Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Reproductive Health
Загружено:
Channabasava Amareshappa0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
42 просмотров8 страницNEET study material
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документNEET study material
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
42 просмотров8 страницReproductive Health
Загружено:
Channabasava AmareshappaNEET study material
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOC, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 8
1. RCH programmes are 3) Family natality programmes.
1) Rehabilitation and Child Health programme 4) All of these
2) Reproductive and Child Health programme 10. Contraceptives are used for
3) Reproductive and Child Health Care 1) Spacing the birth of the child.
programme 2) Preventing unwanted pregnancies.
4) Reproduction and child Health 3) Family natality programmes.
programmes. 4) All of these
2. STD refers to 11. Contraceptives are used for
1) Sexually transmitted diseases 1) Spacing the birth of the child
2) Venereal diseases 2) preventing unwanted pregnancies
3) Sexually transmitted infections. 3) Birth control
4) All the above 4) all of these
3. Cause of world population explosion is 12. Natural or physiological methods of birth
1) better health care Control are based on
2) increased agriculture production 1) Avoiding chances of ovum and sperm meeting
3) more jobs 2) Fertility awareness
4) Fewer wars 3) Both (1) and (2)
4. Preventive birth control measure is 4) neither (1) nor (2)
1) Preventing union of sperm and ovum. 13. Couple without children can be
2) Preventing sperm from entering uterus recommended
3) MTP. to go for
4) test tube babies. 1) Assisted fertility technologies
5. Reduced sperm count of semen is called 2) assisted reproductive technologies
1) spermiogenesis. 3) Assisted contraceptive technologies
2) azoospermia 4) assisted remedial technologies
3) oligospermia. 14. Inability to conceive even after 2 years of
4) spermatogenesis. unprotected sexual cohabitation is called
6. Which represents a condition of highly 1) Insemination 2) infertility
reduced 3) insterility 4) all of these
motility? 15. Couple avoid coitus from day 10 to 17 of the
1) Azoospermia. menstrual cycle as
2) Polyspermy 1) Ovulation takes place on day 10.
3) Oligospermia 2) Ovulation takes place on day 17.
4) Asthenospermia 3) Ovulation takes place on birth day 10 and
7. The term impotency refers to 4) ovulation takes place day 14
1) Absence of sperms in semen. 16. Which of the following is contraception?
2) Abnormally low sperm count in semen. 1) Condom.
3) Abnormal sperms in semen. 2) Cervical cap.
4) Inability to achieve erection of male 3) Oral pills.
Copulatory organ to carryout sexual 4) Abstinence from sex during fertility
intercourse period
8. Assisted reproductive technology helps in 17. The natural contraceptive method where the
overcoming couple avoid coitus around the time of
1) Infertility 2) STD’s ovulation is called
3) Immunologicl disorders 1) Total abstinence.
4) Veneral diseases 2) Coitus interruptus.
9. The key to control over population in third 3) Calendar or rhythm method
word countries is 4) oophorectomy.
1) Family welfare programmes. 18. Withdrawal method is also known as
2) Family planning programmes
1) Menorrhea coitus implantation of the embryo are called
2) coutus interrupt. 1) Extra uterine devices
3) Coitus interruptus. 2) Oral devices
4) Coitus abstinence 3) Intra – uterine devices
19.After parturition, during intense lactation by 4) total – uterine devices
the mother chances of 27. Barrier methods of contraception
1) Contraception is nil. 1) Give protection against sexually transmitted
2) Conception is nil diseases
3) Coitus is nil. 2) Are usually rubber or polyurethane
4) Sterilization is nil. structures
20. Absence of menstruation during the period 3) Prevent sperms from depositing into the
of vagina
breast – feeding the baby is called 4) All of these
1) Gestational amenorrhea. 28. IUD’S increase
2) Lactational dysmenorrheal. 1) Sperm motility
3) Lactational amenorrhea. 2) Phagocytocis of the sperms
4) Gestational dysmenorrheal. 3) Multiplication of sperms
21. The commonly used male condom in India 4) Activation of sperms
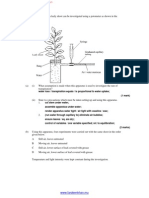
is 29.The diagram is a
1) IUD 2) cervical cap 1) IUD – diaphragm.
3) Nirodh. 4) Diaphragm 2) IUD – condom
22. Condoms 3) IUD – CuT
1) Are used by both males and females 4) IUD – implant.
2) Are used by only males 30.IUD can be inserted
3) Should be discarded after single use. 1) By oneself
4) Both (1) and (3) 2) By common practice
23. Diaphragm is usually filled with 3) By a qualified medical practioner
1) a gel to make it effective 4) None of these
2) a polyethylene to make it effective 31. An IUCD is
3) a spermicide to make it effective 1) Copper – T 2) Condom
4) a jelly to make it effective 3) vasectomy 4) cleavage
24. Pick the correct statements 32. Draw backs of IUD’s include
1) Diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are 1) Perforation of uterus
barriers that are inserted into the female 2) tubal pregnancy
Reproductive tract for contraception 3) Infection
2) Diaphragms, Saheli and vaults are 4) all of these
barriers 33. Copper T/loop prevents
that are inserted into the female 1) Ovulation.
reproduction 2) Fertilization
tract for contraception 3) zygote formation
3) Diaphragms, lippes loop, vaults are 4) cleavage
barriers 34. Method of birth control is
that inserted into the female reproduction 1) GIFT. 2) HJF
tract for contraception 3) IVF – ET 4) IUDs.
4) Diaphragms, cervical caps, Mala-D and 35. Which of the following is a mechanical
nirodh are barriers that inserted into the barrier
female reproduction tract for contraception used in birth control?
25. The cervical cap acts in the same manner as 1) Copper T. 2) Diaphragm.
1) IUD. 2) Diaphragm. 3) Loop. 4) Dalcon shield
3) oral contraceptive 4) condom. 36. Which of the following is a barrier method
26. Devices which prevent fertilization and of
contraception? 3) Progesterone and Lactogenic hormone
1) Condom, diaphragm, cervical caps, 4) Progesterone and estrogen.
2) Copper T. 47. A method of sterilistation is
3) Mala D. 1) IUDCB 2) Diaphragm.
4) Vasectomy 3) Tubectomy 4) Loop
37. A weekly oral contraceptive is 48. Surgical removal of uterus is
1) Mala A. 2) Mala D. 1) Tubectomy 2) hysterectomy
3) Saheli. 4) Saheli 2 3) vasectomy 4) orchidectomy
49. Surgical cutting of fallopian tubes in females
38.Contraceptive oral pills help in birth control to prevent conception is called
by 1) vasectomy 2) Tubectomy
1) Suppressing maturation of ovarian follicles 3) hysterectomy 4) ovarectomes
2) Killing ova. 50. Vasectomy is the
3) Forming barriers between sperms and ova 1) Surgical cutting of fallopian tube and
4) Preventing implantation. ligation of cut ends in females
39.Pills used by women as contraceptives are 2) surgical cutting of ductus deferens and
1) Small doses of androgens ligation of cut ends in males
2) Small doses of androgens 3) removal of uterus in females
3) IUD’s 4) None of 4) removal of testis in males
these 51. Ligation of fallopian tube
40.Which one of the following is a combination (tubectomy) results
of in
oral contraceptive 1) stoppage of menstruation
1) estrogen and progesterone 2) stoppage of ovulation
2) Inhibin and progesterone 3) decreased secretion of gondotropin
3) Relaxin and estrogen 4) loss of unfertilized ovum into the
4) HCG and progesterone peritoneal cavity
41. A contraceptive pill prevents ovulation by 52. Purpose of Tubectomy is to prevent
1) Blocking fallopian tube 1) coitus 2) egg formation
2) inhibiting release of FSH and LH 3) fertilization 4) embryonic development
3) stimulating release of FSH and LH 53. The permanent and sure birth control
4) causing immediate degeneration of method
Released ovum is
42. Hormonal pill ‘saheli’ is 1) Sexual abstinence method.
1) oral contraceptive for males 2) semination
2) was prepared by CDRI, Lucknow 3) sterilization
3) Oral contraceptive for female 4) Saheli
4) both (2) and (3) 54. The process of Tubectomy is carried
43. The non – steroidal ‘once a week’ pill used out
As a contraceptive is 1) under anesthesia
1) Mala – D 2) Mala – L 2) under UV light
3) Saheli 4) Depo-provera 3) under a microscope
44.Birth control pills 4) under tubectoscope
1) check ovulation 55. Sterilization in males and females are
2) are oral contraceptives called_______ and _______ respectively
3) contain se hormones 1) vasectomy, recanalization
4) all of these 2) vasectomy and tuibectomy
45. Small doses of hormones present in oral 3) Tubectomy and vasectomy
contraceptive pills are 4) Tubectomy and vasovasostomy
1) progesterone and prolactin. 56. Vasectomy involves cutting of the
2) Progesteron and hCG
1) Fallopian ducts 1) transfer of a mixture of sperms and ova into
2) fallopian tubes the uterus.
3) vasa deferenita 2) transfer of a mixture of sperms and ova into
4) vasa effernita the fallopian tube
57. Tubectomy involves typing and 3) transfer of embryo into the uterus
chipping of 4) transfer of zygote into the fallopian tube.
1) vagina 67. Which of the following instrument is
2) fallopian canals used for oocyte aspiration?
3) fallopian tubes 1) Catheter 2) Dialyzer
4) fallopian ducts 3) IUD 4) Laparoscope
58. The part of the female reproductive 68. Test tube baby technique refers to
organ that allows the sperm to fertilize the egg 1) development of baby in a test tube
is 2) normal delivery of a baby after the
1) ovary 2) uterus technique of IVF followed by ET.
3) vagina 4) fallopian 3) technique of transfer of gametes directly
tube into the fallopian tube with the help of
59. The instrument used during fallopian Laparoscope
tube ligation is
1) stethoscope 2) laparoscope 4) the removal of baby by cesarean section
3) laparoscopy 4) tracheoscope
60. Which one of the following is not an 69. The first IVF-ET technique success
infertility control technique was reported by
1) IVF. 2) ET. 1) Patrick Steptoe and Robert Edwards
3) Test tube babies 4) Hysterectomy 2) Louis joy brown and Banting best
61. Significant side effects are completely 3) Baylis and taylor
absent in 4) Robert Steptoe and Gilbert Brown
1) usage of IUD’S 70. IVF generated zygote with more then
2) Usage of oral pills 8 blastomeres is transferred into
3) Vasetomy and Tubectomy 1) fallopian tube 2) Uterus
4) vasectomy 3) Cervix 4) none of
62. The sperms, oocytes and embryos are these
cryopreserved in 71. The first test tube baby was
1) Liquid nitrogen 1) a girl born in England
2) Liquid paraffin 2) a boy born in England
3) 70% alcohol 3) a girl born in USA
4) formalin 4) a boy born in USA
63. The technique of transferring gametes 72. GIFT technique is performed
directly into the fallopian tube is referred to as 1) when a female cannot produce ova
1) GIFT 2) ET. 2) when a male cannot produce sperms
3) IVF. 4) ZIFT. 3) when a female can provide suitable
64. The abbreviation ZIFT stands for environment for fertilization but cannot ovulate.
1) zygote inter fallopian tube. 4) when a male has low sperm count.
2) zygote intra fallopian tube 73. Success rate of test tube babies is
3) zygote intra fallopian transfer 1) 100% 2) 50%
4) zygote inter fallopian transfer 3) less then 50% 4) less then
65. The abbreviation GIFt stand for 20%
1) gamete inter fallopian tube. 74. A women who substitutes the real
2) gamete intra fallopian tube. mother no nurse the implanted embryo is called
3) gamete inter fallopian transfer 1) substitute mother
4) gamete inter fallopian transfer 2) biological mother
66. GIFT involves
3) legal mother 3) Female foeticide
4) surrogate mother 4) None of these
75. When the sperm count is low, the 84. AMinocentesis is miss used for
assisted reproductive technique (ART) used is 1) foetal sex determination based on amniotic
1) IUD 2) IUI fluid concentration
3) IUU 4) IUA 2) foetal sex determination based on amniotic
76. What is correct about test tube baby? fluid volume
1) Fertilization inside female genital tract and 3) foetal sex determination based on
growth in test tube chromosomal pattern in amniotic fluid
2) Rearing of prematurely born baby in 4) foetal sex determination based on
incubator antibodies on amniotic fluid
3) Fertilization outside and gestation inside 85. Genetic disorders of a foetus can be
womb of mother determined by
4) Both fertilization and development are 1) it is used to determine genetic discorders
effected outside the female genital tract 2) it is used to abort the foetus
77. The baby produced by conceiving in 3) it is used to determine the sex of the foetus
aculture dist and nursing in the uterus is called 4) it is used to determine the sex of the foetus,
1) ZIFT – baby so that female foetus may be aborted
2) GIFT – baby 86. MTP is also
3) IVF – baby 1) Medical Termination of pregnancy
4) test – tube baby 2) A bortion
78. Fertilization in human beings outside 3) Both (1) and (2)
the body of the mother is called 4) Neither (1) nor (2)
1) In vivo fertilization 87. In india, MTP was legalized by the
2) In vitro fertilization government in
3) Intra fallopian 1) 1970 2) 1971
4) Extra fallopian fertilization 3) 1972 4) 1973
79. IVF followed by embryo transfer into 88. MTP is
the fallopian tube usually involves 1) multi trade practices
1) zygote with 10 blastomeres 2) Malthusian treatise on population
2) zygote with 14 blastomeres 3) multiple temporary phenomena
3) zygote with 12 blastomeres 4) medical termination of pregnancy
4) none of these 89. Medical termination of pregnancy is
80. Introduction of semen into the vagina 1) not legalized in our country
of the female artificially is called 2) legalized in our country
1) intercourse 3) peformed to get rid of unwanted pregbancy
2) coitus 4) Both (2) and (3)
3) artificial injection 90. The major venereal diseases are
4) artificial insemination 1) syphilis and trichominiasis
81. Invitro fertilization is followed by 2) syphilis and chlamydiasis
1) GIFT 2) ZIFT 3) syphilis and genital herpes
3) ET 4) ICSI 4) syphilis and gonorrhea.
82. In IVF-ET, hyperstimulation of 91. Among STD’s the ones that can
ovaries is caused by which of the following spared, by sharing injection needles and through
hormones surgical
1) FSH-LH 2) Estrogen instruments are
3) Progesterone 4) HCG 1) HIv leading to AIDS and genital herpes
83 Who received the Nobel prize for the 2) HIV leading to AIDS and heptatitis-C
incredible work in the fertility treatement IVF? 3) HIV leading to AIDS and hepatitis-A
1) Patrick Steptoe 4) HIV leading to AIDS and hepatitis-B
2) Robert Edward 92. Syphilis is caused by
1) Treponema nessieria 3) ELISA – it is a screening test for HIV
2) Neisseria species antibody
3) Treponema species 4) Gonorrhoea – it is the most curable sexually
4) Treponema pallidum transmitted disease in the world
93. The mother may transmit syphilis to 101. The method of directly injecting a
the new – born baby. This is called sperm into ovum in assisted by reproductive
1) Primary syphilis technology is
2) Secondary syphilis Called
3) Tertiary syphilis 1) GIFT. 2) ZIFT.
4) Congenital syphilis 3) ICSI. 4) ET.
94. The first AIDS case in India was 102. Increased IMR and decreased MMR
reported from in a population will
1) Chennai, Tamil Nadu in 1986 1) a use rapid increase in growth rate
2) Mumbai, in Maharashtra, 1986 2) result in decline in growth rate
3) Alcutta in west Bengal in 1986 3) not cause significant change in growth rate
4) Salem, in Tamil Nadu in 1986 4) result in an explosive population / exp
95. Gonorrhoea is caused by 103. Intensely lacating mothers do not
1) Neisser gonorrhoeae generally conceive due to the
2) Neisseria gonorea 1) Suppression of gondotropins.
3) Neisser gonorrhoeae. 2) hyper secretion of gonddotropins
4) Neisseria gonorrhoeae. 3) suppression of gametic transport
96. Which of the following is not a 4) suppression of fertilization
sexually transmitted disease? 104. Sterilisation techniques are generally fool proof
1) Syphilis 2) Gonorrhoea. methods of contraception with least side effects
3) AIDS 4) yet. This is the last option for the couple
Haemophilia because
97. Which of the following sexually i) It is almost irreversible
transmitted disease do bacteria cause? ii) Of the misconception that it will reduce
1) Gonorrhoea and syphilis sexual urge/drive
2) Gonorrhoea and AIDS iii) It is a surgical procedure
3) Syphilis and AIDS iv)Of lack of sufficient facilities in many parts
4) Gonorrhoea, syphilis and AIDS of the country
98. Which of the following is a cause for chose the correct option
HIV inferction? 1) i and iii 2) ii and iii
1) Sharing the spoon, food and shaking hands 3) ii and iv 4) I, ii, iii and
2) Using contaminated syringes for iv
injection 105. A national level approach to build up a
3) Mosquito bites reproductively healthy society was taken up in
4) Sharing a swimming pool our country in
99. HIV decreases the natural immunity 1) 1950s 2) 1960s
of the body by 3) 1980s 4) 1990s
1) attacking B-lymphocytes 106. Emergency contraceptives are effective if used
2) Attacking T – lymphocytes within
3) destroying erythrocytes 1) 72 hrs of coitus
4) Destroying antibodies 2) 72hrs of ovulkation
100. Find the odd one with the correct 3) 72 hrs of menstruation
reason 4) 72 hrs of implanation
Gonorrhoea, Syphilis, ELISA, AIDS 107. Choose the right one among the statements
1) ELISA – a test used to detect sexually given below
transmitted diseases 1) IUDs are generally inserted by the user
2) Gonorrhoea – it is caused by a virus herself
2) IUDs increase phagocytosis reaction in the 2) Generally chance of conception are nil unit
uterus mother breast – feeds infant upto two years
3) IUDs suppress gamnetogenesis 3) Intrauterine devices like copper – T are
4) IUDs once inserted need not be replaced effective contraceptives
108. Following statements are given regarding MTP. 4) Contraception pills may be take upto one
Choose the correct options given below week after coitus to prevent conception
i) MTPs are generally advised during first 1) A and C are correct
trimester 2) A and B are correct
ii) MTPs are used as a contraceptive method. 3) A, B and C are correct
iii) MTPs are always surgical 4) A and D are correct
iv)MTPs require the assistance of qualified Read the statements A and B in the following
medical personnel. and identify the correct choice
1) 2) 115. Statement A : after ovarectomy, menstrual cycle
3) 4) in women may be stopped statement B : Ovarian
109. From the sexually transmitted disease hormones induce menstrual cycle
mentioned below identify the one which does 1) Both statement A and B are correct
not specifically affect the sex organs 2) Both statement A and B are wrong
1) Syphilis 2) AIDS 3) Statement A is correct and B is wrong
3) Gonorrhea 4) Genital warts 4) Statement B is correct and A is wrong
110. Condoms are one of the most popular 116. Statement A : Saheli is most desirable female
contraceptives because of the following reasons oral contraceptive statement B : It is only non –
1) These are effective barriers for insemination steroidal contraceptive without any side effects
2) They do not interfere with coital act 1) Both statement A and B are correct
3) These help in reducing the risk of STDs 2) Both statement A and B are wrong
4) All of the above. 3) Statement A is correct and B is wrong
111. Choose the correct statement regarding the ZIFT 4) Statement B is correct and A is wrong
procedure 117. Statement A : There is no male contraceptive
1) Ova collected from a female donor are oral pill available as yet Statement B : male
transferred to the fallopian tube to faciulitate spermatogenic cycle are erratic
ztgote formation 1) Both statement A and B are correct
2) Zygote is collected from a female donor and 2) Both statement A and B are wrong
transferred to the fallopian tube 3) Both statement A and B are wrong
3) Zygote is collected from a female donor and 4) Statement B is correct and A is wrong
transferred to the uterus 118. Consider the following two statements and
4) Ova collected from a female donor and answer accordingly
transferred to the uterus 1) R and A both are true
112. The correct surgical procedure as a 2) A is true but R is false
contraceptive method in man is 3) Both are false
1) ovarieetomy. 2) hysterectomy. 4) A and R true but R is not the correct
3) vasectomy 4) castration explanation to A
113. Diaphragms are contraceptive devices used by Assertion (A) : In a women after hysterectomy
the females. Choose the correct option from the her ovarian cycle is stopped
statement given below: Reason (R) : Because TSH is not secreting
1) They are introduced into the uterus (1) (2)
2) They are placed to cover the cervical region (3) (4)
3) They act as physical barriers for sperm entry 119. Statement A : Ovulation is controlled by
4) They act as spermicidal agents oestrogen hormone
114. Consider the statements given below regarding Statement B : Contraceptives contain both
contraception and choose the correct statements oestrigen and progesterone
1) Medical termination of prehancy (MTP) 1) Both statement A and B are wrong
during first trimester is generally safe 2) Both statement A is correct and B is wrong
3) Statement A is correct and B is wrong
4) Statement B is correct and A is wrong
120. Statement A : Generally a women does conceive
during lactation period.
Statement B : During lactation the hormone
prolactin suppresses the production of
gondadotrophins
1) Both statement A and B are correct
2) Both statement A and B are wrong
3) Statement A is correct and B is wrong
4) Statement B is correct and A is wrong
Вам также может понравиться
- AIPMTДокумент59 страницAIPMTChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- AIIMSДокумент47 страницAIIMSChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- AIIMS Paper 2004 Solution PDFДокумент18 страницAIIMS Paper 2004 Solution PDFChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- AIIMS Paper 1997 SolutionДокумент13 страницAIIMS Paper 1997 SolutionChandan KumarОценок пока нет
- HosmaniДокумент6 страницHosmaniChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Biology CLASS: First Year PUC Unit I: Diversity of Living OrganismsДокумент10 страницBiology CLASS: First Year PUC Unit I: Diversity of Living OrganismsChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- Plant Protein Extraction Protocol For SDS PageДокумент7 страницPlant Protein Extraction Protocol For SDS PageAbhinay BatchuОценок пока нет
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Bio - Os Old SyallabusДокумент27 страницBio - Os Old SyallabusChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Brundrett Mycorrhizal TermsДокумент23 страницыBrundrett Mycorrhizal TermsChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Rev Gohre1Документ8 страницRev Gohre1Channabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- AM DocumentДокумент22 страницыAM DocumentChannabasava AmareshappaОценок пока нет
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Crimson Holdings Fact Sheet As of April 14Документ3 страницыCrimson Holdings Fact Sheet As of April 14WDIV/ClickOnDetroitОценок пока нет
- Project Data Collection & Risk ReportingДокумент2 страницыProject Data Collection & Risk Reportinggambler yeagerОценок пока нет
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- CV1000 CV2000 CV3000 Ice Cube Machines SpecsДокумент12 страницCV1000 CV2000 CV3000 Ice Cube Machines SpecsAriel Godoy100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Myths of Greece and Rome PDFДокумент247 страницMyths of Greece and Rome PDFratheesh1981Оценок пока нет
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaДокумент3 страницыThe Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaFreerangecamping60% (5)
- 19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)Документ4 страницы19 - Speed, Velocity and Acceleration (Answers)keyur.gala100% (1)
- Civil ServiceДокумент46 страницCivil ServiceLester Josh SalvidarОценок пока нет
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Frobenius Method for Solving Differential EquationsДокумент9 страницFrobenius Method for Solving Differential EquationsMario PetričevićОценок пока нет
- Fatigue Life Prediction of A320-200 Aileron Lever Structure of A Transport AircraftДокумент4 страницыFatigue Life Prediction of A320-200 Aileron Lever Structure of A Transport AircraftMohamed IbrahimОценок пока нет
- LOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorДокумент1 страницаLOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorHorizon 99Оценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Three Bucket Method & Food ServiceДокумент4 страницыThree Bucket Method & Food Servicerose zandrea demasisОценок пока нет
- r32 - Rb26dett Ecu PinoutДокумент1 страницаr32 - Rb26dett Ecu PinouttospotОценок пока нет
- College of Medicine & Health SciencesДокумент56 страницCollege of Medicine & Health SciencesMebratu DemessОценок пока нет
- SmartRunway SmartLandingДокумент39 страницSmartRunway SmartLandingMikeОценок пока нет
- Fajar Secondary Sec 3 E Math EOY 2021Документ16 страницFajar Secondary Sec 3 E Math EOY 2021Jayden ChuaОценок пока нет
- Appendix C: Time Value of MoneyДокумент15 страницAppendix C: Time Value of MoneyrockerОценок пока нет
- Cdd153167-Samsung Un32d6500vf Un32 40 46 55d6400uf 6420uf 6450uf 6500vf 6900wf Chassis U63a SM PDFДокумент87 страницCdd153167-Samsung Un32d6500vf Un32 40 46 55d6400uf 6420uf 6450uf 6500vf 6900wf Chassis U63a SM PDFMilciades MurilloОценок пока нет
- Orientation Report PDFДокумент13 страницOrientation Report PDFRiaz RasoolОценок пока нет
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Common Herbs and Foods Used As Galactogogues PDFДокумент4 страницыCommon Herbs and Foods Used As Galactogogues PDFHadi El-MaskuryОценок пока нет
- Takara 2012Документ57 страницTakara 2012Deepak Ranjan SahooОценок пока нет
- Sensor Controlled Animatronic Hand: Graduation Project PresentationДокумент24 страницыSensor Controlled Animatronic Hand: Graduation Project PresentationAnonymous D2FmKSxuuОценок пока нет
- Edexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)Документ16 страницEdexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)FardeenKhanОценок пока нет
- News Writing April 2019Документ39 страницNews Writing April 2019Primrose EmeryОценок пока нет
- Gps Vehicle Tracking System ProjectДокумент3 страницыGps Vehicle Tracking System ProjectKathrynОценок пока нет
- NitrocelluloseДокумент7 страницNitrocellulosejumpupdnbdjОценок пока нет
- كونكت بلس - 2 ابتدائي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 2Документ86 страницكونكت بلس - 2 ابتدائي - ترم 1 - مذكرة 2cafubodoОценок пока нет
- Sanchez 07 Poles and Zeros of Transfer FunctionsДокумент20 страницSanchez 07 Poles and Zeros of Transfer FunctionsYasmin KayeОценок пока нет
- GT ĐỀ 04Документ39 страницGT ĐỀ 04Cao Đức HuyОценок пока нет
- Chemistry 12: Provincial ExaminationДокумент25 страницChemistry 12: Provincial ExaminationCát TriệuОценок пока нет
- Datasheet Optris XI 410Документ2 страницыDatasheet Optris XI 410davidaldamaОценок пока нет