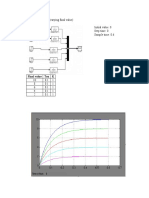
Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Загружено:
Princess Janine CatralОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Effect of PH On Enzyme Activity
Загружено:
Princess Janine CatralАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity
Biochemical Engineering
Problem Statement: Consider an enzyme reaction mechanism where substrate S can be
reversibly protonated and only the protonated form (SH+) can reversibly combine with an
enzyme E to form an active complex (ESH+), which then irreversibly leads to a product PH+.
ki
S + H+ <------> SH+
k-i
k1 k2
SH+ + E <------> ESH+ ------> E + PH+
k-1
a. Derive the rate expression v=dp/dt as a function of S, H, P, and E0. Set up the equations;
solve them only when time permits. The following is the eventual expression, provided
here in case you think you need it to answer questions in the next steps.
b. v=vm*s/(Km*Ki/H+s)
Solution:
See the following files that discuss the effect of pH on enzyme activity ("Mechanism #1,
Acid Enzyme").
o Snapshot of Mathcad Screen (ph.gif)
o Mathcad File (ph.mcd)
Note that the rate expression is different from Eqn (3.45) of Shuler & Kargi.
c. Is the reaction rate higher in acidic or alkaline condition? Roughly sketch a plot of
reaction rate versus pH.
Solution:
Higher reaction rate in acidic conditions.
Вам также может понравиться
- Downstream Bioprocessing StepsДокумент2 страницыDownstream Bioprocessing StepsPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- RAMP RESPONSE (Single Model) Ramp Parameters Values: Slope 1 Start Time 0 Initial Output 0 Tau 0.1 K 1Документ7 страницRAMP RESPONSE (Single Model) Ramp Parameters Values: Slope 1 Start Time 0 Initial Output 0 Tau 0.1 K 1Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Nuevo Series ProloguesДокумент2 страницыNuevo Series ProloguesPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- DTI Project Proposal Edit 1Документ9 страницDTI Project Proposal Edit 1Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Calibration of Rectangular NotchДокумент4 страницыCalibration of Rectangular NotchPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Simulink Exercise - Princess Janine B. CatralДокумент4 страницыSimulink Exercise - Princess Janine B. CatralPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ6 страницChapter 1Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Quiz #4: Biochemical Engineering Fall 2003Документ5 страницQuiz #4: Biochemical Engineering Fall 2003Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Michaelis-MentenДокумент2 страницыComparison of Michaelis-MentenPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Online Biology BookДокумент3 страницыOnline Biology BookPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Quiz #3: Biochemical Engineering Fall 2003Документ5 страницQuiz #3: Biochemical Engineering Fall 2003Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Research PracticumДокумент4 страницыResearch PracticumPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Biodegradation in A Packed Bed ColumnДокумент2 страницыBiodegradation in A Packed Bed ColumnPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Board Questions November 2003Документ3 страницыBoard Questions November 2003Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Environmental Constraints and AnalysisДокумент1 страницаEnvironmental Constraints and AnalysisPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Timeline of Marawi CrisisДокумент8 страницTimeline of Marawi CrisisPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Vince F. Nonato @vincenonatoinq: Amid Boracay Sludge, House Probe Sought On Dot'S Plans For Sustainable TourismДокумент12 страницVince F. Nonato @vincenonatoinq: Amid Boracay Sludge, House Probe Sought On Dot'S Plans For Sustainable TourismPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- InsightДокумент36 страницInsightHuzaifa JalilОценок пока нет
- 2017 Events in PHДокумент5 страниц2017 Events in PHPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Dengvaxia IssueДокумент11 страницDengvaxia IssuePrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Wireless Power-The BasicsДокумент18 страницWireless Power-The BasicsPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Supercritical CO2 ExtractionДокумент6 страницSupercritical CO2 ExtractionPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- ChE Review - Chem and Phy Prin 2Документ4 страницыChE Review - Chem and Phy Prin 2Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- PUV Modernization ProgramДокумент7 страницPUV Modernization ProgramPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Research NotesДокумент2 страницыResearch NotesPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Methodology MORДокумент1 страницаMethodology MORPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ6 страницChapter 1Princess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- Tut. 05 - Cost Targeting FinalДокумент4 страницыTut. 05 - Cost Targeting Finalpeterbookworm2014Оценок пока нет
- Solved Problems in Fluid MechanicsДокумент19 страницSolved Problems in Fluid MechanicsPrincess Janine CatralОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)