Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)
Загружено:
Shubhash Joshi0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
43 просмотров2 страницыLesson Plan of Thermodynamics
Оригинальное название
Lesson Plan
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документLesson Plan of Thermodynamics
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
43 просмотров2 страницыFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)
Загружено:
Shubhash JoshiLesson Plan of Thermodynamics
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer (ME 402)
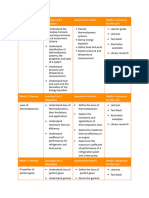
Chapter Topic Details Hours Remarks
1.1 Definition and scope of Engineering Thermodynamics
1.2 Value of energy to society
1.3 Microscopic versus Macroscopic Viewpoint
1.4 Concepts and definitions
1.4.1 System, Surrounding, Boundary and Universe, Closed Systems, Open
Systems, and Isolated Systems This chapter includes the basic introduction to
1 Introduction 6 the course. It also includes the basic
1.4.2 Thermodynamic Properties: Intensive, Extensive and Specific Properties terminology used in the syllabus.
1.4.3 Thermodynamics Equilibrium
1.4.4 State, Process and Path, Cyclic Process, Quasi-equilibrium Process,
Reversible and Irreversible Process
1.4.5 Common Properties, Pressure, Specific Volume, Temperature
1.5 Zeroth Law Thermodynamics, Equality of Temperature
2.1 Energy and its meaning
2.2 Stored Energy and Transient Energy, Total Energy
2.3 Energy Transfer This chapter includes the basics of energy
transfer. The equations of work transfer for
2 Energy and Energy Transfer 2.3.1 Heat Transfer 6 some basic processes are also derived and
students learn to solve basic problems involving
2.3.2 Work Transfer air.
2.4 Expression for displacement work Transfer
2.5 Power
3.1 Pure Substance and State Postulate
3.2 Ideal Gas and Ideal Gas Relations
This chapter includes the concept of pure
3.3 Two Phase (Liquid and Vapor) System: Phase Change, Subcooled Liquid,
substance and the saturation curve for water.
Saturated Liquid, Wet Mixture, Critical Point, Quality, Moisture Content, Saturated
3 Properties of Common Substances 8 The students learn to read the steam tables
Vapor and Superheated Vapor
and solve basic problems involving water and
steam.
3.4 Properties of Two Phase Mixtures
3.5 Other Thermodynamic Properties: Internal Energy, Enthalpy, and Specific
Heats
4.1 First Law of thermodynamics for Control mass, and for Control mass
undergoing cyclic process
This chapter includes the basics of first law of
4.2 First law of Thermodynamics for Control Volume
thermodynamics. Students learn about the
4 First Law of Thermodynamics 10 conservation of energy principle and learn to
4.3 Control Volume Analysis: Steady State Analysis and Unsteady state
perform problems involving heat and work
analysis
transfer.
4.4 Control Volume application: Steady and Unsteady Work Applications and
Steady and Unsteady flow applications
5.2 Entropy and second law of thermodynamics for an isolated system
5.3 Reversible and irreversible Processes
5.4 Entropy and Process Relation for an Ideal Gases and Incompressible
substances
This chapter includes the basics of second law
5.5 Control mass and control volume formulation of second law
of thermodynamics. Students learn about both
5 Second Law of Thermodynamics 10
control mass and control volume and simple
5.6 Isentropic process for an Ideal gas and for an incompressible substances
calculations of both involving air and water.
5.7 Carnot Cycle, Carnot Efficiency
5.7.1 Heat Engine and Thermal Efficiency, Heat Pump, Refrigerator and
coefficient of Performance(COP)
5.7.2 Kelvin-Planck and Clausius Statenebts of the Second law of
thermodynamics and their equivalence
6.1 Classification of Cycles
6.2 Air Standard Analysis
6.2.1 Otto Cycle
This chapter includes the introduction to the
6 Thermodynamic Cycles 6.2.2 Diesel Cycle 10 basic thermodynamic cycles and calculations
involving them.
6.2.3 Brayton Cycle
6.3 Rankine Cycle
6.4 Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle
7.1 Basic Concepts and Modes of Heat Transfer
7.2 One dimensional steady state heat conduction through a plane wall
7.3 Radial steady state heat conduction through a hollow cylinder
This chapter includes the basics of different
7 Introduction to Heat transfer 7.4 Heat flow through composite structures 10
modes of heat transfer and their calculations.
7.4.1 Composite Plane wall
7.4.2 Multilayer tubes
7.5 Electrical Analogy for thermal resistance
Total Hours 60
References
1. “Engineering Thermodynamics”, E. Rathakrishnan, Tata Mc Graw Hill.
2. “Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics”, J. R. Howell & R. O. Buckius, McGraw Hill Publishers
3. “Fundamentals of Thermodynamics”, V. Wylen, Sonntag & Borgnakke, 6th Edition, Wiley
4. “Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics”, M. J. Moran & H. N. Shapiro, 5th Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
5. “Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach”, Y. A. Cengel & M.A. Boles, 5th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2006
6. “Heat Transfer”, J. P. Holman, McGraw-Hill
7. “Heat Transfer: A Practical Approach”, Y. A. Cengel, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill
Вам также может понравиться
- Fundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat TransferДокумент2 страницыFundamentals of Thermodynamics and Heat TransferAnil MarsaniОценок пока нет
- Atd Course HandoutДокумент5 страницAtd Course Handoutmaaz ahmadОценок пока нет
- Classical and Geometrical Theory of Chemical and Phase ThermodynamicsОт EverandClassical and Geometrical Theory of Chemical and Phase ThermodynamicsОценок пока нет
- Thermo SyllabusДокумент2 страницыThermo SyllabusRobert DelfinОценок пока нет
- Steam Turbine Buy OnkarДокумент965 страницSteam Turbine Buy OnkarSandip Kumar100% (5)
- Applied Thermodynamics by Onkar Singh.0001 PDFДокумент330 страницApplied Thermodynamics by Onkar Singh.0001 PDFImran TahirОценок пока нет
- Applied Thermodynamics by Onkar Singh.0001 PDFДокумент330 страницApplied Thermodynamics by Onkar Singh.0001 PDFanon_688074713Оценок пока нет
- ETD E-Note 31072018 104019AM PDFДокумент172 страницыETD E-Note 31072018 104019AM PDFJatin PandeyОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 14 Weeks of HellДокумент7 страницThermodynamics 14 Weeks of HellseirphenyoОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics ManualДокумент99 страницThermodynamics ManualBISHAL AdhikariОценок пока нет
- Course OutlineДокумент6 страницCourse OutlineanleyedemeОценок пока нет
- Intro To ThermoДокумент12 страницIntro To ThermoLilian MumoОценок пока нет
- 208 SyllabusДокумент4 страницы208 SyllabusMaman GocekОценок пока нет
- Applied Thermodynamics Third Edition PDFДокумент965 страницApplied Thermodynamics Third Edition PDFTARUN RAVULAKOL100% (3)
- Basic Thermodynamics SyllabusДокумент4 страницыBasic Thermodynamics SyllabusKrish RobertsОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics by Onkar SinghДокумент330 страницThermodynamics by Onkar SinghVinay Kedhari100% (2)
- Lesson Plan CHE433 150914 3Документ8 страницLesson Plan CHE433 150914 3Mohd Hafiz AhmadОценок пока нет
- Department Dept. Code Course Title Course Code Pre-Requisite(s) Credit Hours Course Objective No. Assigned Program Learning Outcome (PLO) Level ToolДокумент4 страницыDepartment Dept. Code Course Title Course Code Pre-Requisite(s) Credit Hours Course Objective No. Assigned Program Learning Outcome (PLO) Level ToolShahzad AsifОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics: EngineeringДокумент7 страницThermodynamics: EngineeringMayank SoniОценок пока нет
- Bits F111-Course HandoutДокумент3 страницыBits F111-Course HandoutPPОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Thermo - NewДокумент4 страницыLesson Plan Thermo - Newविशाल पुडासैनीОценок пока нет
- Engineering Thermodynamics E-Note 04112015 044130AMДокумент189 страницEngineering Thermodynamics E-Note 04112015 044130AMDipesh Patel100% (3)
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Course Code: 3350505Документ5 страницChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Course Code: 3350505Arpit vaishnavОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsДокумент3 страницыSyllabus Book ME3 Engg ThermodynamicsGautam GunjanОценок пока нет
- Defense Engineering College Department of Motor Vehicle TechnologyДокумент5 страницDefense Engineering College Department of Motor Vehicle TechnologyGODОценок пока нет
- RAC Lecture 4Документ14 страницRAC Lecture 4api-3734466Оценок пока нет
- Full Download Original PDF Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 8th Edition PDFДокумент41 страницаFull Download Original PDF Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 8th Edition PDFwilliam.mayson35098% (40)
- Bai Giang Chuong 1 1Документ15 страницBai Giang Chuong 1 120nclcdutОценок пока нет
- SyllabusДокумент3 страницыSyllabusTMedhin MisganawОценок пока нет
- Thermal Science 2ndДокумент2 страницыThermal Science 2ndSyh TfkОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Документ36 страницChapter 1 - Chemical Equilibrium Part 1Ng Kee NainОценок пока нет
- CHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedДокумент24 страницыCHEM 114 PRELIM Module 1 1st Sem 2020 2021revisedJULLIE MAE SAULON100% (1)
- Basic-Thermodynamics KLS PDFДокумент6 страницBasic-Thermodynamics KLS PDFAnonymous 5HYsyrddpОценок пока нет
- TD Lecture Plan 2022Документ2 страницыTD Lecture Plan 2022Abdul Majid KhanОценок пока нет
- C FakepathBasics Chemical Thermodinamics SyllabusДокумент4 страницыC FakepathBasics Chemical Thermodinamics Syllabusxz4wvhpks6Оценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics 1: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezДокумент35 страницThermodynamics 1: Precious Arlene Villaroza-MelendrezJhonny English100% (1)
- The Thermodynamics of Phase and Reaction Equilibria 2Nd Edition Ismail Tosun Full Chapter PDF ScribdДокумент67 страницThe Thermodynamics of Phase and Reaction Equilibria 2Nd Edition Ismail Tosun Full Chapter PDF Scribdcarolyn.dollar168100% (5)
- Combustión: Análisis Termodinámico, Químico y Transferencia de MasaДокумент365 страницCombustión: Análisis Termodinámico, Químico y Transferencia de MasaPaulo Cæsar SlowОценок пока нет
- 2 005 Coursenotes-1Документ647 страниц2 005 Coursenotes-1Noom NutthawutОценок пока нет
- Hydrothermal Properties of Materials: Experimental Data on Aqueous Phase Equilibria and Solution Properties at Elevated Temperatures and PressuresОт EverandHydrothermal Properties of Materials: Experimental Data on Aqueous Phase Equilibria and Solution Properties at Elevated Temperatures and PressuresVladimir ValyashkoОценок пока нет
- Cash and Cash EquivalentДокумент2 страницыCash and Cash EquivalentJovani Laña100% (1)
- Arnold Emergency Motion 22cv41008 Joseph Et AlДокумент13 страницArnold Emergency Motion 22cv41008 Joseph Et AlKaitlin AthertonОценок пока нет
- HarmanДокумент10 страницHarmanharman04Оценок пока нет
- 05 Solution 1Документ18 страниц05 Solution 1Mohar SinghОценок пока нет
- Editorial by Vishal Sir: Click Here For Today's Video Basic To High English Click HereДокумент22 страницыEditorial by Vishal Sir: Click Here For Today's Video Basic To High English Click Herekrishna nishadОценок пока нет
- Conflict of Laws in Legitimacy, Legitimation and Adoption: Under The Guidance ofДокумент13 страницConflict of Laws in Legitimacy, Legitimation and Adoption: Under The Guidance ofShivansh JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Springfield Development Corporation, Inc. vs. Presiding Judge, RTC, Misamis Oriental, Br. 40, Cagayan de Oro City, 514 SCRA 326, February 06, 2007Документ20 страницSpringfield Development Corporation, Inc. vs. Presiding Judge, RTC, Misamis Oriental, Br. 40, Cagayan de Oro City, 514 SCRA 326, February 06, 2007TNVTRLОценок пока нет
- Afu 08504 - International Capital Bdgeting - Tutorial QuestionsДокумент4 страницыAfu 08504 - International Capital Bdgeting - Tutorial QuestionsHashim SaidОценок пока нет
- Model 9000: Use & Care GuideДокумент12 страницModel 9000: Use & Care GuidevicdiaОценок пока нет
- 7 PDFДокумент123 страницы7 PDFGo GoОценок пока нет
- Preamble 1Документ2 страницыPreamble 1api-273002310Оценок пока нет
- The Following Payments and Receipts Are Related To Land Land 115625Документ1 страницаThe Following Payments and Receipts Are Related To Land Land 115625M Bilal SaleemОценок пока нет
- Ioana Ramona JurcaДокумент1 страницаIoana Ramona JurcaDaia SorinОценок пока нет
- Farooq e Azam Ka Khuaf e KhudaДокумент42 страницыFarooq e Azam Ka Khuaf e KhudaAneeka SyedОценок пока нет
- Motion To Disqualify MCAO - 7-31-13Документ14 страницMotion To Disqualify MCAO - 7-31-13crimefileОценок пока нет
- Federal Discrimination Lawsuit Against City of Evanston, City Manager Wally BobkiewiczДокумент51 страницаFederal Discrimination Lawsuit Against City of Evanston, City Manager Wally BobkiewiczJonah MeadowsОценок пока нет
- K12-14 (FGD) Baase - Henry - GoF5e - Ch9 Professional Ethics and ResponsibilityДокумент32 страницыK12-14 (FGD) Baase - Henry - GoF5e - Ch9 Professional Ethics and ResponsibilityirgiОценок пока нет
- Dell EMC Partner Training GuideДокумент23 страницыDell EMC Partner Training GuideDuško PetrovićОценок пока нет
- Good MoralДокумент8 страницGood MoralMary Grace LemonОценок пока нет
- 00 Introduction ATR 72 600Документ12 страниц00 Introduction ATR 72 600destefani150% (2)
- Controlled Parking Zones Within Tower HamletsДокумент1 страницаControlled Parking Zones Within Tower Hamletsmoshkur.chowdhuryОценок пока нет
- ChrisДокумент5 страницChrisDpОценок пока нет
- RIGHT AGAINST SELF INCRIMINATION-ReviewerДокумент3 страницыRIGHT AGAINST SELF INCRIMINATION-ReviewerAnna Katrina QuanicoОценок пока нет
- Copyreading and HWДокумент16 страницCopyreading and HWJenniferОценок пока нет
- Week 9 11 Intro To WorldДокумент15 страницWeek 9 11 Intro To WorldDrea TheanaОценок пока нет
- Form PDF 344472690310722Документ11 страницForm PDF 344472690310722NandhakumarОценок пока нет
- Phases in Conflict Resolution:: FactsДокумент4 страницыPhases in Conflict Resolution:: FactsCMLОценок пока нет
- Trailhead Virtual Bootcamp For Platform Developer Slide DeckДокумент111 страницTrailhead Virtual Bootcamp For Platform Developer Slide DeckBrenda Paiva100% (1)
- Tumang V LaguioДокумент2 страницыTumang V LaguioKarez MartinОценок пока нет
- Al HallajДокумент8 страницAl HallajMuhammad Al-FaruqueОценок пока нет