Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Multiple Regression
Загружено:
rikar jehadunАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Multiple Regression
Загружено:
rikar jehadunАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Multiple Regression (Assignment 5)
An English teacher was interested in investigating the relationship between motivation,
interest, learning style and students’ learning achievement. He was interested in exploring how
well motivation, interest, and learning style are able to predict students’ learning outcome.
Further, he was also interested in examining which of these (motivation, interest, and learning
style) is the best predictor of learning achievement.
The teacher used the following hypothesis in his research:
H1 : motivation has influence on students’ learning achievement
H2 : interest has influence on students’ learning achievement
H3 : learning style has influence on students’ learning achievement
H4 : motivation, interest, and learning style simultaneously have influence on students’ learning
achievement.
After conducting several tests, the following data were obtained.
No Participants Motivation Interest Learning style Learning achievement
1 AB 75 75 60 80
2 BC 60 70 75 75
3 CD 65 70 70 75
4 DE 75 80 75 90
5 EF 65 75 80 85
6 GH 80 80 65 85
7 IJ 75 85 60 95
8 KL 80 88 70 95
9 MN 65 75 70 80
10 OP 80 75 75 90
11 RS 60 65 75 75
12 TU 65 70 80 75
13 VW 70 70 75 80
14 XY 65 80 75 85
15 ZA 80 90 70 80
16 BC 70 80 60 90
17 DE 65 70 70 95
18 FG 65 75 75 80
19 HI 80 90 75 85
20 JK 70 85 80 80
After data were analyzed using SPSS software, the following results were yielded.
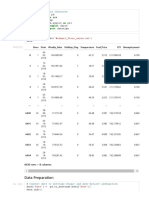
Variables Entered/Removedb
Model Variables Entered Variables Removed Method
1
Learnng Style,
. Enter
Interest, Motivationa
a. All requested variables entered.
b. Dependent Variable: Learning Achievement
Model Summary
Change Statistics
Mode Adjusted R Std. Error of the R Square
l R R Square Square Estimate Change F Change df1 df2 Sig. F Change
1 .564a .318 .190 6.171 .318 2.490 3 16 .097
a. Predictors: (Constant), Learnng Style, Interest,
Motivation
ANOVAb
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 284.430 3 94.810 2.490 .097a
Residual 609.320 16 38.082
Total 893.750 19
a. Predictors: (Constant), Learning Style, Interest, Motivation
b. Dependent Variable: Learning Achievement
Coefficientsa
Standardized
Unstandardized Coefficients Coefficients
Model B Std. Error Beta t Sig.
1 (Constant) 68.504 26.858 2.551 .021
Motivation .255 .313 .262 .817 .426
Interest .201 .288 .215 .698 .495
Learning Style -.255 .239 -.236 -1.069 .301
a. Dependent Variable: Learning Achievement
Source: Analysis results using SPSS Version 16, June 5, 2018
Data interpretation
An English teacher included twenty participants in a research aimed at exploring the
relationship between motivation, interest, learning style and students’ learning achievement. In
his research, the teacher utilized multiple regression. According to Pallant (2010), multiple
regression is used to explore the relationship between one continuous dependent variable and a
number of independent variables or predictors (usually continuous). There are three independent
variables in the research, namely motivation, interest, and learning style. Meanwhile, learning
achievement is considered as continuous dependent variable.
After analyzing the data using SPSS software, the finding of the research are as follows.
In the coefficients section, it revealed that the Sig. value of predictor motivation is .42.
The value is higher than .05 (Sig. value > .05). It shows that motivation does not influence
students’ learning achievement. It can be concluded that H1 was rejected. Similarly, the Sig.
values of predictors interest and learning style are .49 and 0.30 respectively. Similar to
motivation, these two variables do not have influence on students’ learning outcome. The results
indicated that H2 and H3 were rejected. Finally, in the ANOVA section, the output shows that
the Sig. value of regression is .09. The value is higher than .05 (Sig. value > .05). This result
indicates that the predictors: motivation, interest, and learning style simultaneously do not have
influence on students’ learning achievement. It can be inferred that H4 was also rejected.
Reference
Pallant, J. (2010). SPSS Survival Manual 4th Edition. England: Mc Graw Hill.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Efl Analysis, Design, Practices Designing A Lesson PlanДокумент4 страницыEfl Analysis, Design, Practices Designing A Lesson Planrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Assignment 7 Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыAssignment 7 Lesson Planrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Worksheet 7 - Lesson Plan EFL Analysis Design Practice - Luh Putu Rany PrihastutiДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 7 - Lesson Plan EFL Analysis Design Practice - Luh Putu Rany Prihastutirikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Worksheet 7 - Lesson Plan EFL Analysis Design Practice - Luh Putu Rany PrihastutiДокумент4 страницыWorksheet 7 - Lesson Plan EFL Analysis Design Practice - Luh Putu Rany Prihastutirikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Lesson Plan Muhammad Mersandy WirajayaДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan Muhammad Mersandy Wirajayarikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Assignment 7 Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыAssignment 7 Lesson Planrikar jehadun100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Lesson Plan: Name/NIM: Rikardus JehadunДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan: Name/NIM: Rikardus Jehadunrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan MuhammadДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan Muhammadrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Lesson Plan Muhammad Mersandy WirajayaДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan Muhammad Mersandy Wirajayarikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Assignment 7 Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыAssignment 7 Lesson Planrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Lesson Plan Muhammad Mersandy WirajayaДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan Muhammad Mersandy Wirajayarikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Behaviorism: A. Rationale For The EmergenceДокумент5 страницBehaviorism: A. Rationale For The Emergencerikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- An Example of UK Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыAn Example of UK Lesson Planrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- An Example of UK Lesson PlanДокумент3 страницыAn Example of UK Lesson Planrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Simple Correlation Analysis: MidtermДокумент3 страницыSimple Correlation Analysis: Midtermrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Causal Associative (Assignment 3) : Hypothesis For Equality of VariancesДокумент4 страницыCausal Associative (Assignment 3) : Hypothesis For Equality of Variancesrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Simple Correlation Analysis: MidtermДокумент3 страницыSimple Correlation Analysis: Midtermrikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Assignment 1 Descriptive Statistics A. DataДокумент3 страницыAssignment 1 Descriptive Statistics A. Datarikar jehadunОценок пока нет
- Bidding Strategy Using Friedman Model For Building ConstructionДокумент7 страницBidding Strategy Using Friedman Model For Building ConstructionDebasish DeyОценок пока нет
- Chapter Two: Simple Linear Regression Models: Assumptions and EstimationДокумент34 страницыChapter Two: Simple Linear Regression Models: Assumptions and Estimationeferem100% (2)
- Lecture 4Документ17 страницLecture 4Eda UstaogluОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Random Systematic ErrorДокумент1 страницаRandom Systematic ErrorrkblsistemОценок пока нет
- Not For Sale: Quantitative MethodsДокумент90 страницNot For Sale: Quantitative MethodsJayvee ValdepeñaОценок пока нет
- Gretl Empirical Exercise 2 - KEY PDFДокумент3 страницыGretl Empirical Exercise 2 - KEY PDFDaniel Lee Eisenberg JacobsОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Effect of Liquidity, Leverage, Profitability, and Firm Size On The Bond Rating of Banking Sub Sector in Indonesia Stock Exchange 2014 - 2018Документ5 страницThe Effect of Liquidity, Leverage, Profitability, and Firm Size On The Bond Rating of Banking Sub Sector in Indonesia Stock Exchange 2014 - 2018International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Gulf Case Study SolnДокумент9 страницGulf Case Study SolnHarsh SОценок пока нет
- Retail Analysis WalmartДокумент18 страницRetail Analysis WalmartNavin MathadОценок пока нет
- Pesaran 2007Документ48 страницPesaran 2007Seydou OumarouОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- Nama: Matriapsi Yoel Talan Nim: 20180303036 Tugas Pertemuan 13 BiostatistikДокумент14 страницNama: Matriapsi Yoel Talan Nim: 20180303036 Tugas Pertemuan 13 Biostatistikyan kify mohiОценок пока нет
- Data Analysis and Modeling Bcis New CourseДокумент2 страницыData Analysis and Modeling Bcis New CourseSpandan KcОценок пока нет
- Rules For Working On AMOS: Rule No.1:: Analysis of Moment Structure (Amos)Документ18 страницRules For Working On AMOS: Rule No.1:: Analysis of Moment Structure (Amos)Rjendra LamsalОценок пока нет
- Econ 4400 Wpaperfinal 2Документ11 страницEcon 4400 Wpaperfinal 2Gerald GutweinОценок пока нет
- Deloitte Valuing Wind Farm Assets Global 2014Документ24 страницыDeloitte Valuing Wind Farm Assets Global 2014Wilson Pepe GonzalezОценок пока нет
- A Study of Religiousness and OrganizatioДокумент20 страницA Study of Religiousness and OrganizatioDorin TriffОценок пока нет
- Chap 5 AssignmentДокумент10 страницChap 5 AssignmentGenevieve Anne BongcasanОценок пока нет
- 2024 Tutorial 12Документ7 страниц2024 Tutorial 12hathutrang742003Оценок пока нет
- Regression Results MGT 646-2Документ6 страницRegression Results MGT 646-2AMIRUL RAJA ROSMANОценок пока нет
- Capstone Project VivekДокумент145 страницCapstone Project VivekRemyaRS100% (4)
- Unit Root TestsДокумент71 страницаUnit Root Testsanon_754483162Оценок пока нет
- 2010-10-05 010234 Amount Spent Per Week On RecreationДокумент8 страниц2010-10-05 010234 Amount Spent Per Week On RecreationEraj Rehan0% (1)
- Hipotesis 1Документ21 страницаHipotesis 1AkhmadSyukraОценок пока нет
- SPSS Independent Samples T TestДокумент72 страницыSPSS Independent Samples T TestJeffer MwangiОценок пока нет
- Globalization and Industrialization in 64 Developing Countries, 1980-2003Документ36 страницGlobalization and Industrialization in 64 Developing Countries, 1980-2003api-321241380Оценок пока нет
- Natural Factors Affecting Crop Production in India EditДокумент35 страницNatural Factors Affecting Crop Production in India EditprankushОценок пока нет
- Glmcourse 002Документ55 страницGlmcourse 002Ben HarveyОценок пока нет
- A Time Series Analysis of Structural Break Time inДокумент6 страницA Time Series Analysis of Structural Break Time inCristina CОценок пока нет
- SPE 67616 PllAllДокумент13 страницSPE 67616 PllAllJulo DesmazuresОценок пока нет