Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
12 PTSD
Загружено:
alaysa udok0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров1 страницаptsd
Оригинальное название
12-PTSD
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документptsd
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
18 просмотров1 страница12 PTSD
Загружено:
alaysa udokptsd
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Effectiveness of coping resources.
Presence of pre-existing psychopathology.
Posttraumatic stress disorder can occur in a person who has Outcomes of previous experiences with stress/trauma.
witnessed an extraordinarily terrifying and potentially deadly Behavioral tendencies (temperament)
event. After the traumatic event, the person re-experiences all Current psychosocial development stage.
or some of it through dreams or waking recollections and Demographic factors (e.g. age, socioeconomic status,
responds defensively to these flashbacks. New behaviors education)
develop related to the trauma such as sleep difficulties,
hypervigilance, thinking difficulties, severe startle response, THE RECOVERY ENVIRONMENT. It has been suggested that the
and agitation (APA, 2000). quality of the environment in which the individual attempts to
work through the traumatic experience is correlated with the
Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is described by the DSM- outcome. Environmental variable include:
IV-TR as the development of characteristics symptoms
following exposure to an extreme traumatic stressor involving Availability of social supports.
a personal threat to physical integrity or to the physical The cohesiveness and protectiveness of family and
integrity of others. friends.
The attitudes of society regarding the experience
The full symptom picture must be present for more than 1
Cultural and subcultural influences.
month and cause significant interference with social,
occupational, and other areas of functioning. If the symptoms Nursing Interventions:
have not been present for more than 1 month, the diagnosis
assigned is ACUTE STRESS DISORDERS. I. Accept client.
II. Establish trust.
Characteristics symptoms include: III. Stay with client during flashbacks.
IV. Encourage verbalization of trauma when ready.
1. Re-experiencing the traumatic event (Flashbacks)
V. Discuss coping strategies.
2. A sustained high level of anxiety or arousal.
VI. Assist client to try to comprehend the trauma and how it
3. A general numbing of responsiveness.
will be assimilated into his or her persona.
4. Intrusive recollections or nightmares of the event are
common.
PSCYHOSOCIAL THEORY:
On psychosocial model that has become widely accepted
seeks to explain why certain persons exposed to massive
trauma develop PTSD and others do not. Variables include
characteristics that related to (1) the traumatic experience,
(2) the individual, and (3) the recovery environment.
THE TRAUMATIC EXPERIENCE. Specific characteristics relating
to the trauma have been identified as crucial elements in the
determination of an individual’s long-term response to stress.
They include:
Severity and duration of the stressor.
Degree of anticipatory preparation for the event.
Exposure to death
Numbers affected by the life threat
Amount of control over recurrence
Location where the trauma was experienced (ex: familiar
surroundings, at home, in a foreign country)
THE INDIVIDUAL. Variable that are considered important in
determining an individual’s response to trauma include:
Degree of ego strength
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Letting Go of Shame and GuiltДокумент7 страницLetting Go of Shame and Guilteng.tahasuliman100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Nursing Audit ToolДокумент2 страницыNursing Audit Toolalaysa udok100% (2)
- WmsuДокумент2 страницыWmsualaysa udok95% (21)
- TTIДокумент5 страницTTIFarahZahidiОценок пока нет
- SMEPA 2020-2021: May Anne C. AlmarioДокумент19 страницSMEPA 2020-2021: May Anne C. AlmarioMay Anne Almario100% (3)
- 8 Coping With ANXIETYДокумент17 страниц8 Coping With ANXIETYalaysa udokОценок пока нет
- Saussures Model of Communication 2....Документ17 страницSaussures Model of Communication 2....Roan MalicdemОценок пока нет
- Zamboanga City. With An Average Rating of 91.4 PercentДокумент1 страницаZamboanga City. With An Average Rating of 91.4 Percentalaysa udokОценок пока нет
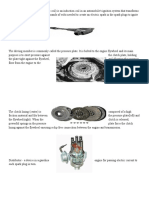
- An Ignition CoiДокумент5 страницAn Ignition Coialaysa udokОценок пока нет
- 0802 PeerДокумент1 страница0802 Peeralaysa udokОценок пока нет
- 9 PsychДокумент2 страницы9 Psychalaysa udokОценок пока нет
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)Документ1 страницаObsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)alaysa udokОценок пока нет
- 9 PsychДокумент2 страницы9 Psychalaysa udokОценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga CityДокумент6 страницRepublic of The Philippines Western Mindanao State University College of Nursing Zamboanga Cityalaysa udokОценок пока нет
- B. Lifestyle Modification ProgramДокумент2 страницыB. Lifestyle Modification Programalaysa udokОценок пока нет
- Module 2 in EL106Документ23 страницыModule 2 in EL106Gretchen TajaranОценок пока нет
- Madeline Cho ResumeДокумент2 страницыMadeline Cho Resumeapi-296561432Оценок пока нет
- Fuzzy & Nural NetworkДокумент24 страницыFuzzy & Nural NetworkRavi ShankarОценок пока нет
- Image Captioning Research PaperДокумент59 страницImage Captioning Research PaperabhishekОценок пока нет
- FML File FinalДокумент36 страницFML File FinalKunal SainiОценок пока нет
- Final Examination - Short Story (Pelecio, Jhaia)Документ3 страницыFinal Examination - Short Story (Pelecio, Jhaia)elianaОценок пока нет
- Behavioral Theories of CompensationДокумент13 страницBehavioral Theories of CompensationPankaj Mishra100% (1)
- EZДокумент52 страницыEZApryll Rose MayoОценок пока нет
- Akhuwat Internship ProgrammeДокумент2 страницыAkhuwat Internship ProgrammeAtiya FalakОценок пока нет
- UHB40102/40202: English For Occupational Purposes: Chapter Two: Job Seeking SkillsДокумент27 страницUHB40102/40202: English For Occupational Purposes: Chapter Two: Job Seeking SkillsSabrina AzharОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Human Exceptionality School Community and Family 12th EditionДокумент36 страницTest Bank For Human Exceptionality School Community and Family 12th Editionsloppy.obsidian.v8ovu100% (46)
- An Analysis of Descriptive Text in English Textbook Using Transitivity System (A Case Study of Reading Passages)Документ12 страницAn Analysis of Descriptive Text in English Textbook Using Transitivity System (A Case Study of Reading Passages)park ji minОценок пока нет
- How To Establish An Effective Reading Program - The EdvocateДокумент19 страницHow To Establish An Effective Reading Program - The EdvocateJobelle CanlasОценок пока нет
- Bertrand RussellДокумент23 страницыBertrand RussellNikhil LallОценок пока нет
- Pau Perez - Trauma, Culpa, Duelo - PsicoterapiaДокумент18 страницPau Perez - Trauma, Culpa, Duelo - PsicoterapiaRonaldoCainãОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент127 страницIntroductiondiona macasaquitОценок пока нет
- 7.1.3 Final Exam - ExamДокумент4 страницы7.1.3 Final Exam - ExamSophia Arredondo100% (1)
- Typology Based in MuseumДокумент3 страницыTypology Based in MuseumJackОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan 2 ExtinctДокумент4 страницыLesson Plan 2 Extinctapi-252208392Оценок пока нет
- Chelseys ResumeДокумент5 страницChelseys Resumeapi-393532659Оценок пока нет
- Individual Report QuestionДокумент7 страницIndividual Report QuestionFang May YeohОценок пока нет
- There Is No Right or Wrong Way Exploring Expressive Dance Assignments in Physical EducationДокумент15 страницThere Is No Right or Wrong Way Exploring Expressive Dance Assignments in Physical EducationWindi SaputraОценок пока нет
- 103ppt Develop Your Leaders From WithinДокумент12 страниц103ppt Develop Your Leaders From WithinA Aezat LKОценок пока нет
- Innovating To Learn, Learn To InnovateДокумент260 страницInnovating To Learn, Learn To Innovatemacovic2Оценок пока нет
- Cambridge IGCSE: GERMAN 0525/03Документ32 страницыCambridge IGCSE: GERMAN 0525/03Yahia Yasser Fathy G BОценок пока нет
- How To Integrate Literacy and Numeracy Skills inДокумент26 страницHow To Integrate Literacy and Numeracy Skills inGEMMA SISONОценок пока нет