Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
IT 111 Lecture Data Processing Cycle
Загружено:
John Michael Rasalan100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
371 просмотров3 страницыThe document provides an overview of computers and their components. It discusses:
1) The basic data processing cycle of input, process, and output.
2) The key elements and components of a computer including the central processing unit, memory, storage, input/output devices, and software.
3) A brief history of early computers from the abacus to modern computers invented by pioneers like Pascal, Babbage, and Engelbert.
4) The different types of computers including personal computers, mainframes, servers and how first generation computers relied on vacuum tubes.
Исходное описание:
IT 111 LECTURE
Оригинальное название
IT 111 Lecture
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document provides an overview of computers and their components. It discusses:
1) The basic data processing cycle of input, process, and output.
2) The key elements and components of a computer including the central processing unit, memory, storage, input/output devices, and software.
3) A brief history of early computers from the abacus to modern computers invented by pioneers like Pascal, Babbage, and Engelbert.
4) The different types of computers including personal computers, mainframes, servers and how first generation computers relied on vacuum tubes.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
100%(2)100% нашли этот документ полезным (2 голоса)
371 просмотров3 страницыIT 111 Lecture Data Processing Cycle
Загружено:
John Michael RasalanThe document provides an overview of computers and their components. It discusses:
1) The basic data processing cycle of input, process, and output.
2) The key elements and components of a computer including the central processing unit, memory, storage, input/output devices, and software.
3) A brief history of early computers from the abacus to modern computers invented by pioneers like Pascal, Babbage, and Engelbert.
4) The different types of computers including personal computers, mainframes, servers and how first generation computers relied on vacuum tubes.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
IT 111 Lecture
COMPUTER DATA PROCESSING CYCLE
Is an electronic programmable device that can
store process data to provide and retrieve a INPUT PROCESS OUTPUT
meaningful information
It is an electronic device, operating under the
control of instructions stored in its own INPUT - The initial data or input data are preparing in
memory, that can accept data, process the data some convenient form for processing.
according to specified rules, produce results,
and store the result. PROCESS -Input design data are changed and usually
combined with other information.
ELEMENTS OF COMPUTER
OUTPUT - Are results of the processing steps are
1. E = Electronic collected.
2. P = Programmable
3. S = Store COMPUTER HISTORY
4. P = Process ABACUS
5. R = Retrieve 4th Century BC
A simple counting aid may have been invented
DATA in Babylonia (Iraq)
It is a collection of unprocess items which can
include text, numbers, images, audio, video. BLAISE PASCAL (1623-1662)
It is the gold of 21st Century In, 1642, the French mathematician and
philosopher Blaise Pascal invented a calculating
device that would come to be called the The
INFORMATION Adding Machine
It a processed data Originally called a NUMERICAL WHEEL
Conveys meaning an it useful to people CALCULATOR or the PASCALINE.
ADVANTAGES OF USING COMPUTER CHARLES BABBAGE
1. S - Speed Born in 1791, and was an mathematician and
2. R - Reliability professor.
3. C - Consistency He was considered to be the FATHER OF
4. S - Storage COMPUTING.
5. C - Communication With CHARLES BABBAGE creation of the
ANALYTICAL ENGINE (1833)
DISADVANTAGES OF USING COMPUTER Analytical Engine - contained an ARITHMETIC
1. V - Violation of Privacy LOGIC UNIT (ALU) a complex digital circuit.
2. P - Public Safety
3. I - Impact of Labor Force DOUGLAS ENGELBERT
4. H - Health Risk An American Engineer and inventor
5. I - Impact of Environment He invented computer MOUSE in 1963, it was
made of WOOD
DATA PROCESSING
It is the manipulation of data into a more useful CATEGORIES OF PROCESSING
form.
Includes not only numbers/numerical calculations 1. M - MECHANICAL DATA PROCESSING
but also operations such as the classification of data uses a combination of manual procedures
and the transmission of data from one place to and mechanical equipment.
another.
2. E - ELECTRONIC DATA PROCESSING
Different types of input, output and storage
development are connected to an
electronic computer are connected to an
electronic computer to process data.
IT 111 Lecture
DATA PROCESSING OPERATIONS to send (transmit) and received data,
instructions to and from one or more
1. R - RECORDING computers.
o refers to the transfer of data onto some
form of document 2. SOFTWARE - also called program is one series
2. V - VERIFYING of related instruction organized a common and
o A careful checking of any errors from now to perform the...
the recorded data. Graphical User Interface (GUI) -
3. D - DUPLICATING interacts with software using text,
o Reproducing of data into many forms or graphics and visual image.
document Icon - A miniature image that
4. C - CLASSIFYING represent a program, an instruction
o This operation separates data into or some other objects.
various categories.
5. S - SORTING TWO CATEGORIES OF SOFTWARE
o Arranging the data in specific order
6. C - CALCULATING 1. SYSTEM SOFTWARE - it is any program that
o Arithmetic manipulation of data controls the computer hardware or that
7. S - SUMMARIZING AND REPORTING controls the computer hardware or than can be
o Reducing masses of data to a usable used to maintain the computer in some way so
form that it runs more efficiently.
8. M - MERGING
o Takes two more sets of data, all sets It serves as the interface between the user,
having been sorted by the same key application software and computer hardware.
and puts them together to form a single
sorted set of data THREE BASIC TYPE OF SYSTEM SOFTWARE
9. S - STORING a. OS = Operating System - it tells the
o Placing similar data into files for a computer how to use its own
future references. components.
10. R - RETRIEVING Ex. Windows, Linux, Macintosh, Ubuntu
o Recovering stored data and/or b. NS = Networking System - it allows
information when needed. computer to communicate and share
data across a network unlike controlling
TWO COMPONENTS OF COMPUTER operations and overseeing the network
security.
1. HARDWARE -it is tangible or the physical part of c. U = Utility - a program that makes the
the computer. computer system or perform highly
a. I - Input Device - any hardware compo- specialized functions. Ex. antivirus
nent that allows you to enter
instruction. Eg. Keyboard, mouse, mic 2. APPLICATION SOFTWARE - it tells the computer
camera etc. how to accomplish specific tasks such as word
b. O - Output Device - hardware that processing or drawing.
conveys information to one or more
people. 3. PEOPLEWARE - The one who design, maintain,
Eg. monitor, printer, speaker, projector and uses the computer system. Ex. Computer
c. S - System Unit (includes processor ) - it Programmer, System Analyst
was a case that contains component of
the computer that are used to process THE USERS ROLE
data. 1. S = Setting up the System
d. S- Storage Device - holds data, instruc- 2. I = Installing Software
tions and information of future use. 3. R = Running Programs
e. C - Communication Device - a hardware 4. M = Managing Files
components, that enables a computer 5. M = Maintaining the Systems
IT 111 Lecture
CATEGORIES OF COMPUTERS deal of electricity, generated a lot of heat, which was
1. PERSONAL COMPUTERS - it is a computer that often the cause of malfunctions.
can perform all of its input, processing, output
and storage activities itself. First generation computers relied on machine
a. D - Desktop Computer - designed that language, the lowest-level programming language
the system unit, input output desires an understood by computers, to perform operations, and
any other devices fit entirely on or they could only solve one problem at a time. Input was
under a desk or a table. based on punched cards and paper tape, and output
b. N - Notebook/Laptop - it is a portable was displayed on printouts.
personal computer often designed to fit
on your lap. The UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer) and
c. T - Tablet Pc's - Resembling a letter size ENIAC Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer
state. A special type that allows you to computers are examples of first-generation computing
write or draw on screen using a digital devices. The vacuum tube was developed by Lee De
pen. Forest. A vacuum tube is a device generally used to
d. M - Mobile Device - is a handheld tablet amplify a signal by controlling the movement of
of other device that is made for electrons in an evacuated space.
portability, and is therefore both
compact and lightweight. CHARACTERISTICS
S - Smart Phones 1) First generation computers were based on vacuum
P - Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) tubes.
H - Handheld Computer 2) The operating systems of the first generation
P - Portable Media Player computers were very slow.
D - Digital Cameras 3) They were very large in size.
G - Games console 4) Production of the heat was in large amount in first
generation computers.
2. SERVERS - it controls access to the hardware 5) Machine language was used for programming.
and software and resources on a network and 6) First generation computers were unreliable.
provide a centralize storage area programs, 7) They were difficult to program and use.
data and information.
3. MAINFRAMES - the large, expensive powerful What are Vacuum Tubes
computer that can handle hundreds or
thousands of connected user simultaneously. Alternatively referred to as an electron tube or valve.
4. SUPERCOMPUTERS - is the fastest, most The vacuum tube is a glass tube that has its gas
powerful computer and the most expensive. it removed, creating a vacuum. Vacuum tubes contain
is capable of processing more than one electrodes for controlling electron flow and were used
quadrillion instruction in a single second. in early computers as a switch or an amplifier.
5. EMBEDDED COMPUTER - a special purpose
computer that function as a component in a EDSAC - Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator
large product . consumer electronic home
automation device, automobiles, process EDVAC - Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic
controllers and robotics, computer devices and Computer
office machines.
Second Generation (1956-1963) Transistors
First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes
The first computers used vacuum tubes for circuitry and
magnetic drums for memory, and were often
enormous, taking up entire rooms. They were very
expensive to operate and in addition to using a great
Вам также может понравиться
- Ict 113 AssignmentДокумент11 страницIct 113 AssignmentTomi Wayne Malenga100% (1)
- LG 102 LectureДокумент532 страницыLG 102 Lectureanime admirersОценок пока нет
- Cavendish University Assignment Provides Solutions to Business Math ProblemsДокумент13 страницCavendish University Assignment Provides Solutions to Business Math ProblemsTomi Wayne Malenga0% (1)
- Computers in Our Daily LifeДокумент27 страницComputers in Our Daily Lifeleah manuelОценок пока нет
- Ict Chapter 3Документ10 страницIct Chapter 3Izwan JamaluddinОценок пока нет
- M I Chapter 2 Forms of CommunicationДокумент6 страницM I Chapter 2 Forms of CommunicationAniket Arun DokeОценок пока нет
- 1.2.2.1 Lab - My Local NetworkДокумент3 страницы1.2.2.1 Lab - My Local NetworksupiyandirОценок пока нет
- Second Syllabus IT E 203 Professional Elective 2 - Web Systems and TechnologiesДокумент6 страницSecond Syllabus IT E 203 Professional Elective 2 - Web Systems and TechnologiesMichaelangelo R. SerranoОценок пока нет
- Ugbs 102 Session 1-8 Combined Slides by AlbertДокумент472 страницыUgbs 102 Session 1-8 Combined Slides by AlbertEricaОценок пока нет
- Networking Principles GuideДокумент37 страницNetworking Principles GuideAdam MuizОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6: Input and Output: Extending Capabilities of Computers and Mobile DevicesДокумент5 страницChapter 6: Input and Output: Extending Capabilities of Computers and Mobile DevicesKim Jo OmolidaОценок пока нет
- Output Devices ExplainedДокумент13 страницOutput Devices Explainededuardo acuniaОценок пока нет
- Intro To CSS: Computer System Servicing NciiДокумент42 страницыIntro To CSS: Computer System Servicing NciiNieves JoshuaОценок пока нет
- Information Communication Technology: Chapter 2: Computers in Our Daily LifeДокумент7 страницInformation Communication Technology: Chapter 2: Computers in Our Daily Lifechenchen gabitanОценок пока нет
- Capstone Project 2 PDFДокумент28 страницCapstone Project 2 PDFBinder GrewalОценок пока нет
- Intro to Computer Programming ConceptsДокумент12 страницIntro to Computer Programming Conceptsiqa11Оценок пока нет
- Disadvantages of IctДокумент17 страницDisadvantages of IctLiezel Tolentino ArmadaОценок пока нет
- Communication Skills PPT PPT Download Communication Skills OhpДокумент84 страницыCommunication Skills PPT PPT Download Communication Skills OhpPrakash ThwalОценок пока нет
- Competitive Exam Skills and Disaster ManagementДокумент15 страницCompetitive Exam Skills and Disaster ManagementYoga KumarОценок пока нет
- Communication Skills - OdtДокумент21 страницаCommunication Skills - OdtKashyap HiwseОценок пока нет
- Computer CompetencyДокумент1 страницаComputer CompetencyHuricane SkyОценок пока нет
- CS6004NP - Application Development - Ashish - Bhandari - 17031918 - CW1Документ68 страницCS6004NP - Application Development - Ashish - Bhandari - 17031918 - CW1Movies. PlexОценок пока нет
- General MathematicsДокумент14 страницGeneral MathematicsJohanna Reina BienОценок пока нет
- Module 8 - Risk Management NewДокумент42 страницыModule 8 - Risk Management NewEmmie GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Cloud Computing in Distributed SystemsДокумент8 страницCloud Computing in Distributed SystemsNebula OriomОценок пока нет
- HCI Lecture on Interaction ModelsДокумент22 страницыHCI Lecture on Interaction Modelskhawar abbasiОценок пока нет
- Data Communications - Transmission ModesДокумент25 страницData Communications - Transmission ModesJeffreyBerida100% (1)
- Nefas Silk Polytechnic College: Level IVДокумент30 страницNefas Silk Polytechnic College: Level IVyetayesh molaОценок пока нет
- MIS Prelim SummaryДокумент225 страницMIS Prelim Summarycyka blyatОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ23 страницыLecture 1Vikas DhimanОценок пока нет
- Article ReviewДокумент17 страницArticle ReviewTemam MohammedОценок пока нет
- MIL Lesson 7 PlagiarismДокумент42 страницыMIL Lesson 7 PlagiarismJulia OhОценок пока нет
- What is a Database DefinitionДокумент4 страницыWhat is a Database DefinitionTesfay WelamoОценок пока нет
- Differences in CultureДокумент13 страницDifferences in CulturexyreneОценок пока нет
- Task Performance: Property of STIДокумент2 страницыTask Performance: Property of STIMheg Ryan O. RamaОценок пока нет
- Annex II - Sample Curriculum Map-CE (OCT. 24, 2017) PDFДокумент5 страницAnnex II - Sample Curriculum Map-CE (OCT. 24, 2017) PDFMarianne Lou PalomarОценок пока нет
- Computer NetworkingДокумент37 страницComputer NetworkingDisha GoyalОценок пока нет
- Math ReviewerFinalsДокумент17 страницMath ReviewerFinalssamgyupОценок пока нет
- ICT Emerging Tech TrendsДокумент43 страницыICT Emerging Tech TrendsDon MadibahОценок пока нет
- System Unit-The Main Part of A Microcomputer, Sometimes Called The Chassis. ItДокумент15 страницSystem Unit-The Main Part of A Microcomputer, Sometimes Called The Chassis. ItJay Ann GonzagaОценок пока нет
- INS Form 1 August 1, 2020 Revision: 3 Page 1 of 7 PagesДокумент7 страницINS Form 1 August 1, 2020 Revision: 3 Page 1 of 7 Pagesgenalie albaricoОценок пока нет
- Lab 08 Practice Exercise On MS-Excel: Objective Current Lab Learning Outcomes (LLO)Документ3 страницыLab 08 Practice Exercise On MS-Excel: Objective Current Lab Learning Outcomes (LLO)Arabs are hilariousОценок пока нет
- A & A Report Writing NotesДокумент53 страницыA & A Report Writing NotesEshet ShumetОценок пока нет
- 1st Chapter PPT - Introduction To Management-SYBCOM IIIДокумент29 страниц1st Chapter PPT - Introduction To Management-SYBCOM III081 Om DhuriОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Assignment: Business AdministrationДокумент1 страницаComprehensive Assignment: Business AdministrationAimms IslamabadОценок пока нет
- Types of NetworkДокумент3 страницыTypes of NetworkCaseelyn Joy NantizaОценок пока нет
- System Tools and Documentation TechniquesДокумент4 страницыSystem Tools and Documentation TechniquesVenice DatoОценок пока нет
- CH 2 MCДокумент37 страницCH 2 MCAschalew AyeleОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Accounting Information Systems: An OverviewДокумент12 страницChapter 1: Accounting Information Systems: An Overviewaji marufОценок пока нет
- L4 Introduction To Business Communication Dec11Документ6 страницL4 Introduction To Business Communication Dec11Jonathan SmokoОценок пока нет
- Introduction to Computers: Definition, Characteristics & ComponentsДокумент143 страницыIntroduction to Computers: Definition, Characteristics & ComponentsAdnan HamadОценок пока нет
- Program security controlsДокумент2 страницыProgram security controlsPartha Deb50% (2)
- Empowerment Tech Module 1Документ8 страницEmpowerment Tech Module 1Don BesicОценок пока нет
- Scoring Rubric For Written AssignmentsДокумент3 страницыScoring Rubric For Written AssignmentsStephanieОценок пока нет
- Week 06 Initiating and Planning Systems Development ProjectsДокумент48 страницWeek 06 Initiating and Planning Systems Development ProjectsMuhd FarisОценок пока нет
- Data Processing Cycle and Basic Elements of ProgrammingДокумент6 страницData Processing Cycle and Basic Elements of ProgrammingLolo SabawОценок пока нет
- Instructional Material: Learning ObjectivesДокумент23 страницыInstructional Material: Learning ObjectivesRichard CoronelОценок пока нет
- 1 ICT LiteracyДокумент10 страниц1 ICT Literacykurt palivinoОценок пока нет
- What Is Computer?Документ5 страницWhat Is Computer?ihussnain209Оценок пока нет
- C. Application Do Activity Sheet 3.1 Pg. 25Документ19 страницC. Application Do Activity Sheet 3.1 Pg. 25John Carlo Fernando100% (1)
- Understanding the Self - USELF 111Документ2 страницыUnderstanding the Self - USELF 111John Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Concept of SelfДокумент1 страницаConcept of SelfJohn Michael Rasalan100% (3)
- Transgenic Organisms Transgenic Organisms Contain Foreign DNA That Has Been Introduced UsingДокумент4 страницыTransgenic Organisms Transgenic Organisms Contain Foreign DNA That Has Been Introduced UsingJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Executive Support SystemДокумент5 страницExecutive Support SystemJohn Michael Rasalan0% (1)
- Lesson 3: Exploring Religious Beliefs and RitualsДокумент3 страницыLesson 3: Exploring Religious Beliefs and RitualsJohn Michael Rasalan83% (24)
- CS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data Sheet 2Документ13 страницCS Form No. 212 Revised Personal Data Sheet 2ferosiacОценок пока нет
- Material SelfДокумент1 страницаMaterial SelfJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Information ManagementДокумент2 страницыInformation ManagementJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Home Loan FormДокумент2 страницыHome Loan FormJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Full Text SONA of Duterte 2018Документ6 страницFull Text SONA of Duterte 2018John Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1Документ2 страницыLesson 1John Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
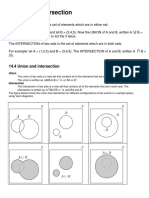
- Union and IntersectionДокумент4 страницыUnion and IntersectionJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- What Is Climate ChangeДокумент7 страницWhat Is Climate ChangeJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Personal Data SheetДокумент4 страницыPersonal Data SheetZerreitug Elppa100% (1)
- AlcoholismДокумент26 страницAlcoholismJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Enhancing of TextДокумент6 страницEnhancing of TextJohn Michael RasalanОценок пока нет
- Maharashtra Auto Permit Winner ListДокумент148 страницMaharashtra Auto Permit Winner ListSadik Shaikh50% (2)
- Lewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Документ8 страницLewis Corporation Case 6-2 - Group 5Om Prakash100% (1)
- EIRA v0.8.1 Beta OverviewДокумент33 страницыEIRA v0.8.1 Beta OverviewAlexQuiñonesNietoОценок пока нет
- What Is A Problem?: Method + Answer SolutionДокумент17 страницWhat Is A Problem?: Method + Answer SolutionShailaMae VillegasОценок пока нет
- GP Rating GSK Exit ExamДокумент108 страницGP Rating GSK Exit ExamMicle VM100% (4)
- 2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapДокумент15 страниц2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDremie WorksОценок пока нет
- Differential Pulse Code ModulationДокумент12 страницDifferential Pulse Code ModulationNarasimhareddy MmkОценок пока нет
- CBT For BDDДокумент13 страницCBT For BDDGregg Williams100% (5)
- Qad Quick StartДокумент534 страницыQad Quick StartMahadev Subramani100% (1)
- Employee Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure AgreementДокумент5 страницEmployee Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure AgreementshamoojeeОценок пока нет
- Wheeled Loader L953F Specifications and DimensionsДокумент1 страницаWheeled Loader L953F Specifications and Dimensionssds khanhОценок пока нет
- Level 10 Halfling For DCCДокумент1 страницаLevel 10 Halfling For DCCQunariОценок пока нет
- GFS Tank Quotation C20210514Документ4 страницыGFS Tank Quotation C20210514Francisco ManriquezОценок пока нет
- Ball Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsДокумент16 страницBall Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsABDUL KADHARОценок пока нет
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism in Infancy: A Guide To DiagnosisДокумент11 страницInborn Errors of Metabolism in Infancy: A Guide To DiagnosisEdu Diaperlover São PauloОценок пока нет
- SiloДокумент7 страницSiloMayr - GeroldingerОценок пока нет
- Philippine Army BDU BidДокумент2 страницыPhilippine Army BDU BidMaria TeresaОценок пока нет
- Equilibruim of Forces and How Three Forces Meet at A PointДокумент32 страницыEquilibruim of Forces and How Three Forces Meet at A PointSherif Yehia Al MaraghyОценок пока нет
- PEDs and InterferenceДокумент28 страницPEDs and Interferencezakool21Оценок пока нет
- Checklist of Requirements For OIC-EW Licensure ExamДокумент2 страницыChecklist of Requirements For OIC-EW Licensure Examjonesalvarezcastro60% (5)
- Alternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesДокумент96 страницAlternate Tuning Guide: Bill SetharesPedro de CarvalhoОценок пока нет
- October 2009 Centeral Aucland, Royal Forest and Bird Protecton Society NewsletterДокумент8 страницOctober 2009 Centeral Aucland, Royal Forest and Bird Protecton Society NewsletterRoyal Forest and Bird Protecton SocietyОценок пока нет
- Chromate Free CoatingsДокумент16 страницChromate Free CoatingsbaanaadiОценок пока нет
- MCQ Ch16solДокумент4 страницыMCQ Ch16solandiswahlongwa870Оценок пока нет
- Stroboscopy For Benign Laryngeal Pathology in Evidence Based Health CareДокумент5 страницStroboscopy For Benign Laryngeal Pathology in Evidence Based Health CareDoina RusuОценок пока нет
- SolBridge Application 2012Документ14 страницSolBridge Application 2012Corissa WandmacherОценок пока нет
- New Hire WorkbookДокумент40 страницNew Hire WorkbookkОценок пока нет
- Propoxur PMRAДокумент2 страницыPropoxur PMRAuncleadolphОценок пока нет
- GS16 Gas Valve: With On-Board DriverДокумент4 страницыGS16 Gas Valve: With On-Board DriverProcurement PardisanОценок пока нет