Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Problem Set M Guide Questions For Midterm Exams
Загружено:
Ian Jimbo ConstantinoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Problem Set M Guide Questions For Midterm Exams
Загружено:
Ian Jimbo ConstantinoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
COLLEGE OF
ENGINEERING
FEEDBACK AND CONTROL SYSTEMS (FCONSYM)
GUIDE QUESTIONS FOR MIDTERM EXAMS
General Instructions: Copy and answer each item, writing your explanation and/or solutions right after the
question. Mark your final answers. Write neatly and legibly. DO NOT PLAGIARIZE; plagiarized work will be
dealt with accordingly.
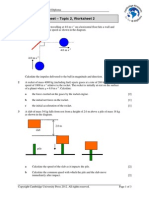
1. Pressure regulator. A cutaway view of a commonly used pressure
regulator is shown at the right. The desired pressure is set by turning a
calibrated screw. This compresses the spring and sets up a force that
opposes the upward motion of the diaphragm. The bottom side of the
diaphragm is exposed to the water pressure that is to be controlled. Thus,
the motion of the diaphragm is an indication of the pressure difference
between the desired and the actual pressures. It acts like a comparator.
The valve is connected to the diaphragm and moves according to the
pressure difference until it reaches a position in which the difference is
zero. Sketch a block diagram showing the control system with the output
pressure.
2. Inverted pendulum. Consider the inverted pendulum shown in the figure at
the right. Sketch the block diagram of a feedback control system using this
figure as the model. Identify the process, sensor, actuator and controller. The
objective is to keep the pendulum in the upright position, that is to keep 𝜃 =
0, in the presence of disturbances.
3. System model. A system is represented by the differential equation
𝑑4 𝑐 𝑑3 𝑐 𝑑2 𝑐 𝑑𝑐 𝑑2 𝑟 𝑑𝑟
+ 7 + 11 + 65 + 123𝑐 = + 21 + 16𝑟
𝑑𝑡 4 𝑑𝑡 3 𝑑𝑡 2 𝑑𝑡 𝑑𝑡 2 𝑑𝑡
Assuming zero initial conditions, find the transfer function 𝐺 (𝑠) = 𝐶 (𝑠)/𝑅(𝑠) and draw a block diagram
representing the input-process-output relationship of this system.
4. Response of laser printer positioning system. A laser printer uses a laser beam to print copy rapidly
for a computer. The laser is positioned by a control input 𝑟(𝑡), so that
4(𝑠 + 50)
𝑌(𝑠) = 2 ⋅ 𝑅(𝑠)
𝑠 + 30𝑠 + 200
The input 𝑟(𝑡) represents the desired position of the laser beam. If 𝑟(𝑡) is a unit step input, find the output
𝑦(𝑡).
5. Transfer function of passive electrical network. Find the transfer
function 𝐺 (𝑠) = 𝑉𝑜 (𝑠)/𝑉(𝑠) for the electrical network shown at the right.
Feedback and Control Systems (FCONSYM) / 2017 – 2018 / Term 2 Page 1 of 2
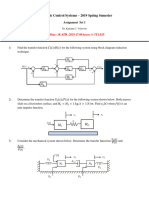
6. Bridged-T network. A bridged-T network is often used is AC control system
as a filter network. The circuit of one bridged-T network is shown at the right.
Find the transfer function 𝑉𝑜 (𝑠)/𝑉𝑖𝑛 (𝑠) when 𝑅1 = 0.5 Ω, 𝑅2 = 1 Ω and
𝐶 = 0.5 F.
7. Lead-lag filter. The circuit shown at the right is called a lead-lag filter.
Determine 𝑉2 (𝑠)/𝑉1 (𝑠) when 𝑅1 = 100 kΩ, 𝑅2 = 200 kΩ, 𝐶1 = 1 uF
and 𝐶2 = 0.1 uF.
8. Cascaded op-amp circuit. Determine the transfer
function 𝑉𝑜 (𝑠)/𝑉(𝑠) for the op-am circuit shown if 𝑅1 =
167 kΩ, 𝑅2 = 240 kΩ, 𝑅3 = 1 kΩ, 𝑅4 = 100 kΩ and 𝐶 =
1 uF. Assume an ideal op-amp.
9. Transfer function of translational
mechanical system. For the system whose
diagram is shown at the right, find the transfer
function 𝐺 (𝑠) = 𝑋1 (𝑠)/𝐹(𝑠).
10. Transfer function of rotational mechanical
system. Determine 𝐺(𝑠) = 𝜃1 (𝑠)/𝑇(𝑠) for the
rotational mechanical system shown at the
right.
==========END OF PROBLEM SET==========
Feedback and Control Systems (FCONSYM) / 2017 – 2018 / Term 2 Page 2 of 2
Вам также может понравиться
- Exam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Документ7 страницExam 3 Material Science MATS 2001 UMN Fall 2012Zaki Smn100% (1)
- Objectives ThermodynamicsДокумент5 страницObjectives ThermodynamicsM.ThirunavukkarasuОценок пока нет
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Документ73 страницыIBO 2010 Korea Theory Paper 2Bikash Ranjan RayОценок пока нет
- Ce001 Quiz 2cДокумент2 страницыCe001 Quiz 2cBee-Anne Bautista FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Photosynthesis Light Reaction ATP Formation Electron Transport Cytochromes ChloroplastsДокумент4 страницыPhotosynthesis Light Reaction ATP Formation Electron Transport Cytochromes ChloroplastsFarooq AliОценок пока нет
- Extra Momentum Transfer QuestionsДокумент5 страницExtra Momentum Transfer QuestionsaОценок пока нет
- Sri Lankan Biology Olympiad 2008Документ5 страницSri Lankan Biology Olympiad 2008Science Olympiad BlogОценок пока нет
- CH 21Документ45 страницCH 21JayelleОценок пока нет
- S4 Aceiteka 2017 Agriculture P2Документ7 страницS4 Aceiteka 2017 Agriculture P2Eremu Thomas100% (1)
- Momentum Transfer Take Home Quiz: Name: Date: Year / Section: ScoreДокумент1 страницаMomentum Transfer Take Home Quiz: Name: Date: Year / Section: ScoreRobert DelfinОценок пока нет
- Files2 BiologyDocuments Biology of CottonДокумент50 страницFiles2 BiologyDocuments Biology of CottonanamikashikhaОценок пока нет
- SPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionДокумент14 страницSPH4U 1.6 - Relative MotionMatthew GreesonОценок пока нет
- Mesl Set 1Документ8 страницMesl Set 1RENE JOSHUA PECASOОценок пока нет
- NQE 2007 Biology SolutionsДокумент2 страницыNQE 2007 Biology SolutionsmartynapetОценок пока нет
- Thermo 1 & 2Документ4 страницыThermo 1 & 2Oloj YuОценок пока нет
- 12th Physics Additional Questions (Vol 1)Документ135 страниц12th Physics Additional Questions (Vol 1)Ashok Pradhan50% (2)
- Topic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisДокумент12 страницTopic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisCedric Williams100% (1)
- Chemistry Units 3 and 4 Practice Questions GuideДокумент51 страницаChemistry Units 3 and 4 Practice Questions GuideElmo Bluey100% (1)
- Laplace Transform Good RevisionДокумент20 страницLaplace Transform Good RevisionraymondushrayОценок пока нет
- PMC Practice Test Questions of Heat & ThermodynamicsДокумент25 страницPMC Practice Test Questions of Heat & ThermodynamicsAb Hadi100% (1)
- Some Study Questions For USABOДокумент32 страницыSome Study Questions For USABORay Sanchez100% (1)
- Measuring Pressure and Temperature with a Steam BoilerДокумент8 страницMeasuring Pressure and Temperature with a Steam BoilerKram YnarОценок пока нет
- 9781292035444Документ7 страниц9781292035444Bwn Jangyeswar KumarОценок пока нет
- IBO 2010 Korea Theory Answers 2Документ30 страницIBO 2010 Korea Theory Answers 2martynapetОценок пока нет
- Pre Board Math B PDFДокумент6 страницPre Board Math B PDFAnjoe Mhar NocheОценок пока нет
- Applications of Laplace Transform Unit Step Functions and Dirac Delta FunctionsДокумент8 страницApplications of Laplace Transform Unit Step Functions and Dirac Delta FunctionsJASH MATHEWОценок пока нет
- 1999 AP Biology TestДокумент25 страниц1999 AP Biology TestTalal NabulsiОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Question BankДокумент3 страницыHeat Transfer Question BankkarthikОценок пока нет
- DAT 2008 Math1Документ3 страницыDAT 2008 Math1Arnelson DerechoОценок пока нет
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis RevisedДокумент60 страницNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis Revisedemanuel coatesОценок пока нет
- Phys 253 Thermal PhysicsДокумент1 019 страницPhys 253 Thermal Physicsdavid_berardo6537Оценок пока нет
- Electrochemistry 494 PDFДокумент55 страницElectrochemistry 494 PDFHarsh SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Equilibrium Post LabДокумент53 страницыChemical Equilibrium Post LabJimilyn Michelle HofeleñaОценок пока нет
- ChE426 HW Additional ProblemsДокумент1 страницаChE426 HW Additional ProblemsShixia XuОценок пока нет
- Food TestsДокумент13 страницFood TestsBilal Shahid100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Kingdom Animalia MCQs PDF Class 11Документ11 страницChapter 10 Kingdom Animalia MCQs PDF Class 11Rahi HabibОценок пока нет
- ME495 Lab - Plate Heat Exchanger - Expt Number 5Документ5 страницME495 Lab - Plate Heat Exchanger - Expt Number 5Kammy LaiОценок пока нет
- Experiment P06: To Show That The Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide Is A First Order ReactionДокумент4 страницыExperiment P06: To Show That The Decomposition of Hydrogen Peroxide Is A First Order ReactionMohd Hafiz Aiman100% (1)
- Stefan Boltzmann Law PDFДокумент3 страницыStefan Boltzmann Law PDFESAKKIMALA SОценок пока нет
- Titration ExerciseДокумент2 страницыTitration ExerciseYemima KurniaОценок пока нет
- Biology NCERT Class 6-12 compilation for UPSC CSE PrelimsДокумент292 страницыBiology NCERT Class 6-12 compilation for UPSC CSE PrelimsSyed100% (1)
- Physics XII / Chapter 1 (HEAT) With KeyДокумент5 страницPhysics XII / Chapter 1 (HEAT) With KeyShujat AbroОценок пока нет
- Diffusion ExamplesДокумент63 страницыDiffusion ExamplesNeelesh TanwarОценок пока нет
- Topic 7Документ6 страницTopic 7Bert ManОценок пока нет
- IB Physics 2 Assess WSE2Документ3 страницыIB Physics 2 Assess WSE2Abhijeet GawandeОценок пока нет
- Polyurethane ChemistryДокумент15 страницPolyurethane Chemistryyoga nayagi punichelvana100% (1)
- Sample Problems in BouyancyДокумент2 страницыSample Problems in BouyancyJohn AgbayaniОценок пока нет
- Bio 101-Exam2KeyДокумент10 страницBio 101-Exam2KeyRobbie GroveОценок пока нет
- Physical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsДокумент2 страницыPhysical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsJerome SadudaquilОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Chapter 3Документ45 страницHeat Transfer Chapter 3Gregory Simmon100% (1)
- TribunaloLo Ex#6Документ14 страницTribunaloLo Ex#6Jaylou OpondaОценок пока нет
- British Biology Olympiad 2004: Part A QuestionsДокумент22 страницыBritish Biology Olympiad 2004: Part A QuestionsMalvina YuanОценок пока нет
- MATLAB Code For Bisection MethodДокумент1 страницаMATLAB Code For Bisection MethodZia JanОценок пока нет
- UNIFAC - Smith, VanNess, Abbott PDFДокумент7 страницUNIFAC - Smith, VanNess, Abbott PDFAlejandra InsuastyОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 2 E7Документ41 страницаThermodynamics 2 E7taya699Оценок пока нет
- Usabo2012 Open ExamДокумент11 страницUsabo2012 Open ExamsiderabioОценок пока нет
- acs_2017s2_assn1Документ5 страницacs_2017s2_assn1MiraelОценок пока нет
- Control system labДокумент15 страницControl system labhassan ullah khanОценок пока нет
- CS Two MarksДокумент7 страницCS Two MarkssivaeinfoОценок пока нет
- acs_2019s1_assn1Документ5 страницacs_2019s1_assn1MiraelОценок пока нет
- R134a Flow Patterns in Small Diameter TubesДокумент8 страницR134a Flow Patterns in Small Diameter TubesIan Jimbo ConstantinoОценок пока нет
- Thinking Out Loud - LTR - Not PDFДокумент5 страницThinking Out Loud - LTR - Not PDFTerence BundelaОценок пока нет
- PsychrometryДокумент17 страницPsychrometryChirag GoyalОценок пока нет
- It Might Be You - LTR - NotДокумент4 страницыIt Might Be You - LTR - NotIan Jimbo ConstantinoОценок пока нет
- Non-Renewable Fuels Environmental Impact: EGEE 102 - Energy Conservation and Environmental ProtectionДокумент40 страницNon-Renewable Fuels Environmental Impact: EGEE 102 - Energy Conservation and Environmental ProtectionIan Jimbo ConstantinoОценок пока нет
- School-Writing Budget of WorkДокумент6 страницSchool-Writing Budget of WorkIan Jimbo ConstantinoОценок пока нет
- Hanna Hi - 2211 - 2210Документ4 страницыHanna Hi - 2211 - 2210Ian Jimbo ConstantinoОценок пока нет
- Problem 115Документ4 страницыProblem 115Ian Jimbo Constantino100% (2)
- Strength of Materials 4th Edition by Pytel and SingerДокумент5 страницStrength of Materials 4th Edition by Pytel and SingerIan Jimbo Constantino82% (11)
- Test Format Light & WaveДокумент7 страницTest Format Light & WaveDewan Olin ChotepadaeОценок пока нет
- Understanding Ball LensesДокумент3 страницыUnderstanding Ball Lensesbraulio.dantas-1Оценок пока нет
- Procal CEMSДокумент4 страницыProcal CEMSIklanОценок пока нет
- 915nm 976nm 10W Fiber Coupled Module Oclaro-1416083626Документ5 страниц915nm 976nm 10W Fiber Coupled Module Oclaro-1416083626thuyОценок пока нет
- Andrew Db983h65e-M PDFДокумент1 страницаAndrew Db983h65e-M PDFjorgeОценок пока нет
- Acoustic Emission Testing and Thermographic TestingДокумент45 страницAcoustic Emission Testing and Thermographic TestingShivam GaurОценок пока нет
- Phototransistor QSE113Документ4 страницыPhototransistor QSE113Jeffo LeoОценок пока нет
- Manufacturing Engineer Laser Optical in Portland OR San Jose CA Resume John LafrentzДокумент2 страницыManufacturing Engineer Laser Optical in Portland OR San Jose CA Resume John LafrentzJohnLafrentzОценок пока нет
- Steven Greer - CE5-CSETI - 06. Additional Equipment - DescriptionДокумент4 страницыSteven Greer - CE5-CSETI - 06. Additional Equipment - DescriptionExopolitika Magyarország100% (1)
- Corus Steel - Stock Range & SpecificationsДокумент53 страницыCorus Steel - Stock Range & SpecificationsseanfsmythОценок пока нет
- Wood Densification and Thermal Modification: Hardness, Set-Recovery and MicromorphologyДокумент12 страницWood Densification and Thermal Modification: Hardness, Set-Recovery and MicromorphologyyonОценок пока нет
- Office Machine Cours OutilneДокумент2 страницыOffice Machine Cours Outilneኮኾብ ጽባሕОценок пока нет
- Determination of Benzene in Gasoline by Astm D6277 With Spectrum TwoДокумент3 страницыDetermination of Benzene in Gasoline by Astm D6277 With Spectrum TwoSerhiyОценок пока нет
- Ultrahigh Strain and Piezoelectric Behavior in Relaxor Based Ferroelectric Single CrystalsДокумент9 страницUltrahigh Strain and Piezoelectric Behavior in Relaxor Based Ferroelectric Single CrystalsgeansoОценок пока нет
- Fire Detection and Alarm SystemДокумент76 страницFire Detection and Alarm SystemShambhu Saran Singh100% (4)
- Ultrasonic Machining (USM) : Dr. Harlal Singh MaliДокумент11 страницUltrasonic Machining (USM) : Dr. Harlal Singh MaliPrashant Singh SankhalaОценок пока нет
- A278955818 - 25375 - 27 - 2019 - Historical Development of Remote SensingДокумент39 страницA278955818 - 25375 - 27 - 2019 - Historical Development of Remote SensingRohit SheemarОценок пока нет
- Ec1011 Television Video EngineeringДокумент21 страницаEc1011 Television Video Engineeringyesyouareesh100% (3)
- Quality Assurance - Schwarz 2015Документ66 страницQuality Assurance - Schwarz 2015Moud Sakly100% (1)
- Bend 4Документ2 страницыBend 4siva_sankar826481Оценок пока нет
- Differences Between Optical and Ultrasonic Electrolyte Analyzer Bubble DetectorsДокумент3 страницыDifferences Between Optical and Ultrasonic Electrolyte Analyzer Bubble DetectorsAbdalrhman FarajОценок пока нет
- Spray Cooling Masters ThesisДокумент151 страницаSpray Cooling Masters ThesisDr. Brian GlassmanОценок пока нет
- Optokon PM 212 enДокумент23 страницыOptokon PM 212 enGeorge MasonОценок пока нет
- Hot Air Plastic Welding For PolyethyleneДокумент24 страницыHot Air Plastic Welding For PolyethyleneAkshay rajanОценок пока нет
- SFP 550e3 PDFДокумент2 страницыSFP 550e3 PDFanoushes1Оценок пока нет
- Laser guidance system for orthopedic surgeryДокумент18 страницLaser guidance system for orthopedic surgerymohadeseОценок пока нет
- M Schemes 33Документ3 страницыM Schemes 33Dhanushka Bandara33% (6)
- Application Instructions - LaserFlexДокумент2 страницыApplication Instructions - LaserFlexFreddy YorroОценок пока нет
- TM 750 116Документ78 страницTM 750 1161Y875Оценок пока нет
- Basic Introduction of Fabrication Flow NewДокумент191 страницаBasic Introduction of Fabrication Flow NewSoojinthiran AhtmanathanОценок пока нет