Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Grade
Загружено:
Antonette McnairИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Grade
Загружено:
Antonette McnairАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Agricultural Science Notes
Grade 11
Topic: Simple Morphology, anatomy and Physiology of Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons
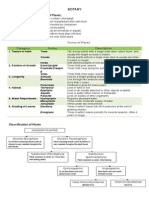
Plants may be classified according to their major groups, family, life cycle or growth habit.
Classification Description
Major groups Seed plants or flowering plants
Family Monocotyledons or Dicotyledons
Life cycle Annuals- complete life cycle in one season ( e.g.
lettuce, tomatoes, peas, corn)
Biennials life cycle in two growing seasons e.g.(
carrot, celery, radish, beetroot)
Perennials – continue to grow for many years (e.g.
citrus, mango, coffee, cocoa)
Growth habit Herbs- plants with soft , non-woody stems usually less
than 2m in height
Shrubs- have stiff, woody stem, produce branches
close to the ground, less than 5m in height (e.g. cherry,
guava, hibiscus)
Trees- tall woody plants with a well-defined trunk and
branches at some distance from the ground (e.g.
mango, breadfruit, cedar, teak, mahogany)
Monocotyledons and Dicotyledons
Monocotyledons Dicotyledons
Seeds have one cotyledon (seed leaf) Seeds have two cotyledons and an embryo
Fibrous root systems Tap root systems
Stems with scattered vascular bundles Stems with cylindrical arrangement of vascular
bundles
Long thin leaves with parallel veins Rounded , broader leaves with net-like
arrangement of veins veins
Flower parts in threes, lack brightly coloured Flower parts are numerous and is brightly
petals or sepals coloured
Mainly herbs and grasses with few trees Herbs, shrubs and trees
e.g. rice, corn, bamboo, sugar cane e.g. cotton, cabbage, citrus
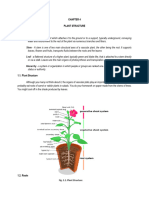
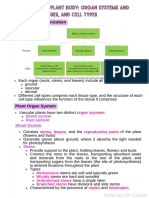
External structures of plants
1. Roots
Function of roots
1. Anchorage
2. Absorption of water and minerals
3. Storage
There are four main types of roots: tap, fibrous, adventitious and aerial roots
Tap roots- a main or tap, root with lateral roots growing out to the side (e.g.
mango, tomato)
Fibrous roots- consist of a cluster of roots growing from the base of the stem
(e.g. coconut palm, corn, grass)
Adventitious roots- roots grow from the base of the stem cuttings (e.g. crotons)
or from leaves (e.g. Bryophyllum)
Aerial roots grow above the ground (e.g. Ficus. Philodendron)
Stems
Functions of stems
1. Transport- the medium through which water and minerals move upward in a plant and
the movement of manufactured food from leaves downwards. Within the stem, vascular
tissues (xylem and phloem) transports materials to places within the plant where they are
most needed. Xylem transports water and minerals absorbed from the roots to the stems,
leaves and flowers. Phloem, carries sugars produced in the leaves to areas in need of
energy, such as the plant's root system.
2. Support- holds the upper parts of the plant
3. Storage- stores manufactured food e.g. sugarcane
Modifications (stems that are especially suited to a particular habitat and environment).
1. Prostrate stems- creep on the ground to form a mat e.g. stolon, runners
2. Underground stems – e.g. rhizomes
3. Twinning stems e.g. yam
4. Stem tendrils e.g. pumpkin
5. Cladodes- stems becoming leaf like e.g. cactus
Leaves
The term leaf refers to the organ that forms the main lateral appendage on the stem of
vascular plants. A typical leaf consist of
Leaf blade or lamina which is the flat part
Leaf stalk or petiole which attaches the lea to the stem
A midrib or main vein, consisting of the transporting tissues
A network of smaller veins
Apex
Simple diagram of a leaf
Functions of the leaf
1. Photosynthesis
2. Transportation
3. Exchange of gases
4. Storage of food
Internally leaves are made up of epidermis, mesophyll and vascular tissues
Epidermis- (upper epidermis and lower epidermis) contains cuticle which slows down
evaporation of water, protects internal tissues
Mesophyll- (palisade mesophyll found in the upper part and spongy mesophyll found in the
lower part) cells with chloroplasts that contains chlorophyll
Vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) xylem transports water and mineral up to the leaf
Phloem transports manufactured food (sugar) from leaves to other parts of the plant
Homework**must be done in notebook
Make drawings of
1. different types of root systems
2. the leaf of monocot and four types of dicot leaf ( two simple leaves and two compound
leaves)
3. the internal structure of a dicot leaf
30 marks
Вам также может понравиться
- Plant Parts and FunctionsДокумент63 страницыPlant Parts and FunctionsmacybnzОценок пока нет
- PLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesДокумент78 страницPLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesAsam100% (1)
- Tree Species in UgandaДокумент7 страницTree Species in Ugandaainejeremiah100% (1)
- Types of Commercial Food Crops in The PhilippinesДокумент34 страницыTypes of Commercial Food Crops in The Philippinesmarjorie gomezОценок пока нет
- Basic Botany 2Документ92 страницыBasic Botany 2Michael OduorОценок пока нет
- Plant Form and FunctionДокумент32 страницыPlant Form and FunctionPaula SanicoОценок пока нет
- 1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Документ180 страниц1 Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Guru temp id-04 for Sekolah-8252 Moe100% (1)
- Ex 5Документ7 страницEx 5leanicaОценок пока нет
- Integrated Pest Management For CacaoДокумент59 страницIntegrated Pest Management For CacaoPlantacion de Sikwate100% (11)
- Evaluation of Lettuce and Tomato Varieties - Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) Interaction Under Upland and Lowland ConditionsДокумент33 страницыEvaluation of Lettuce and Tomato Varieties - Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) Interaction Under Upland and Lowland ConditionsUPLB Office of the Vice Chancellor for Research and ExtensionОценок пока нет
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersОт EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersОценок пока нет
- PLANTДокумент23 страницыPLANTAngelito HalmainОценок пока нет
- Section B-Introduction To Crop ProductionДокумент3 страницыSection B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDaniel DowdingОценок пока нет
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootДокумент14 страницMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALОценок пока нет
- b2875bcb-b6c7-4f3f-bb97-8960c23a9098Документ5 страницb2875bcb-b6c7-4f3f-bb97-8960c23a9098Navin KumarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4Документ5 страницChapter 4Lebanan Aprille MarieОценок пока нет
- PlantsДокумент44 страницыPlantsSanjeev ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Botany StemДокумент36 страницBotany Stemartadiel28Оценок пока нет
- 1osc03 PlantkingdomДокумент4 страницы1osc03 PlantkingdomIrene AragonesesОценок пока нет
- T HN Yi TF Ux WDKi Miaq SLVДокумент29 страницT HN Yi TF Ux WDKi Miaq SLVjennblair0830Оценок пока нет
- Plant Stem - WikipediaДокумент29 страницPlant Stem - WikipediaBashiir NuurОценок пока нет
- PRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4Документ26 страницPRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINOОценок пока нет
- PLANTSДокумент3 страницыPLANTSAbuhanif SaikОценок пока нет
- 03-Flowering PlantsДокумент45 страниц03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelОценок пока нет
- Subject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsДокумент35 страницSubject-Biology Chapter - 5 Morphology of Flowering PlantsNikunj kumar chaurasiyaОценок пока нет
- 3.2 Morfologi BatangДокумент44 страницы3.2 Morfologi Batanglutfiatun nimahОценок пока нет
- Gen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Документ79 страницGen Bio 2 - Chapter 1Samantha AcostaОценок пока нет
- Science B. G8 3rdДокумент16 страницScience B. G8 3rdBen sik ali mohamedОценок пока нет
- Botany 101Документ7 страницBotany 101Gladdin ChloeОценок пока нет
- Anp 508 October 2023 25 Botany of Grasses and LegumesДокумент22 страницыAnp 508 October 2023 25 Botany of Grasses and LegumesJoy GbadeboОценок пока нет
- Alido, Charlito VДокумент5 страницAlido, Charlito VCharlito AlidoОценок пока нет
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsДокумент29 страницMorphology of Flowering PlantssaleemОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)Документ180 страницChapter 1: Plant Classification (Root, Stem and Leaf Morfologi)FITRINESSA IBOLОценок пока нет
- LEAVESДокумент36 страницLEAVESZyraprincess BlancoОценок пока нет
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Документ9 страницLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramОценок пока нет
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 02Документ9 страницExp SC 3 - Chapter 02megamind publicationОценок пока нет
- NR 215 Plant Biology: StemsДокумент39 страницNR 215 Plant Biology: StemsJohn Zephyr TyskaОценок пока нет
- Stem PDFДокумент49 страницStem PDFAstha MishraОценок пока нет
- SN Chapter 3Документ90 страницSN Chapter 3Mohd Razin F2025Оценок пока нет
- This Article Is About The Part of A PlantДокумент51 страницаThis Article Is About The Part of A PlantTess TubieronОценок пока нет
- B 4 Ev 6 y 22 WR Getting 20 To 20 Know 20 Plants 20 PPTДокумент46 страницB 4 Ev 6 y 22 WR Getting 20 To 20 Know 20 Plants 20 PPTatharОценок пока нет
- Class - 6 - Getting To Know Plants - T - 1 PDFДокумент9 страницClass - 6 - Getting To Know Plants - T - 1 PDFParul GuptaОценок пока нет
- SCIENCEДокумент10 страницSCIENCESomen SahaОценок пока нет
- Bot-302 Chap 4 Lec 8Документ35 страницBot-302 Chap 4 Lec 8AbdullahОценок пока нет
- 5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleДокумент2 страницы5 Morphology in Flowering Plants-Notes - SampleManish KumarОценок пока нет
- Plant Biology: Roots and Shoots: Peter ShawДокумент28 страницPlant Biology: Roots and Shoots: Peter Shawashishnarayanmishra2541Оценок пока нет
- SupplementaryДокумент4 страницыSupplementaryxenumaxieОценок пока нет
- Plant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesДокумент5 страницPlant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesRizka Apriliana KumalasariОценок пока нет
- I. Underground Modifications of StemДокумент7 страницI. Underground Modifications of StemElias Libay100% (1)
- Getting To Know Plants: ClimbersДокумент8 страницGetting To Know Plants: ClimbersShivam Zakhmi100% (1)
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 5Документ5 страницMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 5Reality of PoliticsОценок пока нет
- Chapter II. Plant MorphologyДокумент47 страницChapter II. Plant MorphologylovryantadenaamilingacadsОценок пока нет
- Reading Guide Answers PlantsДокумент9 страницReading Guide Answers PlantsNirmal PatelОценок пока нет
- Post Lab Discussion IIДокумент64 страницыPost Lab Discussion IIJeli Mae Ysabel PerezОценок пока нет
- Plant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoДокумент70 страницPlant Anatomy Ruel-VelosoKhy Renz BajajОценок пока нет
- VegetationДокумент14 страницVegetationChris P. BeaconОценок пока нет
- Structures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesДокумент32 страницыStructures and Functions in Plants: Roots, Stems, and LeavesDanielle AnonuevoОценок пока нет
- Diwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenДокумент29 страницDiwey Perez Ikitan Jomer Jireh Pinalapal Jane Prudenciano Ruffa Prudenciano Marvin Carl Chico Tintin Pastor TagapuenKristina PonceОценок пока нет
- GS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsДокумент9 страницGS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsChary Johanne MenesesОценок пока нет
- The Stem Is A Vital Component of The Angiosperm Plant BodyДокумент2 страницыThe Stem Is A Vital Component of The Angiosperm Plant BodyasogwamariankeirukaОценок пока нет
- Activity 1 Bio 1aДокумент3 страницыActivity 1 Bio 1aEPHRAIM JOASH ABEJO GAGANTINGОценок пока нет
- Bot 121Документ12 страницBot 121eirrehs ellaОценок пока нет
- Structures and Functions in PlantsДокумент32 страницыStructures and Functions in PlantsAlvin PaboresОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Документ12 страницCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFОценок пока нет
- Sample SOP - PropagationДокумент4 страницыSample SOP - PropagationFunHunterОценок пока нет
- Hedychium - Ginger Lilies For The Temperate GardenДокумент13 страницHedychium - Ginger Lilies For The Temperate GardenDennis CareyОценок пока нет
- Handling Arabidopsis Plants Book ChapterДокумент23 страницыHandling Arabidopsis Plants Book ChapterIoannisM.ValasakisОценок пока нет
- The Croton PlantsДокумент3 страницыThe Croton PlantsSabre FortОценок пока нет
- Florigen: MechanismДокумент3 страницыFlorigen: MechanismDharmendra SinghОценок пока нет
- Draft Himachal Pradesh Forest (Sale of Timber) Rules, 2009.Документ6 страницDraft Himachal Pradesh Forest (Sale of Timber) Rules, 2009.dsuresh_kОценок пока нет
- Micro Greens Comparison ChartДокумент2 страницыMicro Greens Comparison ChartBhisham SeeparsanОценок пока нет
- DLP Science 1-17-2023Документ7 страницDLP Science 1-17-2023Ser EdОценок пока нет
- Supplementary Notes On Coconut: Hello@Edutap - Co.In 1Документ6 страницSupplementary Notes On Coconut: Hello@Edutap - Co.In 1Madhu Prathipati PОценок пока нет
- Coccinia - 2012Документ7 страницCoccinia - 2012Suhara BeevyОценок пока нет
- Bio CHP 2 MCQ QuestionsДокумент8 страницBio CHP 2 MCQ QuestionsSanjanaОценок пока нет
- Recent DevelopmentsДокумент295 страницRecent DevelopmentsGabriel PinheiroОценок пока нет
- Soaking Up The Sun: Author's ChoiceДокумент3 страницыSoaking Up The Sun: Author's ChoicebuddlightbeerlogОценок пока нет
- A Review On Plant Without Soil - Hydroponics: Mamta D. Sardare, Shraddha V. AdmaneДокумент6 страницA Review On Plant Without Soil - Hydroponics: Mamta D. Sardare, Shraddha V. AdmaneJan Vincent RamonesОценок пока нет
- Production Technology of Brussel SproutsДокумент9 страницProduction Technology of Brussel SproutsjeevithaОценок пока нет
- 7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsДокумент17 страниц7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsTheresa IzaОценок пока нет
- NO Item Name Stock Fisik Bon Keluar Pendingan KPRДокумент7 страницNO Item Name Stock Fisik Bon Keluar Pendingan KPRAndika AqilОценок пока нет
- Indonesian Local Perfume BrandsДокумент15 страницIndonesian Local Perfume BrandsMala WikaОценок пока нет
- Granados Et Al. 2016 New TillandsiaДокумент9 страницGranados Et Al. 2016 New TillandsiaGerardo A. SalazarОценок пока нет
- Unit EvaluationДокумент14 страницUnit EvaluationaliesanaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 FinalДокумент50 страницChapter 1 FinalJr AquinoОценок пока нет
- Alina Biomes of The WorldДокумент22 страницыAlina Biomes of The WorldMujeebMemonОценок пока нет
- Breeding Priorities and StrategiesДокумент15 страницBreeding Priorities and StrategiesDeepak MewarОценок пока нет
- Saline Soil - BasedДокумент260 страницSaline Soil - BasedSethОценок пока нет
- Principles of HorticultureДокумент194 страницыPrinciples of HorticultureNani NazirОценок пока нет
- A New Records of Gaertnera Junghuhniana Miq. Rubiaceae From Southern VietnamДокумент4 страницыA New Records of Gaertnera Junghuhniana Miq. Rubiaceae From Southern VietnamNGUYỄN HOÀNG LINHОценок пока нет