the body as the name suggests.
Loose Connective tissue - These tissues have cells and fibres that are loosely arranged in a semi-fluid ground
substance.
Areolar tissue - It is present beneath the skin, it serves as a framework support for epithelium.
Adipose tissue - This type of tissues is specialized to store fats.
Dense Connective tissue - Fibres and fibroblasts are packed compactly in dense connective tissue. Tendons are
dense regular tissue that attach skeletal muscle to bones and ligaments attach bone to another bones. Collagen is the
dense irregular tissue present in the skin.
Blood —made up of plasma (i.e., liquid extracellular matrix); contains water, salts, and dissolved proteins; erythrocytes
that carry oxygen (RBC), leukocytes for defense (WBC), and platelets for blood clotting.
Connective tissue proper (ctp)—made up of loose connective tissue that is found in the skin and fibrous connective
tissue that is made up of collagenous fibers found in tendons and ligaments. Adipose tissues are also examples of
loose connective tissues that store fats which functions to insulate the body and store energy.
Cartilage —characterized by collagenous fibers embedded in chondroitin sulfate. Chondrocytes are the cells that
secrete collagen and chondroitin sulfate. Cartilage functions as cushion between bones.
Bone —mineralized connective tissue made by bone-forming cells called osteoblasts which deposit collagen. The
matrix of collagen is combined with calcium, magnesium, and phosphate ions to make the bone hard. Blood vessels
and nerves are found at a central canal surrounded by concentric circles of osteons.
Muscle Tissue—these tissues are composed of long cells called muscle fibers that allow the body to move voluntary
or involuntary. Movement of muscles is a response to signals coming from nerve cells. In vertebrates, these muscles
can be categorized into the following:
• Skeletal—striated; voluntary movements
• Cardiac—striated with intercalated disk for synchronized heart contraction; involuntary
• Smooth—not striated; involuntary
Nervous Tissue—these tissues are composed of nerve cells called neurons and glial cells that function as support
cells. These neurons sense stimuli and transmit electrical signals throughout the animal body. Neurons connect to
other neurons to send signals. The dendrite is the part of the neuron that receives impulses from other neurons while
the axon is the part where the impulse is transmitted to other neurons.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- A Prospective On Vagal Tone Via Auricular Stimulation and Deep BreathingДокумент12 страницA Prospective On Vagal Tone Via Auricular Stimulation and Deep BreathingHerald Scholarly Open AccessОценок пока нет
- The Increase of Serum BCL 2 ConcentrationДокумент7 страницThe Increase of Serum BCL 2 ConcentrationAlvian VianОценок пока нет
- Asam BasaДокумент22 страницыAsam BasaHariningtyas Dian RОценок пока нет
- Case Analysis: Pre-OperativeДокумент12 страницCase Analysis: Pre-OperativeMaria ThereseОценок пока нет
- Kami Export - Hamad Alsayer - Gizmo Circulatory System PDFДокумент4 страницыKami Export - Hamad Alsayer - Gizmo Circulatory System PDFbratlyОценок пока нет
- Hope 1 - Q1 - M2Документ12 страницHope 1 - Q1 - M2Bragskada OfficialОценок пока нет
- PEH G7 1st PT 17-18Документ7 страницPEH G7 1st PT 17-18ERICSON DE GUZMANОценок пока нет
- Nursing care plan for cardiomyopathyДокумент7 страницNursing care plan for cardiomyopathyKym RonquilloОценок пока нет
- Seizures NCLEX ReviewДокумент12 страницSeizures NCLEX ReviewVincent Paul PagulayanОценок пока нет
- EcgДокумент18 страницEcgmyla adapОценок пока нет
- The Nervous System: Sensory PhysiologyДокумент6 страницThe Nervous System: Sensory Physiologyanon100% (1)
- COPD Case Study: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseДокумент15 страницCOPD Case Study: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseasecrabby_chicОценок пока нет
- Neuromorphic Engineering: From Biological To Spike Based Hardware Nervous SystemsДокумент33 страницыNeuromorphic Engineering: From Biological To Spike Based Hardware Nervous SystemsSruthy sureshОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - VenipunctureДокумент14 страницChapter 5 - VenipunctureHrvojeОценок пока нет
- L11 - Practice Q - HBДокумент4 страницыL11 - Practice Q - HBEvan YEUNG [09N12]Оценок пока нет
- Abdminal Compartment SyndromeДокумент9 страницAbdminal Compartment SyndromeRafael BagusОценок пока нет
- ECG Categories and AnalysisДокумент99 страницECG Categories and AnalysisDivyansh Jain100% (1)
- Questions ExplanationДокумент17 страницQuestions ExplanationnomintmОценок пока нет
- Afms-3b (Yer 2003) AmeДокумент17 страницAfms-3b (Yer 2003) AmeHimashree GiduguОценок пока нет
- Heart and blood vessels explained in detailДокумент15 страницHeart and blood vessels explained in detailIDKОценок пока нет
- SECTION 1 CHAPTER 1 Vital Signs MeasurementДокумент15 страницSECTION 1 CHAPTER 1 Vital Signs MeasurementRhea Andrea UyОценок пока нет
- Biomarkeri U ACSy III DeoДокумент5 страницBiomarkeri U ACSy III DeodejОценок пока нет
- 5 - Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias DoneДокумент79 страниц5 - Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias Doneclaimstudent3515Оценок пока нет
- BIOS5130 Week 10 Lecture Part 1 SlidesДокумент37 страницBIOS5130 Week 10 Lecture Part 1 SlidesOkikiola JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Dipiro 9th MCQДокумент380 страницDipiro 9th MCQHaymanot AnimutОценок пока нет
- Trauma Injury Management ABCДокумент2 страницыTrauma Injury Management ABCJyl Yan SelasorОценок пока нет
- Orofacial Soft Tissue Injury and Wound HealingДокумент38 страницOrofacial Soft Tissue Injury and Wound HealingSabbir HossainОценок пока нет
- Electrical BurnsДокумент27 страницElectrical BurnsGautam KalraОценок пока нет
- NEWS2 Chart 3 - NEWS Observation Chart - 0 PDFДокумент1 страницаNEWS2 Chart 3 - NEWS Observation Chart - 0 PDFcicaklomenОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 5 Review QuestionsДокумент9 страницBiology Unit 5 Review QuestionsMoa ArmyОценок пока нет