Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
TPP e
Загружено:
Oliva R. SeguraИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TPP e
Загружено:
Oliva R. SeguraАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
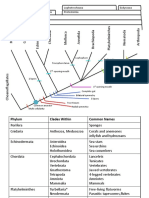
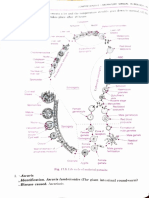
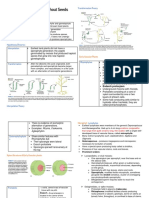
Tracheophyte Phylogeny
Vascular Plants – Systematics and Characteristics
H ornworts, Mosses, Liverworts see "B ryophyte " P hylogeny P oster
homosporous
Lycopodiales
lvs eligulate
sporangia reniform, basal on sporophyll or in terminal strobili Lycopodiaceae
shoots with lycophylls
dichopodial root: protoxylem endarch cormose to rhizotamous
stem protoxylem exarch lvs spiral, in basal rosette
Isoëtales
sporangia dorsiventral and transversely dehiscent microspores monolete
megaspores 50–300 Isoëtaceae
heterosporous
Lycophytes
lvs ligulate sporangia in axils of sporophylls
on 4-sided strobili; lvs 4-ranked
Selaginellales
microspores trilete
megaspores 4 Selaginellaceae
sporangiophores in terminal strobili
lvs whorled, fused into sheaths at base
Equisetales
stems ridged with internal hollow canals
spores with elaters 4–6, straplike Equisetaceae
Ophioglossales
sporophores: each leaf with sterile & fertile segments
(latter inclined relative to former)
Ophioglossaceae
Ferns roots unbranched, root hairs absent
collateral leaf vascular bundles
gametophyte nonphotosynthetic, often subterranean, mycorrhizal
roots absent
Psilotales
lvs reduced, veins 1 or 0
sporangia 2–3, fused: synangium Psilotaceae
Monilophytes
polycyclic siphonostele
Marattiales Marattiaceae
annulus on one side of sporangium
Osmundales Osmundaceae
sporophyte dominant
vascular tissue: receptacle elongate
Hymenophyllales
tracheids + sieve cells lvs thin, usually 1 cell layer
sporangia many sporangia in sori annulus sori marginal Hymenophyllaceae
zygote: tapetum plasmodial
1. division horizontal pseudoendospore + leptosporangia
siphonostele
variously vessels root steles with 3–5 protoxylem poles
Gleicheniales
stem protoxylem mesarch rhizome with scales; veins anastomosing
sporangia maturation simultaneous Gleicheniaceae
annulus transverse, subapical
Schizaeales Anemiaceae Lygodiaceae Schizaeaceae
aquatic; aerenchyma +
Salviniales
stems dichotomizing; leaf dimorphism
hairs heterosporous; sporocarps; annulus – Marsileaceae Salviniaceae
endospore
2-layered
Cyatheales
hairs +
sori terminal on veins Cyatheaceae
Liverworts
Aspleniaceae
Mosses (incl. Asplenoideae, Athyrioideae, Blechnoideae,
sporangial maturation mixed
Hornworts Cystopteridoideae, Diplaziopsidoideae, Rhachidosoroideae,
Polypodiales
sporangium with vertical annulus
euphyll Lycophytes
interrupted by stalk and stomium Thelypteridoideae, Woodsioideae)
leaf gaps
protoxylem exarch Ferns
roots monopodial
(incl. horsetails)
Polypodiaceae
30-kb cp inversion Palmferns
Ginkgo (incl. Polypodioideae, Davallioideae,
Ephedra Didymochlaenoideae, Dryopteridoideae, Hypodematioideae,
Welwitschia
Seed Gymnosperms Gnetum Lomariopsidoideae, Oleandroideae, Tectarioideae)
Conifers
Euphyllophytes
Plants
ANITA grade
Pteridaceae Dennstaedtiaceae
Magnoliids
Angiosperms Monocots Lindsaeaceae Lonchitidaceae
Fabids
Cystodiaceae Saccolomataceae
Rosids Malvids
Lamiids
Asterids Campanulids
in ♀: whorls of individual megasporophylls
Cycadaceae
at trunk apex alternate with trophophylls
pachycaulous; pinnate megaphylls (no seed cones) Cycas
dioecious; males with pollen cones
motile sperm cells released within ovule
roots with N2-fixing cyanobacteria
seed cones with 2[3] seeds
per megasporophyll
Bowenia Ceratozamia Chigua Dioon
Cycadales lignins with syringaldehydes
Zamiaceae Encephalartos Lepidozamia Macrozamia
Microcycas Stangeria Zamia
spermatozoids released from dioecious; stout short shoots with
Ginkgoaceae
branched pollen tube lvs flabelliform, dichotomously veined, deciduous
acting as anchoring organ ovules 2 (basal collar); cotyledons 2 Ginkgo
Ginkgoales xeromorphic, lvs scale-like, sheathed, shed early
stems narrow, striate, photosynthetic
Ephedraceae
seed cones: 1–3 ovules; double fertilization
ovules/seeds not cotyledons 2 Ephedra
enclosed by carpel
pollen tube haustorial
primarily striate pollen caudex
anemophilous binucleate sperm lvs 2 (straplike) life-long continuous growth
dioecious venation parallel
Welwitschiaceae
primary endosperm
no bisexual strobili
vessels
♀ gametophyte tubes grow towards pollen tubes Welwitschia
porose
perforation
ectomycorrhizal
plates
Gymnosperms
lvs opposite, simple, broad, reticulate
Gnetaceae
(angiosperm-like: convergence)
laticifers Gnetum
resin canals; lvs linear (needles)
monoecious
pollen mostly 2-saccate; ovules 2, inverted
Abies Cathaya Cedrus Hesperopeuce
seeds winged
Pinaceae Keteleeria Larix Nothotsuga Pinus Picea
Conifers
eustele
pollen Pseudolarix Pseudotsuga Tsuga
pollen tube lvs broad to acicular
heterospory pollen not saccate
seeds seed cones large, disintegrate
secondary growth cotyledons 2–4
Araucariaceae Agathis Araucaria Wollemia
Seed Plants P
Conifers
roots with nodules; dioecious
Acmopyle Afrocarpus Dacrycarpus Dacrydium Falcatifolium
i 1 ovule/scale, cone often one seeded
Halocarpus Lagarostrobus Lepidothamnus Manoao
Podocarpaceae
receptacle fleshy; epimatium/carpidium fleshy
n cotyledons 2
Microcachrys Nageia Parasitaxus Pherosphaera Phyllocladus
Spermatophytes
Theodor C. H. Cole, Dipl. Biol. a
Podocarpus Prumnopitys Retrophyllum Saxegothaea
Institute of Pharmacy and Molecular Biotechnology
Heidelberg University
l monoecious
e
Sciadopityaceae
Im Neuenheimer Feld 364 lvs as scales; cladodes
D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany s
ovules 7–9 Sciadopitys
evergreen; pollen cones tiny,
loss of spermatozoids
peltate microsporangiophores
Conifers
nucellar siphonogamy
1 ovule, 1 seed/cone, arillate
Amentotaxus Austrotaxus Cephalotaxus
cotyledons 2
Taxaceae Pseudotaxus Taxus Torreya
cone scales
Prof. Dr. Hartmut H. Hilger opposite Actinostrobus Athrotaxis Austrocedrus Callitris
monoecious (except Juniperus dioecious)
Dahlem Centre of Plant Sciences (DCPS) lvs scale-like Calocedrus Chamaecyparis Cryptomeria Cunninghamia
Institute of Biology - Plant Morphology and Systematics pollen not saccate; ovules 1–20 Cupressus Diselma Glyptostrobus Fitzroya Fokienia
Freie Universität Berlin
Altensteinstr. 6
cotyledons many
seed cones terminal Cupressaceae Juniperus Libocedrus Metasequoia Neocallitropsis
D-14195 Berlin, Germany Papuacedrus Pilgerodendron Platycladus
Sequoia Sequoiadendron Taiwania Taxodium
Tetraclinis Thuja Thujopsis Widdringtonia Xanthocyparis
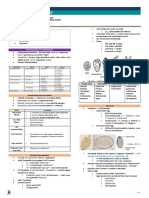
_______________________________________________________
• hypothetical tree based on molecular phylogenetic data (Feb. 2014)
• branch lengths deliberate, not expressing actual time scale position bisexual flower; fruit (ovules enclosed by carpel)
of many characters on tree unclear loss of spermatozoids
• if a character is marked as being a potential synapomorphy at a node/for a clade, pollen tube penetrating stigma/style/nucellus (penetrating siphonogamy)
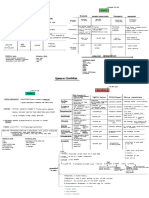
A ngiosperms
this does not mean that all members of that clade possess that character
Angiosperm P hylogeny P oster
vessels; pollenkitt; primarily zoophilous;
• References: Judd W et al. (2007); Simpson M (2010); Soltis DE et al. (2005/2011);
Christenhusz MJM et al. (2011/2014)
double fertilization: triploid endosperm see
see also: Stevens PF (2011) APweb – www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb
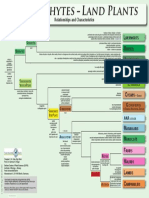
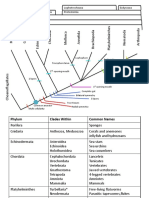
Angiosperm Tracheophte Bryophte
Phylogeny Phylogeny Phylogeny
Poster Poster Poster
Вам также может понравиться
- 2018 BHL Coloring BookДокумент17 страниц2018 BHL Coloring BookOliva R. Segura80% (5)
- A Textbook of Botany. StrasburgerДокумент820 страницA Textbook of Botany. StrasburgerKevin I. SanchezОценок пока нет
- Pulp and Paper Chemistry and Technology Volume 1 - Wood Chemistry and Wood Biotechnology (De Gruyter, 2009)Документ321 страницаPulp and Paper Chemistry and Technology Volume 1 - Wood Chemistry and Wood Biotechnology (De Gruyter, 2009)AllanGuimarães100% (3)
- Pollination Class 12 Biology ProjectДокумент21 страницаPollination Class 12 Biology ProjectASHOK SAGAR85% (20)
- TABLE (Coccidia)Документ8 страницTABLE (Coccidia)TRISHA MAE ORDONAОценок пока нет
- Pollen and Spore Morphology, Plant Taxonomy - ErdtmanДокумент178 страницPollen and Spore Morphology, Plant Taxonomy - ErdtmanAndres Elgorriaga100% (1)
- Science6 Q2 Mod7 v4Документ22 страницыScience6 Q2 Mod7 v4Marijoy GucelaОценок пока нет
- Deuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateДокумент3 страницыDeuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateGiulia CostantiniОценок пока нет
- P3-Cole Al 2018 - Pôster TraqueófitasДокумент1 страницаP3-Cole Al 2018 - Pôster TraqueófitasDayane ValencioОценок пока нет
- Tracheophyte Phylogeny Poster (TPP) - Vascular Plants: Systematics and Characteristics, 2016Документ2 страницыTracheophyte Phylogeny Poster (TPP) - Vascular Plants: Systematics and Characteristics, 2016Dayvson CostaОценок пока нет
- Plant Kingdom ChartДокумент1 страницаPlant Kingdom ChartTanya SiyagОценок пока нет
- 3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Документ10 страниц3.kingdom Plantae NIE Class 11Sasuke UchihaОценок пока нет
- Embryophytes Land Plants - Relationships and Characteristics (2019)Документ1 страницаEmbryophytes Land Plants - Relationships and Characteristics (2019)Videsh RamsahaiОценок пока нет
- Filogenia de Briofitos SensulatoДокумент1 страницаFilogenia de Briofitos SensulatoYuyitoS2714Оценок пока нет
- BOT 3 Laboratory Hand-Out: Exercise 11. MonocotsДокумент5 страницBOT 3 Laboratory Hand-Out: Exercise 11. MonocotsAnna HarietОценок пока нет
- Exercise 6. Spore-Bearing Vascular Plants: Fern Allies: BOT 3 Laboratory Hand-OutДокумент4 страницыExercise 6. Spore-Bearing Vascular Plants: Fern Allies: BOT 3 Laboratory Hand-OutAnna HarietОценок пока нет
- Lecture 11 Systematics and Phylogeny, VirusesДокумент21 страницаLecture 11 Systematics and Phylogeny, Virusesnikitamzamo7Оценок пока нет
- Awesome Biology RecapДокумент2 страницыAwesome Biology Recapcarolinebrongelcopti24Оценок пока нет
- Exercise 12Документ7 страницExercise 12Anna HarietОценок пока нет
- Types of PteridophytesДокумент1 страницаTypes of PteridophytesprathitaprilОценок пока нет
- TABLE (Coccidia)Документ8 страницTABLE (Coccidia)TRISHA MAE ORDONAОценок пока нет
- Bryophyte Phylogeny Poster (BPP) - Systematics and Characteristics of Nonvascular Land Plants (Mosses, Liverworts and Hornworts) v7 (2019)Документ1 страницаBryophyte Phylogeny Poster (BPP) - Systematics and Characteristics of Nonvascular Land Plants (Mosses, Liverworts and Hornworts) v7 (2019)Videsh RamsahaiОценок пока нет
- Seedless Vascular Plants: Pteridophyta (Lycophyta and Monilophyta)Документ110 страницSeedless Vascular Plants: Pteridophyta (Lycophyta and Monilophyta)Maharani Putri ChaniaОценок пока нет
- Gruntmcodneoba Sainjonro Petrologia PDFДокумент233 страницыGruntmcodneoba Sainjonro Petrologia PDFDato ChikvaidzeОценок пока нет
- Diversity AnimalsДокумент20 страницDiversity AnimalsnithinjothimuruganОценок пока нет
- TREMATODESДокумент16 страницTREMATODESBalisi Manuel FranciscoОценок пока нет
- GR 311075Документ4 страницыGR 311075rdmpageОценок пока нет
- Classification of Pteridophytes PDFДокумент15 страницClassification of Pteridophytes PDFsobjanta tech and unboxingОценок пока нет
- Lecture 19 - Ferns and Allies 2 2023Документ37 страницLecture 19 - Ferns and Allies 2 2023rockybrar0238Оценок пока нет
- Malaria - Parasitosis Pediculosis Escabiosis - Toxo LeishmaniosisДокумент163 страницыMalaria - Parasitosis Pediculosis Escabiosis - Toxo LeishmaniosisUC SergioОценок пока нет
- 10 PlantEvol+BWДокумент38 страниц10 PlantEvol+BWgoldenboy3429Оценок пока нет
- BOT 3 Laboratory Hand-Out: Exercise 13: Core Eudicots: AsteridsДокумент4 страницыBOT 3 Laboratory Hand-Out: Exercise 13: Core Eudicots: AsteridsAnna HarietОценок пока нет
- Hours: PlanceДокумент1 страницаHours: PlanceSayandeep DuttaОценок пока нет
- Exercise 7Документ4 страницыExercise 7Anna HarietОценок пока нет
- Plant Kingdom M PDFДокумент10 страницPlant Kingdom M PDFAbu SubhanОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент10 страницPlant KingdomInfinite SinghОценок пока нет
- Functional Hermaphroditism in TeleostsДокумент43 страницыFunctional Hermaphroditism in TeleostsMaik_horaОценок пока нет
- Deuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateДокумент3 страницыDeuterostomia Protostomia Lophotrochozoa Ecdysozoa: Lophophore AcelomateGiulia CostantiniОценок пока нет
- TAB2Документ1 страницаTAB2Mihai ComanОценок пока нет
- Kingdom PlantaeДокумент72 страницыKingdom PlantaeMr. KОценок пока нет
- Maldonado Chapter 16 TREE OF LIFE PDFДокумент20 страницMaldonado Chapter 16 TREE OF LIFE PDFDiego MorodoОценок пока нет
- Plant ClassificationДокумент3 страницыPlant ClassificationAshutosh MishraОценок пока нет
- Lab Rep 14finalДокумент20 страницLab Rep 14finalReign RosadaОценок пока нет
- Agnatha Gnathostomata: - Jawless Vertebrates - Jawed VertebratesДокумент2 страницыAgnatha Gnathostomata: - Jawless Vertebrates - Jawed VertebratesCharles Jeff DoriaОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент156 страницUntitledCRISTIAN VILLOUTAОценок пока нет
- Pteridophytes PDFДокумент80 страницPteridophytes PDFJBОценок пока нет
- Kingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratoryДокумент6 страницKingdom Plantae Division Bryophyta: Systematics LaboratorySIlverОценок пока нет
- Ch. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsДокумент4 страницыCh. 21: Vascular Plants Without Seeds: ConceptsNexОценок пока нет
- 2 PlatyhelminthesДокумент1 страница2 Platyhelminthescameronjuli.patubo.sciОценок пока нет
- Animalia File 2023-1Документ12 страницAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniОценок пока нет
- 25MonocotOrigin PDFДокумент62 страницы25MonocotOrigin PDFPragyaОценок пока нет
- Genetika 1 PDFДокумент13 страницGenetika 1 PDFTiko ZazadzeОценок пока нет
- Economic Botany: San Diego State UniversityДокумент13 страницEconomic Botany: San Diego State UniversityLester MolinaОценок пока нет
- Q CY9qjeEemJ1w4LYV5qDg - Useful Biological Prefixes and SuffixesДокумент3 страницыQ CY9qjeEemJ1w4LYV5qDg - Useful Biological Prefixes and SuffixesPaula Andrea Melo ContrerasОценок пока нет
- Essential Biology 5.5: Classification: Hierarchical Level Acronym PLANT Example: ANIMAL Example: KingdomДокумент6 страницEssential Biology 5.5: Classification: Hierarchical Level Acronym PLANT Example: ANIMAL Example: KingdomjoeyacomineОценок пока нет
- Semiotika: SemioticsДокумент256 страницSemiotika: SemioticsTornike JokhadzeОценок пока нет
- ამოსაბეჭდი- (8 გვერდი)Документ8 страницამოსაბეჭდი- (8 გვერდი)xvichaОценок пока нет
- Sporozoa TableДокумент2 страницыSporozoa TableJoshua TrinidadОценок пока нет
- 1 Pteridophyta PsilotopsidaДокумент25 страниц1 Pteridophyta PsilotopsidaCDB 1st Semester 2077100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Introduction To Mycology HandoutsДокумент12 страницLesson 1 Introduction To Mycology HandoutsKhay Mae DonascoОценок пока нет
- Biol 141n - Exercise 6 - AnoosДокумент3 страницыBiol 141n - Exercise 6 - AnoosNovilla AnoosОценок пока нет
- Cycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisДокумент9 страницCycas Circinalis Div. Pinophyta - Pinus InsularisTers MedinaОценок пока нет
- 올림포스 독해의기본 1 Chapter1-3Документ27 страниц올림포스 독해의기본 1 Chapter1-3DinОценок пока нет
- 올림포스 독해의기본Документ250 страниц올림포스 독해의기본gminju925Оценок пока нет
- 1 3 올림포스+독해의+기본+1+ (1 95쪽) 230530 182909Документ155 страниц1 3 올림포스+독해의+기본+1+ (1 95쪽) 230530 182909당근Оценок пока нет
- Acidity and Antioxidant Activity ofДокумент9 страницAcidity and Antioxidant Activity ofOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Coffee Science - Everything You Need To Know About Milk - Perfect Daily GrindДокумент12 страницCoffee Science - Everything You Need To Know About Milk - Perfect Daily GrindOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- A Mini-Review On Coffee Composition and Health BenefitsДокумент6 страницA Mini-Review On Coffee Composition and Health BenefitsOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Magmile Dining 2010Документ1 страницаMagmile Dining 2010Oliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Revisiting The ClassicsДокумент10 страницRevisiting The ClassicsOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Magmile Interests 2010Документ1 страницаMagmile Interests 2010Oliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- 54 CermakДокумент1 страница54 CermakOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Magmile Shopping 2010Документ1 страницаMagmile Shopping 2010Oliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Audiotour MapДокумент1 страницаAudiotour MapOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Jackson Park Express: Effective December 18, 2011Документ2 страницыJackson Park Express: Effective December 18, 2011Oliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Chicago - Garden - MapДокумент1 страницаChicago - Garden - MapOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Structure HarvesterДокумент3 страницыStructure HarvesterOliva R. SeguraОценок пока нет
- Continuation of Plant KingdomДокумент17 страницContinuation of Plant KingdomMargie BagtasОценок пока нет
- Plant KingdomДокумент10 страницPlant KingdomInfinite SinghОценок пока нет
- Evolution of Seed PlantsДокумент18 страницEvolution of Seed PlantsMnqobi ZuluОценок пока нет
- Plants Adaptations NotesДокумент14 страницPlants Adaptations NotessmedificationОценок пока нет
- Gymnosperm Introduction Notes For BotanyДокумент6 страницGymnosperm Introduction Notes For BotanyAbhimanyu PandeyОценок пока нет
- Plant Kingdom Assertion and ReasonДокумент8 страницPlant Kingdom Assertion and ReasonChandrashekar LokanadamОценок пока нет
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Science Education)Документ41 страницаAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Department of Science Education)Tahirullah KhanОценок пока нет
- B.Sc. II SEM ASSIGNMENTS TOPICSДокумент3 страницыB.Sc. II SEM ASSIGNMENTS TOPICSKs648602Оценок пока нет
- Course HeroДокумент17 страницCourse HeroBalОценок пока нет
- Plant Diversity-Ii (Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Paleobotany)Документ48 страницPlant Diversity-Ii (Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms and Paleobotany)Anshita RajputОценок пока нет
- Adv Sci G7Документ22 страницыAdv Sci G7Ezequiel ManluluОценок пока нет
- Resumé TEC English Cours L2Документ45 страницResumé TEC English Cours L2Ayoub DJIDJELLIОценок пока нет
- Bio 104 2 Notes UploadsДокумент20 страницBio 104 2 Notes UploadsMbah chiomaОценок пока нет
- Past Year Bio320 Plantae Week 10Документ6 страницPast Year Bio320 Plantae Week 10ayunna ayunniОценок пока нет
- Why Is Biodiversity ImportantДокумент21 страницаWhy Is Biodiversity ImportantAishwarya BalamuruganОценок пока нет
- Plant DiversityДокумент9 страницPlant DiversityClaire FilipekОценок пока нет
- Lesson PlanДокумент2 страницыLesson PlanJohny VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Lab Manual BIO320 - Part 2 (F2F)Документ49 страницLab Manual BIO320 - Part 2 (F2F)NUR ALEEYA AFIFA BINTI ZAINAL ABIDINОценок пока нет
- Plant Kingdom-Important QuestionsДокумент3 страницыPlant Kingdom-Important QuestionsAnirudh KhannaОценок пока нет
- Bell Ringer Plant VocabularyДокумент1 страницаBell Ringer Plant VocabularyJosieA_YОценок пока нет
- CH 26 Instructor NotesДокумент15 страницCH 26 Instructor NotesKeith ValmontОценок пока нет
- Biodiversity of Plantae and Animalia (Sbu1023)Документ15 страницBiodiversity of Plantae and Animalia (Sbu1023)Arvind RaveeОценок пока нет
- BLG 1502 Tut Letter-1Документ18 страницBLG 1502 Tut Letter-1Fan eleОценок пока нет
- Kebo 103Документ14 страницKebo 103Devanshu JulkaОценок пока нет