Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Chapter 1 Specification
Загружено:
Basil BautistaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Chapter 1 Specification
Загружено:
Basil BautistaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
SPECIFICATIONS
Concept of specification
Specification is the act or process of making specific through supplying particular details. It aims at
decreasing the generality or vagueness of something by determining or supplying some characteristics
that delimit it to a more precise coverage. In the engineering parlance, specification is a written or
printed description or presentation of something or a plan or proposal for something.
Purpose of specifications
The preparation of specifications needed to understand the nature of the machinery, supplies or the
materials to be furnished or work to be done under a contract should be given an extra time and effort.
Bidders learn from the specifications not only the information on the nature and the amount of work they
undertake, but also derive some ideas on the fairness of the party preparing the specification as well as
in the treatment that they will receive during the work when their bids are accepted.
SECTION 1.0 Scope
This chapter provides the general requirements for works involving machinery design, installation and
operations.
As used in this code, and as defined in article I section 3 paragraph (b) of R.A no. 8495, otherwise known
as The New Mechanical Engineering Law, mechanical equipment/machinery.
SECTION 2.0 Requirements for permit Application
All proposed installations, additions or alterations involving machinery, mechanical equipment or
process shall be covered by the following plans under the supervision of a Professional Mechanical
Engineer signed and sealed by same. Such plans in triplicate shall accompany applications for installation
and operation permit.
SECTION 2.1
General layout plan for each floor drawn to scale not less than 1:200, in heavy lines the equipment with
super-imposed building outline in light or suppressed lines. All names of machinery and brake
horsepower or kilowatt rating should be noted on plan.
SECTION 2.2
Plan elevation of at least one longitudinal and one traverse to show inner floor relations indicating how
machines are supported whether through building structure, separate staging or by foundations from the
ground.
SECTION 2.3 Piping plan in isometric drawing:
I. Assembly of pipes on racks and supports.
II. Complete individual piping system, indicating terminal valves, fittings, size and color code.
SECTION 2.4
Separate plan for different store rooms, fuel tanks, fire extinguisher equipment, fire fighting tools,fire
doors, fire escape ladders etc. which were not incorporated in section 2.1.
SECTION 2.5
For air conditioning and refrigeration installation or ventilation, plans for supply and return ductwork
should indicate the location of outlet dampers, controls, filters, fire proofing, and sound insulations.
SECTION 2.6 Detailed plans of foundations and supports.
SECTION 2.7 Detailed construction and working plans of boilers and pressure vessels, if any.
SECTION 2.8 Location plan preferably drawn scale.
SECTION 2.9 Complete List of Machine Showing:
a. Machinery name
b. Catalogue number, size, model, serial number
c. Rated capacity (e.g. boilers steam capacity in kg/Hr, KW, KJ)
d. Drive and revolutions per minute
1. Direct
2. V-belt or flat belt
3. Gear reducer
4. Hydraulic
5. Magnetic
6. Chain
7. Line shafting
Motor or prime mover showing
1. Kw rating for each machine
2. Speed in RPM
3. Total kW installed, or to be installed
SECTION 2.10 Flow sheet if processing plant, manufacturing, or assembly plant with corresponding
standard symbols.
SECTION 2.11 Other Contents of Mechanical Plans
The plans shall also contain the signature and seal of a Professional Mechanical Engineer with the
following:
a. Registration number
b. Validity number
c. Professional Tax Receipt, date, place of issue
d. Tax Identification Number
SECTION 3.0 Standards for Drawings
SECTION 3.1 Metric Dimension Drawings
Length in metric unit that are most generally used in connection with any work relating to mechanical
engineering are meters and millimeters.
SECTION 3.2 Scales of Drawing
Drawings made using the International System Units. Should not be made to scales of 1:2, 1:4, 1:8 etc. if
the object cannot be drawn full size, it may be drawn 1:2.5, 1:5, etc. if the object is too small and has to
be drawn larger it is 2, 5 or 10 times its actual size. The scale shall be written 2:1, 5:1 and 10:1.
Standard sheet sizes:
Standard sheet size for mechanical plans and drawings shall be based on a width to length ratio of 1:
square root of 2. all borders shall be at least 10mm from the sheet sheet edge; and all title blocks shall be
located at the lower right hand corner inside borders for larger sheets, and throughout the lower sheet
border for smaller sheet.
Smaller sheet sizes shall be as follows:
1. A4: 210 x 297mm
2. A3: 297 x 420mm
3. A2: 420 x 594mm
4. A1: 594 x 840mm
5. 375 x 530mm
6. 530 x 750mm
7. 750 x 1065mm
SECTION 4.0 Inspection
SECTION 4.1
Inspection shall be done during installation to satisfy inspection office to respective government agency
concerned that all materials and methods of erection are inspected in conformance with this code.
SECTION 4.2 Annual inspection shall be made to ensure that:
A. Equipment as originally installed are still safe to operate for at least another year.
B. No change, addition or alteration deviating from the original plan shall be made without prior
permit from the proper government agency concerned.
Вам также может понравиться
- General Requirements: Philippine Mechanical Code 2008Документ72 страницыGeneral Requirements: Philippine Mechanical Code 2008Li ReОценок пока нет
- Buok Chapter 3Документ44 страницыBuok Chapter 3Edmil Jhon AriquezОценок пока нет
- Arcilla, Zoren - Me Lab1 - Exp4 - M4act5Документ12 страницArcilla, Zoren - Me Lab1 - Exp4 - M4act5dracarysОценок пока нет
- Circuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyДокумент2 страницыCircuits1 1 Laboratory Meters and Power SupplyJad DimabuyuОценок пока нет
- PADILLAMD Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 4Документ2 страницыPADILLAMD Module 7 Exercises Problem No. 4Leyzer MalumayОценок пока нет
- Diesel Power Plant With Tons of IceДокумент124 страницыDiesel Power Plant With Tons of IceMycky VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Practice Problems (Pumps Agitation)Документ1 страницаPractice Problems (Pumps Agitation)Lin Xian XingОценок пока нет
- Ee 4101Документ183 страницыEe 4101Franz TabioloОценок пока нет
- Research1 5Документ44 страницыResearch1 5izzeah ramodОценок пока нет
- Uniform Mechanical Code - 2009 Chapter 1Документ10 страницUniform Mechanical Code - 2009 Chapter 1memosplumbingОценок пока нет
- Pns Paes 248 2010Документ18 страницPns Paes 248 2010Glaiza Abad FernandezОценок пока нет
- Keys Problem SetДокумент1 страницаKeys Problem SetMark AgusОценок пока нет
- Ideal Gas Refrigeration Cycle & R-134a Vapor Compression Refrigerator PerformanceДокумент3 страницыIdeal Gas Refrigeration Cycle & R-134a Vapor Compression Refrigerator Performanceanask15Оценок пока нет
- Study of Performance Characteristics of Francis TurbineДокумент6 страницStudy of Performance Characteristics of Francis TurbineBandam Nitish kumarОценок пока нет
- Ass No. 3Документ2 страницыAss No. 3Ako C. IvanОценок пока нет
- Fluid Flow Contuity (Tutorial Part 3)Документ13 страницFluid Flow Contuity (Tutorial Part 3)Harold MangaОценок пока нет
- Hydro Electric Power Plant: V P H H Y HДокумент10 страницHydro Electric Power Plant: V P H H Y HLim VanthienОценок пока нет
- Melab1 Exp3Документ11 страницMelab1 Exp3privateziel100% (1)
- MD2 Brakes 3Документ16 страницMD2 Brakes 3Chrstn VllmrОценок пока нет
- Experiment No. 1 Measurement of Heating Surface of A Firetube BoilerДокумент16 страницExperiment No. 1 Measurement of Heating Surface of A Firetube BoilerAli Requiso MahmudОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Steam Power Plant ReviewerДокумент9 страницChapter 5 - Steam Power Plant ReviewerKyle YsitОценок пока нет
- FLR - Performance of A Tubular CondenserДокумент12 страницFLR - Performance of A Tubular CondenserNazario Emil LintagОценок пока нет
- Decentralized WTF For Liloan Cebu Public MarketДокумент7 страницDecentralized WTF For Liloan Cebu Public MarketN.a. M. TandayagОценок пока нет
- Fans and Blowers Practice ProblemsДокумент2 страницыFans and Blowers Practice ProblemsFour AyesОценок пока нет
- MAPÚA UNIVERSITY WRITTEN REPORT ON PNEUMATICSДокумент14 страницMAPÚA UNIVERSITY WRITTEN REPORT ON PNEUMATICSAndreОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 1Документ2 страницыProblem Set 1JiiiОценок пока нет
- R22 Refrig Plant Cylinder Dimensions COP PowerДокумент2 страницыR22 Refrig Plant Cylinder Dimensions COP PowerAndrew PantaleonОценок пока нет
- Machine Design II Lecture Material TIPQCДокумент13 страницMachine Design II Lecture Material TIPQCChrstn VllmrОценок пока нет
- Ref Systems Lecture Notes 1Документ9 страницRef Systems Lecture Notes 1Retro GamerОценок пока нет
- Heat Transfer Chapter 1 ProblemsДокумент8 страницHeat Transfer Chapter 1 ProblemsVon A. Damirez0% (1)
- Air Conditioning DefinitionsДокумент29 страницAir Conditioning DefinitionsRay RavelОценок пока нет
- DZL Series Chain Grate Boiler OkДокумент10 страницDZL Series Chain Grate Boiler OkCarlos LehmanОценок пока нет
- Plate 1, 2 3 No AnsДокумент4 страницыPlate 1, 2 3 No AnsRika MaeОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic AnsweranssДокумент11 страницHydraulic AnsweranssJanelle D. Puti-anОценок пока нет
- AEng 173 Notes Part 2.5Документ4 страницыAEng 173 Notes Part 2.5Jester NavarquezОценок пока нет
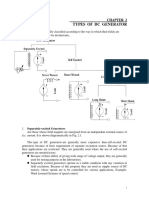
- Handout 3 Types of DC GeneratorsДокумент11 страницHandout 3 Types of DC GeneratorsAdriel JohnОценок пока нет
- Retrofitting of Refrigeration TrainerДокумент21 страницаRetrofitting of Refrigeration TrainerRome John FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Bolt SOlved ExampleДокумент4 страницыBolt SOlved ExampletarekОценок пока нет
- ME543: Me Laws, Contracts, Specifications, and EthicsДокумент13 страницME543: Me Laws, Contracts, Specifications, and EthicsEm JhayОценок пока нет
- Front Page and Expirement Number 1Документ3 страницыFront Page and Expirement Number 1Ron Kristian OpolintoОценок пока нет
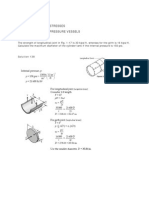
- 1.2 Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsДокумент4 страницы1.2 Thin-Walled Pressure VesselsCla OrillazaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 ProblemsДокумент3 страницыChapter 15 ProblemsJoshua Phillip Austero FederisОценок пока нет
- Neil Chester C. Hernaez: Even If Others Are Not Even If Others Will Not Even If Others CannotДокумент3 страницыNeil Chester C. Hernaez: Even If Others Are Not Even If Others Will Not Even If Others CannotSka dooshОценок пока нет
- PPE TerminologiesДокумент3 страницыPPE TerminologiesJamiel CatapangОценок пока нет
- Ventilation Lesson Guide Natural Forced CoolingДокумент13 страницVentilation Lesson Guide Natural Forced CoolingMohammed SiddiqueОценок пока нет
- Rac Problems Set 1Документ6 страницRac Problems Set 1Mohammad Umair100% (1)
- Speed Measuring InstrumentsДокумент7 страницSpeed Measuring InstrumentsJoshua GarciaОценок пока нет
- Chapter II Fluid MachineryДокумент90 страницChapter II Fluid MachineryFad TajudinОценок пока нет
- Refrigeration Engineering: MerefengДокумент62 страницыRefrigeration Engineering: MerefengPrecious Gallardo DerainОценок пока нет
- Basic ThermodynamicsДокумент1 страницаBasic ThermodynamicsJim Albert De Asis100% (1)
- MD2 Flywheel EditedДокумент11 страницMD2 Flywheel EditedChrstn VllmrОценок пока нет
- Powerplant and Industrial Plant Engineering Trial 1: 1 PointsДокумент8 страницPowerplant and Industrial Plant Engineering Trial 1: 1 PointsJerdОценок пока нет
- X X H H S S: Department of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент5 страницX X H H S S: Department of Mechanical EngineeringSeila MolinaОценок пока нет
- Copy of Power Plant Plate-A Revised ENGLISH VersionДокумент3 страницыCopy of Power Plant Plate-A Revised ENGLISH VersionMariel MirafloresОценок пока нет
- Gas Compressors Quiz ProblemsДокумент1 страницаGas Compressors Quiz ProblemsJason Dequin VillarosaОценок пока нет
- Requirements for machinery design, installation and operation plansДокумент48 страницRequirements for machinery design, installation and operation plansLurking RogueОценок пока нет
- DuctworksДокумент7 страницDuctworksphilipyapОценок пока нет
- Hvac Tech, Doc For Tender - II 02 03Документ108 страницHvac Tech, Doc For Tender - II 02 03kishore vpОценок пока нет
- Technical Specifications For CDU II VFD RoomДокумент12 страницTechnical Specifications For CDU II VFD RoomMohan VarkeyОценок пока нет
- Computer-Room Air ConditionersДокумент19 страницComputer-Room Air ConditionersAbdullah.N FAAliОценок пока нет
- Thermo Lectures (Intro, Units & Properties)Документ13 страницThermo Lectures (Intro, Units & Properties)Basil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Themodynamics 1 C&oДокумент7 страницThemodynamics 1 C&oBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Auto Trans ConceptsДокумент32 страницыAuto Trans ConceptsnavedОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Automobile: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningДокумент25 страницIntroduction To The Automobile: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningpallabОценок пока нет
- Themodynamics 1 C&o - Heat EnginesДокумент4 страницыThemodynamics 1 C&o - Heat EnginesBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Auto Parts 2Документ25 страницAuto Parts 2TjMarceloОценок пока нет
- Themodynamics 1 C&o - Ideal Gas ProblemДокумент3 страницыThemodynamics 1 C&o - Ideal Gas ProblemBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics - Isothermal ProcessДокумент8 страницThermodynamics - Isothermal ProcessBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- NUДокумент1 страницаNUBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To The Engine: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningДокумент30 страницIntroduction To The Engine: © 2012 Delmar, Cengage LearningAkatew Haile MebrahtuОценок пока нет
- APPLICATION and GUIDELINES OF ASEAN ENGINEERING REGISTRY PDFДокумент30 страницAPPLICATION and GUIDELINES OF ASEAN ENGINEERING REGISTRY PDFBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Identifying Engine Systems andДокумент67 страницIdentifying Engine Systems andBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Letter of Intent For Job 4 PDFДокумент1 страницаLetter of Intent For Job 4 PDFradzОценок пока нет
- Application For Associate Asean Engineer: PTC-AER Form 02-12Документ2 страницыApplication For Associate Asean Engineer: PTC-AER Form 02-12Vincent Donie PletadoОценок пока нет
- Energy Conversion 2ed by Clup PDFДокумент577 страницEnergy Conversion 2ed by Clup PDFBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Oil Shale Resources Development in JordanДокумент98 страницOil Shale Resources Development in JordanBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- 1 FundamentalsДокумент6 страниц1 FundamentalssunnyopgОценок пока нет
- Application Form: Explore The World of TomorrowДокумент1 страницаApplication Form: Explore The World of TomorrowMuhamad HanifudinОценок пока нет
- LEC ThermoI 5-AirStandardCycleHeatEngineДокумент17 страницLEC ThermoI 5-AirStandardCycleHeatEngineBasil Bautista33% (3)
- LEC ThermoI 3-GasLawEquationStateДокумент23 страницыLEC ThermoI 3-GasLawEquationStateBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- Auto Parts 2Документ25 страницAuto Parts 2TjMarceloОценок пока нет
- Thermodynamics (Mapua U)Документ12 страницThermodynamics (Mapua U)Basil Bautista0% (1)
- Lect11 Combustion ProcessДокумент28 страницLect11 Combustion ProcessKhairi Maulida AzhariОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 SpecificationДокумент4 страницыChapter 1 SpecificationBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
- CombustionДокумент1 страницаCombustionBasil BautistaОценок пока нет
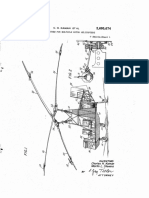
- 1950 Kaman Servoflap US2695674Документ23 страницы1950 Kaman Servoflap US2695674jorge paezОценок пока нет
- Sobek Endurance ToolsДокумент14 страницSobek Endurance ToolsAhmet KöseleciОценок пока нет
- S8 Automobile Engg 2013 Syllabus - BTech MechДокумент2 страницыS8 Automobile Engg 2013 Syllabus - BTech MechMathew JohnОценок пока нет
- Lecture - Convective Heat TransferДокумент17 страницLecture - Convective Heat TransferPaul Bryan OcampoОценок пока нет
- Boiler Controls: Low Water Cut-Offs - Mechanical For Steam BoilersДокумент1 страницаBoiler Controls: Low Water Cut-Offs - Mechanical For Steam BoilersAlfredo Mitzi HernandezОценок пока нет
- MC 10172225 0001Документ9 страницMC 10172225 0001Abdelmoumen BenharzallahОценок пока нет
- Escort Limited Champion F 11 Brand Name - FarmtracДокумент12 страницEscort Limited Champion F 11 Brand Name - Farmtrachugo fernandezОценок пока нет
- Abrasive Wear Mechanisms PDFДокумент9 страницAbrasive Wear Mechanisms PDFRBZОценок пока нет
- Final Twoway SlabДокумент20 страницFinal Twoway Slabvishnumani3011Оценок пока нет
- High Pressure Gear Pump GuideДокумент12 страницHigh Pressure Gear Pump GuideMauricio Ariel H. OrellanaОценок пока нет
- Permanent Magnet DC MotorДокумент4 страницыPermanent Magnet DC MotorSourav Kumar100% (1)
- PR 724 Crawler TractorДокумент18 страницPR 724 Crawler TractorCarlosОценок пока нет
- Hyster j2 2 3 5xnДокумент12 страницHyster j2 2 3 5xnBraveBoy JalloОценок пока нет
- Retrofit BMBS InstructionsДокумент3 страницыRetrofit BMBS InstructionsPradipta SahooОценок пока нет
- 4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesДокумент23 страницы4 Ideal Models of Engine CyclesSyedОценок пока нет
- IMO G12 - 218 Despacho Guaduas PDFДокумент21 страницаIMO G12 - 218 Despacho Guaduas PDFCarlos Andres Arias LopezОценок пока нет
- Depressurisation - A Practical GuideДокумент20 страницDepressurisation - A Practical GuideAhmad Firman Masudi100% (2)
- Geankoplis 2.6-4 2.7-4Документ7 страницGeankoplis 2.6-4 2.7-4BenePicarОценок пока нет
- Parts Manual Current Products I21Документ166 страницParts Manual Current Products I21juancglugoОценок пока нет
- Cadworx Cadworx Cadworx Cadworx Syllabus Syllabus Syllabus SyllabusДокумент6 страницCadworx Cadworx Cadworx Cadworx Syllabus Syllabus Syllabus SyllabusSelvaОценок пока нет
- Basic Motor Technical + Safe Area MotorsДокумент74 страницыBasic Motor Technical + Safe Area MotorsmayureshrmahajanОценок пока нет
- Buckling Analysis: The Theory of BucklingДокумент6 страницBuckling Analysis: The Theory of BucklingKing Everest100% (2)
- Curriculam Vitae: Mohamed Ibrahim.mДокумент4 страницыCurriculam Vitae: Mohamed Ibrahim.mAzizul AnwarОценок пока нет
- QUY150C 150t Crawler Crane BrochureДокумент59 страницQUY150C 150t Crawler Crane BrochureliftОценок пока нет
- Design and Analysis of Three Dimensional Structural Analysis of Airfoil To Various Composite MaterialsДокумент4 страницыDesign and Analysis of Three Dimensional Structural Analysis of Airfoil To Various Composite MaterialsSri Tech EngineeringОценок пока нет
- Modelling, Identification and Control of A 2 DOF Helicopter PrototypeДокумент6 страницModelling, Identification and Control of A 2 DOF Helicopter PrototypeosdacavОценок пока нет
- Archimedes PrincipleДокумент4 страницыArchimedes Principleraviteja036Оценок пока нет
- 2019 - Uniflair Room Cooling BrochureДокумент92 страницы2019 - Uniflair Room Cooling BrochureJeff100% (2)
- Modal Analysis Example ExcelДокумент1 страницаModal Analysis Example Excelkaranbir123Оценок пока нет
- AE-SB-05 Seismic Loads - How They Relate To Cooling TowersДокумент1 страницаAE-SB-05 Seismic Loads - How They Relate To Cooling TowerspamelaОценок пока нет