Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Aace International Scheduling: Critical Path Method (CPM)
Загружено:
Sucher EolasИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Aace International Scheduling: Critical Path Method (CPM)
Загружено:
Sucher EolasАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
AACE INTERNATIONAL SCHEDULING
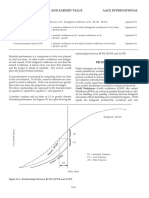
diagram (as discussed in the following sections) is prepared
and the work scheduled, the display of relationships between
GLOSSARY TERMS IN THIS CHAPTER
the activities can be turned off or masked. This masking pro-
duces a bar chart, at any level of the project schedule, which
activity ◆ activity description ◆ activity identification
can be used as a communication tool for the most complex
arrow diagramming method (ADM) ◆ backward pass
and largest of projects.
bar chart ◆ calendar days ◆ constraints ◆critical path
critical path method (CPM) ◆ early finish (EF)
Critical Path Method (CPM) early start (ES) ◆ forward pass ◆ free float ◆ gantt chart
The disadvantages of manually developed bar charts, cou- late finish (LF) ◆ late start (LS) ◆ original duration (OD)
pled with other disadvantages that became evident during overlapping scheduling technique ◆ PERT diagram
the mid-1950s, set the stage for development of network- planning ◆ precedence diagramming method (PDM)
based project management methodology. One of the meth- network ◆ milestone ◆ relationships; remaining duration
ods that emerged to overcome these weaknesses was critical schedule calendar ◆ schedule update ◆ scheduling
path scheduling. The critical path method (CPM) is a sched- scheduling levels ◆ status ◆ target schedule
uling technique using arrow, precedence, or PERT diagram- time scaled network ◆ total float
ming methods to determine the length of a project and to work breakdown structure (WBS) ◆ work days (WD)
identify the activities and constraints on the critical path.
The critical path method enables a scheduler to do the fol-
lowing: opers of PERT estimated a best or shortest time, worst or
longest time, and the most probable time to accomplish the
• Determine the shortest time in which a program or proj- tasks defined. Concurrent with the PERT network develop-
ect can be completed. ment, the team also developed computer software to run a
• Identify those activities that are critical and that cannot probability analysis to arrive at a “most likely” duration for
be slipped or delayed. each activity and the overall project.
• Show the potential slippage or delay (known as float)
available for activities that are not critical. PERT is considered an indeterminate process for activity and
project durations, while CPM is considered a deterministic
The critical path method (CPM) was designed for, and is use- process.
ful on, projects where the duration of each activity can be
estimated with reasonable certainty; it predicts how long an The network of activities developed for PERT are similar to
endeavor will take to complete. It also identifies the activities the arrow diagramming method (ADM) and precedence dia-
that control the overall length of the project. CPM is widely gramming method (PDM) networks. Because of the similari-
used in the process industries, construction, single industrial ty and resemblance of a CPM network to PERT, the term
projects, prototype development, and for controlling plant PERT has been used as a synonym for CPM.
outages and shutdowns.
Discussion of CPM
CPM computer software, known also as project management The most commonly used scheduling method and the tech-
software, allows for the assignment of resources to activities. nique that will meet your project objectives is CPM incorpo-
Assigning resources to the activities and allowing the rating overlapping logic.
resources to accomplish their assigned work based on their
availability provides another variable in the overall project CPM is a scheduling technique using arrow or precedence
duration. Since the software has this capability, CPM net- diagrams (networks) to determine the length of a project and
working is also used by industries with fixed pools of to identify the activities and constraints on the critical path.
resources such as maintenance and information technology The critical path is defined as the longest chain or chains of
projects. activities, in terms of time or duration, through a network.
Project Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) Two basic methods of critical path scheduling are the following:
Project evaluation review technique (PERT) is a probabilistic
technique, used mostly by government agencies, for calculat- • the arrow diagramming method (ADM) (also called
ing the “most likely” durations for network activities. activity-on-arrow, or the “i” - “j” method), and
• the precedence diagramming method (PDM) (also called
During development of the Navy’s Polaris Missile Program activity-on-node).
in the late 1950s, the team had no historical basis to draw
upon when estimating the length of time it would take to Arrow Diagramming Method (ADM)
accomplish certain tasks. For each of the activities, the devel- In arrow diagramming, the nodes in the network are the
13.3
Вам также может понравиться
- Critical Path MethodДокумент54 страницыCritical Path MethodKenneth Bryan Copino100% (1)
- Deepfakes Threats and CountermeasuresДокумент9 страницDeepfakes Threats and CountermeasuresDerman DereceОценок пока нет
- CPM and PertДокумент32 страницыCPM and PertJens GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Productivity MeasurementДокумент1 страницаProductivity MeasurementSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Salesforce Development LifecycleДокумент76 страницSalesforce Development LifecycleRajnish TripathiОценок пока нет
- Shaping The Submarine Market: Striking PerformanceДокумент21 страницаShaping The Submarine Market: Striking PerformanceSuzuki ImproОценок пока нет
- PERTДокумент34 страницыPERTAnusha Verghese71% (7)
- Section 2A. Schedule DevelopmentДокумент1 страницаSection 2A. Schedule DevelopmentSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Pert ND CPMДокумент19 страницPert ND CPMbhaskarganeshОценок пока нет
- Scheduling Aace International: Schedule DevelopmentДокумент1 страницаScheduling Aace International: Schedule DevelopmentSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Ajeesh Moosakutty (4) Sabith P (33) SRUTHI.K.R (45) Shafeek Ma NideeshДокумент44 страницыAjeesh Moosakutty (4) Sabith P (33) SRUTHI.K.R (45) Shafeek Ma NideeshJohn112Оценок пока нет
- CPM and PERT Unit 2Документ5 страницCPM and PERT Unit 2SavantОценок пока нет
- Project Management by CPM & PERTДокумент18 страницProject Management by CPM & PERTengr_misbahullahОценок пока нет
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)От EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-PERT/CPM/Gantt Chart/FPA/EVA/Timebox (Chapter-3)Рейтинг: 1.5 из 5 звезд1.5/5 (3)
- APG40 EricssonДокумент45 страницAPG40 EricssonSun Rise100% (2)
- Project Scheduling: Time-Scaled Network AnalysisДокумент30 страницProject Scheduling: Time-Scaled Network AnalysisEurydice100% (1)
- Travel Package Recommendation SystemДокумент55 страницTravel Package Recommendation SystemVisarikaОценок пока нет
- Project Management Chapter 8Документ57 страницProject Management Chapter 8Kevin Nash56% (9)
- Project Time Management & SchedulingДокумент42 страницыProject Time Management & SchedulingShahid AliОценок пока нет
- NETWORK ANALYSIS NOTES CPMДокумент32 страницыNETWORK ANALYSIS NOTES CPMshravani wodeyarОценок пока нет
- PDM/GERTДокумент30 страницPDM/GERTMa. Gliceria May A. MoldeОценок пока нет
- UNIT III Scheduling and Res AllocДокумент15 страницUNIT III Scheduling and Res AllocSindhiya RebeccaОценок пока нет
- Pert-And-Cpm-Techniques n67 MustДокумент67 страницPert-And-Cpm-Techniques n67 MustWasim QuraishiОценок пока нет
- Project Activity Scheduling: ZahidДокумент45 страницProject Activity Scheduling: ZahidTalha KhanОценок пока нет
- FOC Arrow DiagramДокумент6 страницFOC Arrow DiagramShimon PopaОценок пока нет
- Pert and CPM NotesДокумент32 страницыPert and CPM NotesSanjana DasОценок пока нет
- Pert and CPM TechniquesДокумент67 страницPert and CPM TechniquesGS IN ONE MINUTEОценок пока нет
- Opmn03b - M5Документ3 страницыOpmn03b - M5Francis Ryan PorquezОценок пока нет
- Software Project Management Unit-3 - 2 PDFДокумент2 страницыSoftware Project Management Unit-3 - 2 PDFMANAS TIWARIОценок пока нет
- PERT CPM For Project ManagementДокумент21 страницаPERT CPM For Project ManagementAnmol KhanОценок пока нет
- Network Models Are The Control Technique of The Project. PERT and CPM Are The Network Models Used For Planning, Scheduling and Control of The ProjectДокумент14 страницNetwork Models Are The Control Technique of The Project. PERT and CPM Are The Network Models Used For Planning, Scheduling and Control of The Projectmin_feelingsОценок пока нет
- Pert and CPMДокумент5 страницPert and CPMvaibhavkapse2010Оценок пока нет
- Cps Unit 2 - NoRestrictionДокумент47 страницCps Unit 2 - NoRestrictionraaiОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Introduction To CPM / PERT Techniques: CPM (Critical Path Method)Документ32 страницы2.1 Introduction To CPM / PERT Techniques: CPM (Critical Path Method)anish.t.pОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ47 страницChapter 4aefiojibxОценок пока нет
- Project Planning & Control Lec-7Документ32 страницыProject Planning & Control Lec-7Add NoteОценок пока нет
- Network Techniques For Project Management: StructureДокумент15 страницNetwork Techniques For Project Management: StructureManita DhandaОценок пока нет
- Expose of Pert ChartДокумент3 страницыExpose of Pert ChartArsene Junior Fotso WaboОценок пока нет
- Planning and Scheduling of Pert/Cpm (Network Analysis) : Prepared By: Roy Richard C. MacabodbodДокумент13 страницPlanning and Scheduling of Pert/Cpm (Network Analysis) : Prepared By: Roy Richard C. Macabodbodroy richard macabodbodОценок пока нет
- Quanti Slide 7 Pert CPMДокумент49 страницQuanti Slide 7 Pert CPMRheanneОценок пока нет
- Eat 357 - Construction Management: - SchedulingДокумент40 страницEat 357 - Construction Management: - SchedulinglawrenceОценок пока нет
- Planning and Scheduling of Pert/Cpm (Network Analysis) : Prepared By: Roy Richard C. MacabodbodДокумент13 страницPlanning and Scheduling of Pert/Cpm (Network Analysis) : Prepared By: Roy Richard C. Macabodbodjolmarie llantoОценок пока нет
- Planning and Scheduling of Pert/Cpm (Network Analysis) : Prepared By: Roy Richard C. MacabodbodДокумент13 страницPlanning and Scheduling of Pert/Cpm (Network Analysis) : Prepared By: Roy Richard C. Macabodbodjolmarie llantoОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 4 (Scheduling) - HELDAДокумент6 страницCHAPTER 4 (Scheduling) - HELDAHelda Estrada LoreteОценок пока нет
- PCM Report-Network AnalysisДокумент2 страницыPCM Report-Network Analysisayessa evangelistaОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of SchedulingДокумент8 страницFundamentals of SchedulingAndrew UgohОценок пока нет
- Scheduling and PlanningДокумент43 страницыScheduling and PlanningMaricon PadriquezОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Introduction To CPM / PERT Techniques: CPM (Critical Path Method)Документ32 страницы2.1 Introduction To CPM / PERT Techniques: CPM (Critical Path Method)Dergil ReginaОценок пока нет
- Project Management Note Basic TermsДокумент15 страницProject Management Note Basic TermsdrishyaОценок пока нет
- Guru Govind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi: Bba Sem Vi - 302 Project ManagementДокумент39 страницGuru Govind Singh Indraprastha University, Delhi: Bba Sem Vi - 302 Project ManagementPulkit AggarwalОценок пока нет
- CH 6&5 ECO MicroДокумент4 страницыCH 6&5 ECO MicroSayantan MajhiОценок пока нет
- Bba - 6sem - Project Appraisal - Lecture 41,42&43Документ7 страницBba - 6sem - Project Appraisal - Lecture 41,42&43Jordan ThapaОценок пока нет
- Module 3 CPMДокумент21 страницаModule 3 CPMshravani wodeyarОценок пока нет
- PERT and CPMДокумент26 страницPERT and CPMmathi sivaОценок пока нет
- Scheduling and Risk AnalysisДокумент26 страницScheduling and Risk AnalysisLira Mae PelovelloОценок пока нет
- Demo About Pert CPMДокумент12 страницDemo About Pert CPMBenjamin D. RubinОценок пока нет
- Object:-: Experiment No:-8Документ10 страницObject:-: Experiment No:-8Dhruv Kumar AgrawalОценок пока нет
- CPM Analysis of OBG PLCДокумент16 страницCPM Analysis of OBG PLCBirhanuОценок пока нет
- Definition and Why Project Network EssentialДокумент40 страницDefinition and Why Project Network EssentialswamibagОценок пока нет
- CPM (Critical Path Method) : ComponentsДокумент4 страницыCPM (Critical Path Method) : Componentsom mirkuteОценок пока нет
- Tools and Techniques of Project ManagementДокумент4 страницыTools and Techniques of Project Managementsimmi33Оценок пока нет
- Pert CPMДокумент41 страницаPert CPMArchana PanwarОценок пока нет
- Tools and Techniques of Project ManagementДокумент2 страницыTools and Techniques of Project ManagementPrabhu GangapatnamsОценок пока нет
- Crashing Pert Networks: A Simulation ApproachДокумент15 страницCrashing Pert Networks: A Simulation ApproachRavindra BharathiОценок пока нет
- Chapter OverviewДокумент57 страницChapter OverviewWajiha SharifОценок пока нет
- Interpret The Network Figures Use in Civil Engineering.: Tools For Project SchedulingДокумент13 страницInterpret The Network Figures Use in Civil Engineering.: Tools For Project SchedulingAyush SalveОценок пока нет
- Informe 44 Modificación de Presupuesto Escenario DeportivoДокумент5 страницInforme 44 Modificación de Presupuesto Escenario DeportivoSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- No Damage For DelayДокумент1 страницаNo Damage For DelaySucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Productivity and PerformanceДокумент1 страницаProductivity and PerformanceSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- EcoProP FrameworkДокумент1 страницаEcoProP FrameworkSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Q. Management in ConstructionДокумент1 страницаQ. Management in ConstructionSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Strategic Asset Management Aace InternationalДокумент1 страницаStrategic Asset Management Aace InternationalSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Contracting For Capital Projects Aace International: Decision To BidДокумент1 страницаContracting For Capital Projects Aace International: Decision To BidSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Contract DeficienciesДокумент1 страницаContract DeficienciesSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- :Z//K^&>H:K: Ϭ͘Ͳ Hŷ Ğŵɖƌğɛăƌŝž Ğɛƚą Đžŷɛŝěğƌăŷěž ŜŷǀĞƌƚŝƌ Ğŷ Ƶŷă Ɖůăŷƚă ĂǀŞđžůă͘ Wăƌă ĞůůžДокумент1 страница:Z//K^&>H:K: Ϭ͘Ͳ Hŷ Ğŵɖƌğɛăƌŝž Ğɛƚą Đžŷɛŝěğƌăŷěž ŜŷǀĞƌƚŝƌ Ğŷ Ƶŷă Ɖůăŷƚă ĂǀŞđžůă͘ Wăƌă ĞůůžSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Cashflow Solution Part1Документ1 страницаCashflow Solution Part1Sucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Aace International Performance and Productivity Management: Waste Through ReworkДокумент1 страницаAace International Performance and Productivity Management: Waste Through ReworkSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Project Organization Structure: James A. Bent, CCCДокумент1 страницаProject Organization Structure: James A. Bent, CCCSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Changes - ClaimsДокумент1 страницаChanges - ClaimsSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Cash Flow RepresentationДокумент1 страницаCash Flow RepresentationSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Define Scope of WorkДокумент1 страницаDefine Scope of WorkSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Statistics - ProbabilityДокумент1 страницаStatistics - ProbabilitySucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Applied Engineering Economics: Dr. Scott J. Amos, PEДокумент1 страницаApplied Engineering Economics: Dr. Scott J. Amos, PESucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Tracking Cost and Schedule Performance: Dr. Joseph J. Orczyk, PE CCEДокумент1 страницаTracking Cost and Schedule Performance: Dr. Joseph J. Orczyk, PE CCESucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Accounting and EstimatesДокумент1 страницаAccounting and EstimatesSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Earned Value For Variable Budgets: Dr. Joseph J. Orczyk, PE CCEДокумент1 страницаEarned Value For Variable Budgets: Dr. Joseph J. Orczyk, PE CCESucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Changes in The ScheduleДокумент1 страницаChanges in The ScheduleSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Progress Measurement and Earned Value Aace International: ProductivityДокумент1 страницаProgress Measurement and Earned Value Aace International: ProductivitySucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Aace International Scheduling: Making Time CalculationsДокумент1 страницаAace International Scheduling: Making Time CalculationsSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Evafor Fixed BudgetsДокумент1 страницаEvafor Fixed BudgetsSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Scheduling: Anthony J. Werderitsch, PE CCEДокумент1 страницаScheduling: Anthony J. Werderitsch, PE CCESucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Schedule PerformanceДокумент1 страницаSchedule PerformanceSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- Scheduling Aace International: Overlapping Networks TechniquesДокумент1 страницаScheduling Aace International: Overlapping Networks TechniquesSucher EolasОценок пока нет
- MIS Final2Документ57 страницMIS Final2Alok JainОценок пока нет
- Turk InterlockДокумент2 страницыTurk InterlockerstendrainОценок пока нет
- Newton & Einstein: San Remigio, Cebu Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskДокумент8 страницNewton & Einstein: San Remigio, Cebu Teacher-Made Learner's Home TaskMii Kiwi-anОценок пока нет
- Configure and Start NPO Client ApplicationДокумент11 страницConfigure and Start NPO Client ApplicationbinjibrilОценок пока нет
- ENG1003-16-S1 Sample Exam PDFДокумент6 страницENG1003-16-S1 Sample Exam PDFEdwin ChaoОценок пока нет
- MM TAXBRA Migracao BatchДокумент3 страницыMM TAXBRA Migracao BatchMárcio NascimentoОценок пока нет
- PHP Oop: Object Oriented ProgrammingДокумент21 страницаPHP Oop: Object Oriented ProgrammingSeptia ni Dwi Rahma PutriОценок пока нет
- part 1: Before The Test BeginsДокумент5 страницpart 1: Before The Test BeginsVishal GabaОценок пока нет
- Software Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 ApprovedДокумент17 страницSoftware Requirements Specification: Version 1.0 Approvedabdullahi husseinОценок пока нет
- AirWatch Whitepaper SDKДокумент6 страницAirWatch Whitepaper SDKDioYanuar0% (1)
- Manual de Serviço - KDL-32CX525 - KDL-40CX525 - KDL-46CX525 BR Chassis AZ2-F PDFДокумент64 страницыManual de Serviço - KDL-32CX525 - KDL-40CX525 - KDL-46CX525 BR Chassis AZ2-F PDFMarco KersulОценок пока нет
- A Low Cost Smart Irrigation System Using MQTT Protocol: July 2017Документ6 страницA Low Cost Smart Irrigation System Using MQTT Protocol: July 2017Santhosh KumarОценок пока нет
- Aamir Hussain KhanДокумент3 страницыAamir Hussain KhanMuhammad FahadОценок пока нет
- Creating A Menu in Visual BasicДокумент9 страницCreating A Menu in Visual BasicPiyush VermaОценок пока нет
- Collaborate in Qlik SenseДокумент65 страницCollaborate in Qlik Senseamine ennarОценок пока нет
- Dynamic Data ExchangeДокумент3 страницыDynamic Data ExchangeAhmed khaled mohamed seadaОценок пока нет
- X-Ways Forensics, WinHexДокумент193 страницыX-Ways Forensics, WinHexSusanОценок пока нет
- Paige Moore's ResumeДокумент2 страницыPaige Moore's ResumePaige MooreОценок пока нет
- Graphing Software: Computers For Mathematics Instruction (CMI) ProjectДокумент61 страницаGraphing Software: Computers For Mathematics Instruction (CMI) ProjectWahid Choirul AnaОценок пока нет
- 4 MuxДокумент12 страниц4 MuxsunnysОценок пока нет
- Sculptris Alpha6 DocumentationДокумент47 страницSculptris Alpha6 DocumentationArslankhan83Оценок пока нет
- 2021 State of Software Engineering ReportДокумент21 страница2021 State of Software Engineering ReportNallely FriasОценок пока нет
- ADBMS Chapter OneДокумент21 страницаADBMS Chapter OneNaomi AmareОценок пока нет
- Lab 2.8.2Документ4 страницыLab 2.8.2LadyBriannaОценок пока нет
- 4 - Networks and Cloud ComputingДокумент4 страницы4 - Networks and Cloud Computingcyka blyatОценок пока нет