Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hvac
Загружено:
Jon West0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
3 просмотров1 страницаHvac
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документHvac
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
3 просмотров1 страницаHvac
Загружено:
Jon WestHvac
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC)[1] is the technology of indoor and
vehicular environmental comfort. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and
acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical
engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics and heat
transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation, as HVAC&R
or HVACR or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-
rated circuit breakers).
HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes,
apartment buildings, hotels and senior living facilities, medium to large
industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals, on ships and
submarines, and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions
are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fresh air from
outdoors.
Ventilating or ventilation (the V in HVAC) is the process of exchanging or
replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality which involves
temperature control, oxygen replenishment, and removal of moisture, odors, smoke,
heat, dust, airborne bacteria, carbon dioxide, and other gases. Ventilation removes
unpleasant smells and excessive moisture, introduces outside air, keeps interior
building air circulating, and prevents stagnation of the interior air.
Ventilation includes both the exchange of air to the outside as well as circulation
of air within the building. It is one of the most important factors for maintaining
acceptable indoor air quality in buildings. Methods for ventilating a building may
be divided into mechanical/forced and natural types.[2]
Вам также может понравиться
- App A For PrintingДокумент28 страницApp A For PrintingJon WestОценок пока нет
- BeamДокумент1 страницаBeamJon WestОценок пока нет
- Ise690 Catalog TopicsДокумент1 страницаIse690 Catalog TopicsJon WestОценок пока нет
- App C For PrintingДокумент4 страницыApp C For PrintingJon WestОценок пока нет
- BeamДокумент1 страницаBeamJon WestОценок пока нет
- Tom DwanДокумент1 страницаTom DwanJon WestОценок пока нет
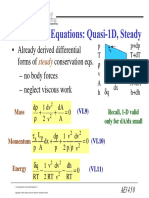
- Already Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkДокумент3 страницыAlready Derived Differential Forms of Conservation Eqs. - No Body Forces - Neglect Viscous WorkJon WestОценок пока нет
- Henry DarcyДокумент1 страницаHenry DarcyJon WestОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент1 страницаScienceJon WestОценок пока нет
- Lorem IsponДокумент1 страницаLorem IsponpriiiiiimeyerОценок пока нет
- Lorem IsponДокумент1 страницаLorem IsponpriiiiiimeyerОценок пока нет
- ImportsДокумент1 страницаImportsJon WestОценок пока нет
- Solar EngineeringДокумент1 страницаSolar EngineeringJon WestОценок пока нет
- ConstructionДокумент1 страницаConstructionJon WestОценок пока нет
- CocaineДокумент3 страницыCocaineJon WestОценок пока нет
- HvacДокумент2 страницыHvacJon WestОценок пока нет
- Count BasieДокумент2 страницыCount BasieJon WestОценок пока нет
- Air FilterДокумент1 страницаAir FilterJon WestОценок пока нет
- SteamДокумент1 страницаSteamJon WestОценок пока нет
- RazorДокумент1 страницаRazorJon WestОценок пока нет
- Mach NumberДокумент1 страницаMach NumberJon WestОценок пока нет
- Numerical AnalysisДокумент2 страницыNumerical AnalysisJon WestОценок пока нет
- Dibo RaneДокумент2 страницыDibo RaneJon WestОценок пока нет
- VirginiaДокумент2 страницыVirginiaJon WestОценок пока нет
- Chesapeake BayДокумент2 страницыChesapeake BayJon WestОценок пока нет
- East Coast of The USAДокумент1 страницаEast Coast of The USAJon WestОценок пока нет
- Chesapeake BayДокумент2 страницыChesapeake BayJon WestОценок пока нет
- Piscataway TribeДокумент1 страницаPiscataway TribeJon WestОценок пока нет
- Washington DCДокумент3 страницыWashington DCJon WestОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)