Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Operations Management. - CH 1: 1-Discuss The Concept of Operations Management and Operations Function?
Загружено:
Long Dong MidoОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Operations Management. - CH 1: 1-Discuss The Concept of Operations Management and Operations Function?
Загружено:
Long Dong MidoАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
- Operations Management.
- CH 1
1-Discuss the concept of Operations management and operations
function?
- Operations management is the activity of managing the resources which
produce and deliver products and services.
- The operations function: is the part of the organization that is responsible for
this activity. Every organization has an operations function because every
organization produces some type of products and\or services.
- Operations managers are the people who have particular responsibility for
managing some, or all; of the resources which compose the operations function.
2- What are the Three core functions and support functions?
The operations function is central to the organization because it produces the
goods and services which are its reason for existing, but it is not only function.
These are:
- The marketing (including sales) function-which is responsible for
communicating the organization’s products and services to its markets in order to
generate customer requests for service;
- the product/ service development function – which is responsible for creating
new and modified products and services in order to generate future customer
requests for service ;
- The operations function-which is responsible for fulfilling customer requests for
service through the production and delivery of products and services.
In addition, there are the support functions which enable the core
functions to operate effectively. these include for example:
[Type text] Page 1
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
-The accounting and finance function- which provides the information to help
economic decision-making and manages the financial resources of the
organization;
-The human resources function- which recruits and develops the organization’s
staff as well as looking after their welfare.
3-What is the Broad definition of operations?
We treat much of the product\service development, technical and information
systems activities and some of the human resource, marketing, and accounting
and finance activities as coming within the sphere of operations management.
4- What is the role of operations management in the smaller
organization?
Operations management is just as important in small organizations as it is in
large ones. Irrespective of their size, all companies need to produce and deliver
their products and services efficiently. However, in practice, managing operations
in a small or medium-size organization has its own set of problems. Large
companies may have the resources to dedicate individuals to specialized tasks but
smaller companies often cannot, so people may have to do different jobs as the
need arises. Such an informal structure can allow the company to respond quickly
as opportunities or problems present themselves.
5- Operations decisions are the same in commercial and not-for-profit
organizations. discuss?
Operations have to take the same decisions- how to produce products and
services, invest in technology, contract out some of their activities, devise
performance measures, and improve their operations performance and so on.
However, the strategic objectives of not-for-profit organizations may be more
complex and involve a mixture of political, economic, social and environmental
[Type text] Page 2
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
objectives. Because of this there may be a greater chance of operations decisions
being made under conditions of conflicting objectives.
6- what is meant by The new operations agenda?
Modern business pressures have changed the operations agenda.
These operations responses form a major part of a new agenda for
operations. Parts of this agenda are trends which have always existed
but have accelerated, such as globalization and increased cost
pressures .part of the agenda involves seeking ways to exploit new
technologies, most notably the internet. When businesses have to cope
with a more challenging environment, they look to their operations
function to help them respond. The changes in the business
environment are shaping anew operations agenda.
- The business environment is changing…..For example,
-increased cost based competition
-higher quality expectations
-demands for better service
-more choice and variety
-rapidly developing technologies
-frequent new product\service introduction
-increased ethical sensitivity
-environmental impacts are more transparent
-more legal regulation
[Type text] Page 3
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
-greater security awareness
- Prompting operations responses…..For example,
-Globalization of operations networking
- information -based technologies
- internet -based integration of operations activities
-supply chain management
-customer relationship management
-flexible working patterns
-mass customization
-fast time-to-market methods
-lean process design
-environmentally sensitive design
-supplier partnership and development
-failure analysis
-business recovery planning
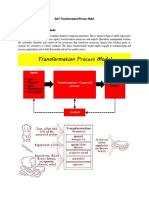
7-Explain the transformation process model?
All operations produce products and services by changing inputs into outputs
using an،input-transformation-output’process.Operations are processes that take
in a set of input resources which are used to transform something, or are
transformed themselves, into outputs of products and services. And although all
operations conform to this general input-transformation-output model, they
differ in the nature of their specific inputs and outputs.
[Type text] Page 4
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
Transformed
resources
-materials
-information
-customers
THE
TRANSFORMATION Output Customers
Input products and
resources PROCESS services
Transforming
resources
-facilities
-staff
8- What are the parts of Inputs to the process?
-Transformed resources :One set of inputs to any operation’s processes are
transformed resources. That are treated, transformed or converted in the
process.
- Materials – operations which process materials could do so to transform their
physical properties (shape or composition, for example)
-Information –operations which process information could do so to transform
their informational properties (that is the purpose or form of the information);
accountants do this.
-Customers – operations which process customers might change their physical
properties in a similar way to materials processors: for example, hairdressers or
cosmetic surgeons.
[Type text] Page 5
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
- Transforming resources:These are the resources which act upon the
transformed resources. There are two types which form the building blocks of all
operations:
Facilities staff: Facilities – the buildings, equipment, plant and process
technology of the operation;
Staff – the people who operate, maintain, plan and manage the operation.
9- What are the parts of outputs from the process?
or- distinguish between product and service?
- Tangibility: although products and services are different, the distinction can be
subtle. Perhaps the most obvious difference is in their respective tangibility. You
can physically touch a television set or a newspaper. Services are usually tangible.
You cannot touch consultancy advice or a haircut. The life of a services is often
much shorter. for example the service of accommodation in a hotel room for
tonight will perish if it is not sold before tonight. Some operations produce just
products and others just services, but most operations produce a mixture of the
two.
11- what is the processes hierarchy?
A process is ،an arrangement of resources that produce some mixture of products
and services’.Each process is, at the same time, an internal supplier and an
internal customer for other processes. This internal customer concept provides a
model to analyse the internal activities of an operation. It is also a useful
reminder that, by treating internal customers with the same degree of care as
external customers, the effectiveness of the whole operation can be improved.
12-Operation processes have different characteristics.
Discuss?
[Type text] Page 6
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
Although all operations processes are similar in that they all transform inputs,
they do differ in a number of ways, four of which known as the four vs, are
particularly important:
-the volume of their output;
-The variety of their output;
-the variation in the demand for their output;
-The degree of visibility which customers have of the production of their output.
1-The volume dimension:
Volume has important implications for the way Mcdonald’s operations are
organized. The first thing you notice is the repeatability of the tasks people are
doing and the systematization of the work where standard procedures are set
down specifying how each part of the job should be carried out.
2-the variety dimension:
To offer this variety it must be relatively flexible. Drivers must have a good
knowledge of the area, and communication between the base and the taxis must
be effective. However, the cost per kilometer travelled will be higher for a taxi
than for a less customized form of transport such as a bus service.
The visibility is a slightly more difficult dimension of operations to envisage. It
refers to how much of the operations activities its customers experience, or how
much the operation is exposed to its customers. Generally , customer- processing
operations. But even customer-processing operations have some choice as to
how visible they wish their operations to be. For example, a retailer could operate
as a high-visibility.
[Type text] Page 7
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
Ch 2
1- What are the five operations performance objectives?
These are the five basic performance objectives and they apply to all types of
operation.
1- the quality objectives:
Quality is consistent conformance to customers’expectations, in other words,
doing things right, but the things which the operation needs to do right will vary
according to the kind of operation. All operations regard quality as a particularly
important objective. Quality is the most visible part of what an operation does.
-Quality reduces costs: the fewer mistakes made by each process in the
operation, the less time will be needed to correct the mistakes and the less
confusion and irritation will be spread.
-Quality increases dependability: increased costs are not the only consequence
of poor quality.
At the supermarket it could also mean that goods run out on the supermarket
shelves with a resulting loss of revenue to the operation and irritation to the
external customers.
2- Speed :
means the elapsed time between customers requesting products or services and
receiving them. The main benefit to the operation’s (external) customers of
speedy delivery of goods and services is that the faster they can have the product
or service, the more likely they are to buy it, or the more they will pay for it, or
the greater the benefit they receive.
Speed inside the operation:Inside the operation speed is also important .fast
response to external customers is greatly helped by speedy decision-making and
speedy movement of materials and information inside the operation.
[Type text] Page 8
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
-Speed reduces inventories: take, for example, the automobile plant. Steel for
the vehicle’s door panels is delivered to the press shop
Speed reduces risks: forecasting tomorrow’s events is far less of a risks than
forecasting next year’s.
3-Dependability is judged over time:
Dependability means doing things in time for customers to receive their goods or
services exactly when they are needed, or at least when they were promised.
Customers might only judge the dependability of an operation after the product
or services has been delivered.
-Dependability inside the operation:Inside the operation internal customers
will judge each other’s performance partly by how reliable the other processes
are in delivering material or information on time.
-Dependability saves time:Take, for example, the maintenance and repair
centre for the city bus company.
-Dependability saves money: Ineffective use of time will translate into extra
cost. The spare parts might cost more to be delivered at short notice and
maintenance staff will expect to be paid even when there is not a bus to work on.
4-Flexibility means being able to change in some way:
Flexibility means being able to change the operation in some way. This may mean
changing what the operation does, how it is doing it, or when it is doing it.
Specifically, customers will need the operation to change so that it can provide
four types of requirement:
-Product/service flexibility - the operation’s ability to introduce new or modified
products and services;
-mix flexibility - the operation’s ability to produce a wide range or mix of products
and services;
[Type text] Page 9
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
-Volume flexibility - the operation’s ability to change its level of output or activity
to produce different quantities or volumes of products and services;
-delivery flexibility – the operation’s ability to change the timing of the delivery of
its services or products.
-Flexibility inside the operation:Developing a flexible operation can also
have advantages to the internal customers within the operation.
-Flexibility speeds up response:fast service often depends on the operation
being flexible.
-Flexibility saves time: in many parts of the hospital, staff have to treat a wide
variety of complaints.
-Flexibility maintains dependability:internal flexibility can also help to keep
the operation on schedule when unexpected events disrupt the operation’s plans.
5-The cost objective:
To the companies which compete directly on price, cost will clearly be their major
operations objective. The lower the cost of producing their goods and services,
the lower can be the price to their customers. Even those companies which do
not compete on price will be interested in keeping costs low.
Low cost is a universally attractive: the short-case ، everyday low prices at Aldi,
describes how one retailer keeps its costs down.
Productivity: is the ratio of what is produced by an operation to what is
required to produce it.
𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
Productivity=
𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
[Type text] Page 10
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
Single-factor productivity: this is called a single-factor measure of
productivity.
𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
Single-factor productivity=
𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
This allows different operations to be compared excluding the effects of input
costs.
𝑜𝑢𝑡𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
Multi-factor productivity=
𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡 𝑡𝑜 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
-cost reduction through internal effectiveness: Each of the various
performance objectives has several internal effects, but all of the them affect
cost.
-high-quality operations do not waste time or effort having to re-do things,
[Type text] Page 11
25732792 -99706005 :ت innovation academy معهد دهشام
Вам также может понравиться
- Operations Management Chap 1Документ6 страницOperations Management Chap 1Amani Abdeen AL 6Оценок пока нет
- Om Final ExamДокумент6 страницOm Final Examaster sebsbeОценок пока нет
- Om NotesДокумент134 страницыOm NotesGovernment PolytechnicОценок пока нет
- The Management of Operations Notes FinalДокумент88 страницThe Management of Operations Notes FinalSantiago LinderОценок пока нет
- 9 Session 21 Pillar 02 Supply Chain Management Part 1Документ19 страниц9 Session 21 Pillar 02 Supply Chain Management Part 1Azfah AliОценок пока нет
- OMGT-1013Документ29 страницOMGT-1013Alexa Nicole GuillermoОценок пока нет
- OM Sem IIДокумент125 страницOM Sem IImakoya3170Оценок пока нет
- Relevance of Operations in Organisations and Evolution of Operations ManagementДокумент16 страницRelevance of Operations in Organisations and Evolution of Operations ManagementFaruqОценок пока нет
- Operations ManagementДокумент50 страницOperations ManagementpolohachikoОценок пока нет
- Operation Management and Inventory ControlДокумент34 страницыOperation Management and Inventory ControlVijay Sane100% (2)
- History of OMДокумент101 страницаHistory of OMKarishma ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Operations Management CourseДокумент16 страницOperations Management CourseJelena BieberОценок пока нет
- Production/Operations ManagementДокумент97 страницProduction/Operations Managementdinesh0014Оценок пока нет
- Expo Final de MetodologíaДокумент5 страницExpo Final de MetodologíaanajulcaОценок пока нет
- Production and Operations Managment NotesДокумент65 страницProduction and Operations Managment NotesEbe Nezer GОценок пока нет
- 01 Operations Management - IntroductionДокумент44 страницы01 Operations Management - IntroductionJhanna Mae PacibleОценок пока нет
- StudocuДокумент34 страницыStudocuOmunet NapthalОценок пока нет
- Process (Pius Pinto S) :: Among The Demonstrated Outcomes AreДокумент5 страницProcess (Pius Pinto S) :: Among The Demonstrated Outcomes Arepius pintoОценок пока нет
- What Is Operations ManagementДокумент11 страницWhat Is Operations Managementdivya2390Оценок пока нет
- WK1-BUS5040 - SURVEY OF PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT-topic 1 Introduction-2Документ28 страницWK1-BUS5040 - SURVEY OF PRODUCTION AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT-topic 1 Introduction-2Moses SosiОценок пока нет
- University of Gondar Production Planning and Control ChapterДокумент27 страницUniversity of Gondar Production Planning and Control ChapterantehenОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Operations ManagementДокумент41 страницаIntroduction To Operations ManagementLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSОценок пока нет
- Chapter 10Документ2 страницыChapter 10Jeil Francisco100% (1)
- Operations Management GuideДокумент43 страницыOperations Management GuideViraja GuruОценок пока нет
- Operation and StrategyДокумент58 страницOperation and StrategyAliya RaheelОценок пока нет
- 12mba32 Om NotesДокумент68 страниц12mba32 Om NotessanthoshОценок пока нет
- What is Operations Management? Key Responsibilities and ImportanceДокумент17 страницWhat is Operations Management? Key Responsibilities and Importanceankit_bhasinОценок пока нет
- POM AssignmentДокумент3 страницыPOM AssignmentFlorence Tresvalles AlticheОценок пока нет
- SELF STUDY - Operations ManagementДокумент15 страницSELF STUDY - Operations Managementstudd77Оценок пока нет
- Production & Operation ManagementДокумент42 страницыProduction & Operation ManagementSandeep GhatuaryОценок пока нет
- Operations and Supply Chain Management Week 1Документ8 страницOperations and Supply Chain Management Week 1Rhyn RutherfordОценок пока нет
- Course Code: Mba 632 Credit Hours: 3: By: Messele Kumilachew (PHD)Документ38 страницCourse Code: Mba 632 Credit Hours: 3: By: Messele Kumilachew (PHD)Global internetОценок пока нет
- Unit-1 - Operations ManagementДокумент21 страницаUnit-1 - Operations ManagementRudr ShiyaniОценок пока нет
- OM Ch01 Operations and Productivity HeizerДокумент31 страницаOM Ch01 Operations and Productivity HeizerSaimuna YeasminОценок пока нет
- Production/ Operations Management: Estrella Y. Yu, DBMДокумент76 страницProduction/ Operations Management: Estrella Y. Yu, DBMTristan ZambaleОценок пока нет
- 0Intro to OMДокумент16 страниц0Intro to OMkunal.nhidclОценок пока нет
- Ops mgmt essentialsДокумент34 страницыOps mgmt essentialsKawsar Ahmed BadhonОценок пока нет
- Operations and Supply Chain ManagementДокумент61 страницаOperations and Supply Chain ManagementSandeep SonawaneОценок пока нет
- Production Ops Mgmt Guide with FAQsTITLEProf Rupesh's Prod Ops Mgmt Class NotesДокумент51 страницаProduction Ops Mgmt Guide with FAQsTITLEProf Rupesh's Prod Ops Mgmt Class NotesJayendra Patel100% (1)
- Operations Management: An IntroductionДокумент35 страницOperations Management: An IntroductionAprile Margareth Hidalgo100% (1)
- Module 1 - Introduction Into Operations ManagementДокумент20 страницModule 1 - Introduction Into Operations ManagementBharathKumarM86% (14)
- Introduction To Operations Management - Graduate Jobs, Internships & Careers Advice - Inside CareersДокумент3 страницыIntroduction To Operations Management - Graduate Jobs, Internships & Careers Advice - Inside CareersMUINDI MUASYA KENNEDY D190/18836/2020Оценок пока нет
- MGT-629/422 Operations and Supply Chain ManagementДокумент4 страницыMGT-629/422 Operations and Supply Chain ManagementChaqib SultanОценок пока нет
- Production NotesДокумент19 страницProduction NotesShabi AhmedОценок пока нет
- MS NotesДокумент109 страницMS NotesIshika AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Chapter Outline on Introduction to Operations ManagementДокумент24 страницыChapter Outline on Introduction to Operations ManagementMonevaОценок пока нет
- IB Business Management SL StudyguideДокумент99 страницIB Business Management SL StudyguideJoshua EtienneОценок пока нет
- Impruve Business PracticeДокумент105 страницImpruve Business PracticeEmuyeОценок пока нет
- CBM ReviewerДокумент8 страницCBM Reviewerkrain dropОценок пока нет
- Business ProcessДокумент13 страницBusiness ProcessAshu MoglaОценок пока нет
- Operations ManagementДокумент11 страницOperations ManagementAlly MendezОценок пока нет
- About The CourseДокумент5 страницAbout The Courseashish sunnyОценок пока нет
- Advanced Engineering Informatics: Yoichiro Suzuki, Majid Yahyaei, Yan Jin, Hideo Koyama, Gahee KangДокумент19 страницAdvanced Engineering Informatics: Yoichiro Suzuki, Majid Yahyaei, Yan Jin, Hideo Koyama, Gahee KangHavidHarjoSuwitoОценок пока нет
- OPerations Management IntroductionДокумент59 страницOPerations Management IntroductionYaredОценок пока нет
- ISP531 Chapter 1Документ48 страницISP531 Chapter 1Amar MurshidОценок пока нет
- CH 1Документ15 страницCH 1Razan BashaОценок пока нет
- First Chapter: IntroductionДокумент16 страницFirst Chapter: IntroductionMominul MominОценок пока нет
- Operations Management Lecture - 2Документ6 страницOperations Management Lecture - 2tusharОценок пока нет
- Bam 199 - P1Документ9 страницBam 199 - P1Mae RapadasОценок пока нет
- No Boundaries: How to Use Time and Labor Management Technology to Win the Race for Profits and ProductivityОт EverandNo Boundaries: How to Use Time and Labor Management Technology to Win the Race for Profits and ProductivityОценок пока нет
- OM - Chp. 1Документ31 страницаOM - Chp. 1Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- T306A TMA Fall 2016Документ8 страницT306A TMA Fall 2016Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- IKEA's Quality Assurance for SuppliersДокумент16 страницIKEA's Quality Assurance for SuppliersLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Module 1 Introduction and Business Start-UpДокумент25 страницModule 1 Introduction and Business Start-UpLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- CH - 01 EntrepreneurshipДокумент53 страницыCH - 01 EntrepreneurshipPriscilla SamaniegoОценок пока нет
- DD309 ATMA2016 FirstДокумент4 страницыDD309 ATMA2016 FirstLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 EntrepreneurshipДокумент35 страницLecture 1 EntrepreneurshipLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Corporate Social Responsibility SamsungДокумент1 страницаCorporate Social Responsibility SamsungGediya RockyОценок пока нет
- Major/ Omar Alnufais Military Number:-37465Документ4 страницыMajor/ Omar Alnufais Military Number:-37465Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: How To Design A Language?Документ2 страницыChapter 1: How To Design A Language?Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- CH 03Документ22 страницыCH 03Usman KhalidОценок пока нет
- Major/ Omar Alnufais Military Number:-37465Документ4 страницыMajor/ Omar Alnufais Military Number:-37465Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Opmlecture2 140326062902 Phpapp01Документ67 страницOpmlecture2 140326062902 Phpapp01Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- 2011 NEC Env MGT ToolsДокумент103 страницы2011 NEC Env MGT ToolsLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Analyzing the Complex Reputation of the Dalai LamaДокумент4 страницыAnalyzing the Complex Reputation of the Dalai LamaLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Measuring Coefficients of Linear Expansion for MetalsДокумент3 страницыMeasuring Coefficients of Linear Expansion for MetalsLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Samsung Case StudyДокумент17 страницSamsung Case StudyLong Dong Mido100% (1)
- Tensile Test: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыTensile Test: ObjectiveLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Soft SystemsДокумент12 страницChapter 2 Soft SystemsLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Impact Test: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыImpact Test: ObjectiveLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Tensile Test: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыTensile Test: ObjectiveLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- A Linguistic Toolkit Chapters 7-9Документ20 страницA Linguistic Toolkit Chapters 7-9Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- ShabuДокумент14 страницShabuLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Experiment 11Документ3 страницыExperiment 11Long Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Tensile Test: ObjectiveДокумент4 страницыTensile Test: ObjectiveLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Charpy and Izod Impact Tests Measure Material ToughnessДокумент4 страницыCharpy and Izod Impact Tests Measure Material ToughnessLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Tourism in KuwaitДокумент16 страницTourism in KuwaitLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Transformation 4vsДокумент10 страницTransformation 4vs李雨佳Оценок пока нет
- Systems Thinking ApproachesДокумент5 страницSystems Thinking ApproachesLong Dong MidoОценок пока нет
- Full Download Fundamentals of Management Seventh Canadian Edition Canadian 7th Edition Robbins Test BankДокумент36 страницFull Download Fundamentals of Management Seventh Canadian Edition Canadian 7th Edition Robbins Test Bankbloomaryonrush2qp6100% (38)
- Ratan TataДокумент7 страницRatan TatadrankurshahОценок пока нет
- Ride Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, KarthickДокумент3 страницыRide Details Bill Details: Thanks For Travelling With Us, KarthickKarthick P100% (1)
- Places and Landscapes in a Changing WorldДокумент9 страницPlaces and Landscapes in a Changing WorldRazel G. Taquiso80% (10)
- SHASHIKANT SHARMA CVДокумент3 страницыSHASHIKANT SHARMA CVsanamsharmaОценок пока нет
- FAR1 ASN01 Balance Sheet and Income Statement PDFДокумент1 страницаFAR1 ASN01 Balance Sheet and Income Statement PDFira concepcionОценок пока нет
- Amazon's Rise from Online Bookseller to Global Retail GiantДокумент2 страницыAmazon's Rise from Online Bookseller to Global Retail GiantJuliana MorenoОценок пока нет
- Portfolio Management - Chapter 7Документ85 страницPortfolio Management - Chapter 7Dr Rushen SinghОценок пока нет
- 12 Risks With Infinite Impact PDFДокумент212 страниц12 Risks With Infinite Impact PDFkevin muchungaОценок пока нет
- Solutions: ECO 100Y Introduction To Economics Midterm Test # 2Документ15 страницSolutions: ECO 100Y Introduction To Economics Midterm Test # 2examkillerОценок пока нет
- Data Prep - Homogeneity (Excel)Документ5 страницData Prep - Homogeneity (Excel)NumXL ProОценок пока нет
- 10th March: by Dr. Gaurav GargДокумент2 страницы10th March: by Dr. Gaurav GarganupamОценок пока нет
- Mumbai MetroДокумент23 страницыMumbai MetroTarun AnandОценок пока нет
- LANDON LTDДокумент2 страницыLANDON LTDStephanie ChristianОценок пока нет
- Energia Solar en EspañaДокумент1 страницаEnergia Solar en EspañaCatalin LeusteanОценок пока нет
- List of Maharashtra Pharrma CompaniesДокумент6 страницList of Maharashtra Pharrma CompaniesrajnayakpawarОценок пока нет
- Aviation Industry in India - Challenges For The Low Cost CarriersДокумент11 страницAviation Industry in India - Challenges For The Low Cost Carrierstake3Оценок пока нет
- Form 32 A Central: Treasury or Sub TreasuryДокумент1 страницаForm 32 A Central: Treasury or Sub TreasuryMuhammad AsifОценок пока нет
- 4 93-F Y B A - Micro-EconomicsДокумент3 страницы4 93-F Y B A - Micro-EconomicsSanjdsgОценок пока нет
- IBT-REVIEWERДокумент10 страницIBT-REVIEWERBrenda CastilloОценок пока нет
- Jagath Nissanka,: Experience Key Roles and ResponsibilitiesДокумент2 страницыJagath Nissanka,: Experience Key Roles and ResponsibilitiesJagath NissankaОценок пока нет
- KOKEBE TSIBAH 2021 Grade 12 Civics Work SheetДокумент20 страницKOKEBE TSIBAH 2021 Grade 12 Civics Work Sheetmmree yyttОценок пока нет
- Option To PurchaseДокумент3 страницыOption To PurchaseAlberta Real EstateОценок пока нет
- K&N Case Group - 3Документ41 страницаK&N Case Group - 3priya_pritika6561100% (1)
- Mishkin Econ13e PPT 17Документ25 страницMishkin Econ13e PPT 17Huyền Nhi QuảnОценок пока нет
- CIR V Toledo (2015)Документ2 страницыCIR V Toledo (2015)Anonymous bOncqbp8yiОценок пока нет
- 12 Jun 2019 PDFДокумент12 страниц12 Jun 2019 PDFAnonymous dy7g4jzo7Оценок пока нет
- Volume II AppendicesДокумент378 страницVolume II AppendicesGus BovaОценок пока нет
- The World Trade Organiation and World Trade Patterns: Chapter - 40Документ8 страницThe World Trade Organiation and World Trade Patterns: Chapter - 40Halal BoiОценок пока нет
- Ashmore Dana Obligasi Nusantara: Fund Update Jul 2019Документ2 страницыAshmore Dana Obligasi Nusantara: Fund Update Jul 2019Power RangerОценок пока нет